Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Lumma is an information stealer, developed using the C programming language. It is offered for sale as a malware-as-a-service, with several plans available. It usually targets cryptocurrency wallets, login credentials, and other sensitive information on a compromised system. The malicious software regularly gets updates that improve and expand its functionality, making it a serious stealer threat.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2022
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2022
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 876
876
 0
0

 522
522
 0
0

 2816
2816
 0
0
Lumma is a widely accessible malware stealer that is sold openly across Dark Web forums and Telegram channels. Although not as popular as other stealers, such as RedLine and Formbook, it has gained considerable traction among cybercriminals that focus on exfiltrating sensitive information from unsuspecting victims. Operated by a group believed to originate from former USSR countries, LummaC2 Stealer has been actively evolving since its initial emergence in 2022, getting substantial updates that enhance its capabilities.
Lumma Stealer poses a significant threat to a wide range of computer systems, targeting devices running Windows operating systems from Windows 7 up to Windows 11. This broad compatibility allows the malware to infiltrate a vast network of systems, increasing its potential reach and impact.
Since it operates under a malware-as-a-service model, Lumma Stealer is accessible to anyone with the financial means to purchase a subscription. This accessibility has contributed to the malware's widespread adoption. There are three subscription plans, each providing a varying range of features to users, including access to a command-and-control (C2) panel, which allows criminals to monitor and manage the malware's activities on compromised machines.
Lumma enables criminals to engage in a variety of illicit activities and a has a long list of capabilities, including:
Lumma malware analysis shows a vast range of features that make it a versatile tool for cybercriminals. For instance, all data transmitted by the stealer is decrypted on the server side, which makes it more difficult to analyze the malware’s traffic during the exfiltration process.
Another notable capability of the malware is its neighbor detection, which notifies operators about other instances of the malware running on the same system. The malware supports ARM, x86, and x64 architectures, demonstrating its cross-platform compatibility and ability to target a wide range of devices.
The stealer can also be configured to be used via a Telegram bot.
ANY.RUN lets us expose the malicious activities of Lumma Stealer and collect IOCs by uploading its sample to the sandbox.
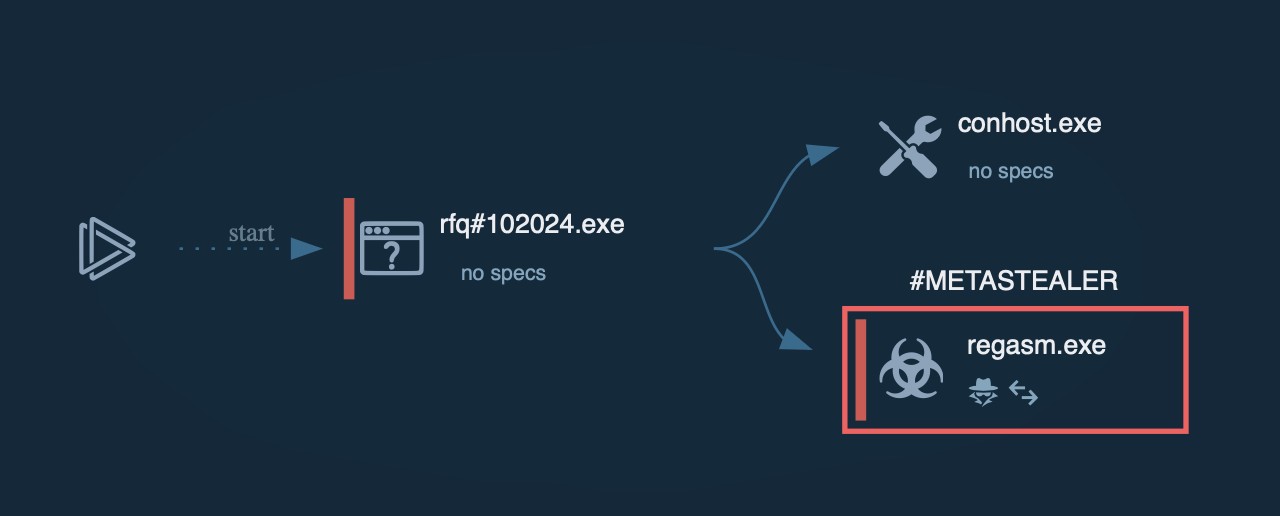
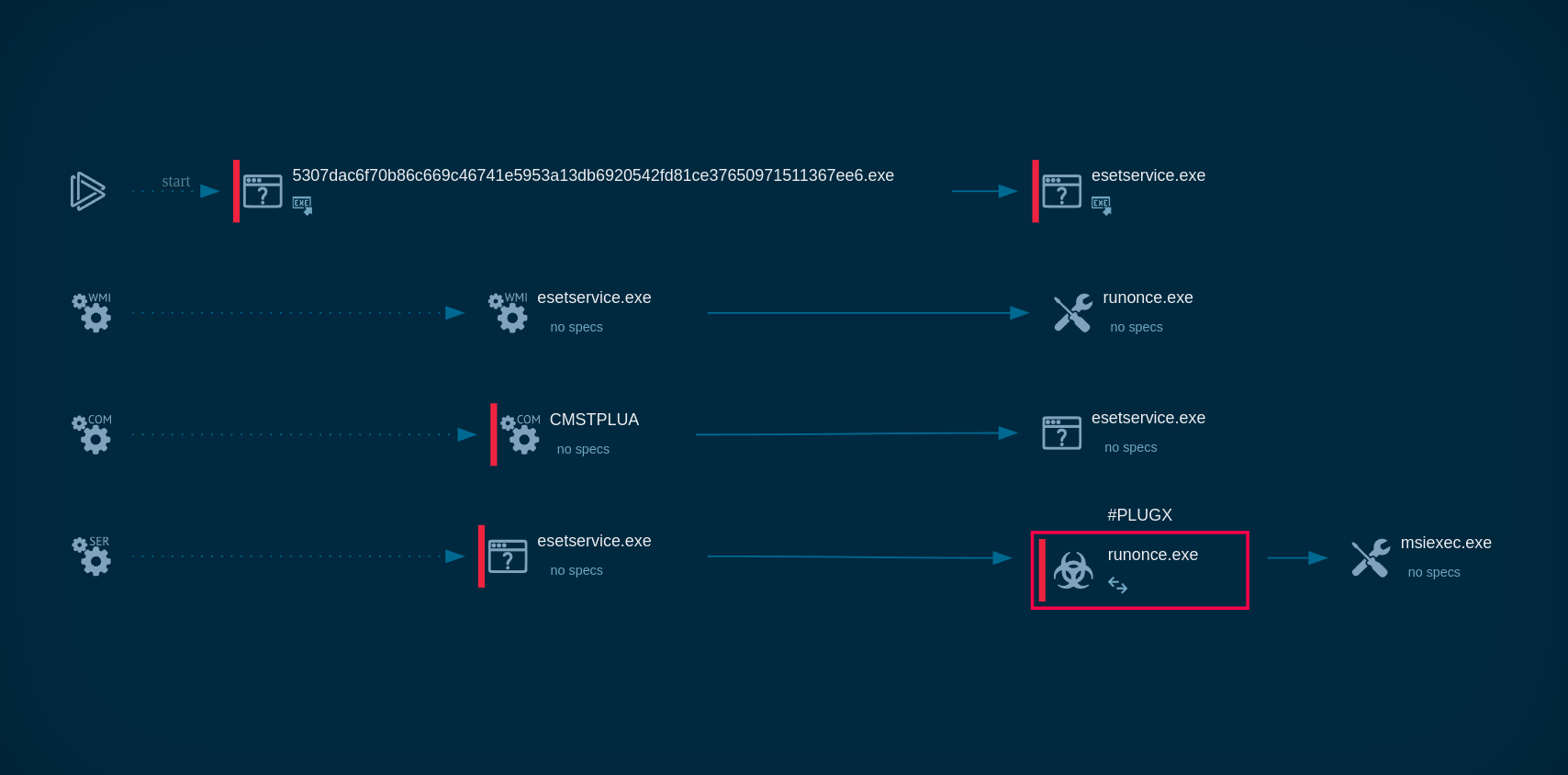
Since stealers are trying their best to hide their activities, the execution chain of malware Lumma is kept as simple as possible. Therefore, there are not a lot of processes, and no usage of system tools occurs inside the infected OS. After the payload makes its way into the infected system, it immediately starts execution.
 The process graph of Lumma Stealer demonstrated by the ANY.RUN sandbox
The process graph of Lumma Stealer demonstrated by the ANY.RUN sandbox
The only process of the malware is responsible for carrying out all malicious activities, including data theft, C&C server communication, etc. If there is no connection with the C&C, Lumma stops its execution.
To collect up-to-date intelligence for Lumma stealer malware analysis and better understand what is Lumma malware, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service gives you access to a vast database filled with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
With over 40 customizable search parameters, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts, you can efficiently gather relevant data on threats like Lumma Stealer.
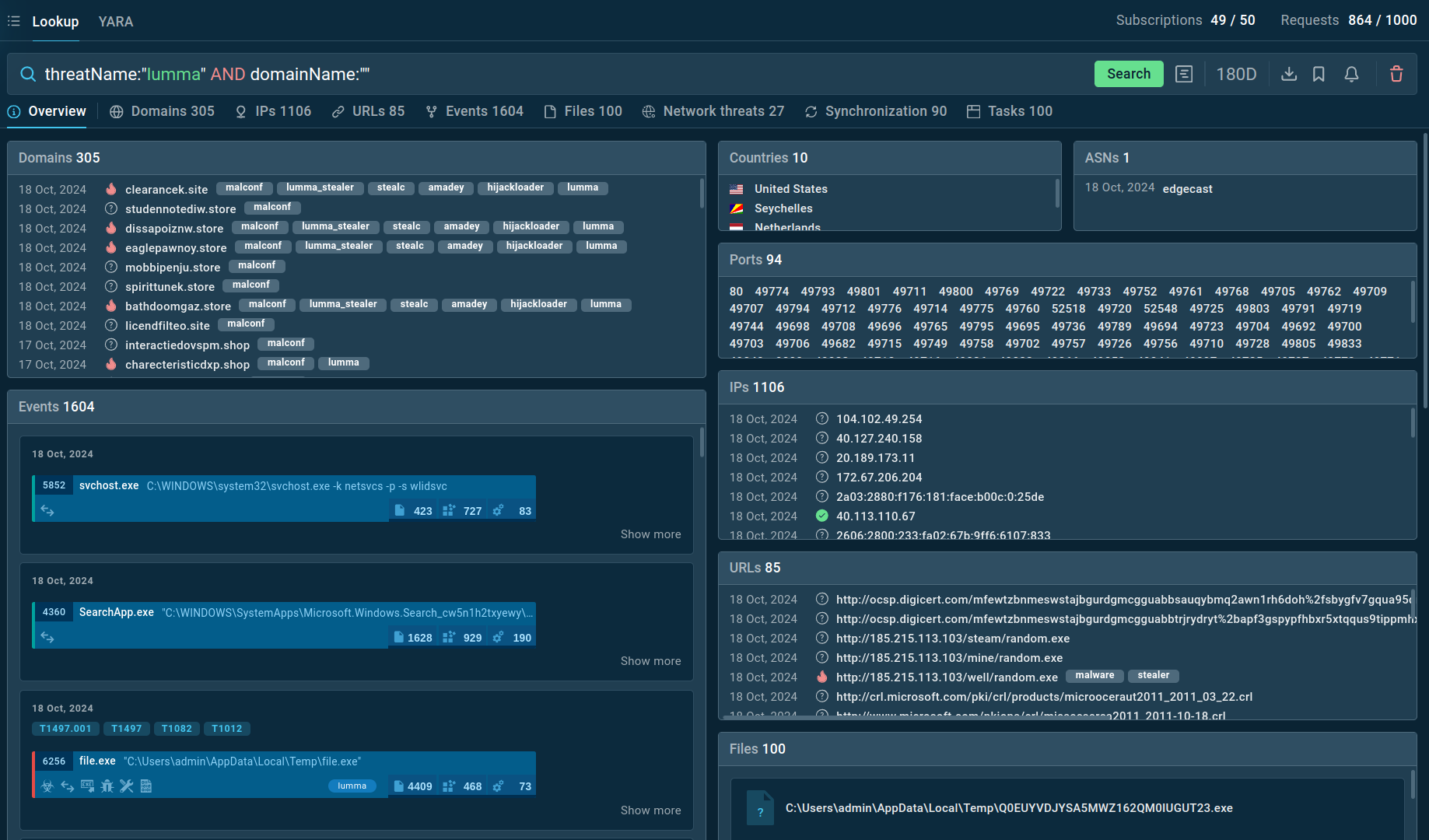 Search results for Lumma Stealer in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Lumma Stealer in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, you can search directly for the threat name or use related indicators like hash values or network connections. Submitting a query such as threatName:"Lumma" AND domain:"" will generate a list of files, events, domain names, and other data extracted from Lumma samples along with sandbox sessions that you can explore in detail to gain comprehensive insights into this malware’s behavior.
Lumma malware is utilized by numerous threat actors, both individuals and groups, who employ a variety of ways to deliver the payload to the target system.
The growing threat of LummaC2 Stealer calls for a proactive approach to cybersecurity. As this malware becomes more common, individuals and organizations must be aware of its diverse delivery methods and take steps to protect themselves. Malware analysis sandboxes, such as ANY.RUN are a valuable tool for identifying and analyzing Lumma Stealer.
ANY.RUN is an advanced tool that provides a unique way to study malware. You can interact with infected systems in a safe cloud environment to observe how the malware behaves. It goes beyond simple observation by generating a detailed report that includes IOCs and malware configuration information, enabling you to take action against malware threats.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!