Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


DarkComet RAT is a malicious program designed to remotely control or administer a victim's computer, steal private data and spy on the victim.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
France
Origin
:
|
|
12 February, 2008
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
France
Origin
:
|
|
12 February, 2008
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 443
443
 0
0

 2320
2320
 0
0

 4485
4485
 0
0
DarkComet is a remote access trojan developed by Jean-Pierre Lesueur in 2008. According to him, the program was never intended to be used illegally. But it got viral in 2012 after the Syrian incident: the government used the RAT to spy and destroy the protestor’s network.
It’s a standard remote control malware – a hacker rules over the infected computer and gets access to the camera and microphone. That is why DarkComet serves as a tool to monitor victims’ actions, take screenshots, do key-logging, or steal credentials.
The malware has had several versions, and DarkComet 5.3.1 is still available in 2022.
Crooks try to make targets download and run the RAT using different social engineering techniques. And in some cases, attackers use DarkComet to deliver other malicious programs to the infected machine. Hackers may involve the victim machine in a botnet scheme, such as sending spam.
ANY.RUN allows researchers to analyze DarkComet samples and monitor the malware’s activity in real-time using an interactive sandbox
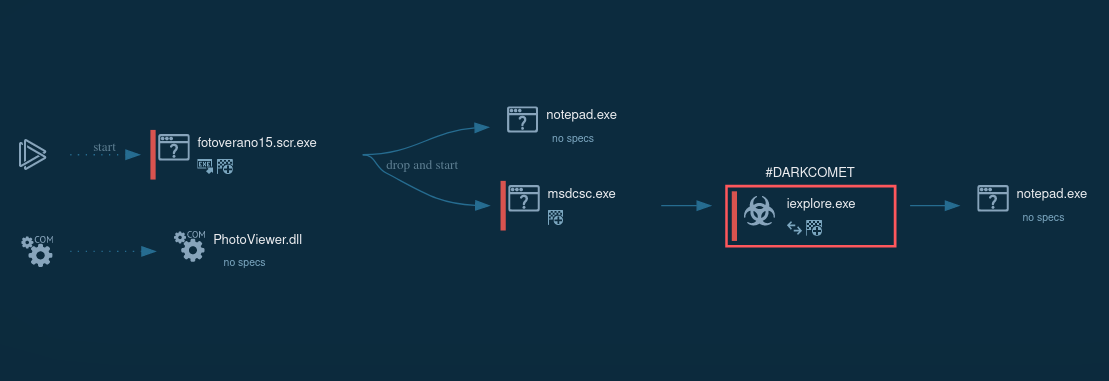
Figure 1: Process graph of DarkComet execution generated by ANY.RUN
DarkComet has a typical RAT execution.
The infected system connects to the hacker’s computer and gives the attacker full access. Crooks may exploit all the system's features: the infected machine is ready to get packets and perform the commands.
Systems communicate via TCP to the chosen DarkComet malware port on the selected IP/domain. Then C&C traffic begins with RC4-256 encryption.
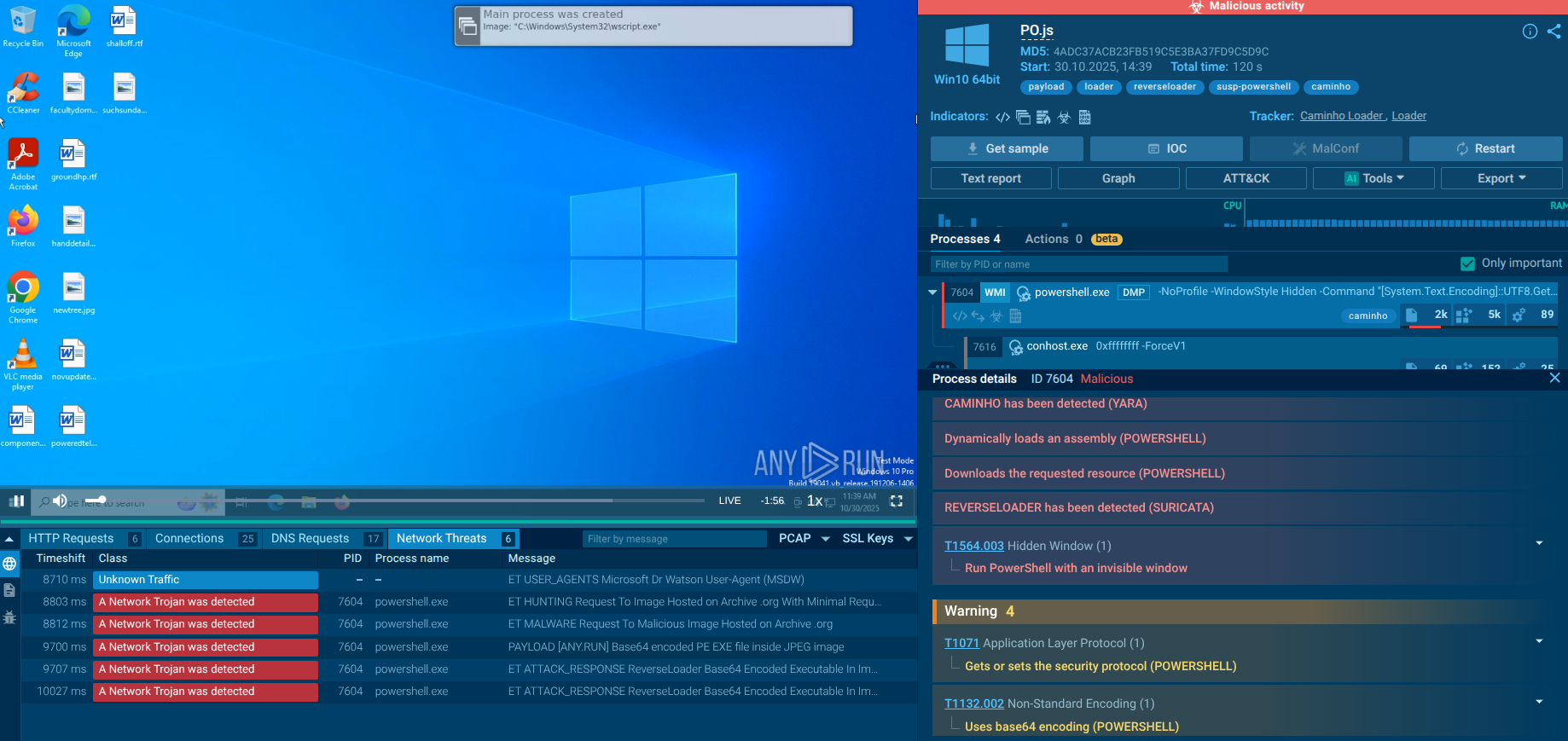
The execution process of the DarkComet varies depending on the sample and version. The most straightforward execution is just one process that makes all activities in the infected system.
In some cases, malware may use system utilities to defend against evasion or persistence. For example, in this task, it uses the T1564.001 technique: malware starts attrib.exe through cmd.exe to hide the main executable. In the system process, iexplorer was injected with malicious code and provided the main malicious activity afterward.
To trick people into downloading and installing programs such as Quasar RAT, njRAT, and DarkComet cybercriminals use:
Emails may include malicious content in various formats like Microsoft Office documents, PDF documents, .exe files, ZIP and RAR archives, JavaScript files, etc.
After a user is tricked into downloading and then opening a file, it installs other malware.
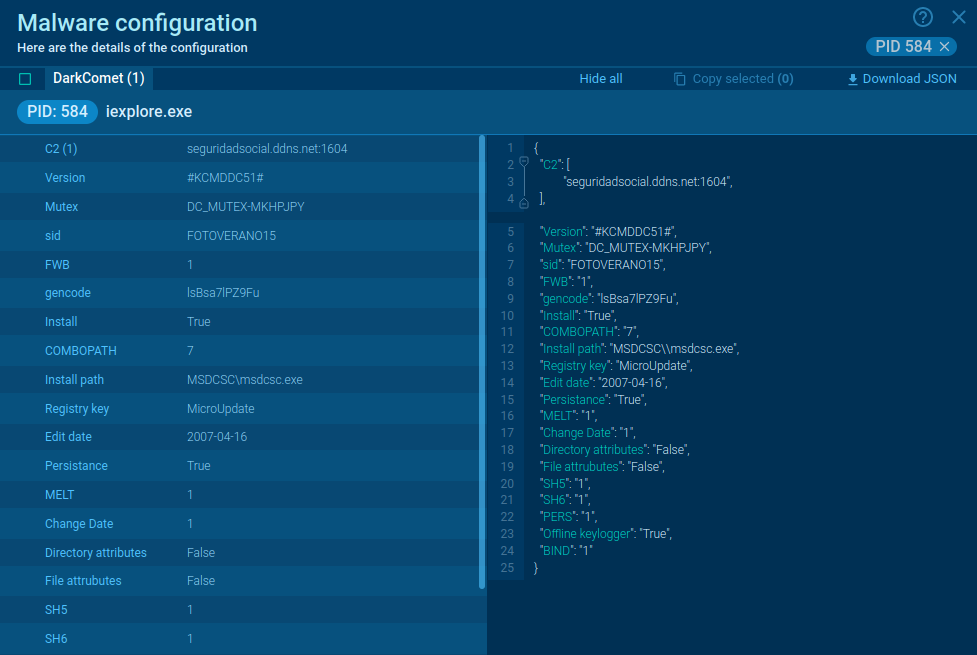
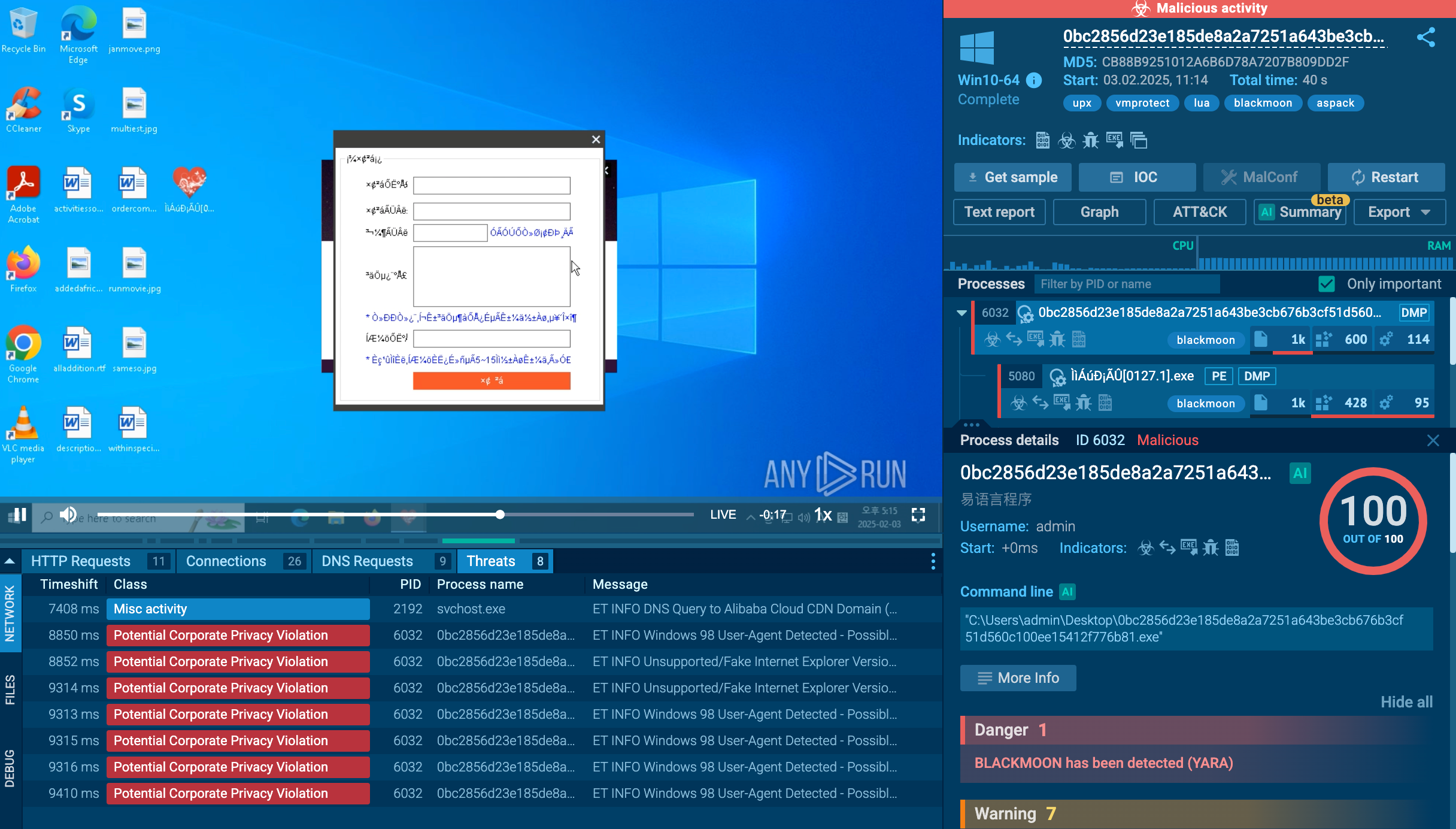
Figure 2: DarkComet memory dump
ANY.RUN automatically creates a memory dump of the running process and matches it with the Yara rule. After DarkComet detection, its config is available to researchers for subsequent analysis in no time.
In our example, malware configuration was extracted just 10 seconds after the task launch.
Having DarkComet downloaded on your working station can cause severe issues. And it’s better to get rid of it immediately. Concerning the SOC’s specialists' goal, the analysis of the RAT’s infection should be carried out as soon as possible. And with ANY.RUN sandbox it’s easy to do.