Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


First identified in March 2021, PureCrypter is a .NET-based loader that employs obfuscation techniques, such as SmartAssembly, to evade detection. It has been used to distribute malware families including AgentTesla, RedLine Stealer, and SnakeKeylogger. The malware is typically delivered through phishing campaigns and malicious downloads, often masquerading as legitimate files with extensions like .mp4 or .pdf. PureCrypter utilizes encryption and compression to conceal its payloads and can inject malicious code into legitimate processes to maintain persistence on the infected system.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
2 March, 2021
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
2 March, 2021
First seen
:
|
28 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 876
876
 0
0

 522
522
 0
0

 2816
2816
 0
0
PureCrypter is a .NET-based loader malware first observed in March 2021. It is designed to deploy various payloads, including remote access trojans (RATs), information stealers, and other malicious tools on compromised systems. The malware is often sold on underground forums, with prices ranging from $20 to $60 per build, making it accessible to a wide range of cybercriminals.
The malware was developed by a threat actor known as PureCoder, who markets it as a customizable and reliable loader for spreading malware. PureCrypter has been linked to notable campaigns distributing AgentTesla, SnakeKeylogger, RedLine Stealer, and AsyncRAT, targeting individuals and organizations worldwide.
PureCrypter has been used in campaigns targeting financial institutions, healthcare organizations, and individual users. Its ability to deliver a wide variety of malware makes it a versatile and dangerous tool in the hands of cybercriminals.
To see how PureCrypter actually operates, you can upload its sample into ANY.RUN sandbox and check its behavior inside a secure environment.
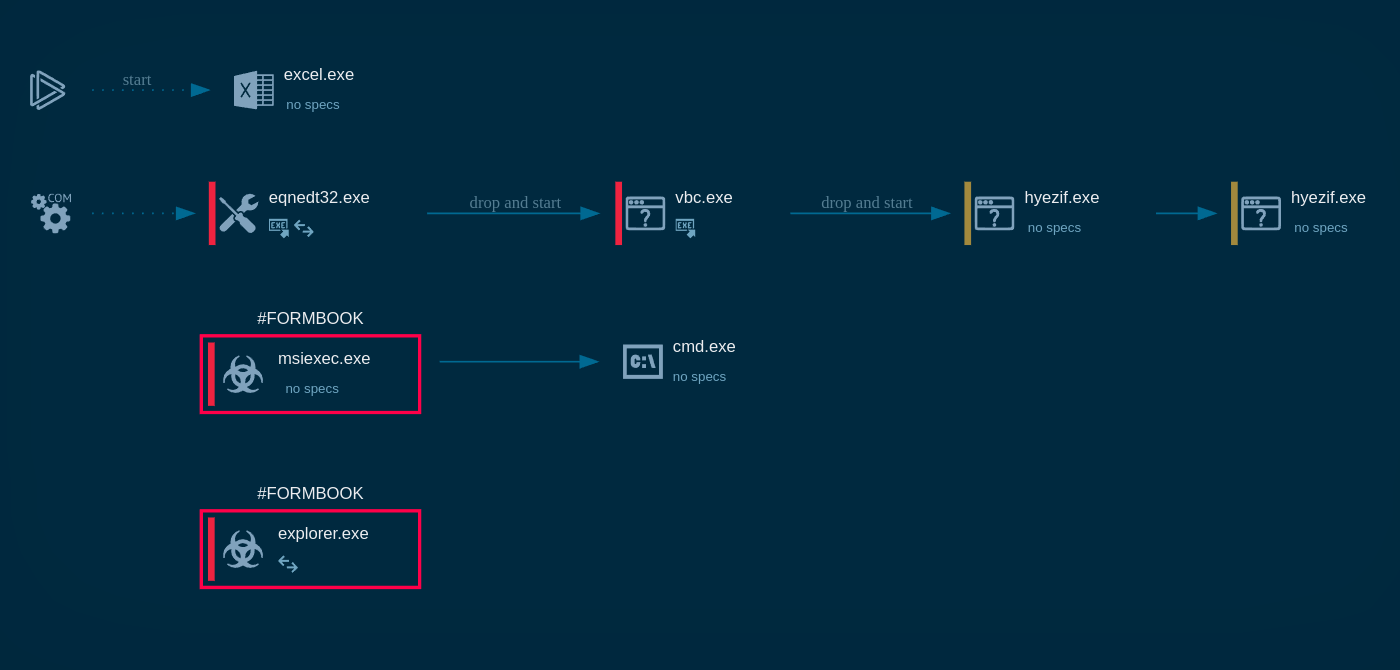
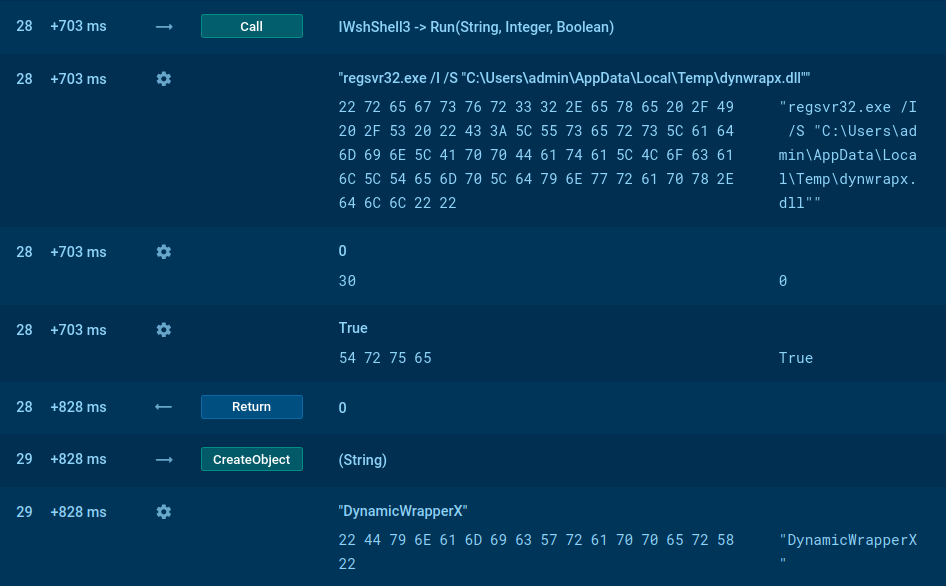
 PureCrypter analyzed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
PureCrypter analyzed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
The primary functionalities and features of PureCrypter include:
Often used in campaigns against financial, healthcare, and individual targets globally.
To see how PureCrypter operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
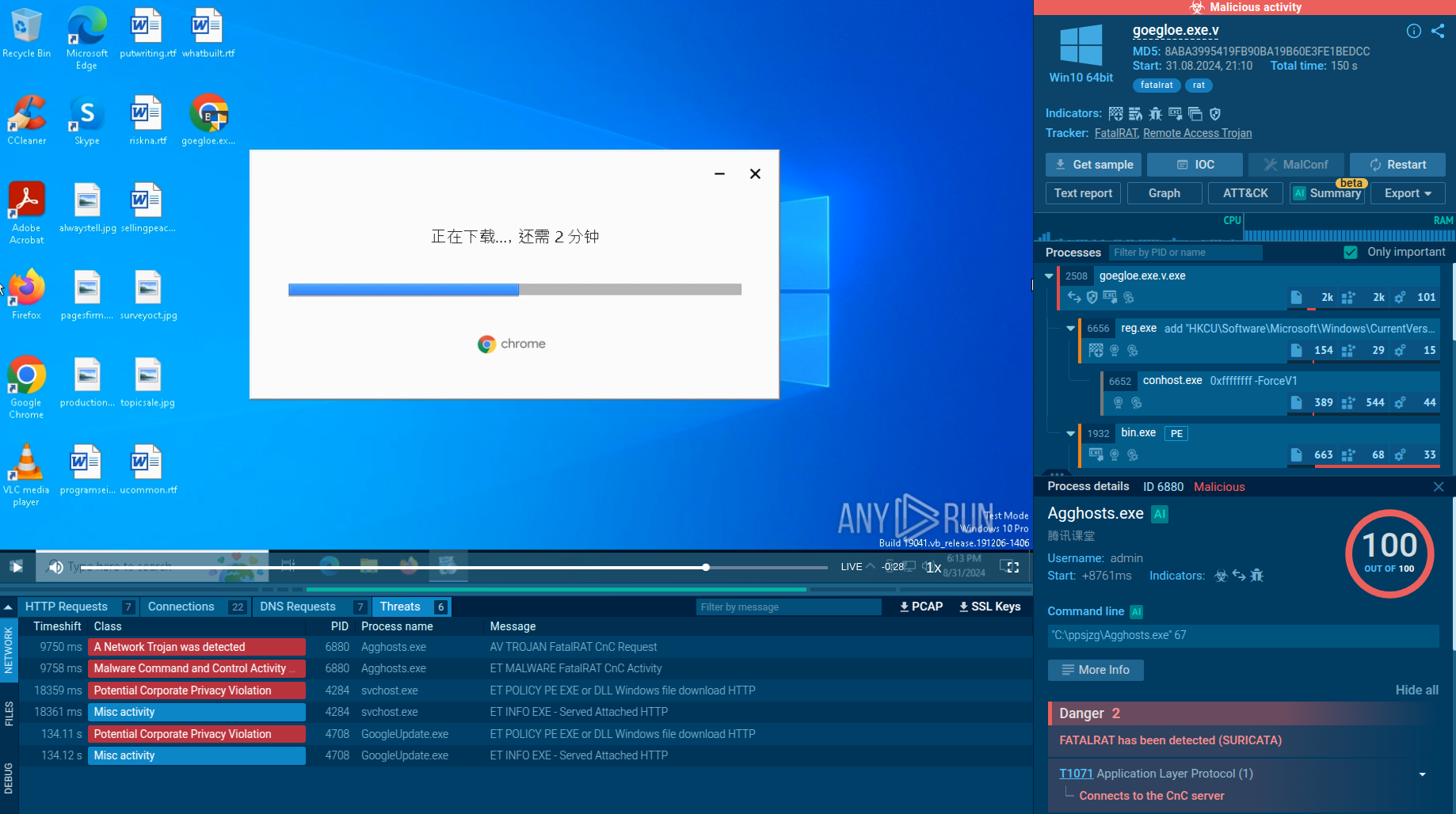
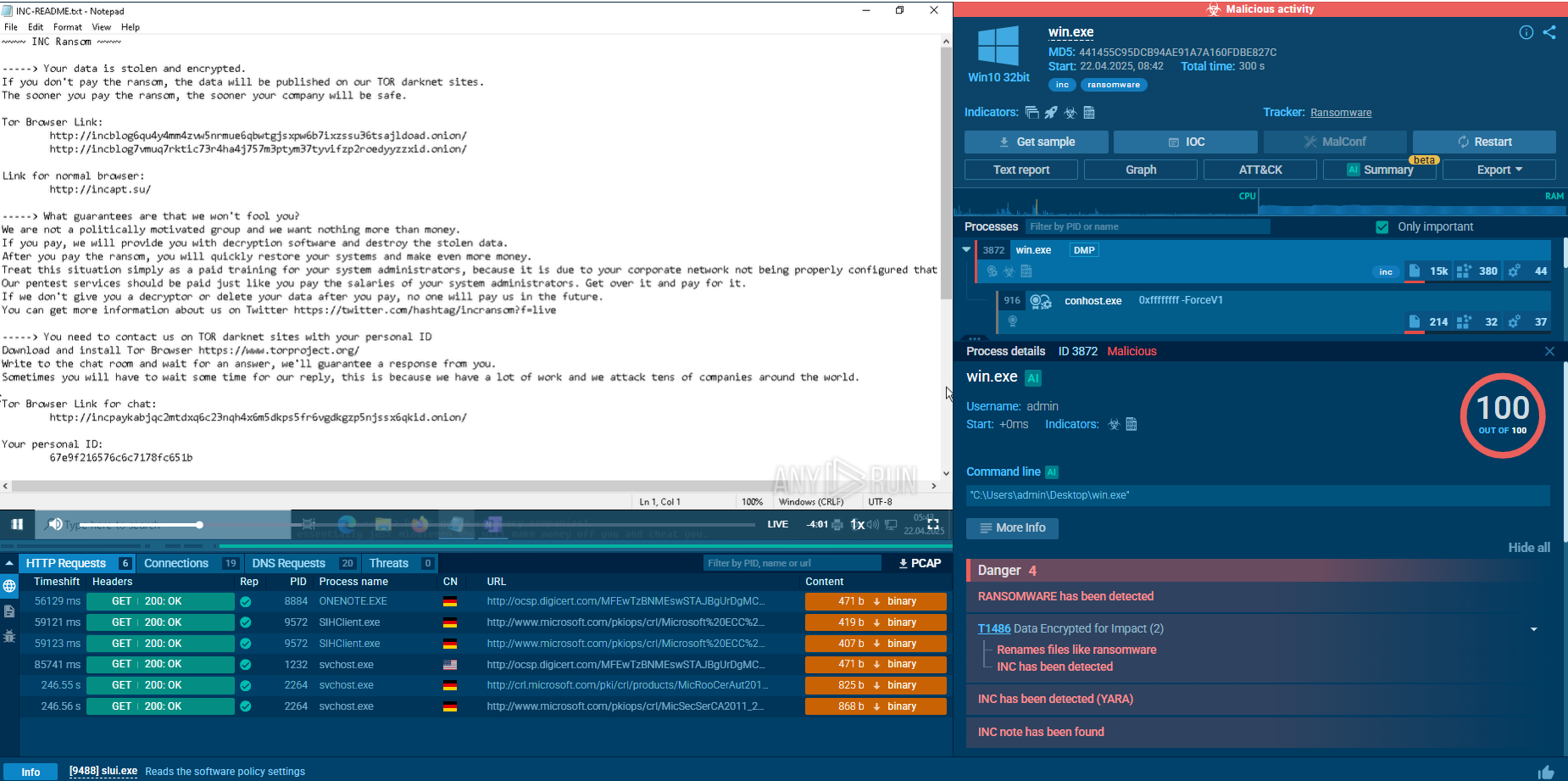
PureCrypter typically spreads through malicious downloads or phishing attacks. Once a user executes the infected file, the malware begins its execution chain. Upon execution, PureCrypter decrypts its payload in memory to avoid leaving traces on the disk, making it harder for traditional antivirus solutions to detect. The decrypted payload is then injected into a legitimate system process, helping the malware blend in with normal system activities and further evade detection.
In our case, the targeted process is MSBuild, but PureCrypter may also inject into other legitimate system processes, such as InstallUtil.
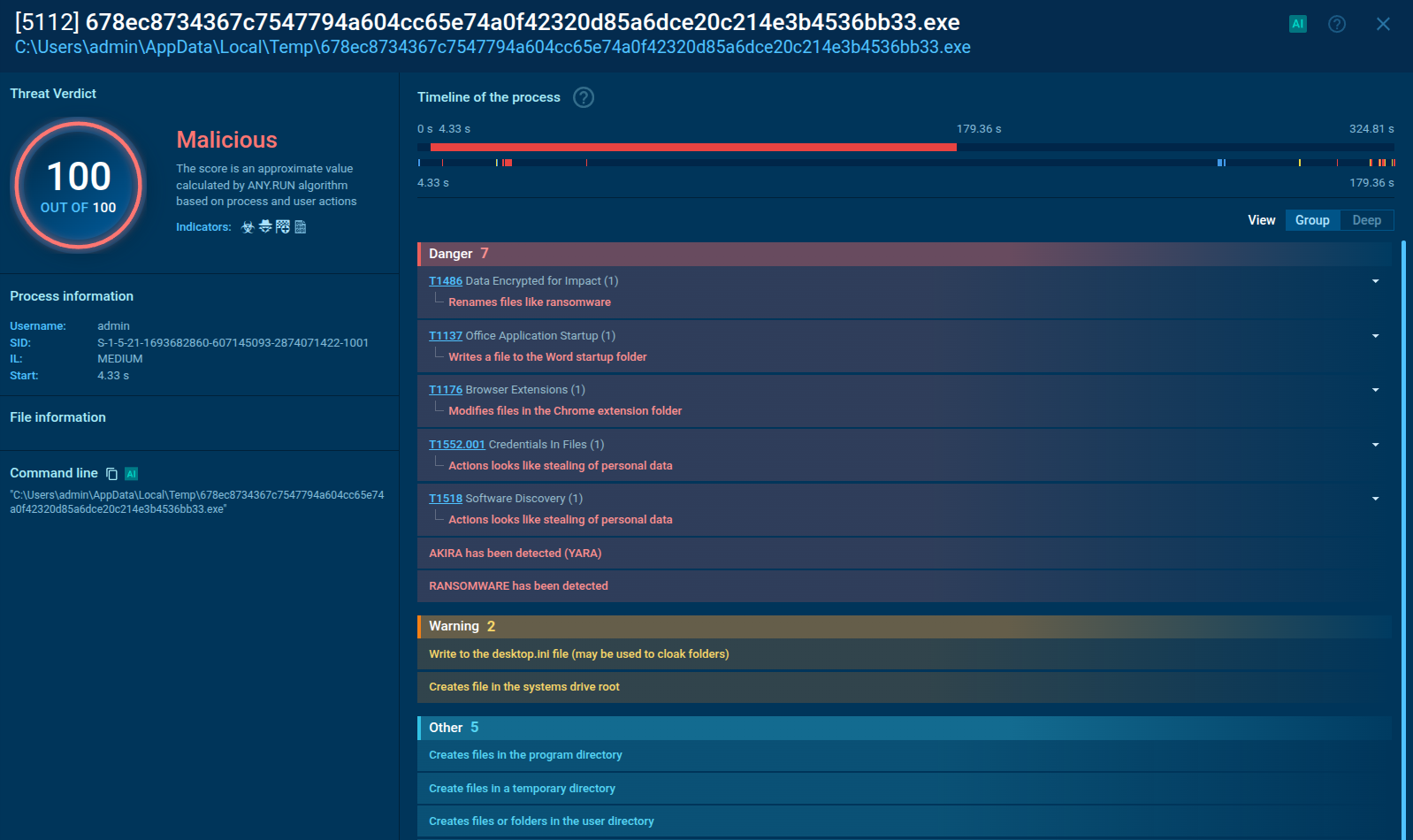
 Malicious process displayed in ANY.RUN sandbox
Malicious process displayed in ANY.RUN sandbox
In addition to process injection, PureCrypter leverages various trusted system tools. For example, in this scenario, it ran PowerShell to add Product.exe and its associated processes to the antivirus exclusion list, reducing the likelihood of detection.
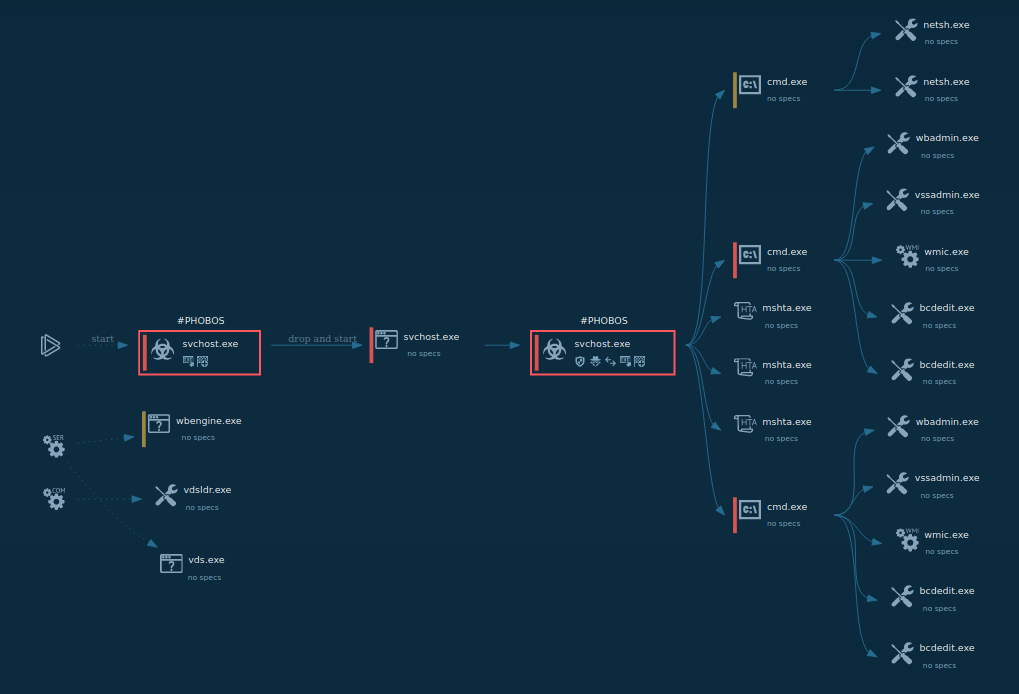
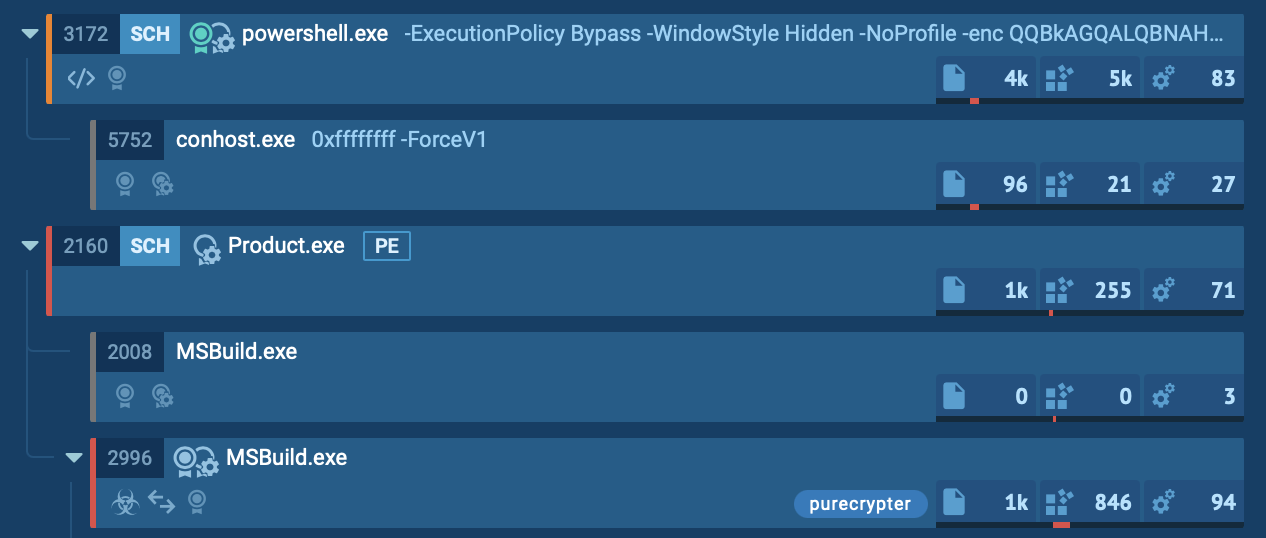 Process tree of PureCrypter analysis inside ANY.RUN
Process tree of PureCrypter analysis inside ANY.RUN
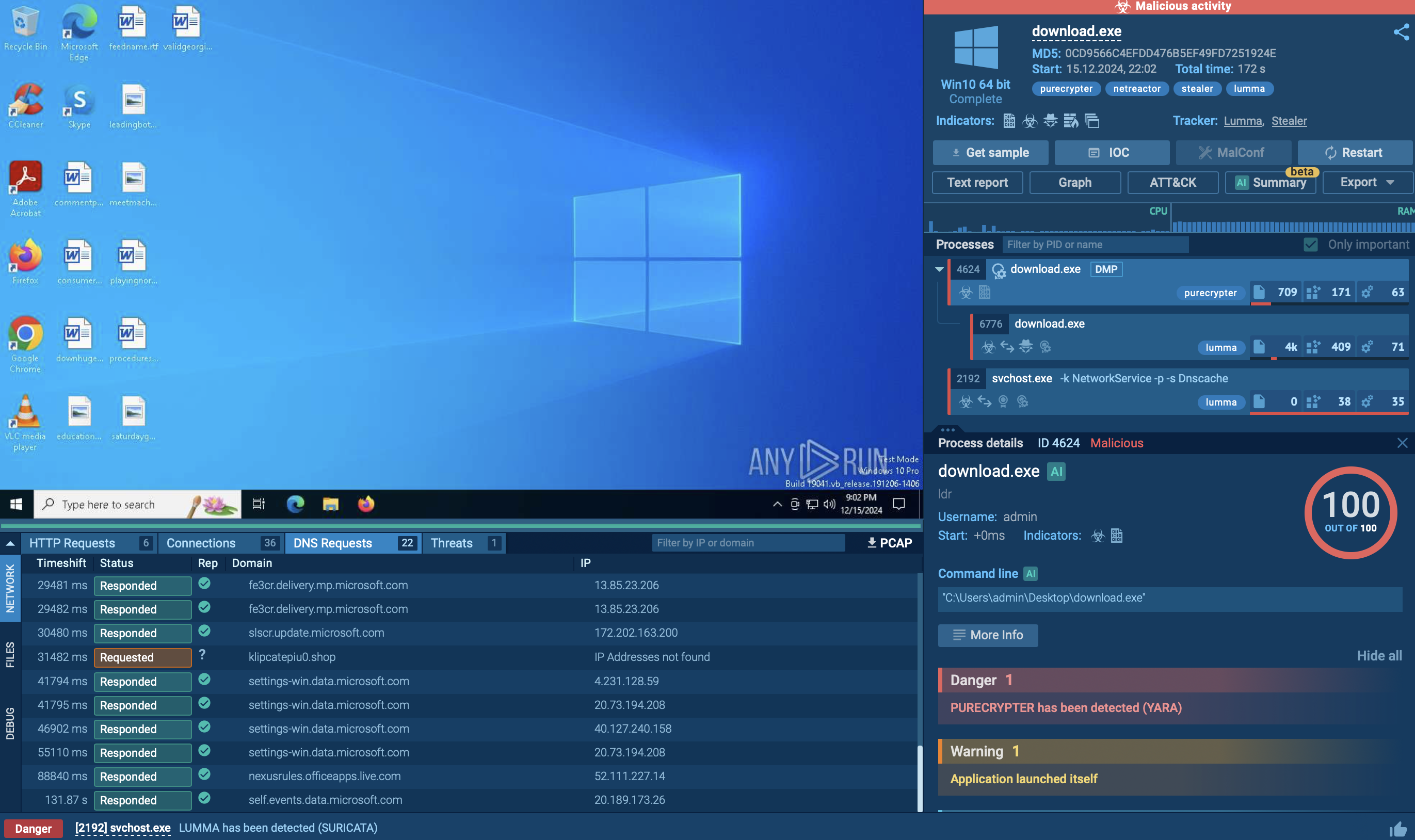
After establishing itself within a legitimate process, PureCrypter connects to its command-and-control (C2) server. Through this connection, attackers can issue commands, download additional payloads, or exfiltrate data from the infected machine. Ultimately, PureCrypter executes its primary malicious payload, which can range from ransomware or spyware to other forms of malware designed to steal data or compromise the system.
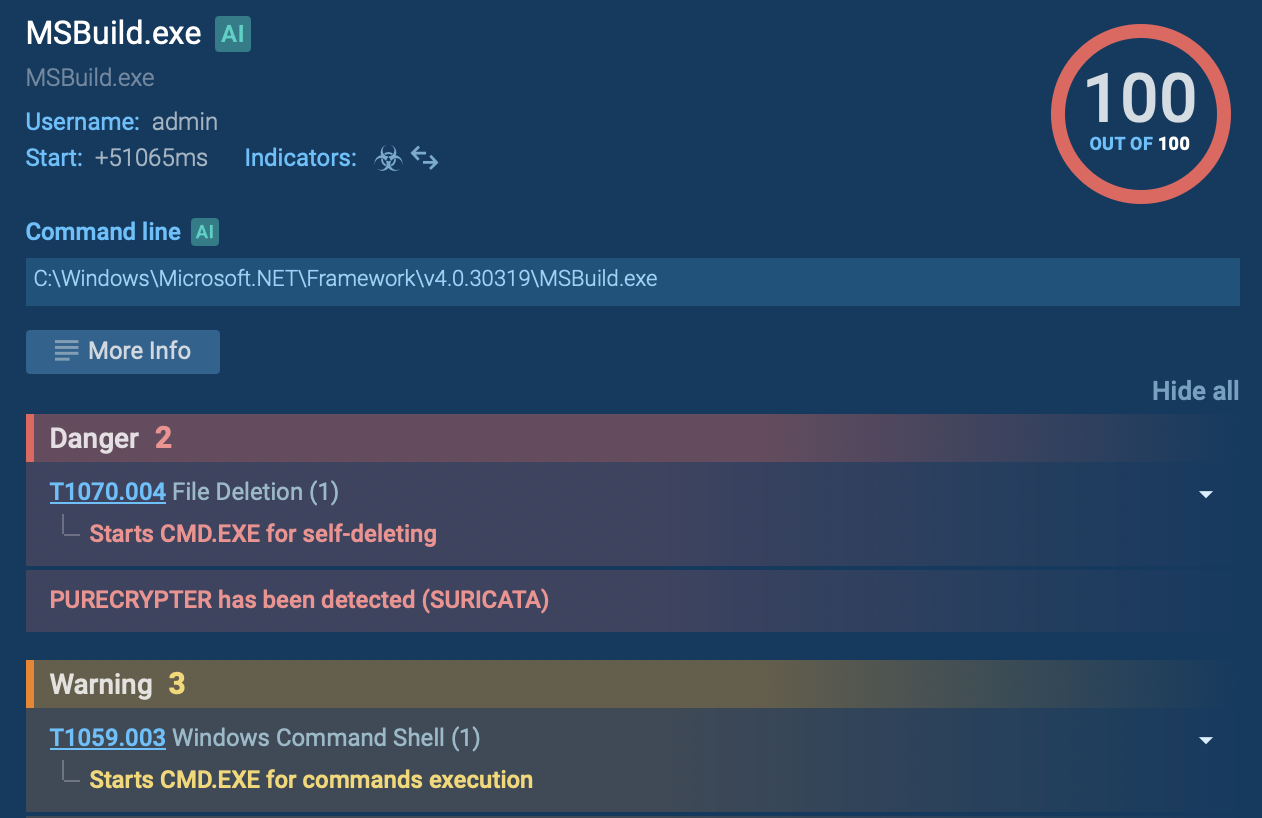
To ensure persistence after a reboot, PureCrypter may modify registry entries, create scheduled tasks, or use other persistence techniques. It can also self-delete after execution to erase evidence of its presence.
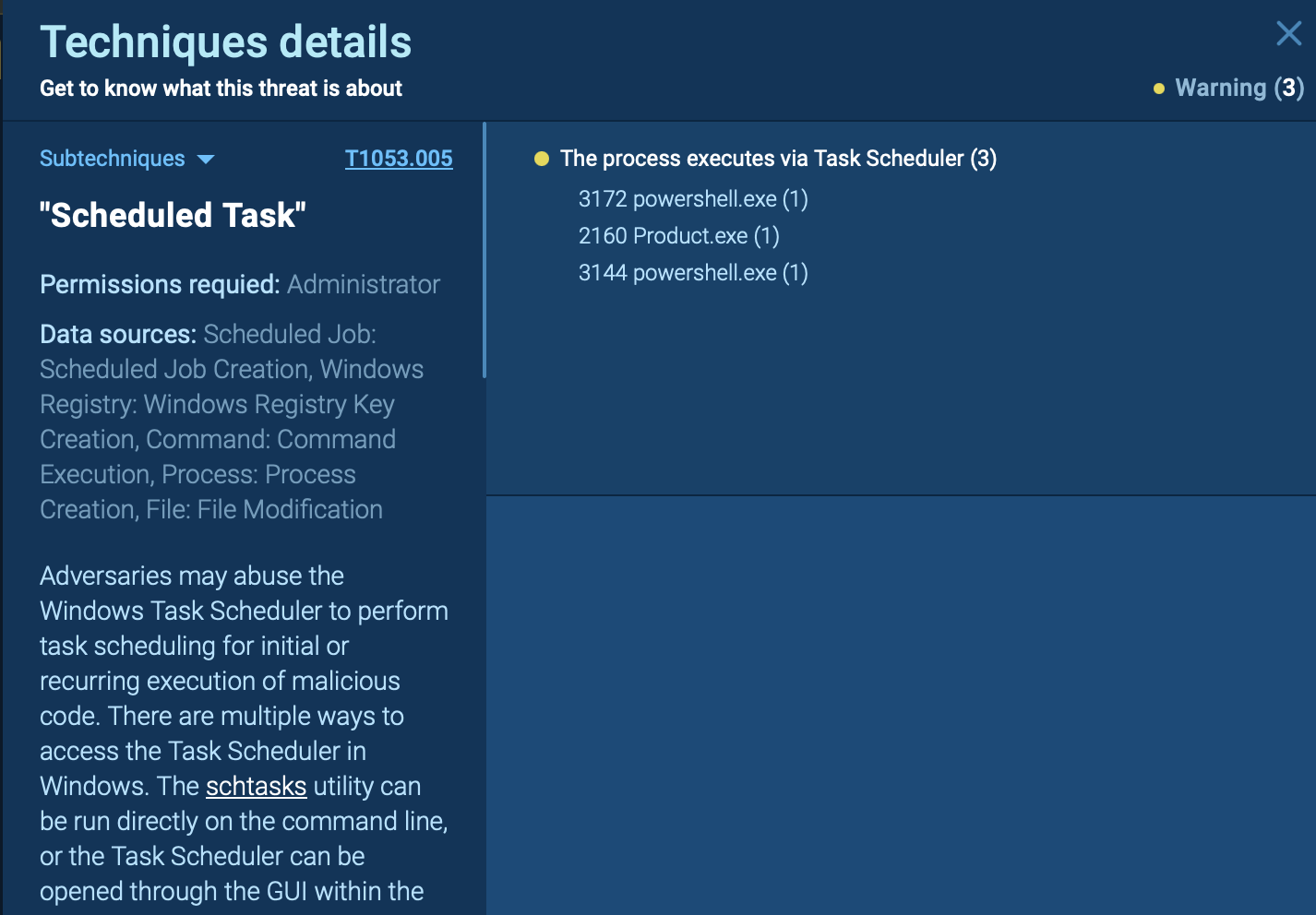 MITRE ATT&CK sub-technique identified by ANY.RUN sandbox
MITRE ATT&CK sub-technique identified by ANY.RUN sandbox
In our example, the injected MSBuild process ran the Command Prompt (CMD) to terminate itself and remove the initial Product.exe file.
To collect up-to-date intelligence on PureCrypter, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service provides access to a vast database with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox. With over 40 customizable search parameters, users can gather detailed data on threats, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts.
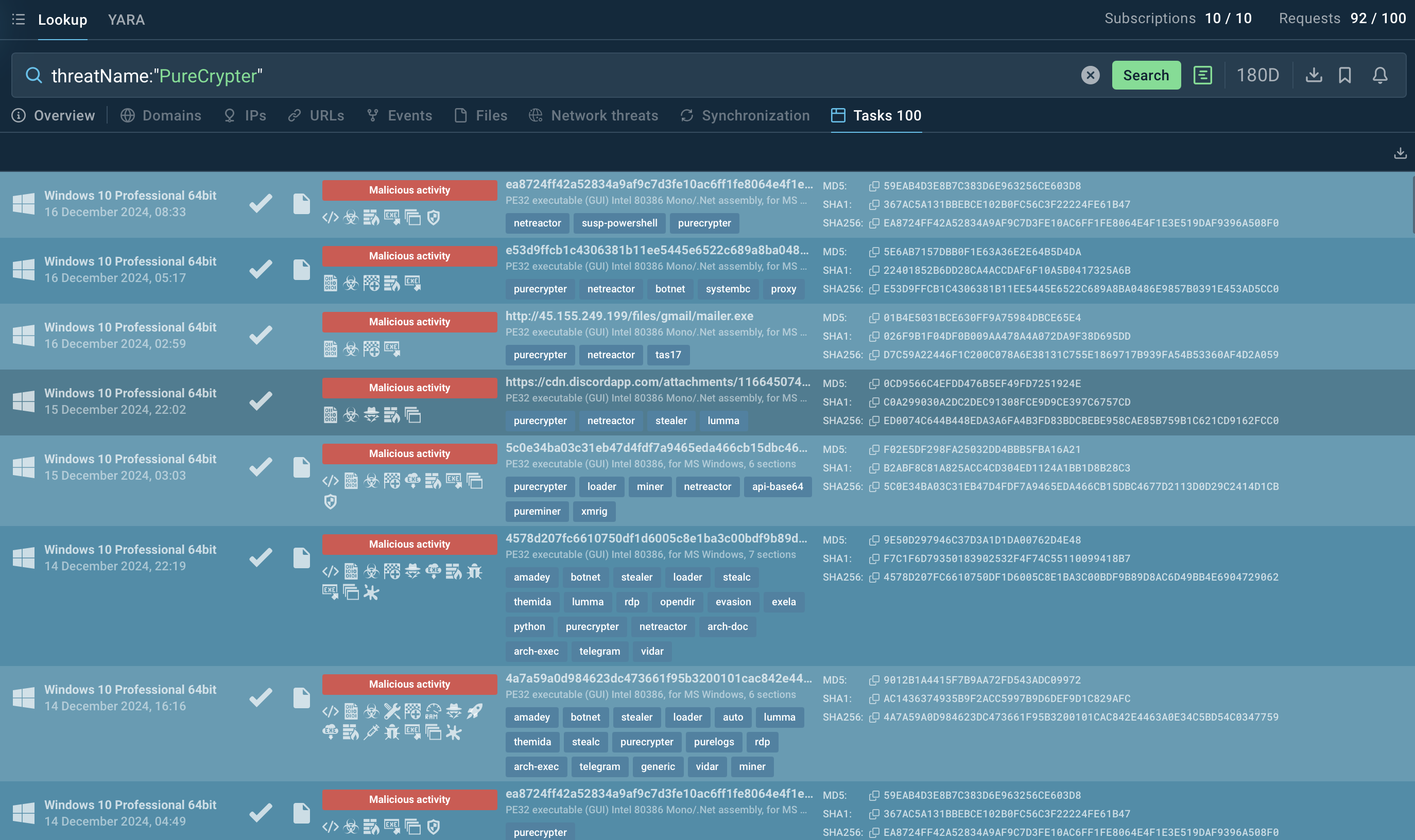 Search results for PureCrypter in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for PureCrypter in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For instance, to investigate PureCrypter, you can search by its threat name or use a related artifact. A query like threatName:"PureCrypter" will retrieve all associated samples and sandbox results relevant to this loader malware.
PureCrypter is a dangerous malware capable of deploying various threats while evading detection through obfuscation and encryption. Tools like ANY.RUN can help to analyze suspicious files and URLs to prevent attacks.
ANY.RUN offers real-time malware analysis with features like visual execution chains and script tracing, helping users detect threats effectively.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today and analyze unlimited malware attacks!