Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Orcus is a modular Remote Access Trojan with some unusual functions. This RAT enables attackers to create plugins using a custom development library and offers a robust core feature set that makes it one of the most dangerous malicious programs in its class.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Canada
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2016
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Canada
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2016
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 842
842
 0
0

 502
502
 0
0

 2779
2779
 0
0
Orcus, previously known as Schnorchel, is a Remote Access Trojan, which enables remote control of infected systems. Although Orcus RAT malware is mostly a typical member of the RAT family, it has some competitive advantages over similar malware and unique features.
In addition, Orcus RAT has a modular structure, and it gives users the ability to create custom plugins for the malware. The modularity of this trojan gives it higher than standard scalability and management, allowing it to tailor the malware to the needs of various campaigns.
The first time we heard about this malware was from a forum post by one of its authors. The post announced the development of a new RAT that was named Schnorchel at the time. Soon after the announcement, the malware became commercially available under the name “Orcus RAT” and was presented to the public as legal software for remote administration, similar to Teamviewer. Interestingly, the authors claimed that the abbreviation RAT stood for Remote Administration Tool and not Remote Access Trojan.
Apart from a few exceptions, Orcus RAT malware has a relatively standard but robust feature set for a technologically advanced Remote Access Trojan. The malware can grab screenshots and record user input, activate the webcam, steal passwords, record audio, and steal information. In addition, Orcus comes with the ability to detect if it’s being launched on a virtual machine to complicate the analysis by security researchers.
The functions described above already make this malware quite capable. However, it offers a few unusual functions that enhance its functionality. Namely, the RAT in question supports plugins, and besides offering the ability to build them, it has a whole library of already created plugins that attackers can choose from. Furthermore, Orcus RAT plugins can be written in multiple languages, including C#, C++, and VB.Net.
To make the development of extensions more streamlined, malware creators rolled out a dedicated development environment. What’s more, those who lack the skills to build plugins from scratch on their own can follow detailed tutorials and benefit from well-maintained documentation libraries.
Additionally, Orcus had a Github page where authors have published samples of created plugins.
Another relatively unique feature that the malware authors packed into this virus is real-time scripting. Real-time scripting allows Orcus to write and run code on machines that it infected.
Speaking of Orcus RAT malware authors, we know that the virus was developed by a 36-year-old John Revesz, also known as “Armada" on the underground forums. In 2019, Canadian authorities accused Revesz of operating an international malware distribution scheme.
In his defense, Revesz claimed that the RAT is, in fact, a legitimate program for remote administration, and his company “Orcus Technologies” is a legal business. However, an examination of the functionality clearly revealed that the software is intended for malicious use cases, which resulted in the arrest of Revesz.
It is believed that Revesz wasn’t working alone. Therefore, a joint development effort theory makes sense, especially considering the technological complexity of certain aspects of this malware. For example, Orcus RAT consists of multiple components, with the control panel being a separate component. In addition, the server that the malware establishes a connection with after infection does not hold an admin panel. This architecture provides several advantages to the attackers, for example, the ability to share access to infected PCs from the same server. Additionally, it allows for greater scalability or infected networks.
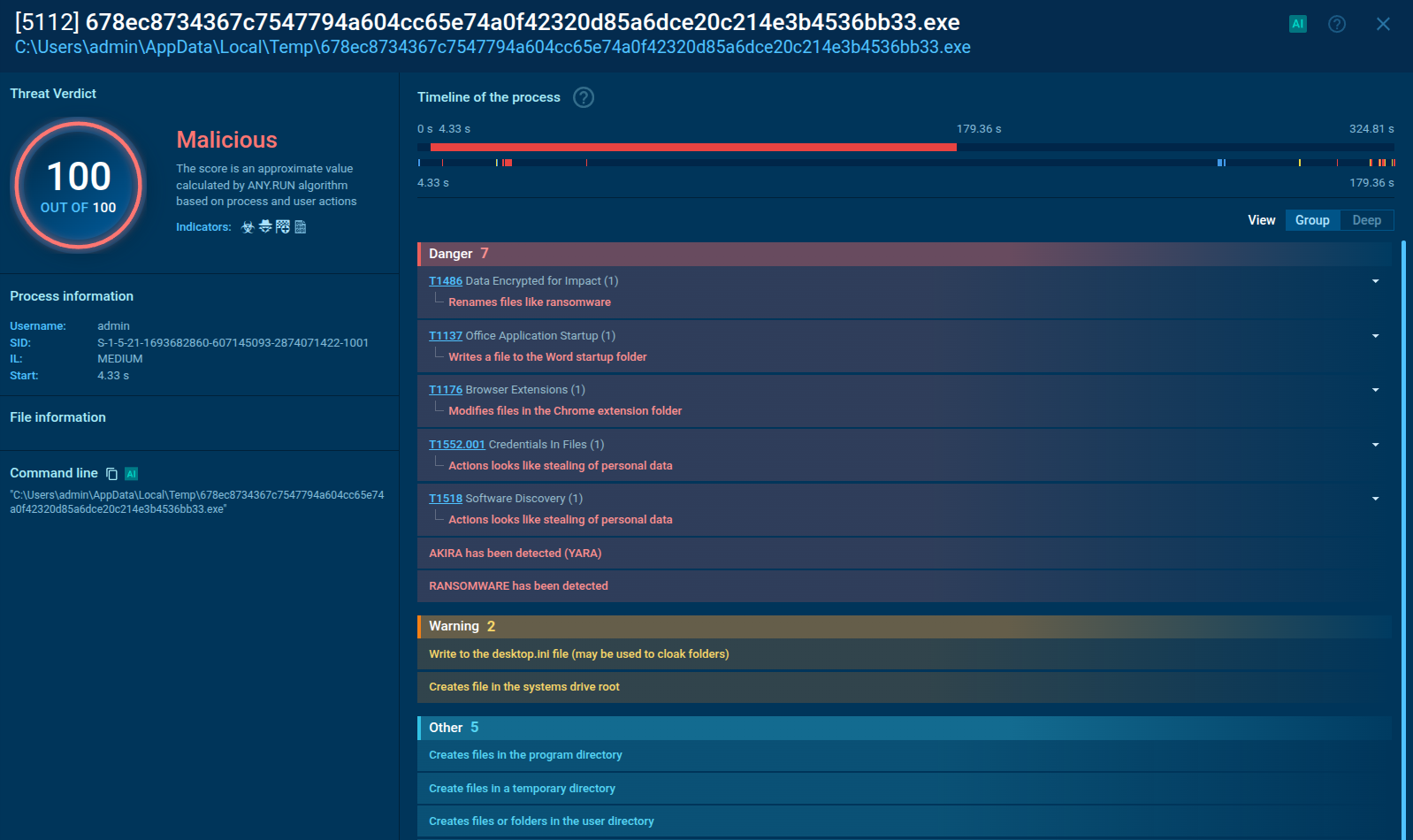
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN interactive malware hunting service displays the execution process of Orcus RAT in real-time.
Read a detailed analysis of OrcusRAT in our blog.
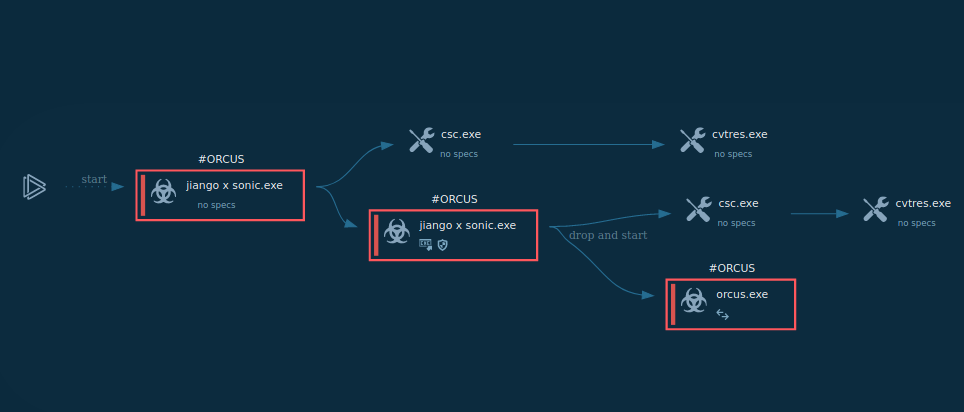
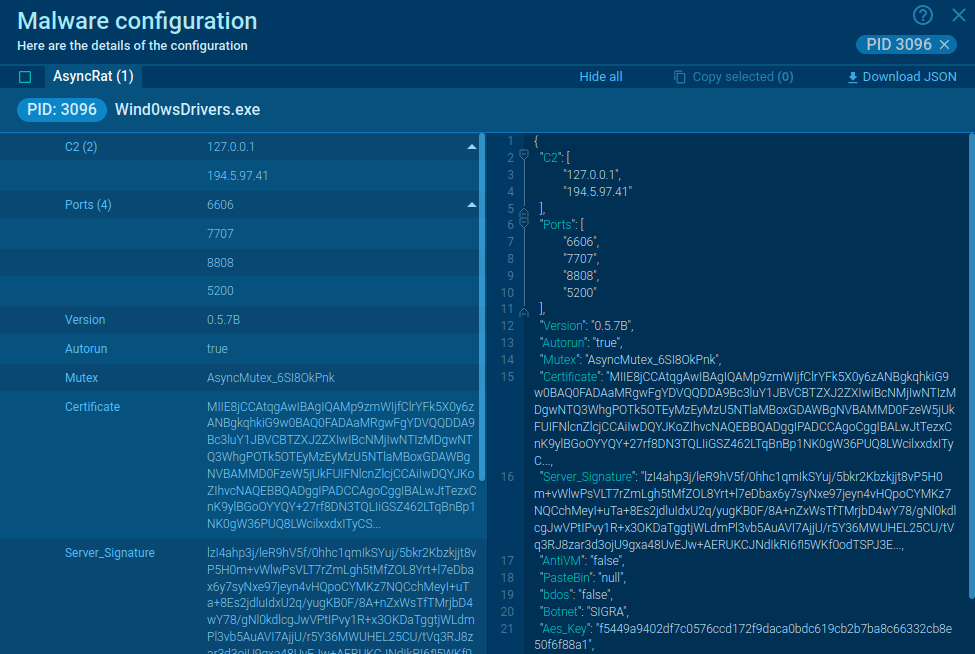
Figure 1: Displays the execution process of the Orcus RAT. This visualization was generated by ANY.RUN.
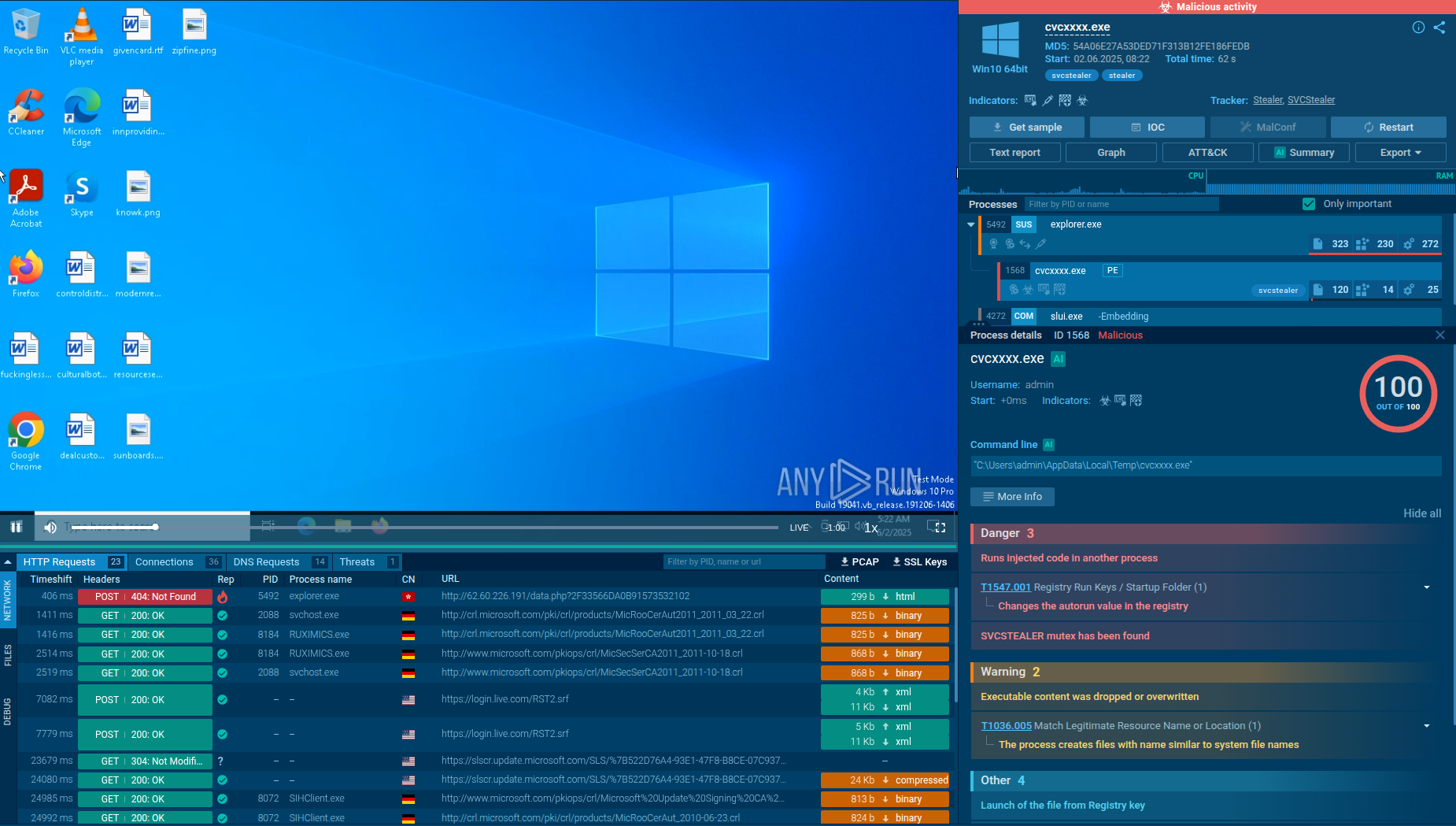
Figure 2: Displays a text report generated by ANY.RUN. Text reports are useful for demonstration and can be customized by a user to show necessary data.
The execution process of the Orcus RAT is straightforward. This malware often disguises itself as a cheat code or crack, so it is mostly delivered to a system as an archive file with the compressed executable file inside. Since this trojan was written in C#, it often uses .NET infrastructure, available in Windows. To compile the C# source code, our sample started Visual C# compiler, which, in turn, started the Resource File To COFF Object Conversion Utility. After it was compiled, the executable file began its execution and malicious activity. Note that Orcus remote access tool does not always make its way into an infected system, as described above. In some cases, it comes as a precompiled executable file which only needs a user to double click on it to start the execution.
Orcus RAT commonly makes its way into target machines as a downloadable attachment in malicious spam emails. Campaigns are often highly targeted and aim at organizations rather than at individuals.
Attackers use phishing and social engineering to trick victims into downloading an attachment or visiting a link that points to a server that holds the payload. In order to begin execution, Orcus does require user input. However, in most cases, it is unable to infect the system without user interaction.
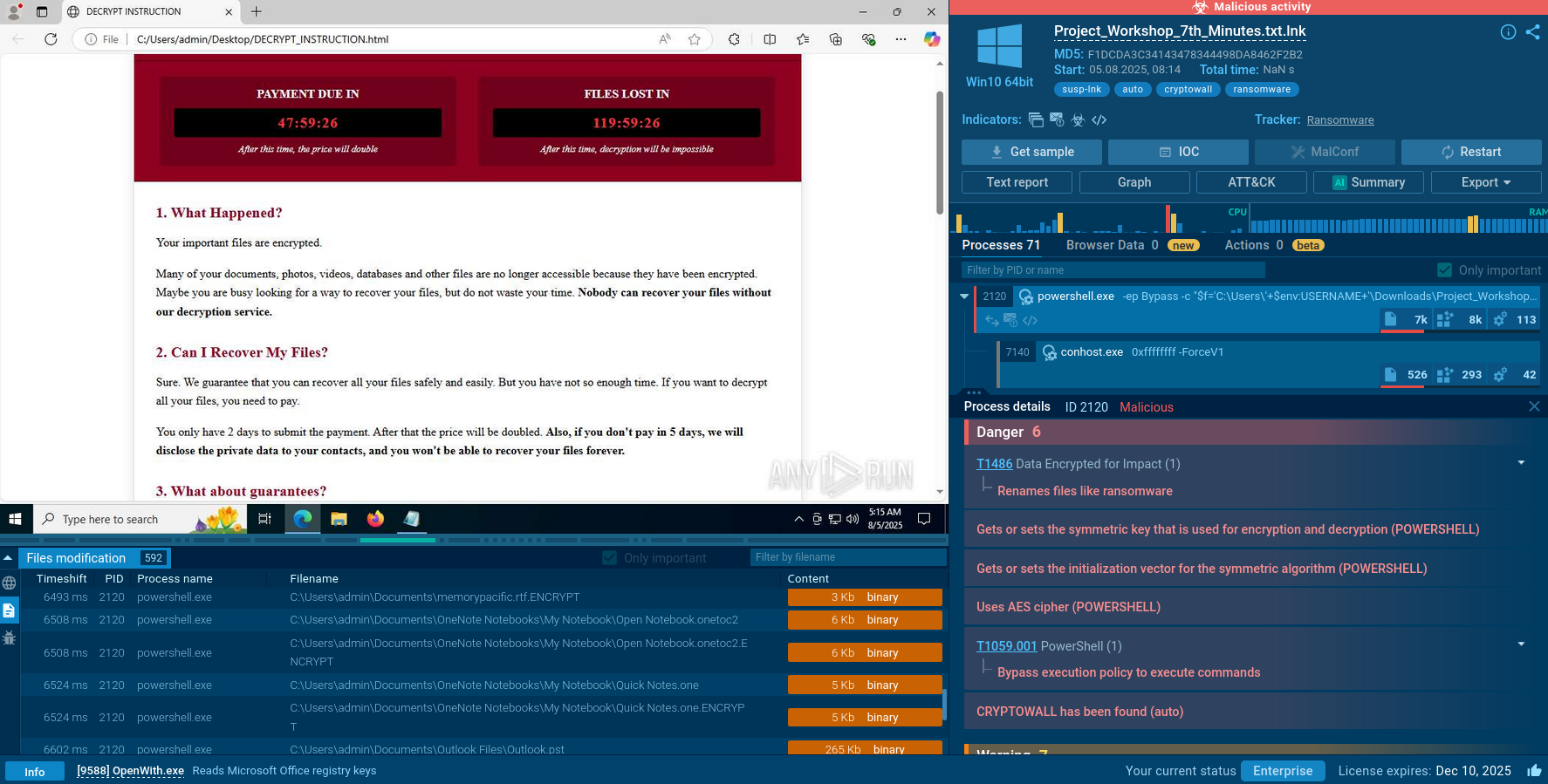
This malware creates files that allow analysts to detect it with a high degree of certainty. To identify the Orcus RAT, open the "Advanced details of process" by clicking on the "More info" button and switch events display to "Raw." This trojan often creates files with "Orcus" in the names, so all we need is to find such a file. To make it easier, type the word "Orcus" in the filename field. If such a file is found, you can be sure that Orcus RAT is in front of you.
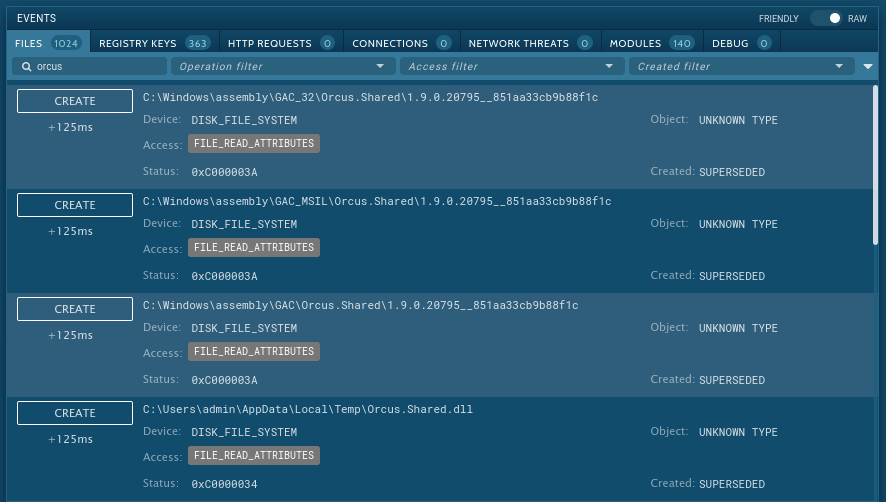
Figure 3: Files created by Orcus RAT
Orcus RAT malware is a sophisticated trojan that offers some unusual functions on top of solid basic info-stealing capabilities. Technical complexity was complemented by an affordable price of just 40 USD. Today, interested users can download a leaked version of Orcus for free. Unfortunately, this, along with excellent support and documentation, ensured the popularity of Orcus RAT.
Since its deployment in 2016, researchers have been observing Orcus RAT campaigns, and the popularity of this malware is still on the rise. As a result, we can expect several new attacks utilizing malicious software in the future.
Researchers can analyze Orcus RAT using the ANY.RUN malware hunting service to study this malware or other RATS such as Quasar RAT or njRAT. ANY.RUN is an interactive sandbox that allows researchers to stop and correct the simulation at any point, which ensures pure research results. In addition, useful information that can be obtained from the analysis can be added to our growing database of cyber threats to help combat internet crime worldwide.