Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

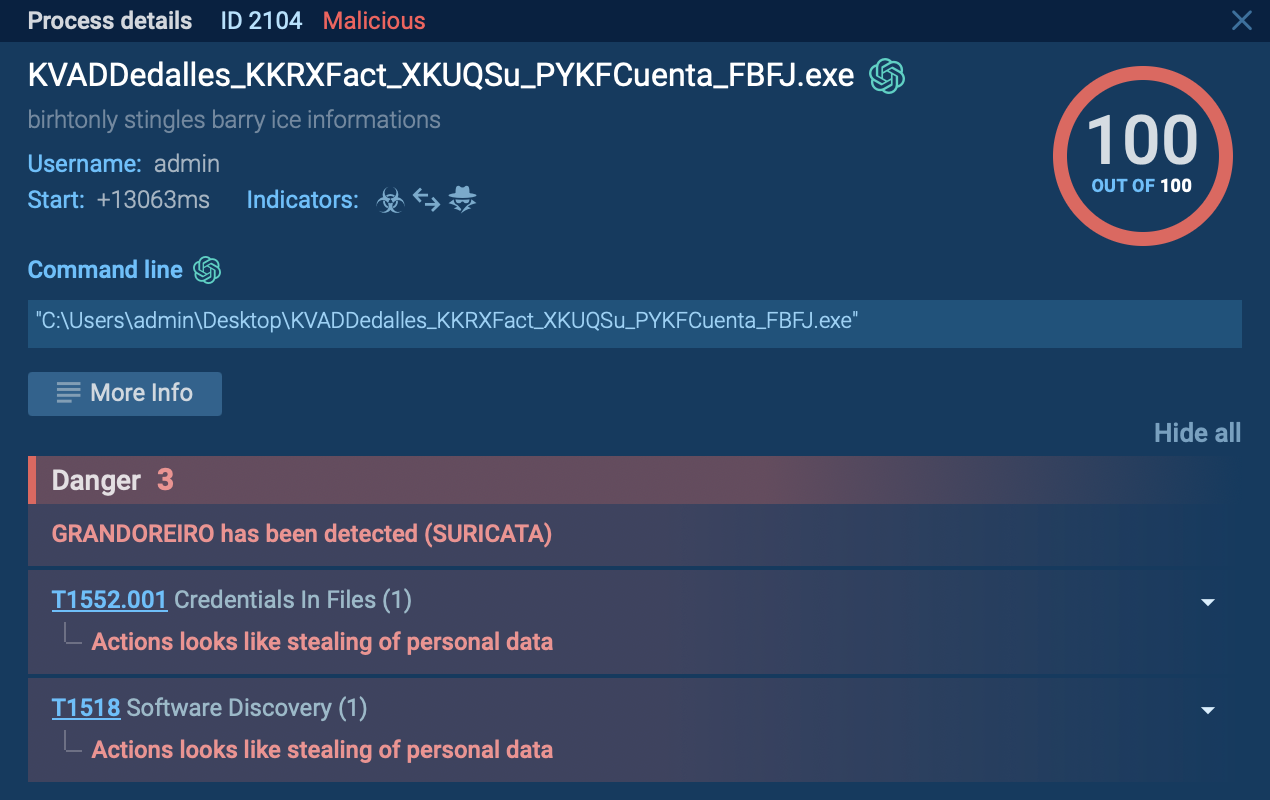
Quasar is a very popular RAT in the world thanks to its code being available in open-source. This malware can be used to control the victim’s computer remotely.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2015
First seen
:
|
1 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2015
First seen
:
|
1 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 975
975
 0
0

 572
572
 0
0

 2925
2925
 0
0
Quasar is a remote access trojan is used by attackers to take remote control of infected machines. It is written using the .NET programming language and is available to a wide public as an open-source project for Microsoft Windows operating systems, making it a popular RAT featured in many attacks.
Quasar RAT was first discovered in 2015 by security researchers, who, at the time, speculated that an in-house development team wrote this RAT after performing the analysis of a sample. However, Quasar is an evolution of an older malware called xRAT, and some of its samples can carry out as many as 16 malicious actions.
Over the course of its lifetime, the malware has been updated several times, improving its overall functionality. The last version of the malware, which the original author developed, is v. 1.3.0.0. It was released in 2016. Since then, several third parties have adapted the RAT and issued their own version, both minor and major, with the last major version being v. 2.0.0.1.
The RAT we are reviewing today consists of two main components – the server-side component and the Quasar client-side component. The server is equipped with a graphical user interface, and it is used for managing connections with the client-side programs. The Quasar client-server architecture is also utilized to build malware samples which are eventually delivered to potential victims. Malware users can select attributes and customize the executable to fit the attacker's needs. The Quasar client and server run on different OSs including all Windows versions.
The functionality of the resulting malware includes remote file management on the infected machine, registry alterations, recording the actions of the victim, establishing remote desktop connections, and more. All of the data including requests are sent to the host server with the user-agent strings.
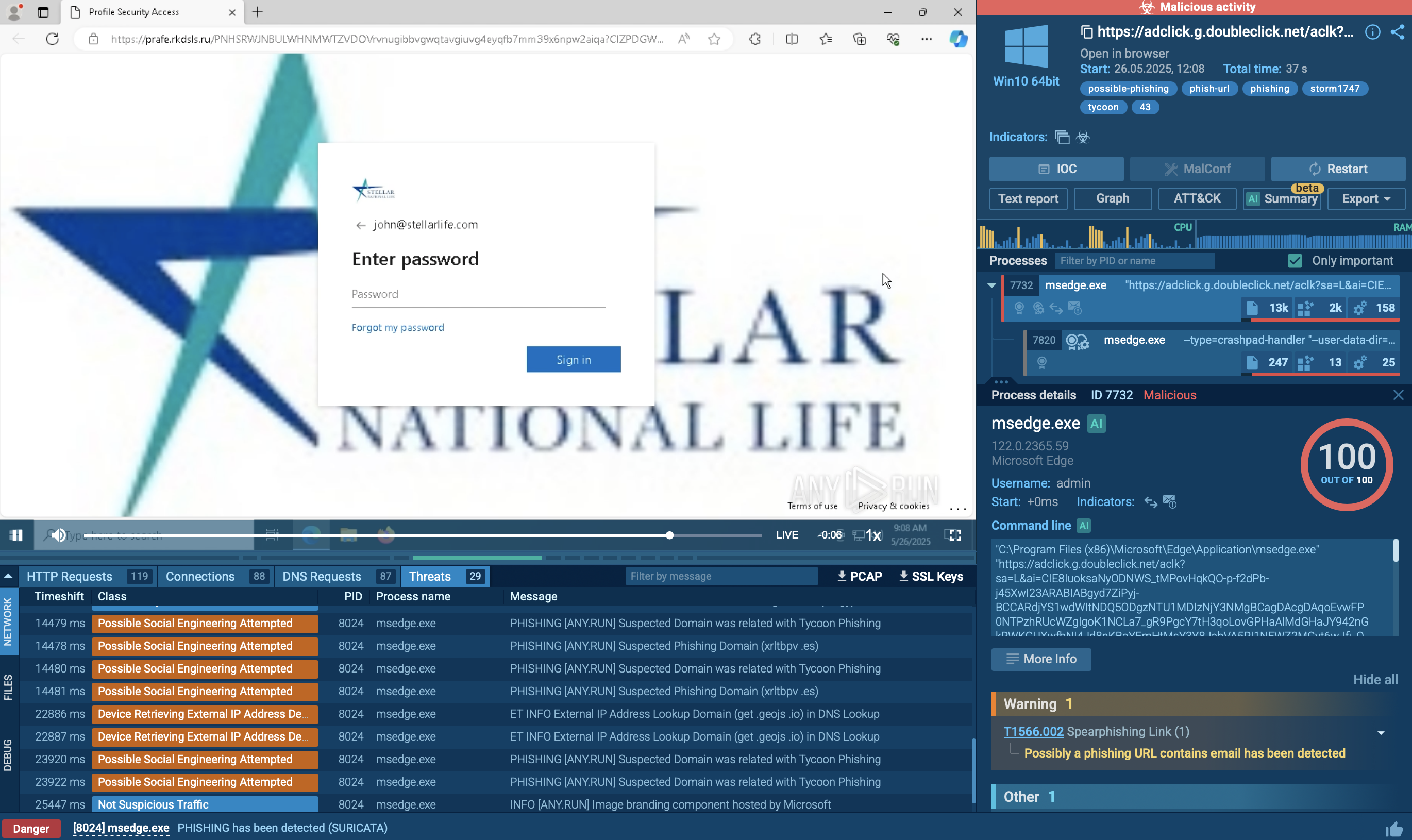
It should be noted that Quasar's execution can unfold completely silently. Thus, once the victim downloads and launches the Quasar client, usually delivered in a document via email, it can stay active for a long period of time, stealing data and giving the hacker control over the infected PC. The malware does generate a process that can be discovered using the Windows Task Manager or a similar application, but active user actions are required to discover Quasar trojan's presence on a machine.
As far as creators of this malware are concerned, the group of people or a person behind the original version of this malware managed to remain anonymous. As a result, the little-known information that we do have does not go beyond the name of the GitHub page author, which states “quasar.”
As evident from the description on the “official” Quasar GitHub page, this malware is presented as a legitimate remote administration program, which is clearly misleading. In fact, Quasar was featured in an attack aimed at the US government early in 2017. Later the same year, another wave of attacks using this malware occurred, targeting the private sector.
The execution process of this malware can be viewed in a video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service, allowing to perform analysis of how the contamination process unfolds.
 Figure 1: Displays the lifecycle of Quasar in a visual form, as shown on the graph generated by ANY.RUN.
Figure 1: Displays the lifecycle of Quasar in a visual form, as shown on the graph generated by ANY.RUN.
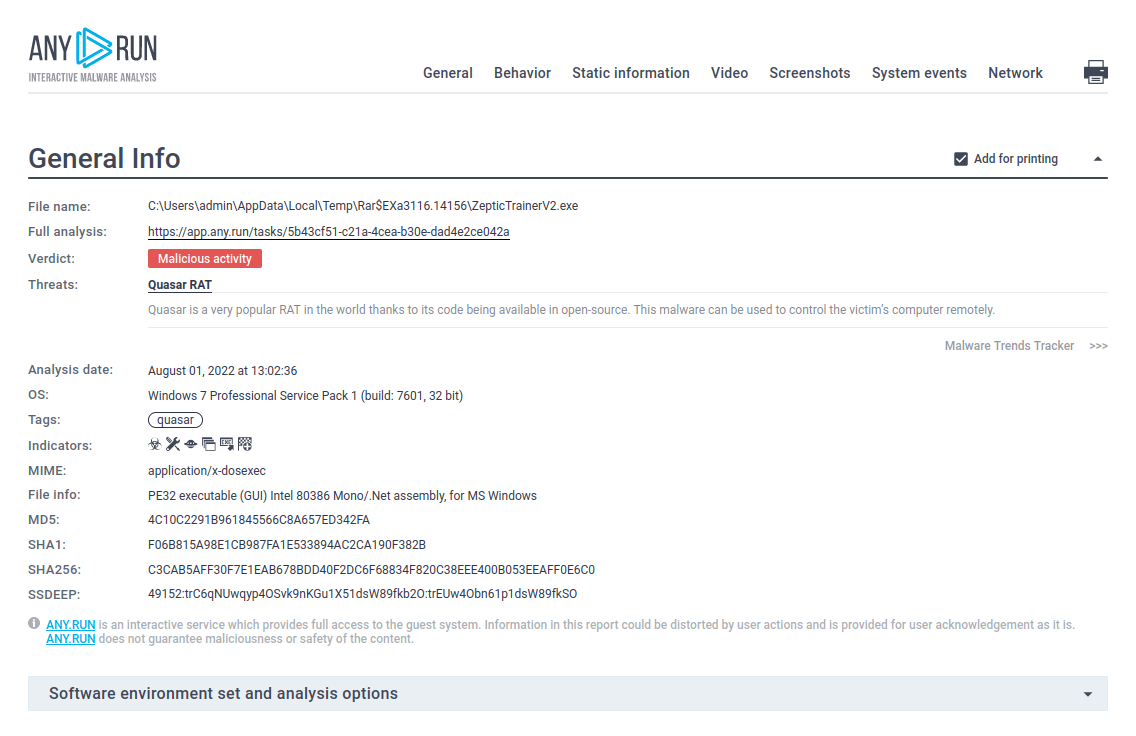 Figure 2: Shows a customizable text report generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service.
Figure 2: Shows a customizable text report generated by the ANY.RUN malware hunting service.
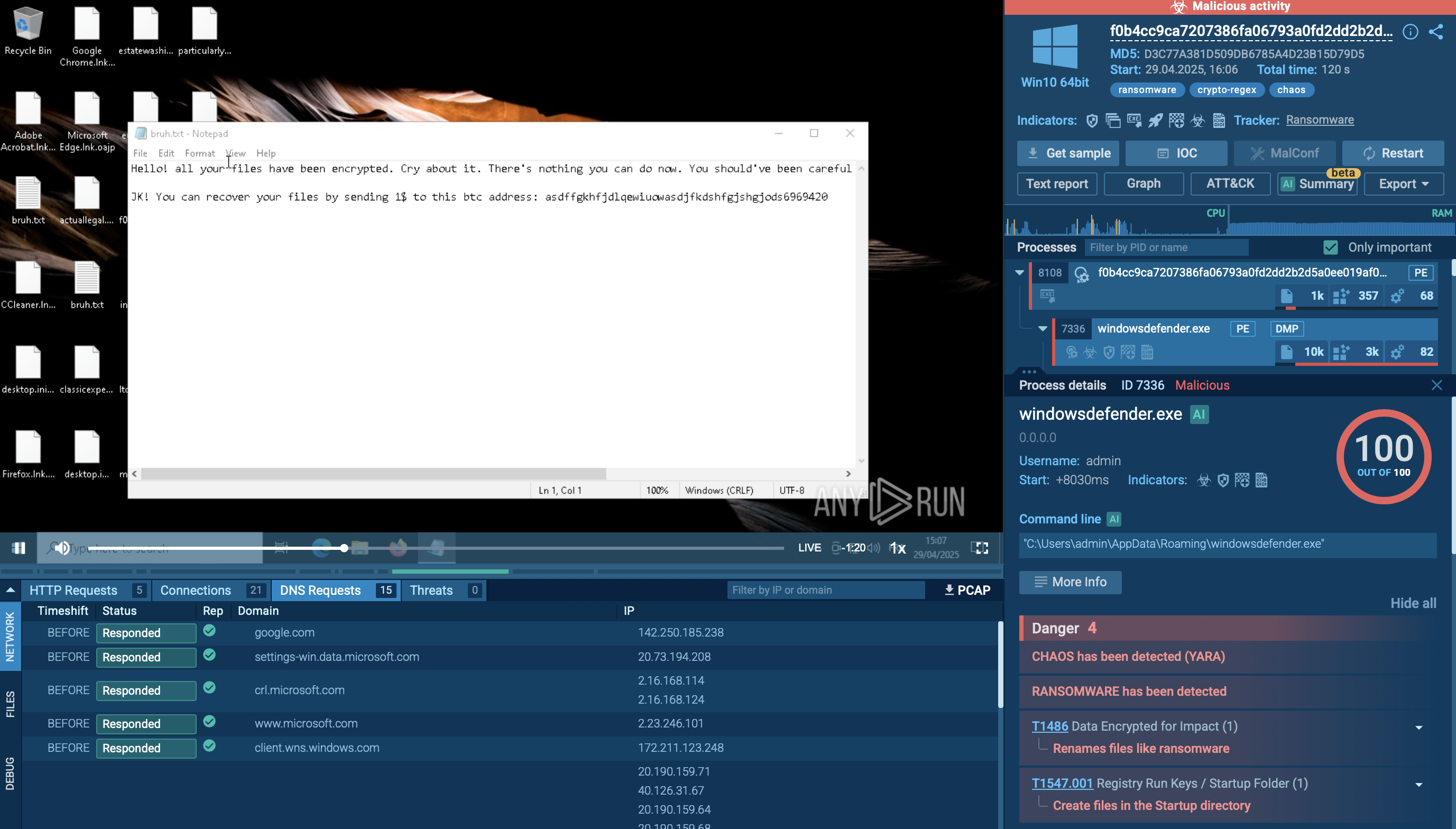
Based on the analysis, Quasar execution is pretty straightforward but can vary in minor details from sample to sample. The RAT's user-agent strings fake various processes such as a browser running on Windows. In the given example, Quasar was dropped from a Microsoft Office file. Then, the dropped file changed the registry value to run with every operating system start, checked for external IP, and copied itself at another location. After all these steps, the malware started the main malicious activity - collecting information about the operating system and waiting for commands from the C2 server. Quasar allows malware users to collect host system data.
Quasar trojan writes itself into scheduled tasks and uses registry keys to achieve persistence, allowing the malware the run every time a machine is started. The persistence method is chosen based on user privileges. If the user has admin rights, the malware uses schtasks to create a scheduled task that launches after a user logs on with the highest run level. If admin rights are lacking, then the scheduled task can only go as far as adding a registry value configured in the client builder and added to the current path as the startup program. The best way to avoid infection is for cybersecurity specialists gt to know various user-agent strings that exist in their network, and identify suspicious user-agent strings.
Like most other RATs, for example Crimson RAT or Orcus RAT, Quasar is distributed in email spam campaigns that carry the malware’s loader. The loader is embedded in a malicious file attachment which usually carries a name designed to trick the user into thinking that they are receiving some sort of a document. Sometimes these files will have a double extension such as docx.exe. Again, this is done to trick the victim into thinking that the attached file is harmless. Of course, once opened, such files start a command prompt rather than Microsoft Office.
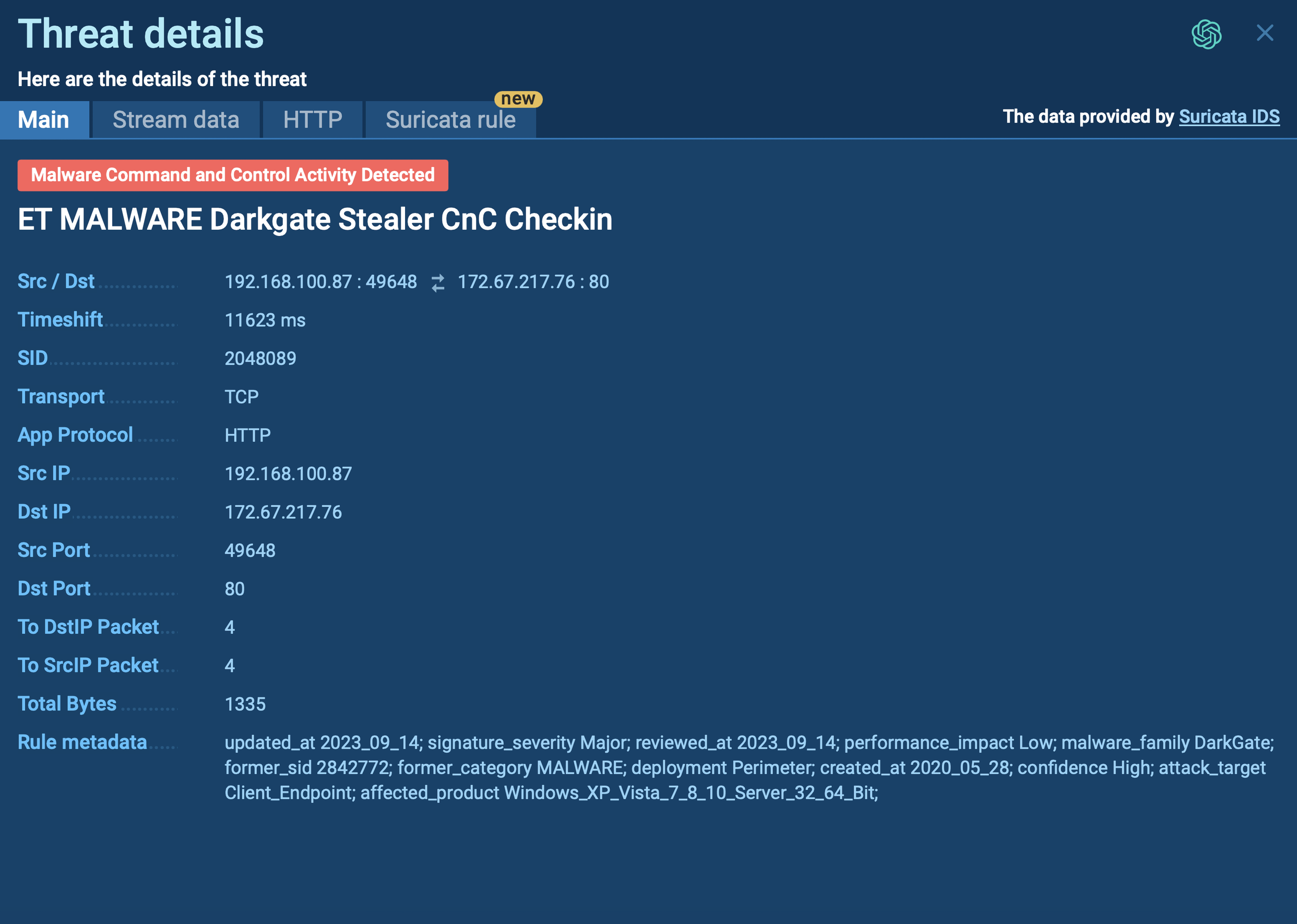
ANY.RUN uses Suricata IDS rule sets, so if malware tries to communicate with C&C servers, it will be detected. To look at what threats were detected, just click on the "Threats" section of the "Network" tab.
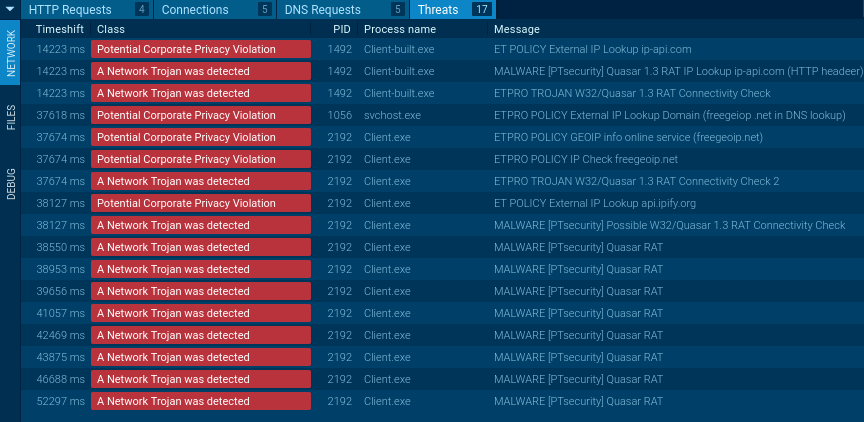 Figure 3: Quasar network threats
Figure 3: Quasar network threats
Quasar trojan is a powerful open-source malware equipped with a robust persistence mechanism and a complete feature set of malicious capabilities. Being available to anybody with programming knowledge, Quasar became a widely used RAT which was even featured in an attack targeted at the American government.
However, unlike other more advanced Trojans, Quasar RAT does not have extremely sophisticated anti-analysis features, which makes setting up robust cyber-defense an easier task, especially when using malware hunting services like ANY.RUN to simplify and streamline the research process.