Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


FormBook is a data stealer that is being distributed as a MaaS. FormBook differs from a lot of competing malware by its extreme ease of use that allows even the unexperienced threat actors to use FormBook virus.
|
Spyware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2016
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2016
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 890
890
 0
0

 530
530
 0
0

 2830
2830
 0
0
FormBook stealer is an infostealer trojan available as a malware-as-service. This malware is often used by attackers with low technical literacy and little programming knowledge. FormBook can be used to steal various information from infected machines.
Despite how easy it is to set up and use, the malware has advanced stealing and evasion functions including the ability to pull stored and recorded user input. In addition, the FormBook stealer is capable of searching for, viewing, and interacting with files, and taking screenshots. Even though the stealing capability of this virus can be considered somewhat average, its ease of operation, the injection schema, and a set of effective measures that the malware takes to avoid detection by antivirus software made FormBook a popular virus in the hacker community and, unfortunately, its popularity is only continuing to rise in 2019.
Written in C and x86 assembly language, FormBook is sold as a PHP control panel and can be purchased on highly accessible online forums for merely 30 dollars.
Uniquely, unlike the majority of existing viruses that exploit the latest vulnerabilities or zero-days, FormBook can inject into processes and set up function hooks utilizing already known issues. Hence the claim made by the makers, that the virus will work flawlessly regardless of the Windows version.
Together with its stealer functionality and evasion techniques, the virus knows how to execute instructions from a control server that includes starting new processes, their injection, and rebooting the victim’s PC. What’s more, the virus is able to record Windows’ ntdll.dll module into memory and call it directly, which makes API monitoring and user-mode hooking almost insufficient.
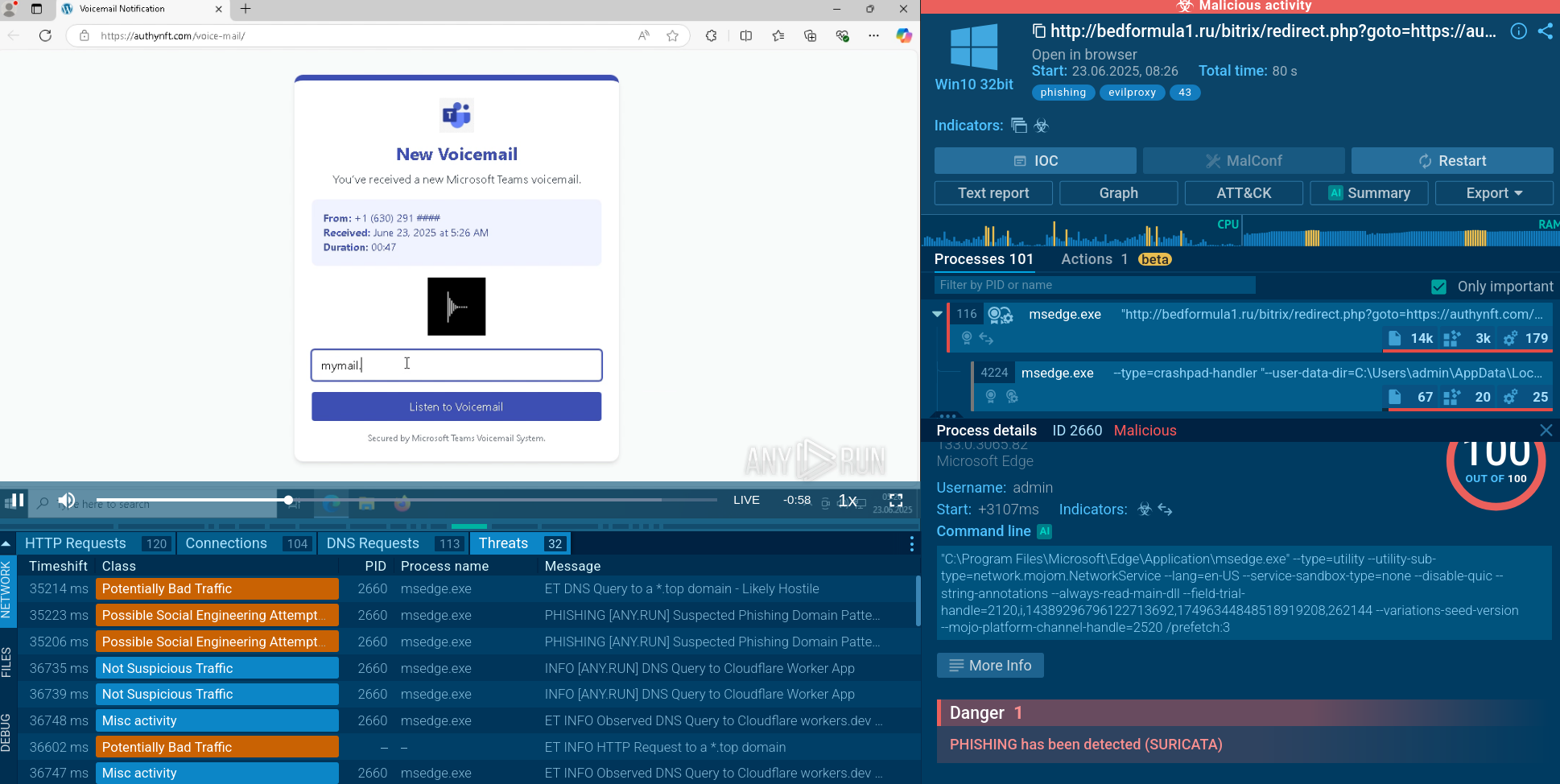
A video simulation recorded on the ANY.RUN interactive malware analysis service allows us to take an in-depth look at the behavior of this clever virus and other malware such as Dridex and Lokibot with their elaborate anti-evasion techniques.
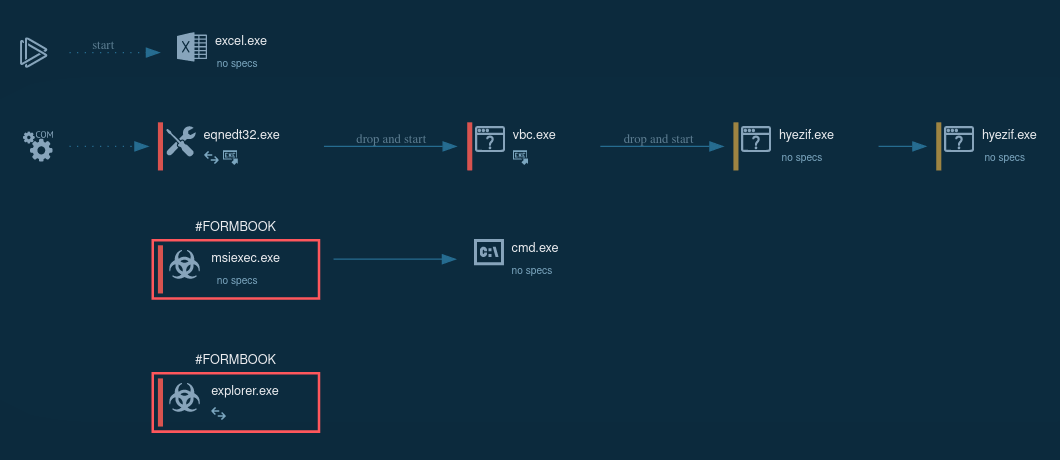
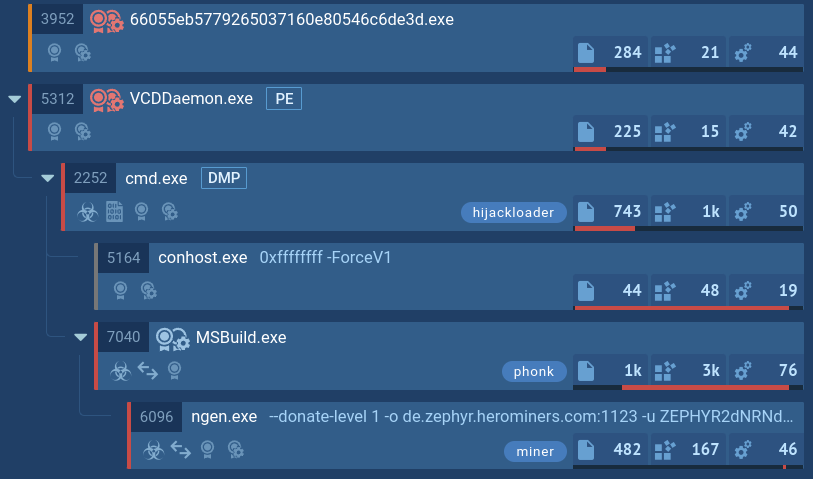
Figure 1: Processes created by FormBook during execution as shown by ANY.RUN simulation
According to FormBook analysis, malware is usually distributed via email campaigns that utilized a wide array of infecting mechanisms and can contain a number of various file attachments. Among the most commonly observed attachments are either PDFs, DOC or EXE, or ZIP, RAR, ACE, and ISO files.
Campaigns in which the virus is distributed through files with PDF extensions are known to utilize shipping-related themes and usually include a download link that points at the malicious code instead of the actual virus. DOC and EXE campaigns utilize macros to install and run the virus. Often, the virus is retrieved as a .PDF file in such a case. Finally, archive campaigns are considered to be the most common attack vector for this virus and usually revolve around a business-related theme, such as a payment order. In the case of this attack vector, attachments either contain a link to the FormBook stealer EXE file or install and run the virus on victims' PCs directly.
In 2020 Formbook has become quite popular as it used Covid-themed emails for decoys with subject headings such as “Government Response to Coronavirus Covid-19”.
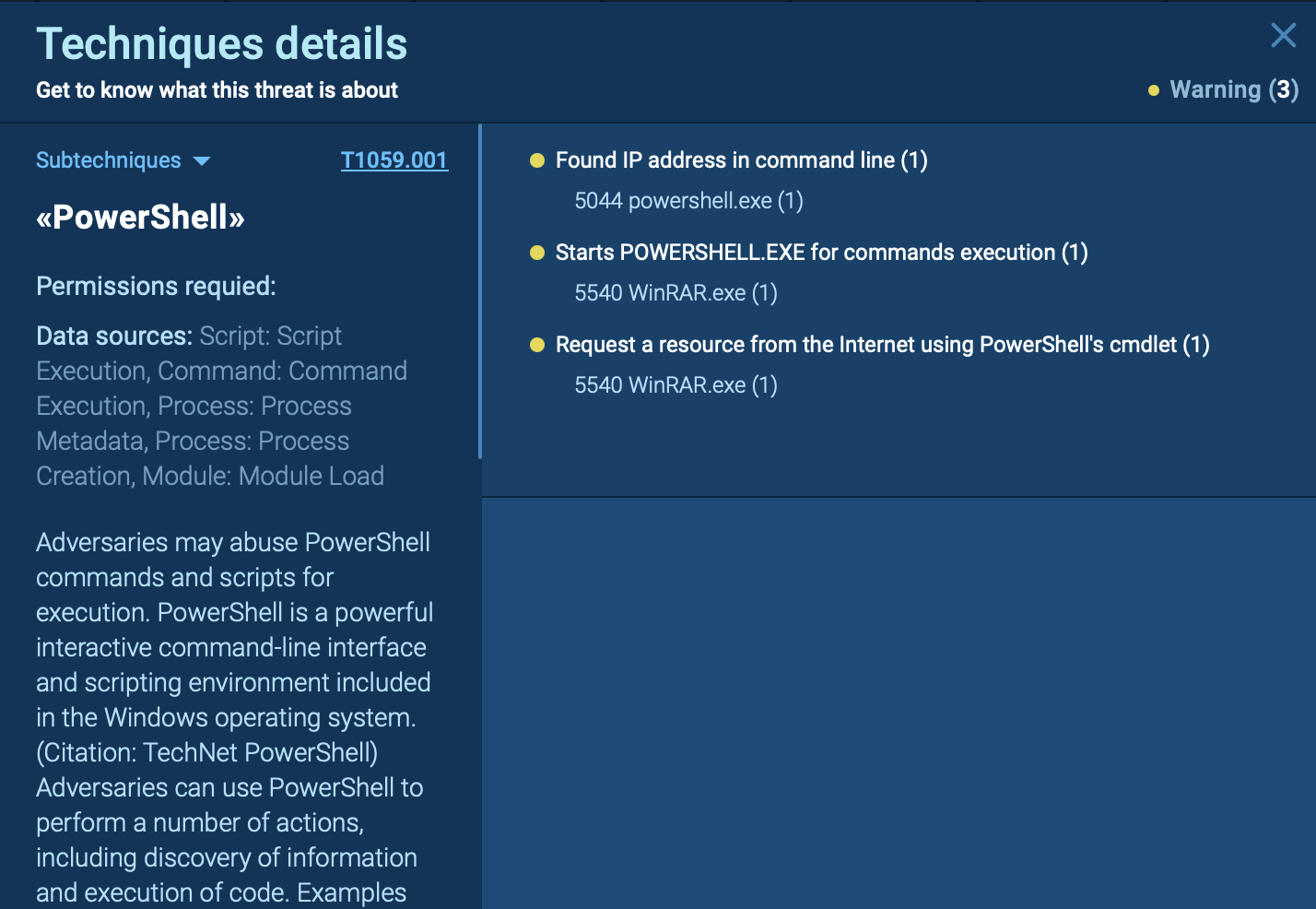
Sandbox simulation performed on the ANY.RUN interactive malware hunting service allows us to detect and investigate the behavior of FormBook in a lot of detail.
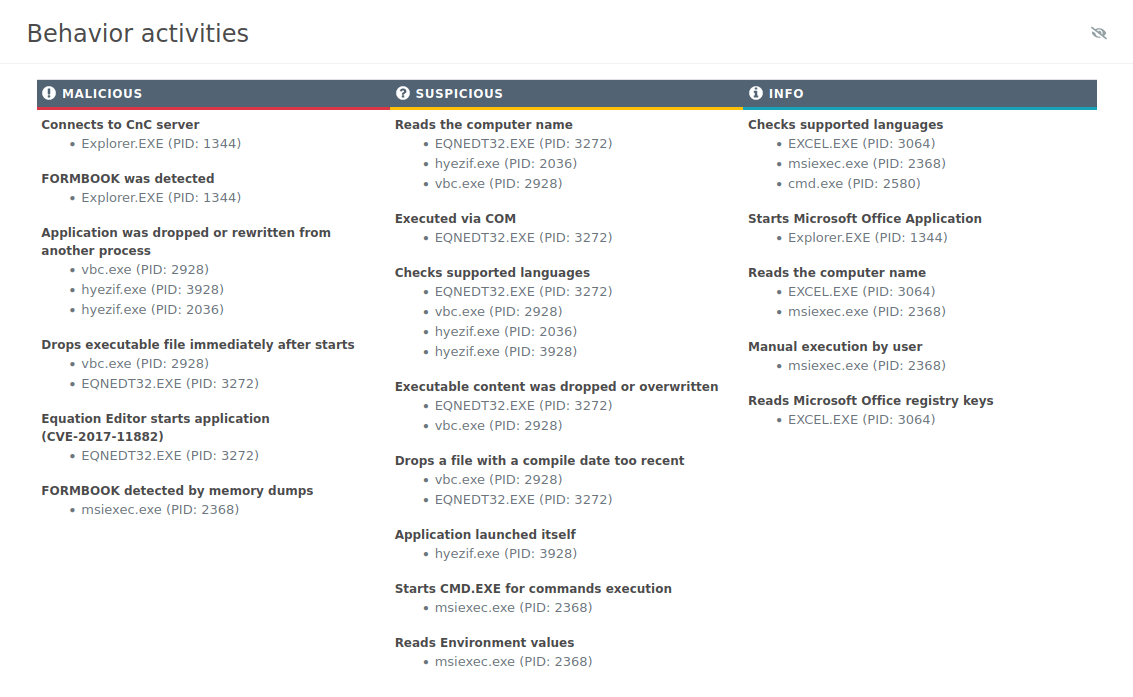
Figure 2: A text report generated by ANY.RUN
After downloading the malicious file the only thing needed to start the contamination is for the file to be opened. In a case when Microsoft Office file (doc, xls, rtf) is used as an infection source, after it is opened the malware exploits the CVE-2017-11882 vulnerability, thus Microsoft Office Equation Editor proceeds to download a malicious executable file and run it.
After infecting the victim's PC, the virus copies and renames itself into a directory that differs based on the privileges of the user. If an admin account is used, the virus installs itself in either %ProgramFiles% or %CommonProgramFiles%. On the other hand, if the privileges are not elevated, then the virus will copy itself into %TEMP% or %APPDATA.
Also, Formbook trojan changes the autorun value in the registry depending on is it was running with normal or elevated privileges. Next, the malware copies itself into a directory it proceeds to check if it’s being run on a virtual machine or analyzed, evaluating the best anti-evasion option that can be utilized in a particular situation. Meanwhile, the virus will try to evaluate the USERNAME environment variable to find out if it’s launched in simulation, while also checking for the presence of debuggers. It should be noted that the malware uses particularly clever techniques while performing an analysis, for example, all shared strings such as command server names are decoded only briefly if they are absolutely required, which makes FormBook highly elusive. In the next step, the virus uses the same injection method to an active explorer.exe process which is only employed as a non-permanent staging ground.
The virus occasionally performs injections into web browser processes and explorer.exe. After injecting into the process, the virus chooses a random application from a static list. Then, the virus proceeds to run the chosen application in suspended mode and copy itself in the address space of the suspended process, thus mimicking a genuine Microsoft process. Next, the virus exits the original process which leaves FormBook's dead code in explorer.exe as a result. From this stage, new FormBook processes can inject targeted applications like web browser processes, which in the case of this particular ANY.RUN simulation is Firefox.
Depending on the objective process, the virus can establish various function hooks. Being run from inside the context of an already generated process, the virus starts to go through every currently active process, trying to identify targeted programs. As soon as a target is found, FormBook will inject itself into it and install a particular set of API hooks, that are based on the target program. The data is then saved in files in the %APPDATA% directory until it is sent to the C&C server. Pay attention to this function to detect malware.
The best counteraction technique is to exhibit caution when receiving emails with attachments from unknown senders. Attackers usually use social engineering to trick victims into downloading and opening infected files.
Deleting any suspicious emails from the inbox is a good way to stay safe. If the infection is already detected, a good practice is to carry out an analysis of all devices connected to the network for established CnC or potentially malicious URL connections. Once a suspicious email is received, perimeter settings can be adjusted to block all related emails in the future. Finally, if an infected file is already downloaded, the host should be quarantined until the threat is completely mitigated.
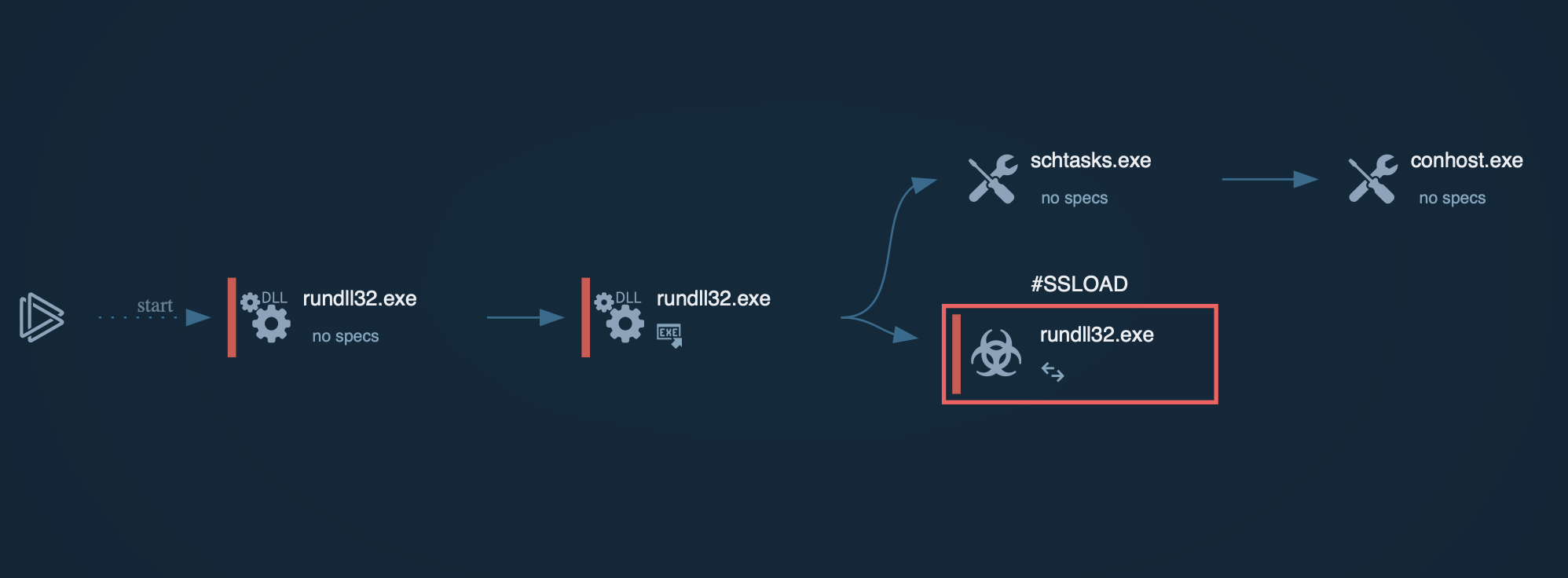
Formbook trojan usually injects into explorer.exe and another processes from the list, such as firefox.exe and msiexec.exe. Knowing this malware's function you can take a look at the process tree after a while during execution and easily determine either the sample is Formbook or not.
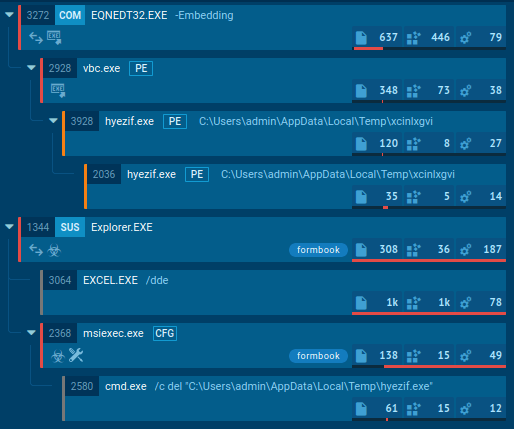 Figure 3: A tree of processes created by Formbook during its execution
Figure 3: A tree of processes created by Formbook during its execution
Thanks to extreme ease of use and low cost, FormBook is gaining traction in the criminal community. Not only is the virus's functionality freely accessible for download on open hacker forums and easy to set up without any programming knowledge, but it also comes equipped with some highly advanced anti-evasion techniques, that make detecting it with anti-virus software ultra-difficult. ANY.RUN interactive malware hunting service enables to study FormBook in detail from a secure environment and implement cybersecurity measures accordingly.