Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Remcos is a commercially distributed remote administration and surveillance tool that has been widely observed in unauthorized deployments, where threat actors use it to perform remote actions on compromised machines. It is actively maintained by its vendor, with new versions and feature updates released on a frequent, near-monthly basis.
|
Remote access tool
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2016
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Remote access tool
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2016
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 429
429
 0
0

 2259
2259
 0
0

 4388
4388
 0
0
Remcos is a commercially distributed remote administration and surveillance tool developed and marketed by Breaking Security, a company registered in Hong Kong. The tool is advertised for legitimate purposes including remote device management, authorized penetration testing, security audits, and approved remote administration.
However, security researchers and threat intelligence organizations have extensively documented abuse of Remcos by unauthorized threat actors in numerous phishing campaigns, espionage operations, and targeted attacks against critical infrastructure, government agencies, and commercial organizations.
Remcos has been available since 2016 and receives active updates with new releases documented nearly every month. The tool is sold through legitimate commercial channels.
The software is equipped with features commonly found in remote administration tools, such as remote desktop control, file management, keystroke logging, and screenshot capabilities. These same technical capabilities have made it an effective tool for malicious deployment by threat actors when installed without authorization.
Unauthorized deployments of Remcos employ multiple delivery techniques in phishing campaigns. Threat actors have been observed distributing Remcos through deceptive executable files with names designed to appear legitimate, as well as through Microsoft Office documents that exploit application vulnerabilities to facilitate remote payload download and execution. Such cases also involve the use of anti-analysis techniques and code obfuscation to evade detection by security software.
ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox provides a safe, cloud-based environment for detonating programs and URLs to detect the presence of malicious activity.
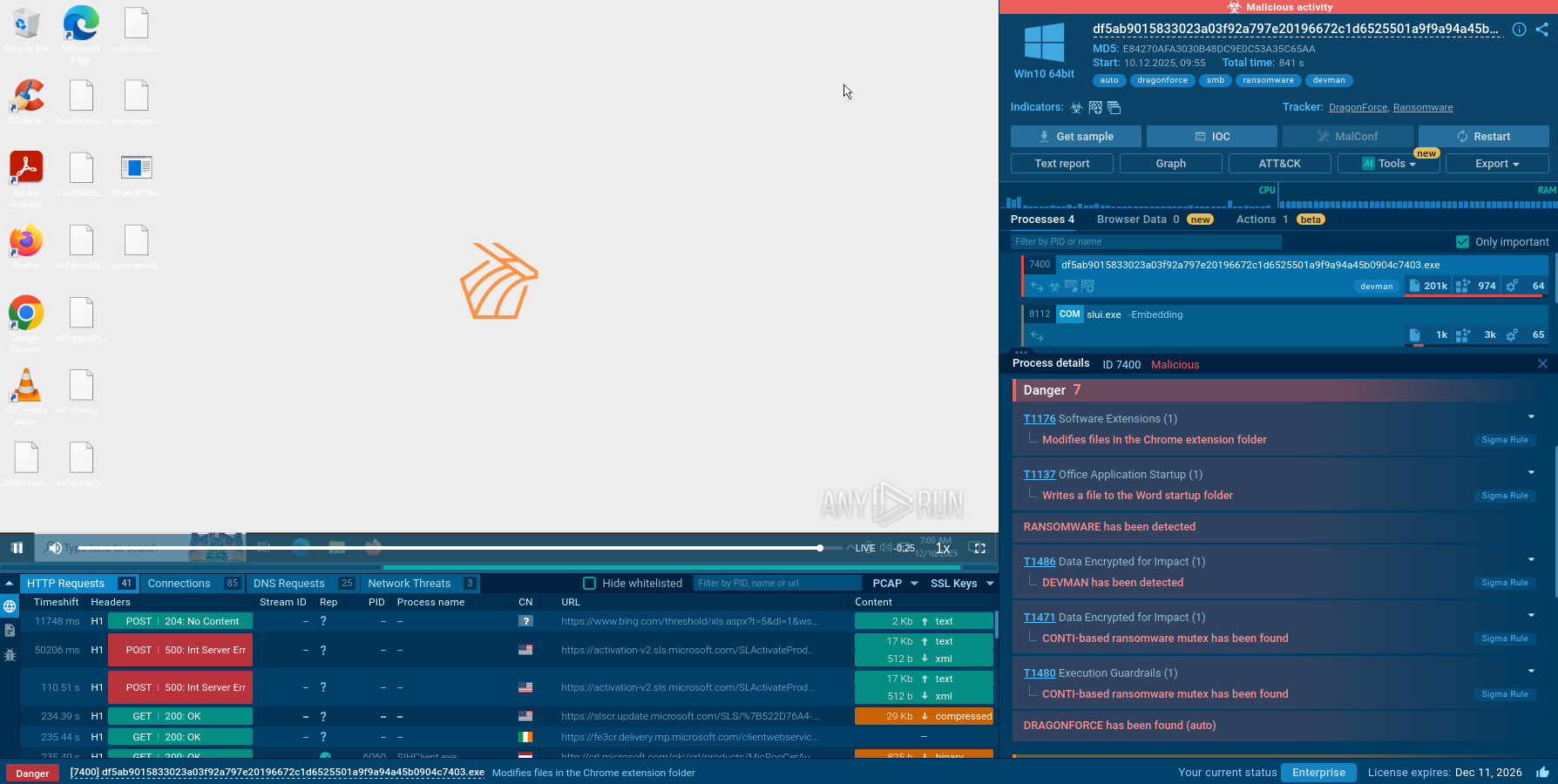
ANY.RUN sandbox analysis of an unauthorized Remcos deployment documents the following execution chain:
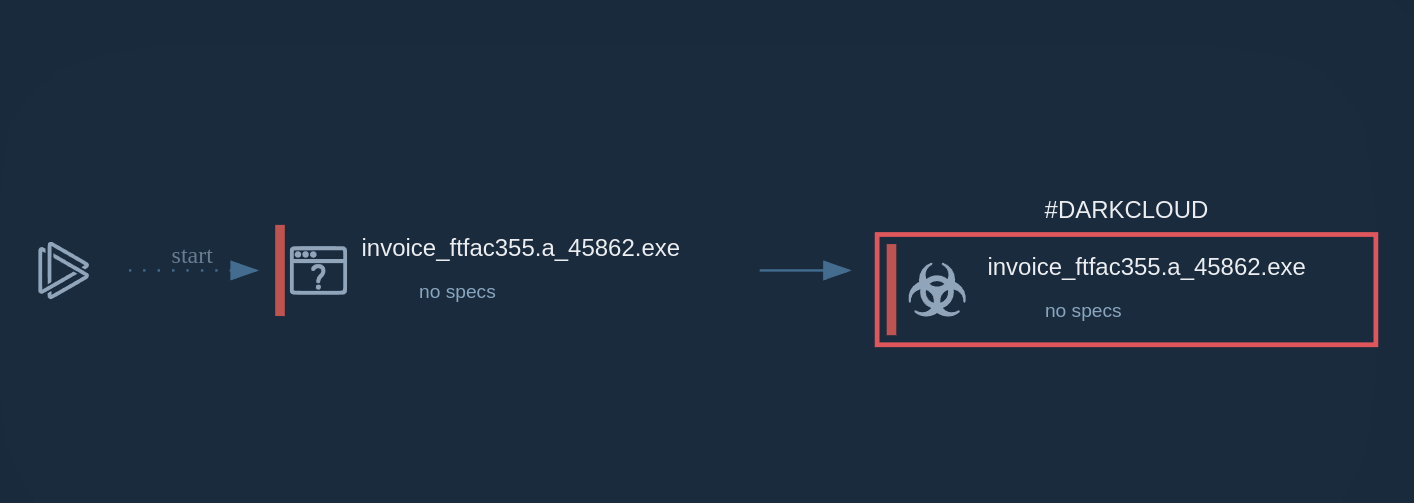
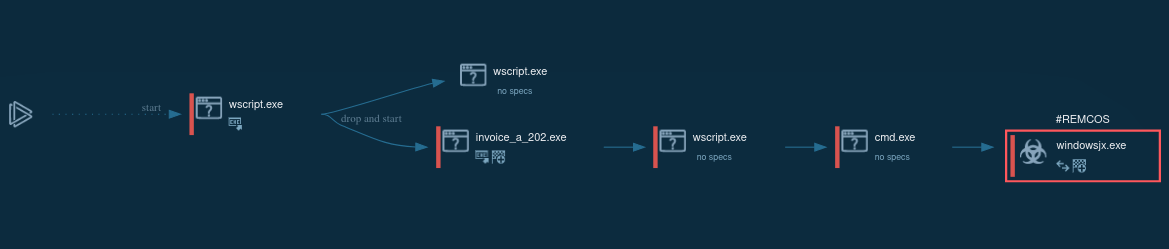 Figure 1: Displays the lifecycle of an unauthorized Remcos use as presented by a visual graph generated by ANY.RUN
Figure 1: Displays the lifecycle of an unauthorized Remcos use as presented by a visual graph generated by ANY.RUN
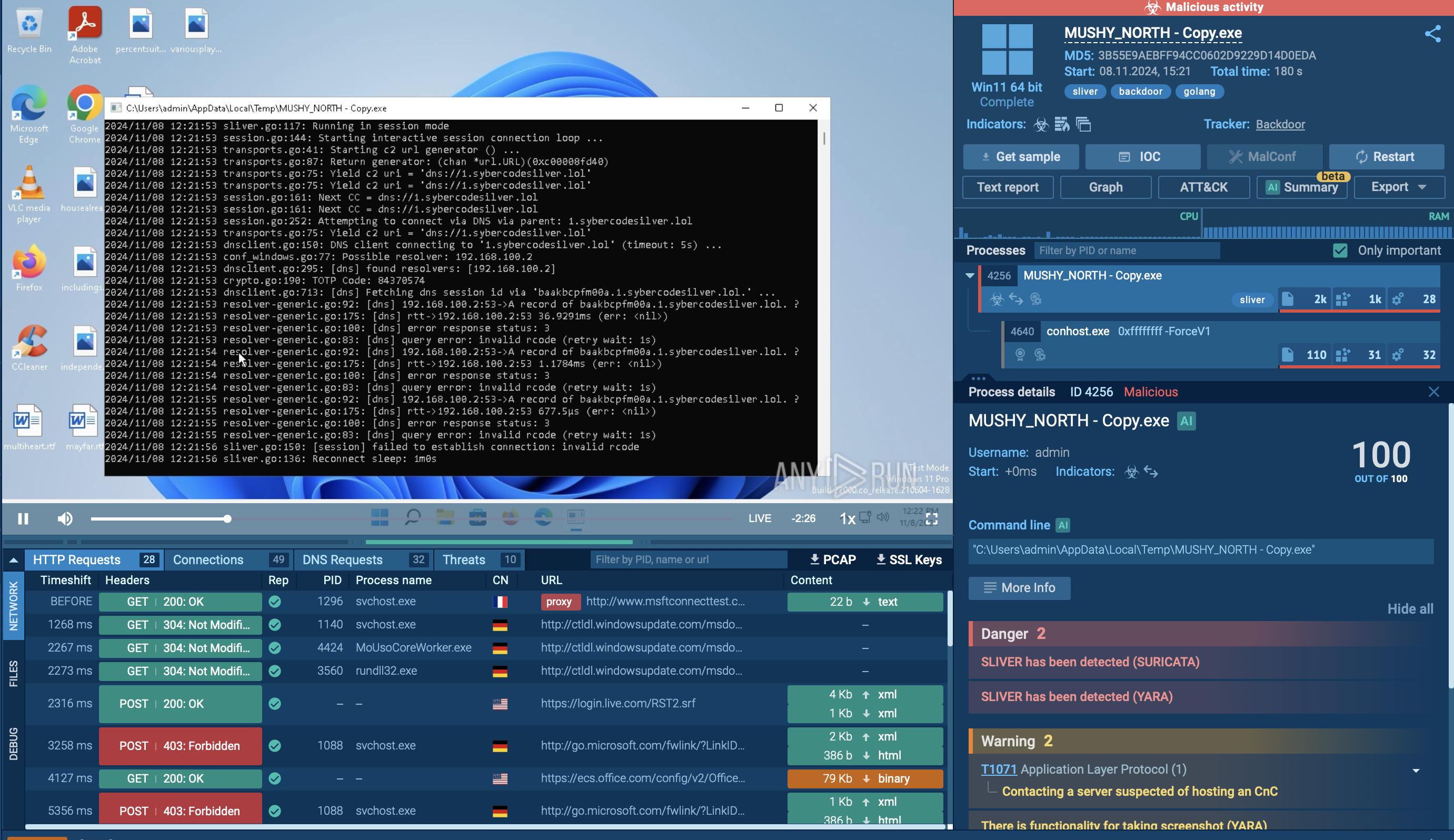
 Figure 2: A customizable text report generated by ANY.RUN is a feature specifically developed to simplify the sharing of analysis results.
Figure 2: A customizable text report generated by ANY.RUN is a feature specifically developed to simplify the sharing of analysis results.
Security analysts can identify unauthorized Remcos deployments through registry artifact analysis. Threat actors deploying Remcos have been observed creating registry entries in the user hive containing identifying markers.
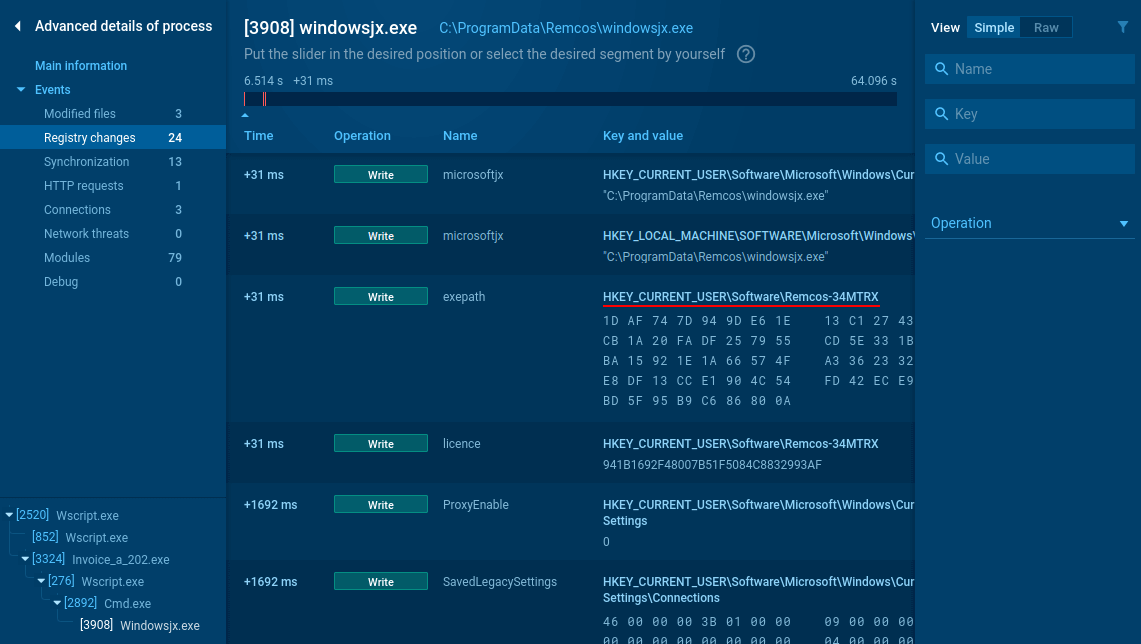 Figure 3: Remcos registry changes analysis
Figure 3: Remcos registry changes analysis
When analyzing suspicious processes in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox, examiners can review registry modification events by selecting the process and accessing the detailed information view. The presence of registry keys matching the pattern "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Remcos-{digits_letters}" is a strong indicator of unauthorized Remcos deployment and can be used as a forensic artifact for detection and incident response.
Security teams can collect up-to-date intelligence on unauthorized Remcos deployments using ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup.
The service provides access to a centralized repository of millions of IOCs, IOAs, and IOBs extracted from live interactive malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN Sandbox by a community of 500,000+ researchers and 15,000 SOCs.
With 40+ customizable search parameters—including file hashes, IPs, domains, command lines, registry paths, MITRE techniques, and process artifacts—analysts can efficiently identify and correlate Remcos-related indicators across sandbox sessions.
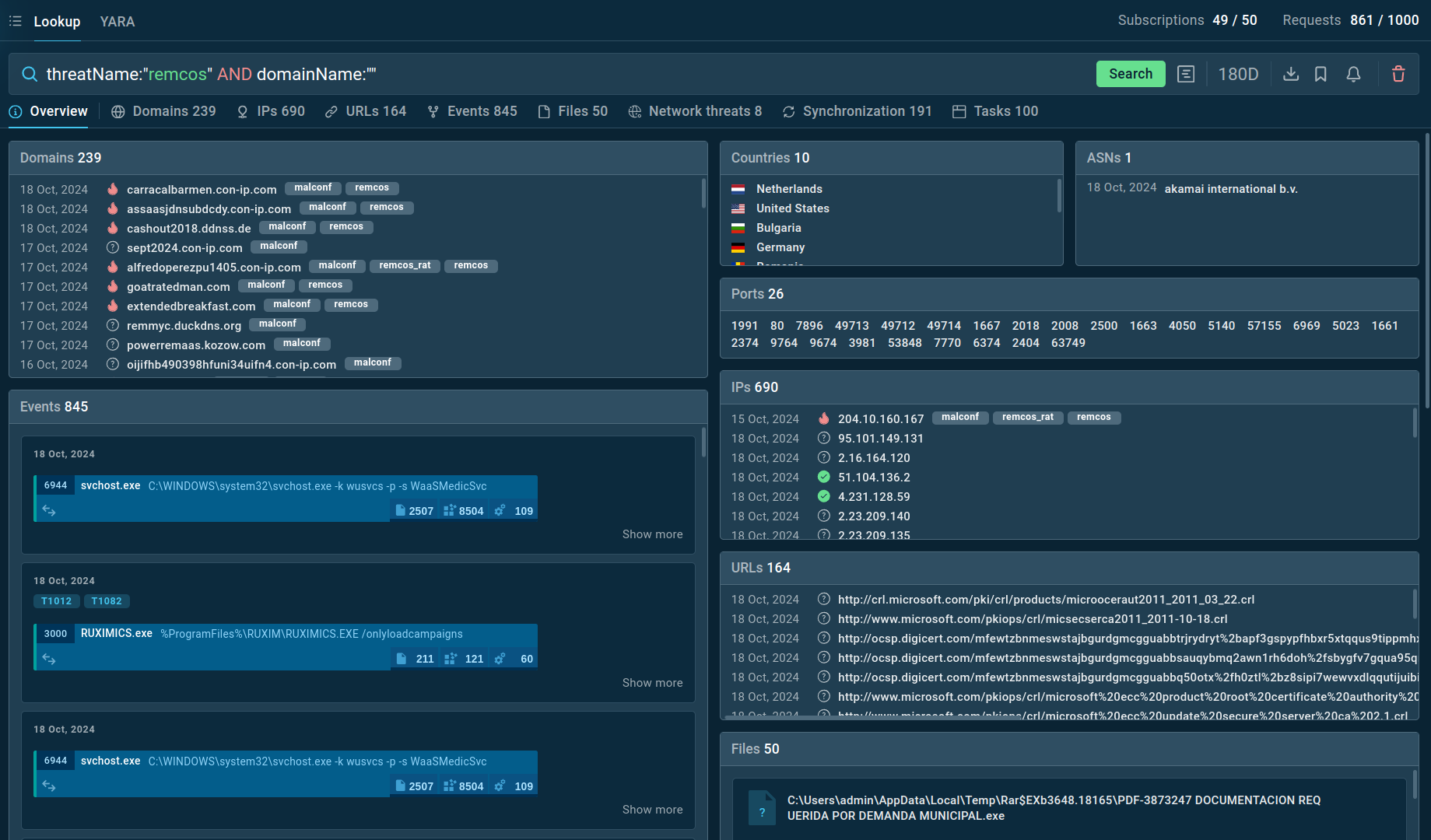 Figure 4: Search results for Remcos in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Figure 4: Search results for Remcos in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, you can search directly for the threat name or use related indicators like hash values or network connections. Submitting a query such as threatName:"remcos" AND domainName:"" will generate a list of files, events, domain names, and other data extracted from Remcos samples along with sandbox sessions that you can explore in detail to gain comprehensive insights into this malware’s behavior.
Threat intelligence reports document multiple distribution vectors for unauthorized Remcos deployments, including bundling with mass mailing tools marketed as legitimate distribution services. Analysis of phishing campaigns reveals that Remcos payloads most frequently arrive via malicious email attachments, with threat actors employing social engineering lures to prompt users to enable macros in Microsoft Office documents.
A common attack chain:
Once macros are enabled, the reconstructed executable downloads and launches the Remcos component, establishing persistence and C2 communication as documented in sandbox executions.
Unauthorized deployments of Remcos represent a significant security concern, as threat actors can obtain access to feature-rich remote access capabilities at relatively low cost and leverage them to manage compromised hosts at scale. When abused in this way, Remcos has been used to create and control networks of infected devices, exfiltrate data, and maintain long-term access in support of broader malicious campaigns.
Fortunately, modern analysis and threat intelligence solutions provide security teams with extensive capabilities to investigate suspicious samples, observe execution behavior, and enrich indicators related to Remcos-based activity. Interactive sandboxing and integrated threat intelligence from ANY.RUN enable analysts to safely analyze suspected Remcos deployments, correlate them with known campaigns, and implement effective countermeasures across their environments.
Create an ANY.RUN account to start your first investigation!