Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Phorpiex is a malicious software that has been a significant threat in the cybersecurity landscape since 2016. It is a modular malware known for its ability to maintain an extensive botnet. Unlike other botnets, Phorpiex does not concentrate on DDoS attacks. Instead, it has been involved in numerous large-scale spam email campaigns and the distribution of other malicious payloads, such as LockBit.
|
Botnet
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2016
First seen
:
|
24 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2016
First seen
:
|
24 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 779
779
 0
0

 476
476
 0
0

 2720
2720
 0
0
Phorpiex is a botnet malware written in C++ that was first spotted back in 2016. Originally, it relied on brute forcing for infiltrating devices through the use of default login credentials. Once on the system, the malicious software received instructions from its authors to deliver extra payloads, thus, serving as a loader. Another feature of the threat is its worm-like behavior that allows it to spread via USB drives.
The malware has been used to infect thousands of devices and install various malicious programs, including ransomware and cryptojacking software. It was also employed in sextortion campaigns that involved distributing phishing emails to users from a leaked database, requesting them to pay to the attackers.
In August 2021, it was deactivated by its operators. During this time, Phorpiex’s source code was put up for sale on a dark web forum. This, however, did not spell the end to the malware, as it was back in operation by the end of the year. This time, the malware heavily targeted virtual currency users through crypto clipping. In these attacks, the botnet automatically replaced victims’ crypto wallet addresses with those of the operators, duping them into transferring funds to the criminals.
In 2024, the malware made a serious comeback as part of another large-scale phishing campaign, sending thousands of emails to victims containing the LockBit ransomware.
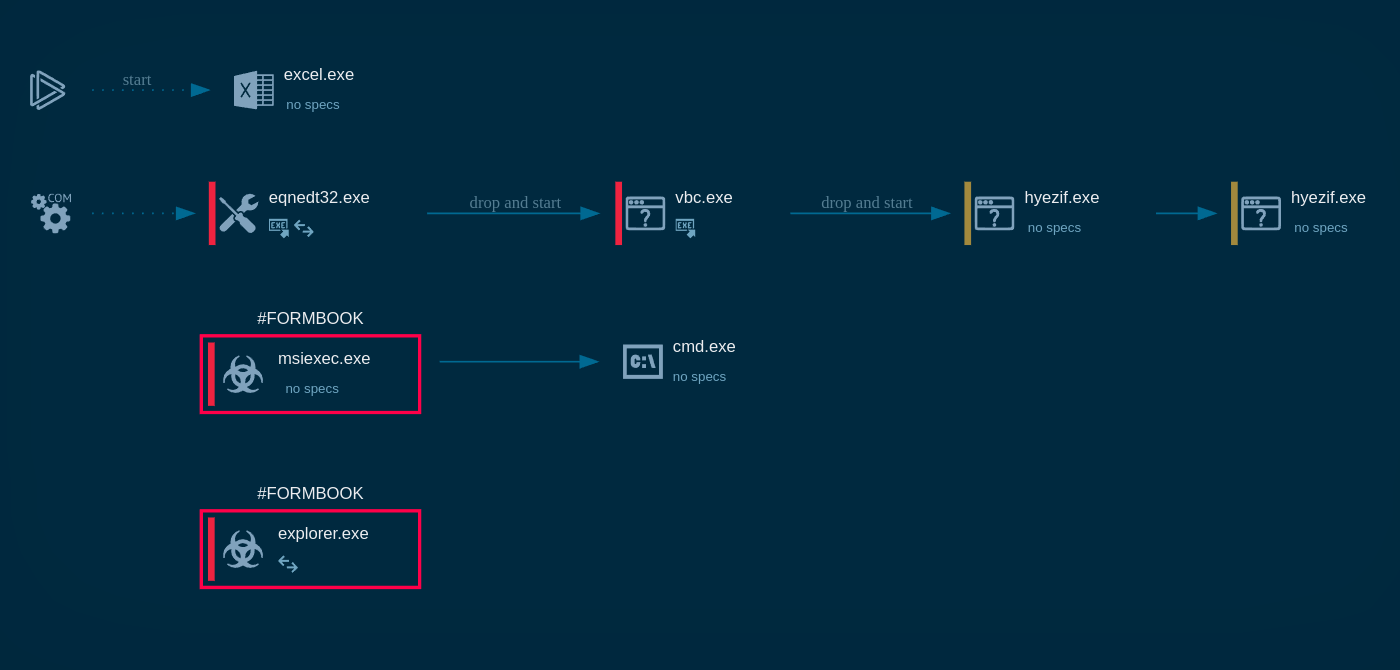
To see how the latest version of the malware operates on an infected system, let’s upload its sample to ANY.RUN’s cloud malware sandbox .
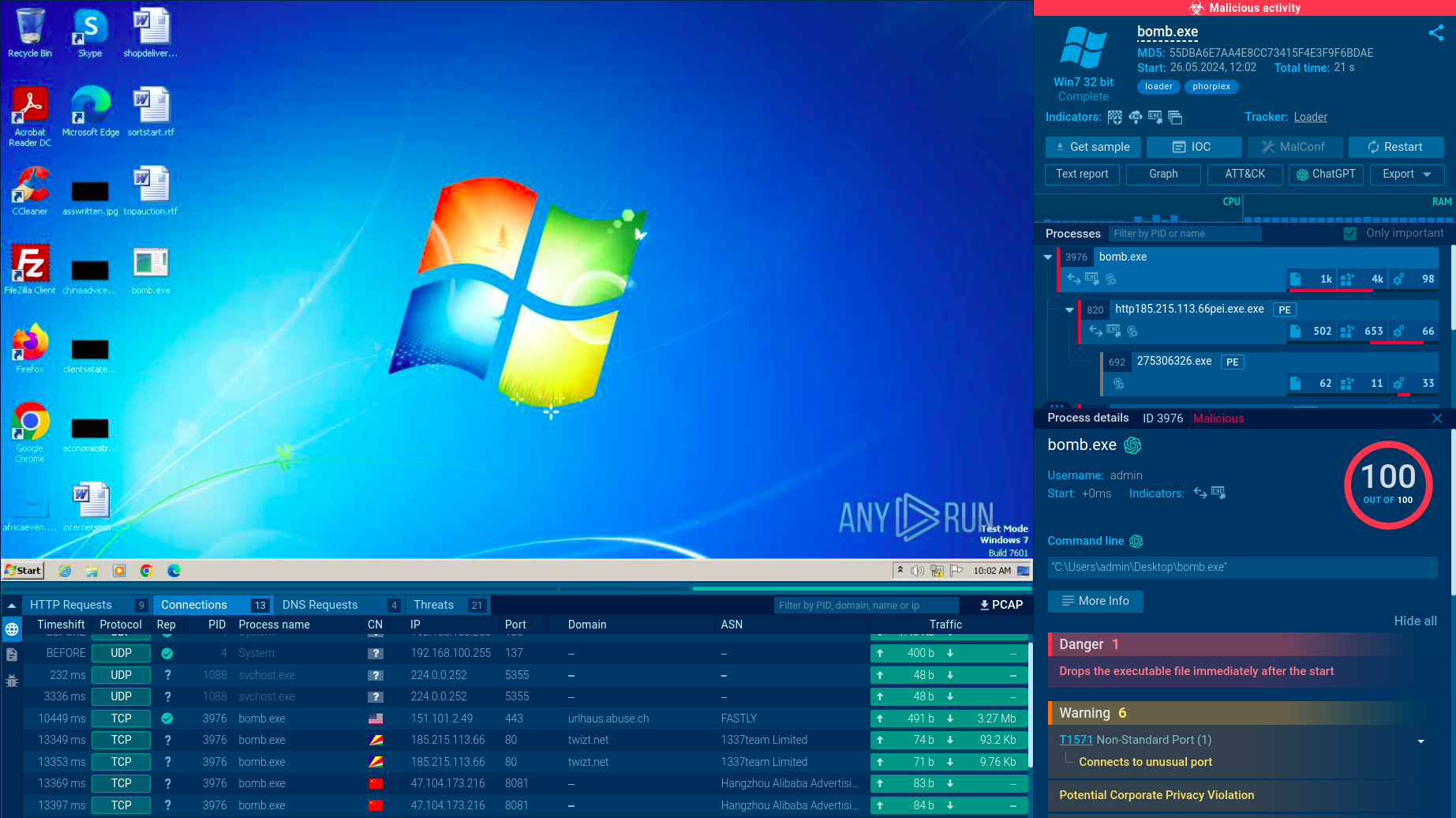 Phorpiex sample analysis in ANY.RUN sandbox
Phorpiex sample analysis in ANY.RUN sandbox
After Phorpiex malware is delivered and installed on the machine, it adds a registry key to ensure it runs automatically at startup. It also introduces a mutex to prevent multiple instances from running.
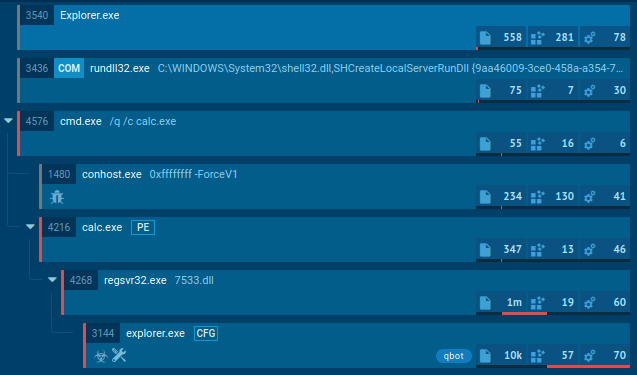
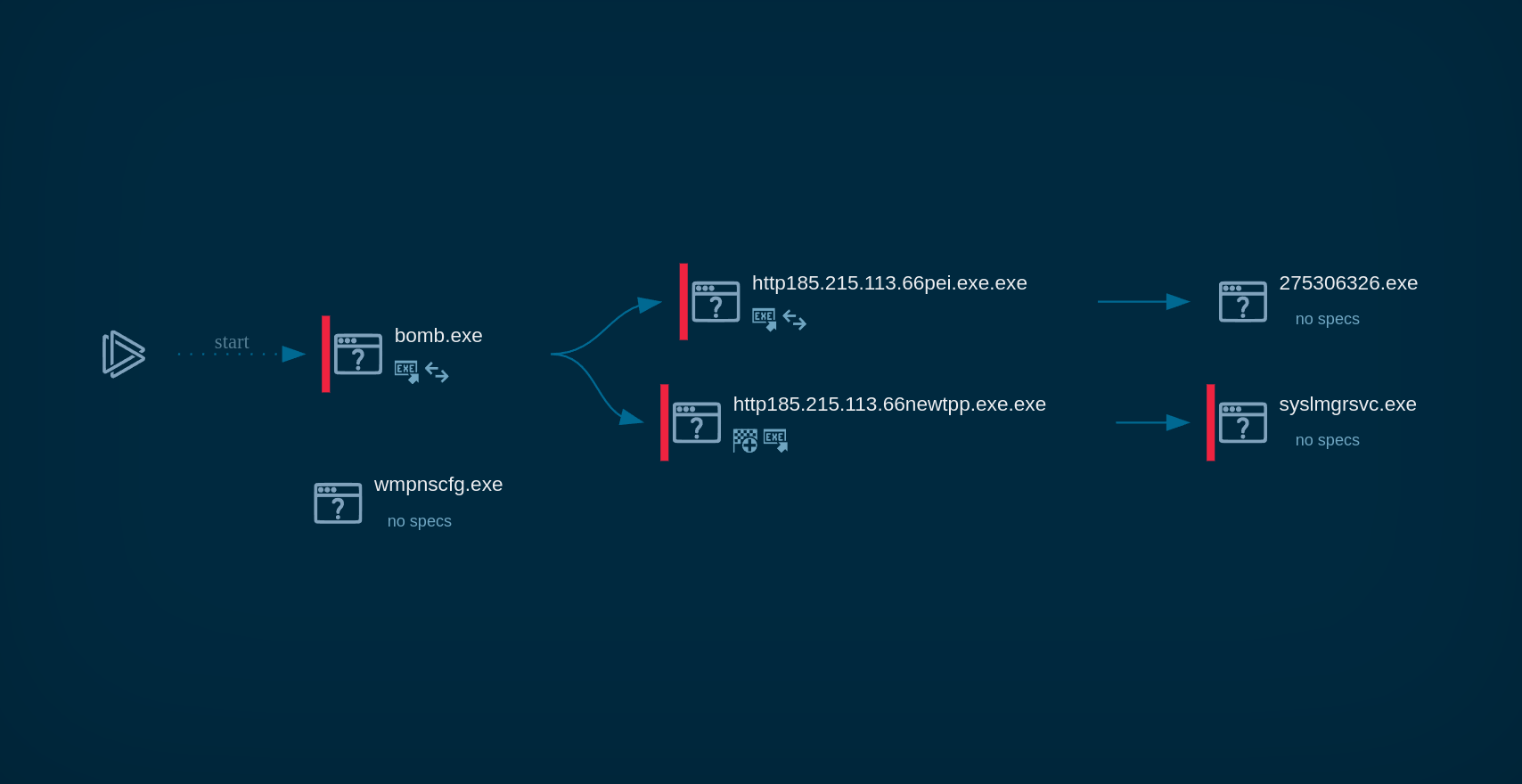 Phorpiex process graph in ANY.RUN
Phorpiex process graph in ANY.RUN
Since the malware acts as a worm, it instantly starts infecting removable and shared drives by creating copies of itself on these drives to spread. Phorpiex can compromise system security by disabling security features, allowing it to maintain persistence and continue spreading.
The malware also tries to connect to malicious command and control (C2) servers. If the connection is successful, Phorpiex downloads and executes additional malware, such as cryptominers or ransomware like LockBit Black.
As mentioned, Phorpiex can be used to send spam emails, including those with malicious attachments or links. In the absence of active C2 servers, Phorpiex can operate in P2P mode, enabling it to continue spreading and executing malware without relying on centralized control.
Phorpiex is a modular malware, meaning that it has dedicated modules for different types of malicious activities.
The key function of Phorpiex since its launch has been creating a network of bots, compromised systems, which then can be leveraged to conduct malicious activities. Unlike botnets, such as Mirai or Gafgyt, Phorpiex does not use its infrastructure to carry out DDoS attacks. Instead, it has been observed to orchestrate spam email campaigns. In 2018, the malware’s database of over 40 million target email addresses was exposed, revealing the extent of its campaigns. A typical spam email from Phorpiex involves an attachment containing a malicious payload and a message, accompanying it, that asks the user to open the attachment.
The malware is equipped with a loader module that lets it distribute other malicious payloads on the systems it manages to infiltrate. Over the years, it has been utilized to push different malware families, including Nemty and GandCrab
It also has crypto clipping capabilities, supporting dozens of wallet types and cryptocurrencies. The malware changes the crypto addresses copied by the victim to the clipboard and tricks them into sending their virtual funds to the attacker’s wallets.
The latest version of the malware operates in the peer-to-peer mode. This means that devices infected with Phorpiex can not only spread the malware further but also control other machines in the network.
Some of the older variants of the malware also used XMRig to mine the Monero cryptocurrency using the resources of the infected hosts.
The malware possesses anti-vm and anti-debugging capabilities. It ensures persistence by modifying registry entries to run automatically. Some versions of the malware are also capable of disabling common detection systems, such as Windows Defender.
According to some estimates, since its release, Phorpiex has been used to infect over a million devices. One of the primary reasons for its extensive reach is its worm module, which allows it to self-propagate across networks and devices. A worm module is a component of malware that enables it to replicate itself and spread to other systems without the need for human interaction.
However, the worm module is not the only method Phorpiex uses for distribution. It has also been known to spread through spam emails. These emails often contain malicious attachments or links to download sites. Additionally, Phorpiex has been observed being dropped by other loader malware.
Phorpiex remains a significant cybersecurity threat to organizations and individuals. To ensure the infection does not occur it is crucial to implement proper security controls. One of the key components of a solid security strategy is the use of a malware analysis sandbox.
ANY.RUN's interactive sandbox offers a number of features that simplify and accelerate the process of malware analysis, as it: