Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


The Arechclient2 malware is a sophisticated .NET-based Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that collects sensitive information, such as browser credentials, from infected computers. It employs various stealth techniques, including Base64 encoding to obscure its code and the ability to pause activities to evade automated security tools. The malware also can adjust Windows Defender settings and uses code injection to manipulate legitimate processes.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 November, 2019
First seen
:
|
26 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 November, 2019
First seen
:
|
26 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 861
861
 0
0

 511
511
 0
0

 2797
2797
 0
0
Arechclient2 is a .NET Remote Access Trojan (RAT) that was first observed in 2019. It is also widely known under the name SectopRAT. This malware is designed to steal sensitive data from browsers and cryptocurrency wallets, posing a significant threat to users' personal and financial information.
The distribution of Arechclient2 is typically carried out through malicious links, executable file uploads, and fake application updates. In some cases, it may be distributed as an LNK file or as an ISO file containing a malicious executable, making it difficult for users to detect and avoid infection.
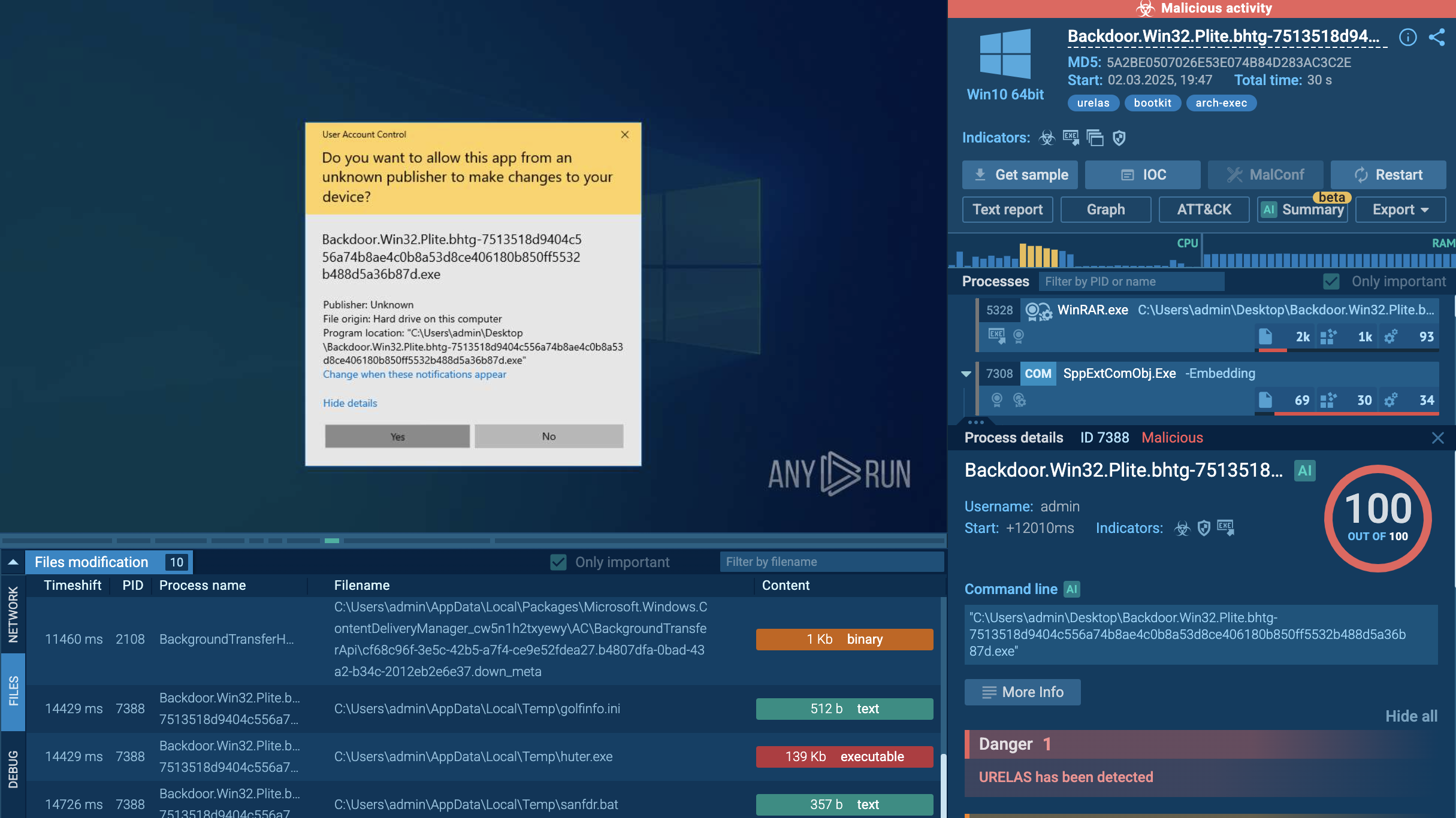
 Arechclient2 analyzed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Arechclient2 analyzed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Analysis in ANY.RUN’s interactive malware sandbox shows that ArechClient2 makes considerable use of scripts and process injection to facilitate infection.
Some of the primary capabilities of the Arechclient2 malware include:
Let’s take a closer look at the stages of Arechclient2 infection by analyzing its sample inside ANY.RUN’s cloud sandbox for malware analysis.
 ANY.RUN identifies malicious processes and lists all the actions performed by the malware
ANY.RUN identifies malicious processes and lists all the actions performed by the malware
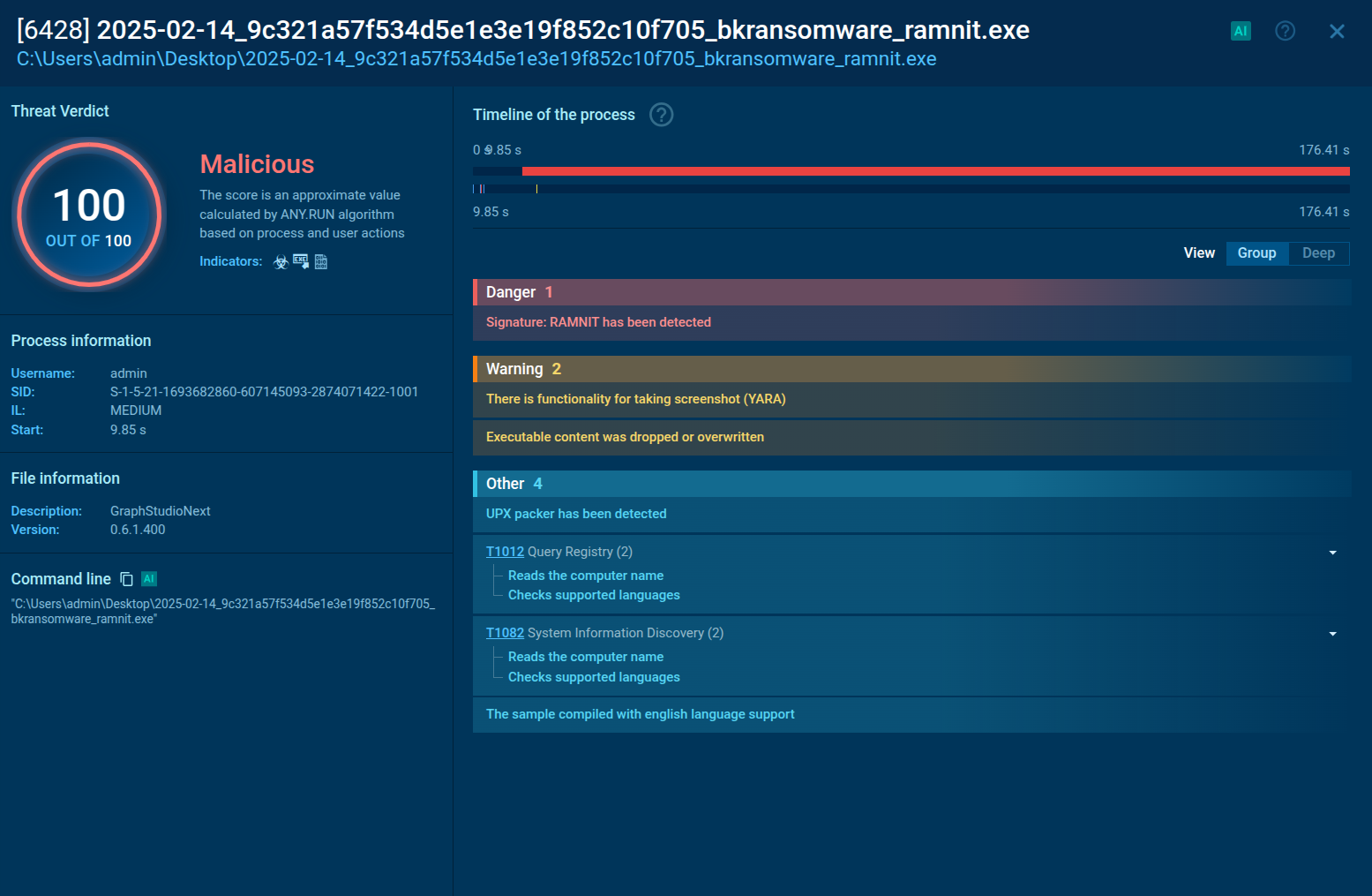
The process starts with the delivery of a malicious first-stage payload, which can vary between campaigns. It may be distributed as an LNK file or as an ISO file containing a malicious executable. These files are often spread through unknown initial attack vectors, likely involving social engineering or phishing tactics that trick users into executing them.
When the LNK file is double-clicked, it starts the system utility forfiles.exe to achieve indirect command execution by running PowerShell. An ISO file is mounted like a CD, and the executable may run automatically, initiating the infection process. Upon execution, the payload may extract files into a newly created directory within the victim’s temporary files. This extraction process also initiates multiple child processes crucial to the RAT’s functionality. The execution chain often uses AutoIT, further complicating detection efforts.
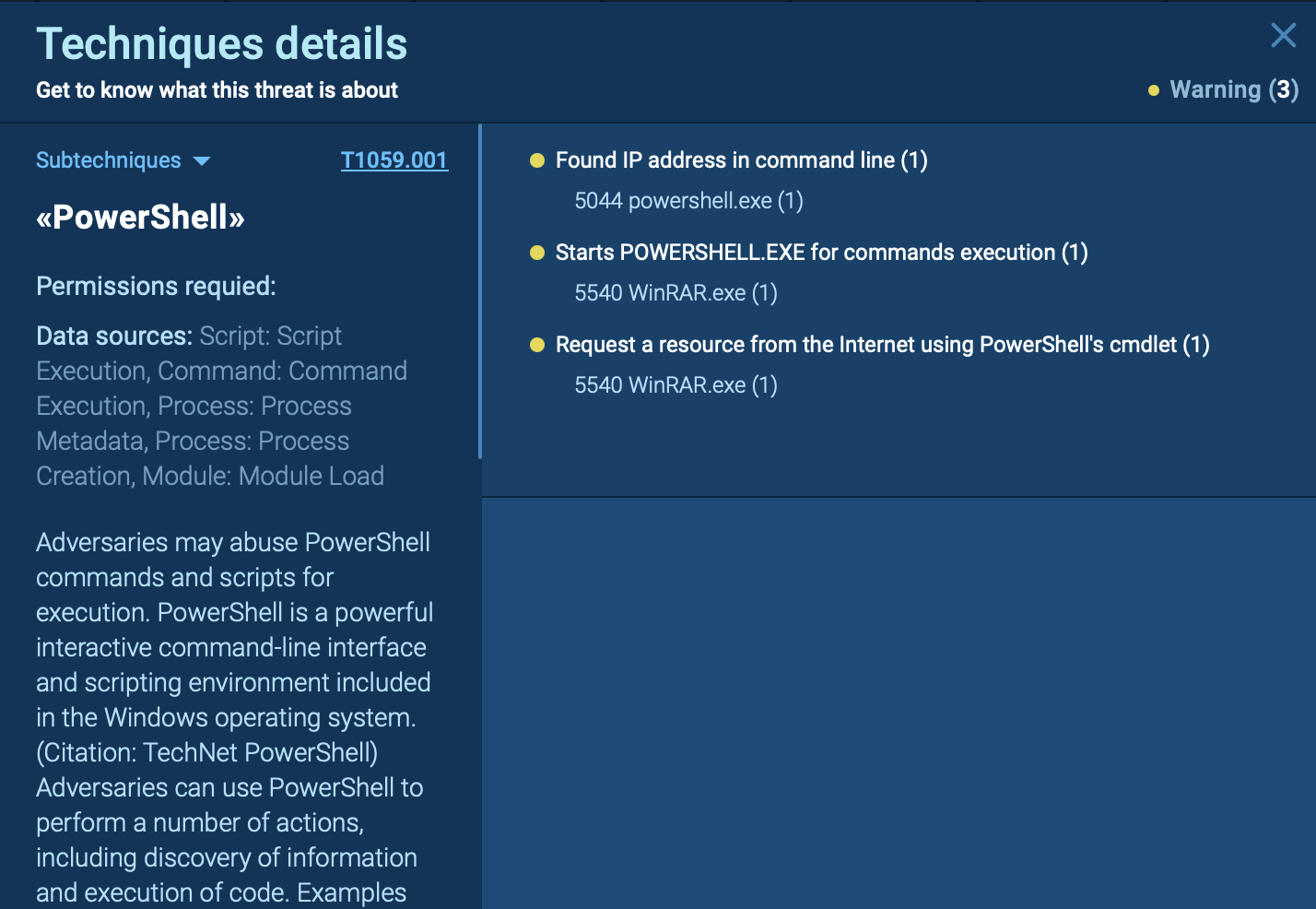
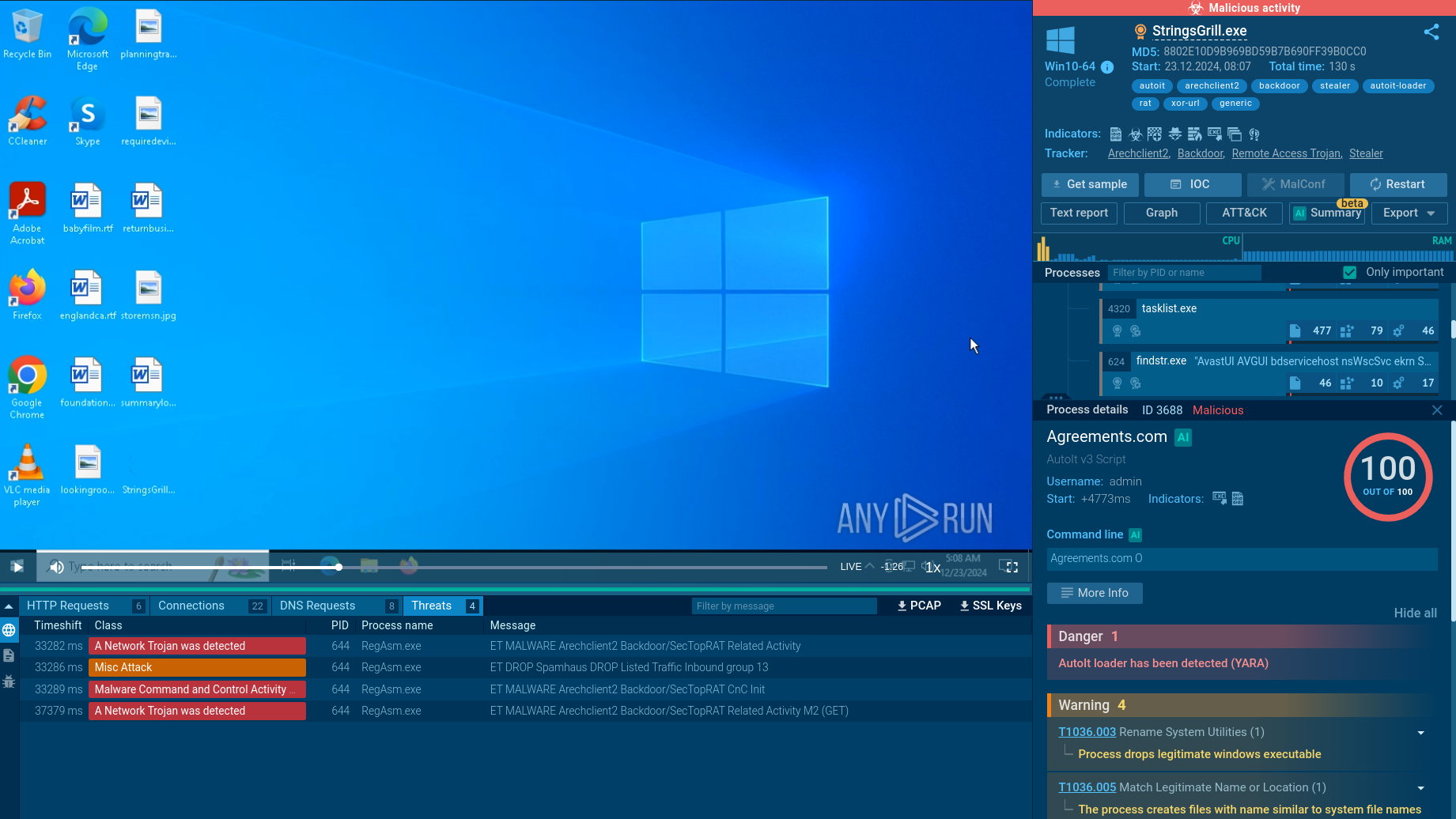
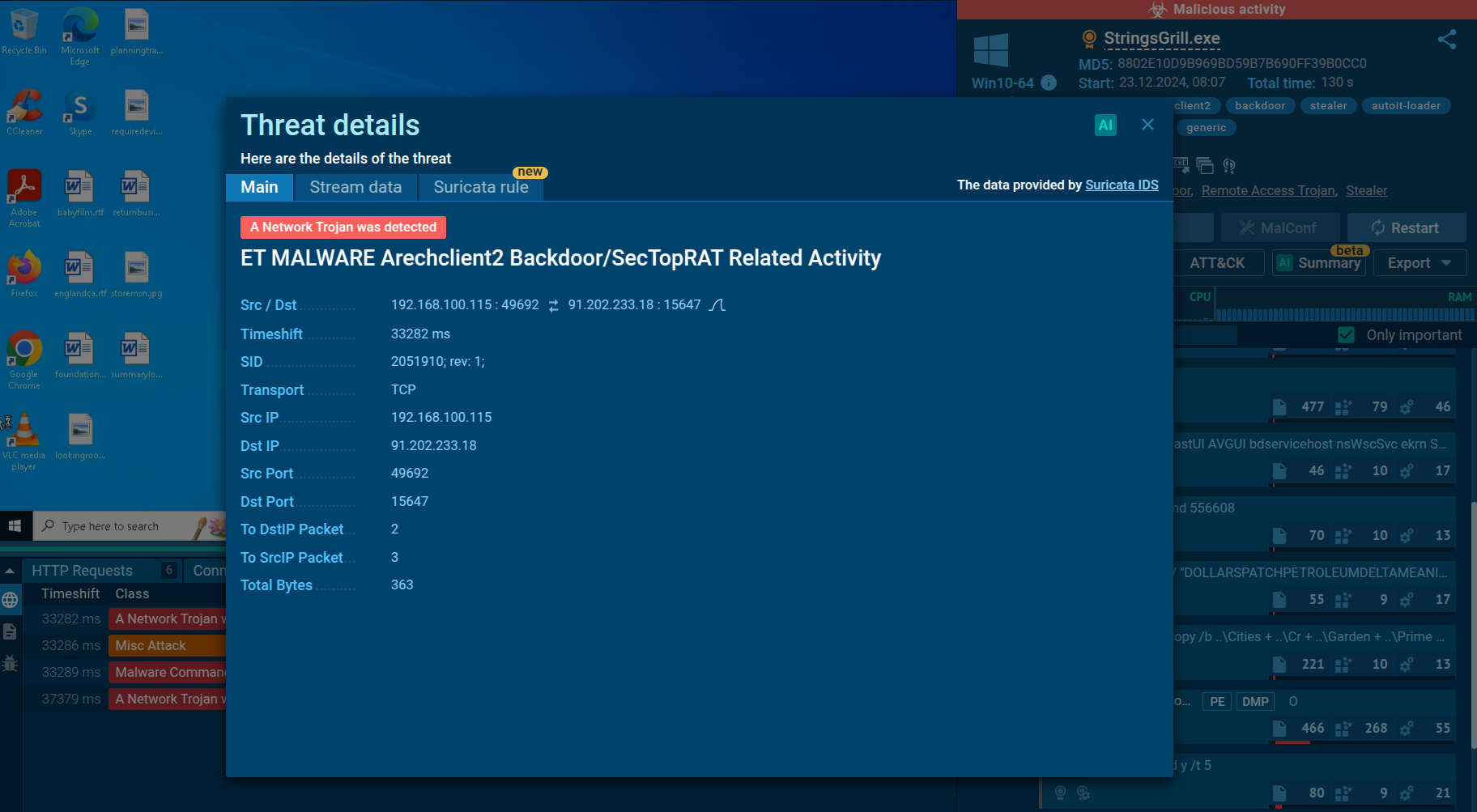 ANY.RUN uses Suricata IDS to spot malicious network activities
ANY.RUN uses Suricata IDS to spot malicious network activities
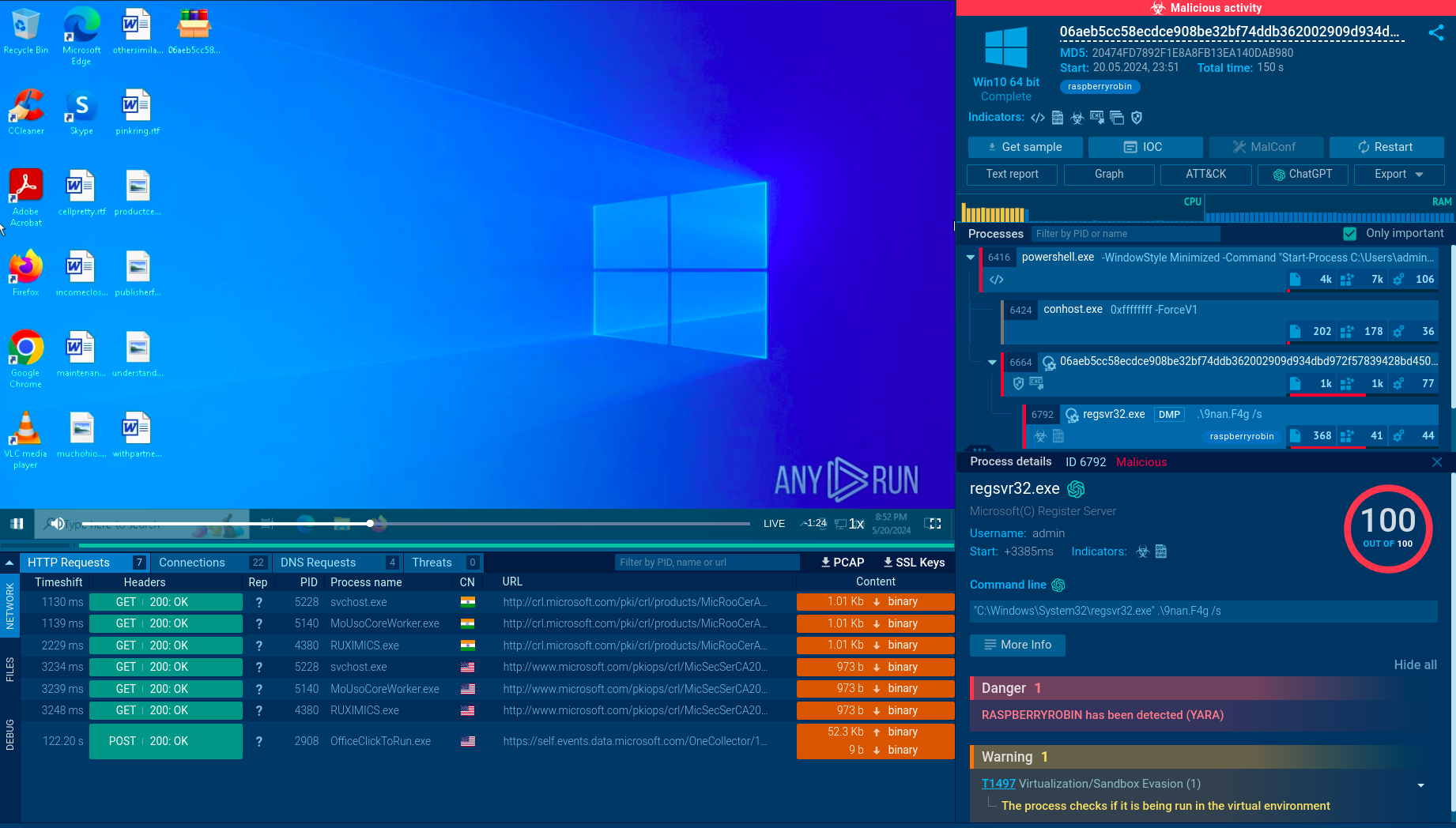
The malware injects its payload into legitimate processes (e.g., InstallUtil.exe) using a function that facilitates injection while avoiding antivirus hooks by copying necessary files from system directories. This step is critical for maintaining stealth and ensuring continued control over the infected machine. Arechclient2 connects to its command and control (C2) server on port 15647 to receive commands. The communication includes encrypted data, which can switch to plaintext if encryption is disabled during interception. This allows attackers to issue commands remotely, manipulate settings, or extract sensitive information from the victim’s system.
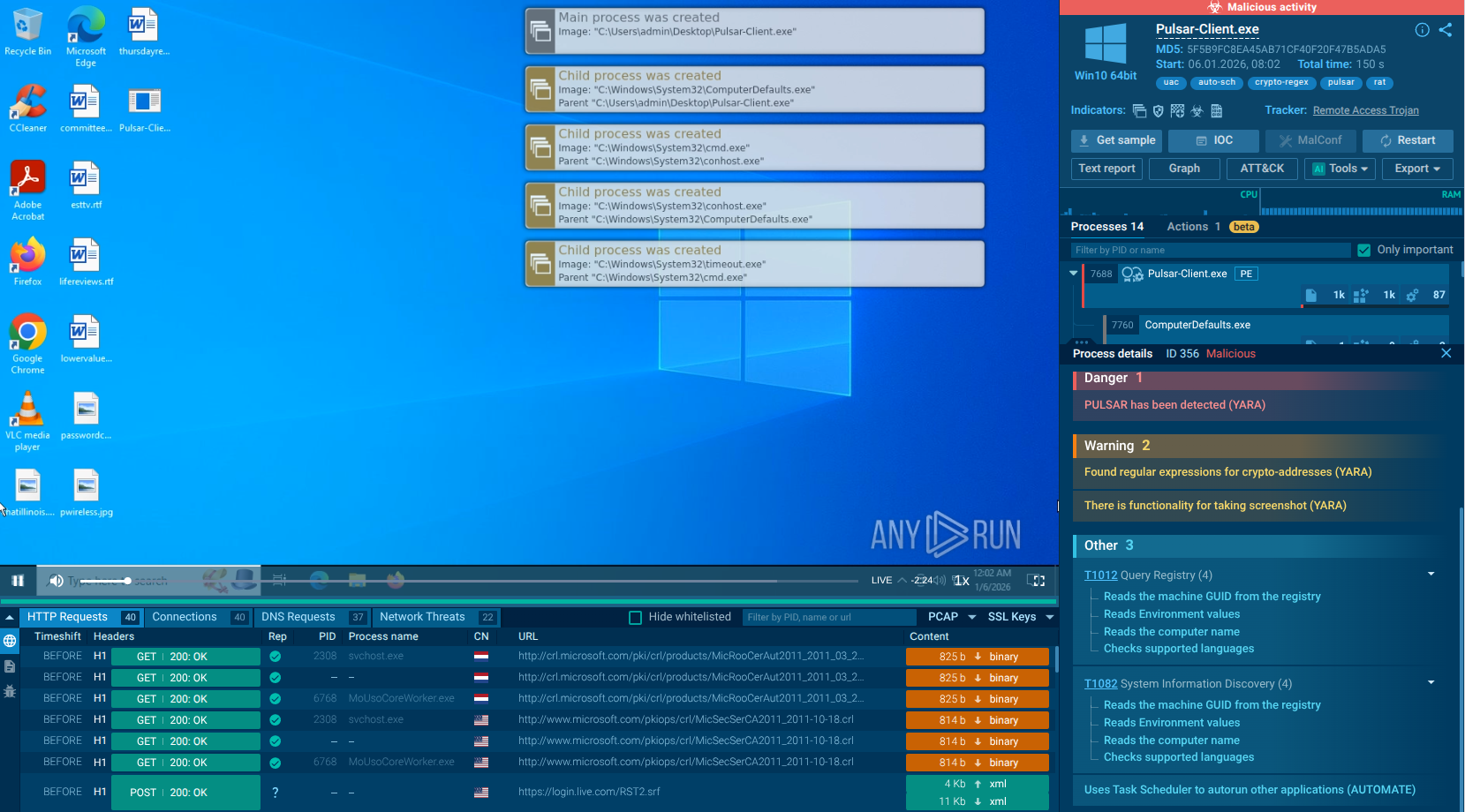
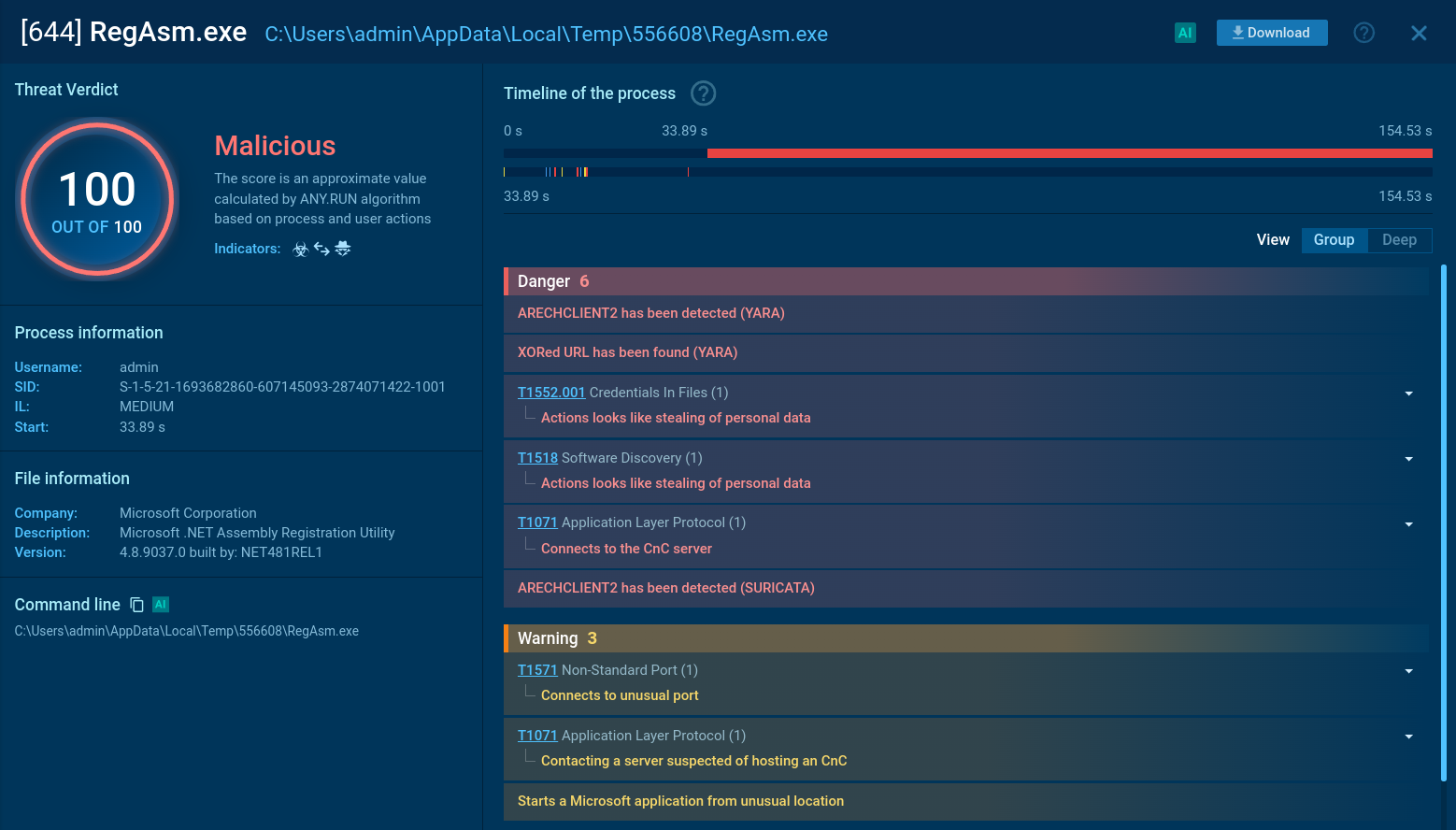
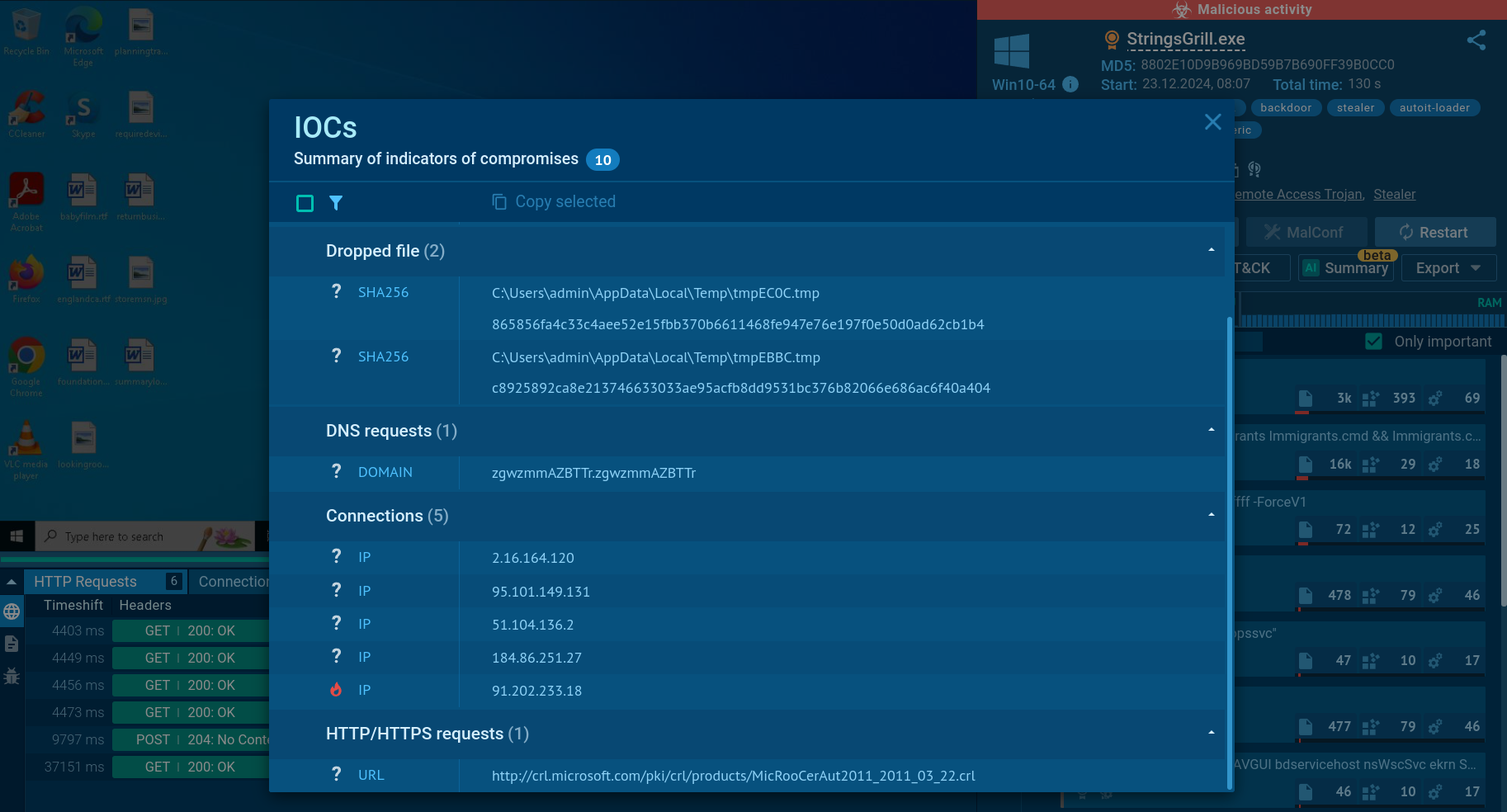 After analysis in ANY.RUN, you can collect a detailed threat report and IOCs
After analysis in ANY.RUN, you can collect a detailed threat report and IOCs
The RAT can extensively profile victim systems, stealing sensitive information such as browser data and cryptocurrency wallet details. It can also launch hidden sessions to monitor user activity without detection.
ArechClient2 uses various methods to trick users into clicking on harmful links that look legitimate.
Phishing techniques are employed to convince users to open files containing malicious content, which starts the infection process.
One common distribution method is to disguise the malware as updates for popular applications like Brave Browser, TOR, Signal, and Telegram.
By appearing as genuine updates, the malware takes advantage of users' trust in these applications to increase the chances of infection.
To obtain up-to-date intelligence on ArechClient2, utilize Threat Intelligence Lookup from ANY.RUN. This service grants access to a vast database containing Indicators of Compromise (IOCs), Indicators of Attack (IOAs), and Indicators of Behavior (IOBs) from millions of malware analysis sessions performed within the ANY.RUN sandbox. With over 40 customizable search parameters, users can retrieve data on threats, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts associated with ArechClient2.
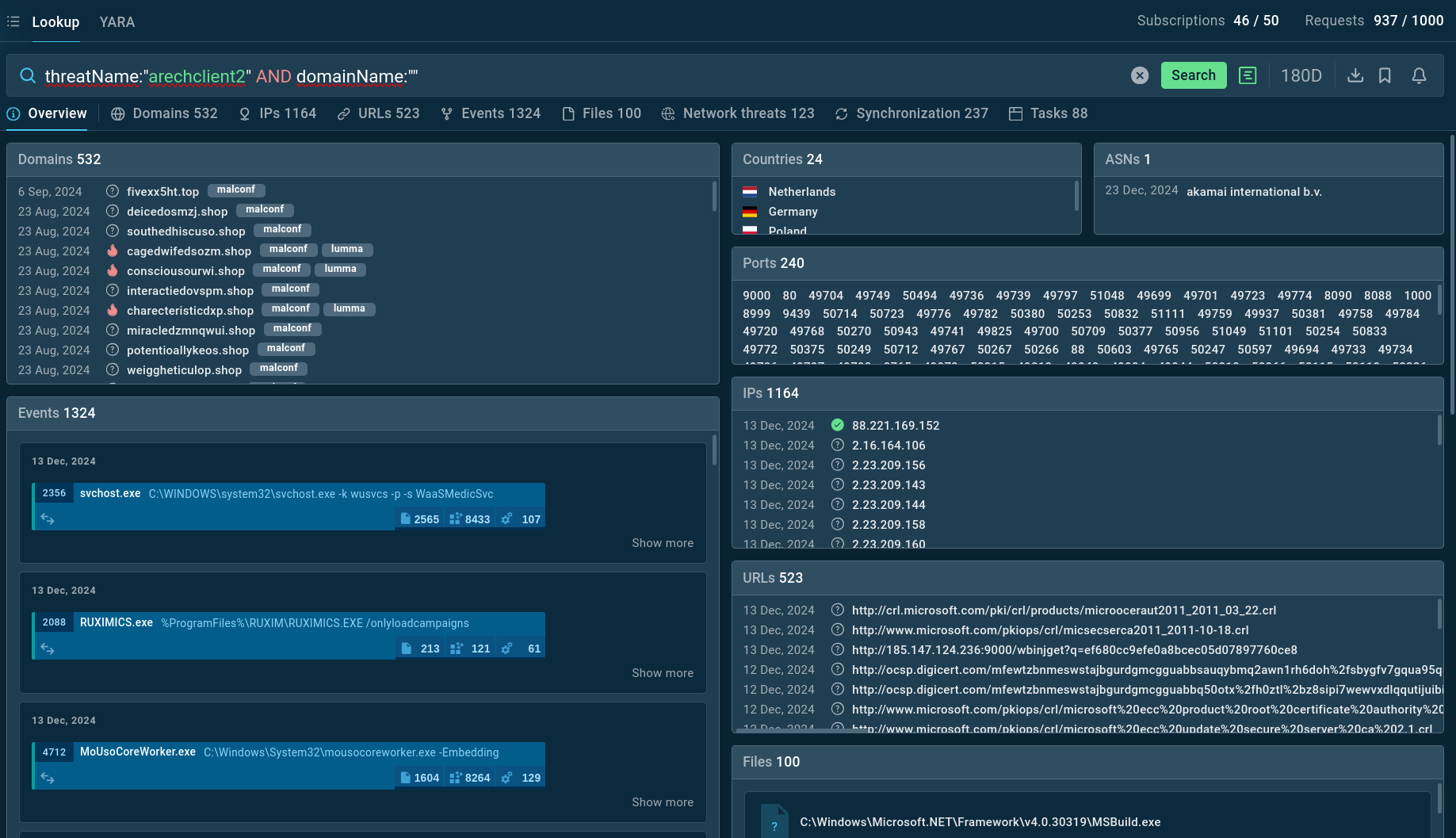 TI Lookup helps you enrich your investigations with additional threat context
TI Lookup helps you enrich your investigations with additional threat context
For instance, to gather information on ArechClient2, you can search using its threat name or related artifacts. Inputting a query like threatName:"arechclient2" AND domainName:"" will produce a list of files, events, domain names, and other data extracted from malware samples, along with sandbox sessions that can be examined in detail to gain in-depth understanding of this malware’s behavior.
Arechclient2, also known as SectopRAT, is a sophisticated malware able to evade detection and circumvent security systems. Its activity may lead to direct financial losses.
Whether you would like to research Arechclient2 in detail, or just check some suspicious link or file, use ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox. It knows how to withstand VM-detection techniques and is integrated with Threat Intelligence Lookup to provide you with the data for proactive protection measures.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account to analyze cyber threats with no limit →