Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Latrodectus is a malicious loader that is used by threat actors to gain a foothold on compromised devices and deploy additional malware. It has been associated with the IcedID trojan and has been used by APT groups in targeted attacks. The malware can gather system information, launch executables, and detect sandbox environments. It uses encryption and obfuscation to evade detection and can establish persistence on the infected device.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 857
857
 0
0

 508
508
 0
0

 2788
2788
 0
0
Latrodectus is a type of malware known as a "loader," which is designed to download and install additional malicious software onto a compromised computer. It is believed to have been developed by the same individuals or group behind the IcedID trojan, a sophisticated and widespread banking malware.
Since 2023, Latrodectus has been extensively used by a variety of threat actors, including advanced persistent threat (APT) groups such as TA578 and TA577, which was previously observed delivering the Qbot malware, a banking trojan family.
Latrodectus is typically delivered as part of multi-stage attacks, which often begin with a phishing email containing a malicious JavaScript file attachment. However, it has also been known to be dropped by other malware, including the DanaBot trojan.
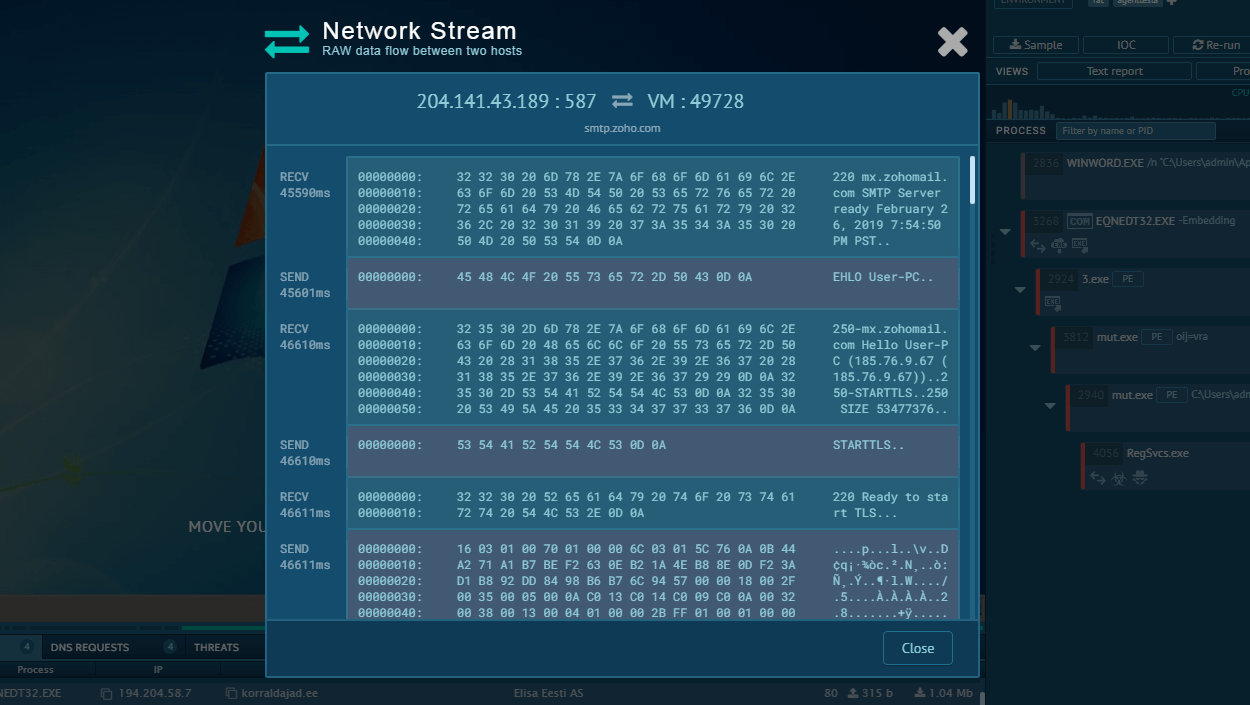
One of the key features that has allowed security researchers to link Latrodectus to the IcedID authors is the use of a similar command and control (C2) infrastructure. C2 servers are used by malware to communicate with their operators, receive instructions, and exfiltrate data.
The primary functionality of Latrodectus is to receive commands from the attackers and perform them.
Some of the key capabilities of Latrodectus include:
A typical Latrodectus infection chain begins with a JavaScript file that is responsible for downloading a malicious .msi file, which then leads to the deployment of the final payload on the system.
The malware implements obfuscation techniques, such as encrypting strings, to make it more difficult for researchers to analyze. It communicates with its command and control (C2) server via HTTPS, with both requests and responses encrypted using RC4 and base64 encoding.
Furthermore, Latrodectus has a built-in sandbox detection mechanism that works by enumerating the number of active processes on the device and checking for the presence of a MAC address.
The malware can establish a scheduled task for persistence, ensuring that it remains active on the infected machine even after a reboot. It also verifies if the computer is already infected with Latrodectus and exits execution if the result is positive.
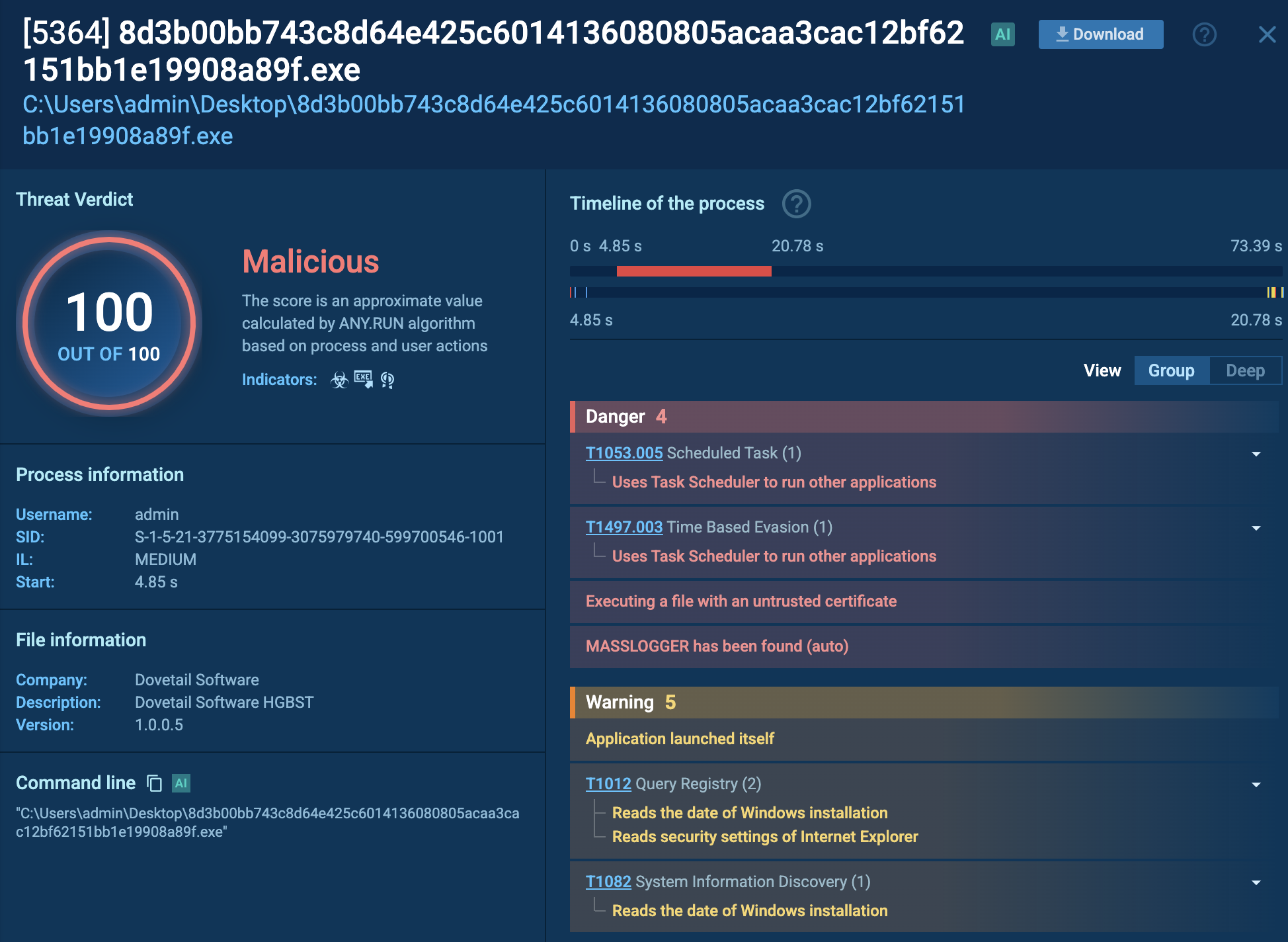
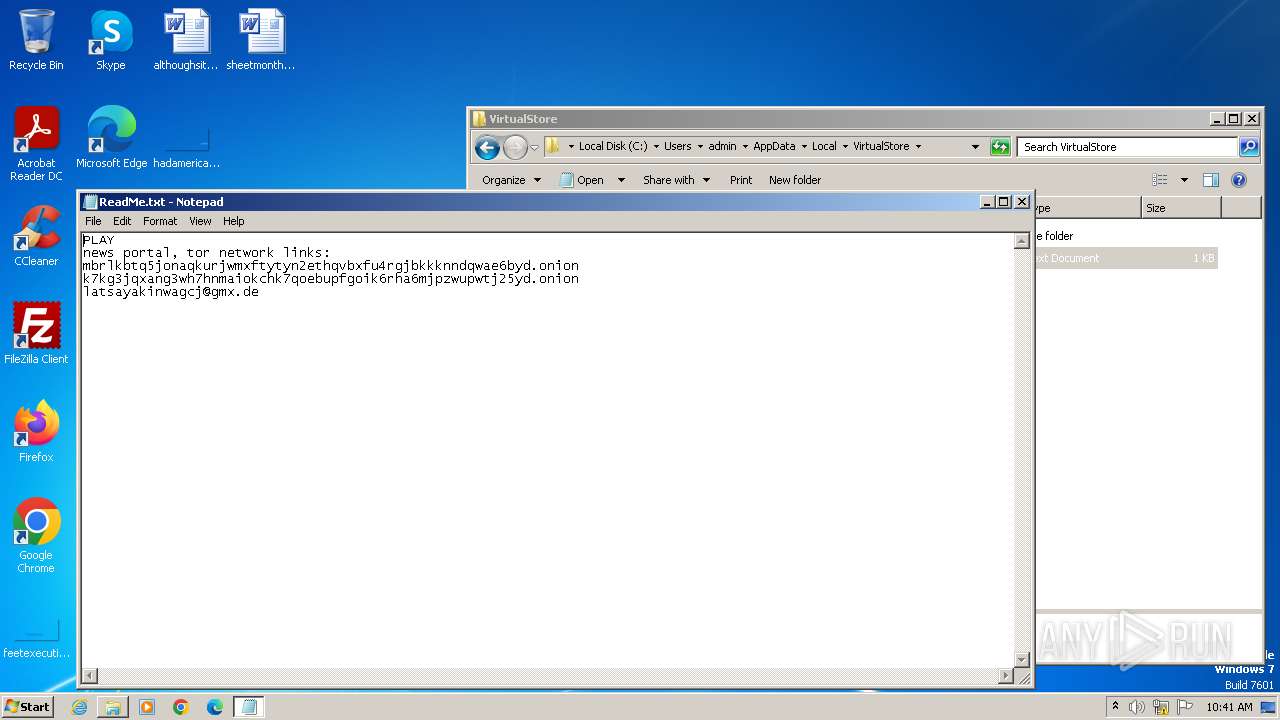
Let’s detonate a sample of the Latrodectus malware in the ANY.RUN sandbox to observe its execution chain.
The infiltration process of the Latrodectus malware involves a sequence of steps that ultimately lead to its successful operation on a target system.
Upon launching a JavaScript file, it automatically retrieves an installer MSI. This MSI file implants a Latrodectus Dynamic Link Library (DLL) onto the system, allowing the malware to maintain persistence even after the system is rebooted.
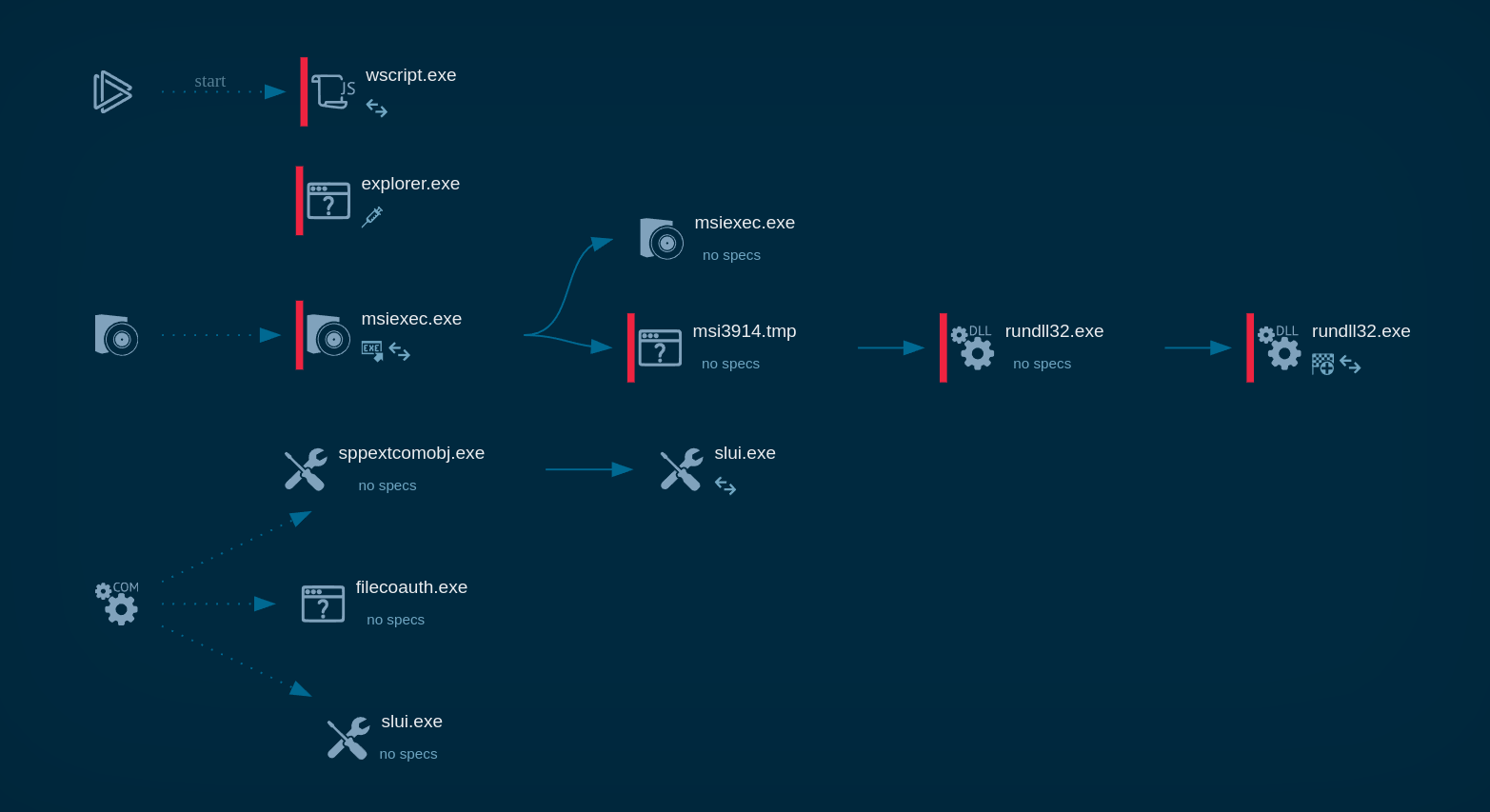 Latrodectus process graph in ANY.RUN
Latrodectus process graph in ANY.RUN
Once implanted, the Latrodectus malware establishes communication with its command-and-control (C2) server, providing remote access to the infected device for malicious actors.
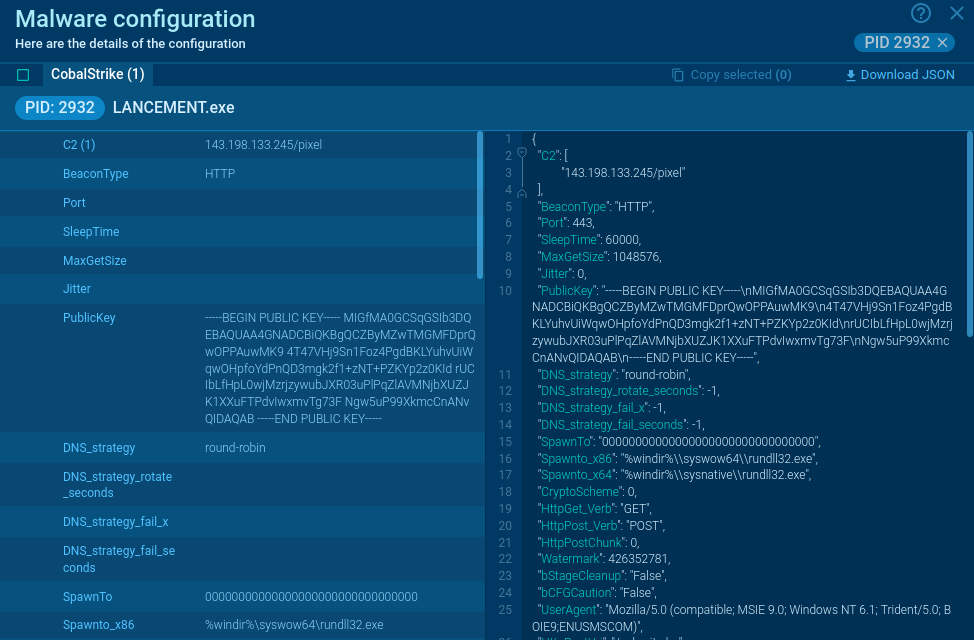
To collect up-to-date intelligence on Latrodectus, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service gives you access to a vast database filled with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
With over 40 customizable search parameters, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts, you can efficiently gather relevant data on threats like Latrodectus.
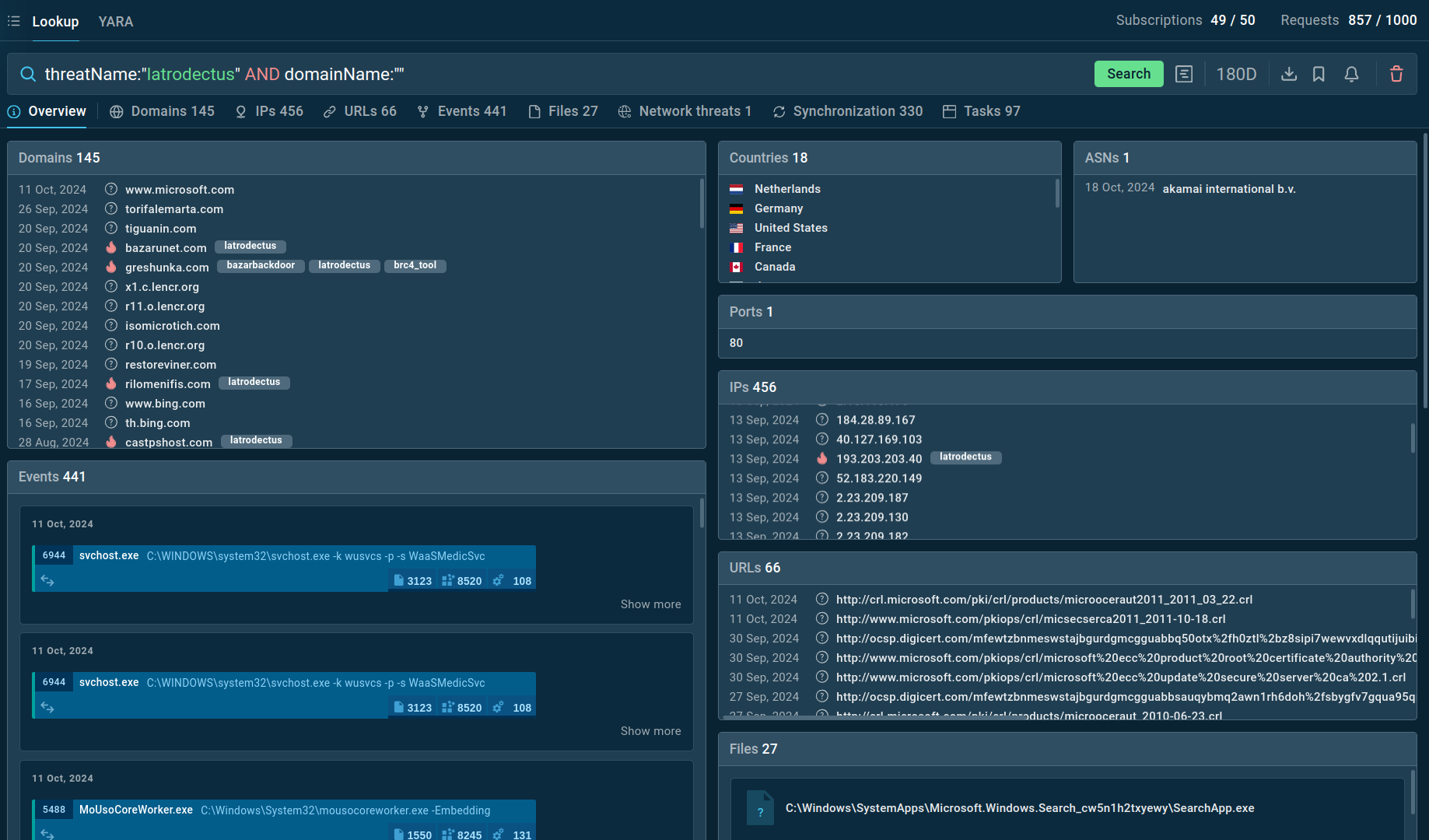 Search results for Latrodectus in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Latrodectus in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, you can search directly for the threat name or use related indicators like hash values or network connections. Submitting a query such as threatName:"latrodectus" AND domainName:"" will generate a list of other data extracted from Lumma samples along with sandbox sessions that you can explore in detail to gain comprehensive insights into this malware’s behavior.
Phishing emails are the most common attack vector by threat actors for distributing Latrodectus malware. These emails are typically designed to appear as if they have been sent from a legitimate organization or individual, to trick the recipient into opening an attached file or clicking on a malicious link.
In one particular campaign, the threat actor group TA578 was observed to be spreading Latrodectus as part of a scheme that involved accusing target companies of copyright infringement. The phishing emails in this campaign were designed to look like they were sent from a legitimate organization.
In another instance, a fake Azure page was used to initiate the infection chain.
Latrodectus is a noteworthy loader that presents a challenge due to its widespread use by professional cyber criminal groups. Its capacity to deploy payloads, along with its advanced obfuscation and evasion methods, as well as continuous development contribute to its potential to become an even more serious threat.
ANY.RUN is a cloud-based service that can be used to safely analyze suspicious files and URLs, including Latrodectus malware. It allows you to observe malware behavior and collect indicators of compromise in a secure environment. Using ANY.RUN can help you understand Latrodectus's tactics and improve your defenses against it.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!