Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Nemty is ransomware with an unusually complex encryption algorithm. This malware encrypts user files and demands money so that they can be unlocked again. It may be connected to other famous ransomware, but we don’t know for sure.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
ex-USSR territory
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2019
First seen
:
|
21 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR territory
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2019
First seen
:
|
21 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 876
876
 0
0

 522
522
 0
0

 2816
2816
 0
0
Nemty, also known as NEMTY PROJECT is a ransomware-type of malware. A virus that puts encryption on all files that are stored on infected machines and only allows to restore them if victims pay a certain ransom amount.
Nemty has surfaced not so long ago. It was first observed in the wild in August 2019. Due to some similarities in the code and behavior, researchers think that Nemty might be related to GandCrab and Sodinokibi, though direct correlation hasn’t been proved. In any case, it is safe to assume that this is very advanced malware.
Additionally, the malware’s code apparently includes an affiliate ID which may indicate that Nemty is available as a Ransomware as a Service. If this information is correct Nemty has the potential to become a very widespread malware due to its easy availability.
Nemty ransomware is being actively upgraded by its creators. In fact, several versions of the virus have already been released and nothing suggests that this development should stop anytime soon.
Among other upgrades, threat actors employed a very strong encryption algorithm. It is actually so strong that no malware before Nemty has used anything similar. The RSA-8192 used here is 8192-bit encryption which is considered to be an overkill for use in malware. Even though this encryption protocol makes data decryption more difficult it also presents its own complications. For example, it causes longer encryption and key generation times and only encrypts 1024 bytes at a time.
Despite this, researchers have been able to create decryptors that work with versions 1.4, 1.5 and 1.6 of the malware, for example, the Avast Nemty decryption tool. This means that victims that have been attacked by the version of the malware mentioned above can restore their information without having to pay the ransom to the attackers.
Without the decryptors like the Avast Nemty tool, victims would have to pay a ransom of about $1000 equivalent in Bitcoin to the attackers. The ransom can be paid through a payment portal that is hosted using the TOR network. And if not paid on time, the amount is doubled to a $2000 equivalent.
We don’t know for sure who the people behind Nemty are. The malware has code that checks if the victim is from one of the following countries: Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, or Ukraine.
However, victims from the countries mentioned above can still get attacked by the ransomware. This is strange since usually, viruses that check for the origins of victims terminate execution to avoid getting attention from local law enforcement structures.
In the case of Nemty, users from all over the world are in danger of being infected.
However, there are other interesting oddities in the code that point to a ex-USSR origin of the virus. The code contains a link to a similar picture that was linked in GandCrab’s code. Except, this time it contains on an overlay of the Russian president’s portrait. There are other weird things to be found in the code of this malware. For example, if you dig deep enough you will find a direct message to cybersecurity professionals telling them to, well, “mind their own business” in a less polite form.
More evidence suggesting the x-USSR origin of the malware creators is that the payment page is in the Russian language. Maybe the creators are in fact Russian or they are trying to plant a false lead and mislead researchers.
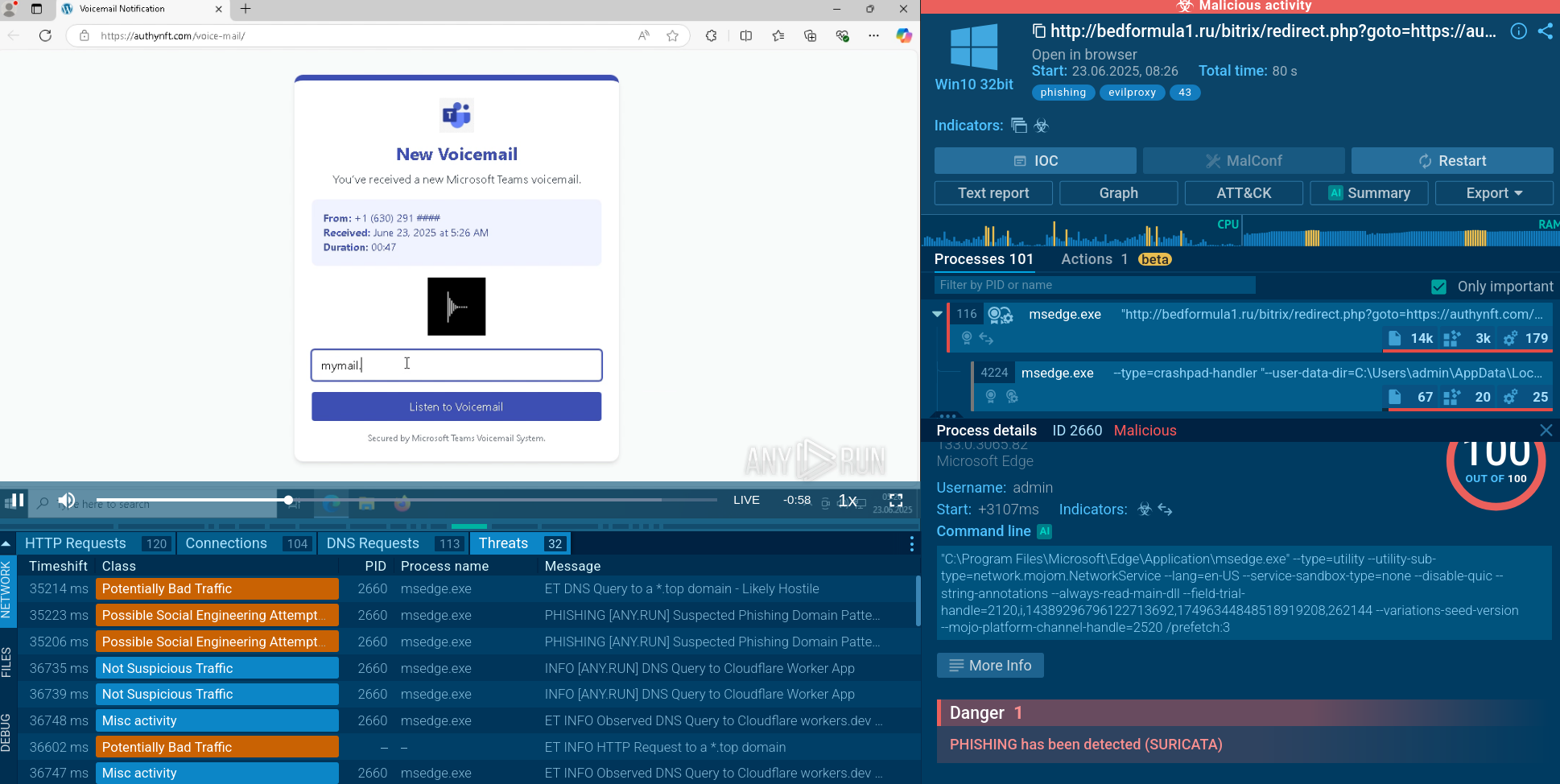
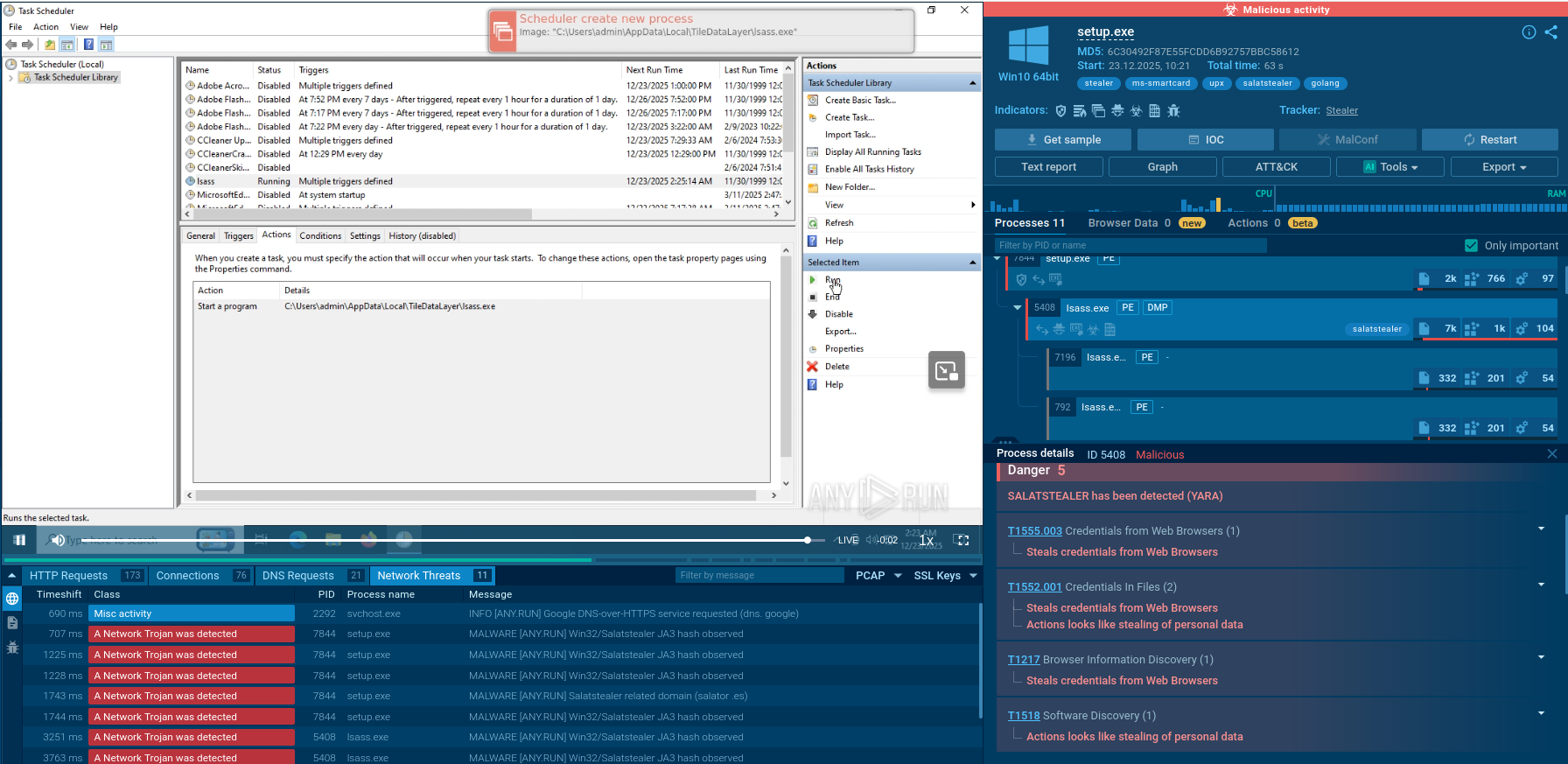
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service allows us to take a look at the execution of this malware in action.
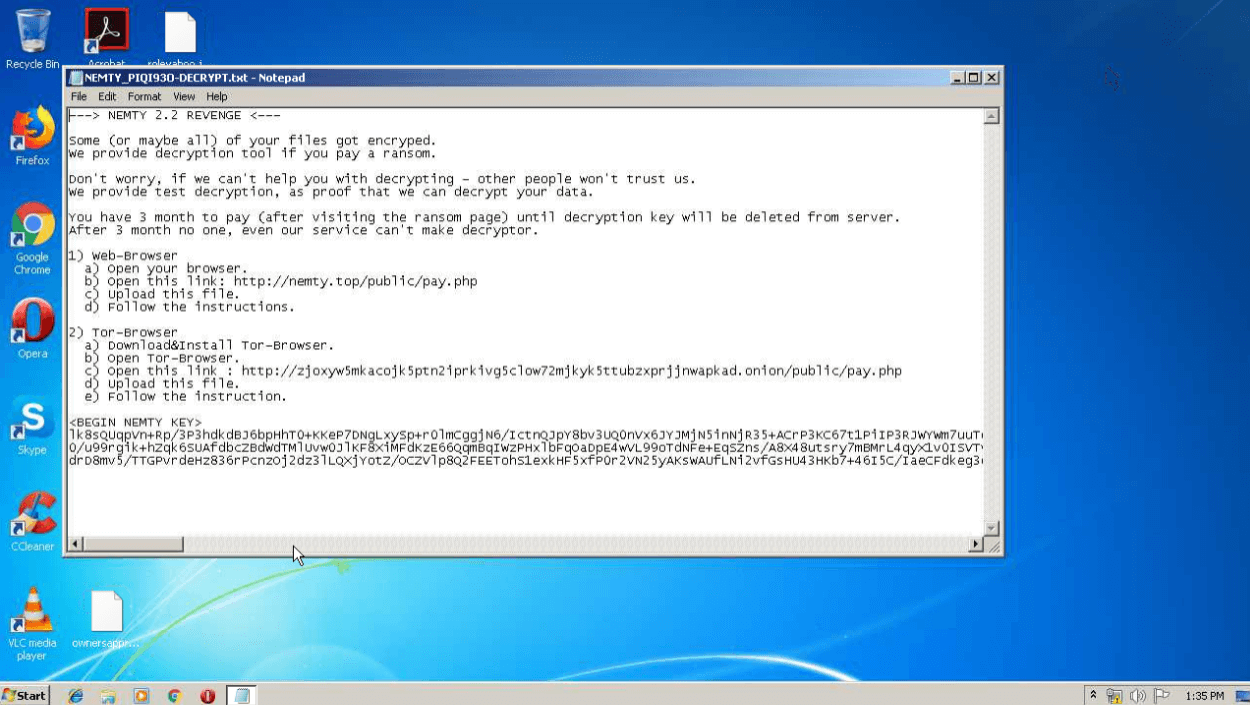
Figure 1: Nemty's ransom note
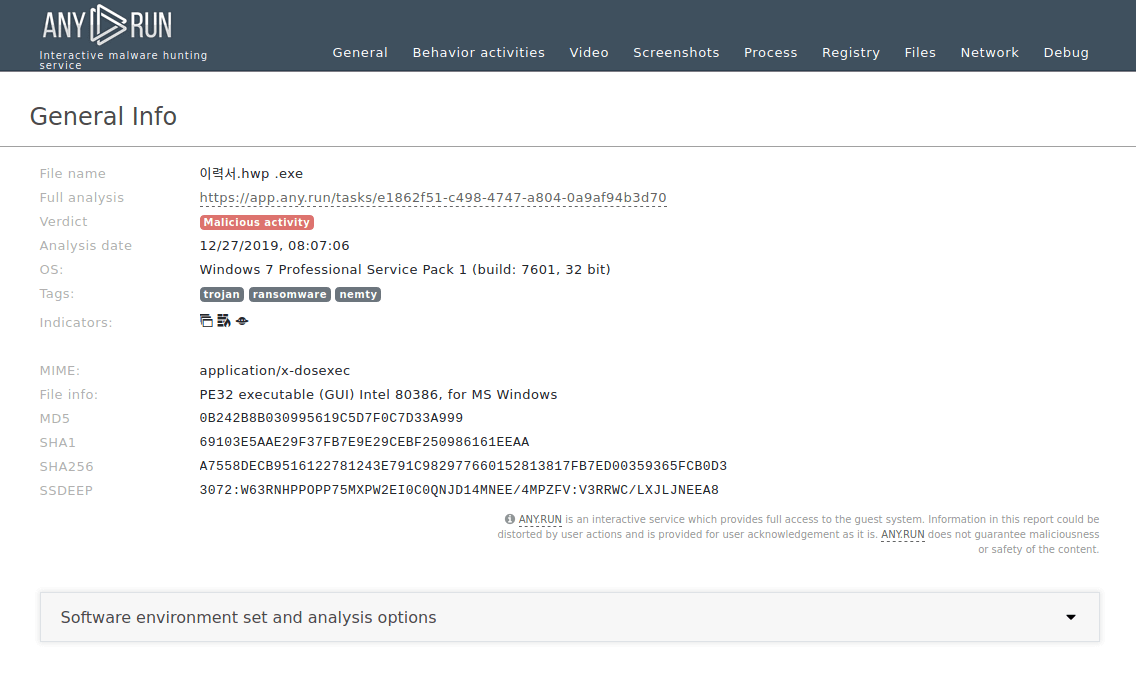
Figure 2: Shows a customizable text report generated by the ANY.RUN malware analysis service which allows diving deeper into the details of the Nemty execution process.
The execution process of the Nemty ransomware is relatively typical for this type of malware. After the executable file makes its way into an infected system and runs, the main malicious activity begins. Like many other ransomware families, Nemty deletes shadow copy files. It also stops and kills processes from the hardcoded list. The malware creates a text file with a ransom note in every folder with encrypted files.
The interesting thing is that Nemty, as well as Sodinokibi, creates a registry key in which it stores values such as a public key and a file extension for encrypted files.
Initially, Nemty was using RIG and Radio EK exploit kits for distribution purposes. In addition to that, malware authors employed spam email campaigns to distribute the virus primarily in Korea and China. These two countries are where the bulk of all Nemty infections is happening.
However, with the newer versions of the malware coming out, threat actors started using new distribution methods. Possibly they were trying to expand the reach of the malware and gain the ability to infect more victims.
One of such methods is a fake PayPal website that promises to save money with an unusually high cashback. The website is designed to look identical to the genuine PayPal and prompts users to download a file called “cashback.exe”. Although unsuspecting victims might think that they are downloading a PayPal app, in reality, they are installing and executing the Nemty ransomware.
In addition, later versions of the malware are delivered using the Trik botnet. Apparently, the authors of Nemty have partnered up with people behind Trik to increase their range.
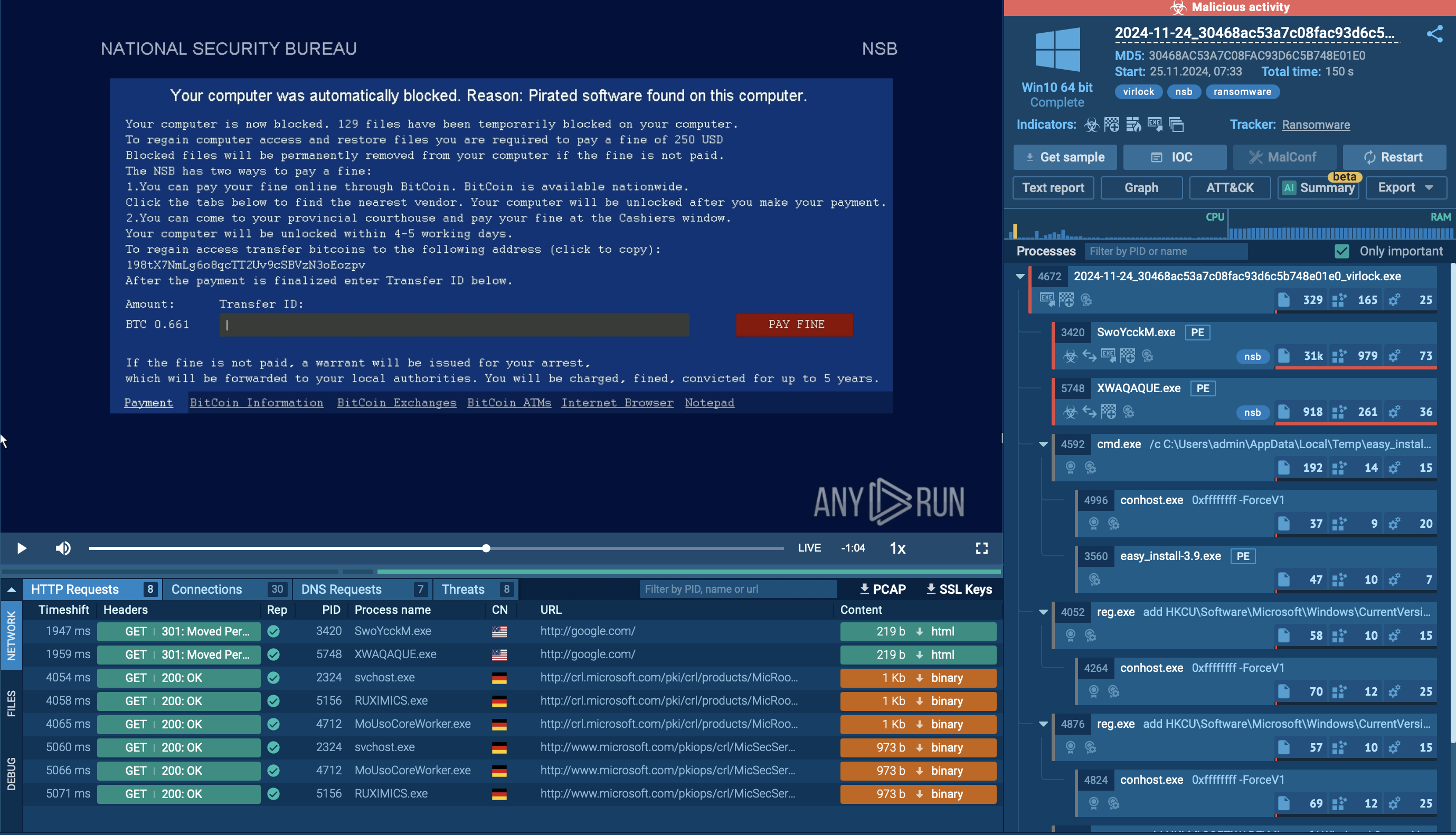
To determine whether the sample under review is Nemty or not, you can take a look at the changes that it made in the registry. To do so, open "Advanced details of process" of the malicious process and look at the "Registry changes" tab in the "Events" section. If a process has created values with the names "cfg", "pbkey" or "fid" into the key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\NEMTY, you can be sure that the given sample is Nemty.
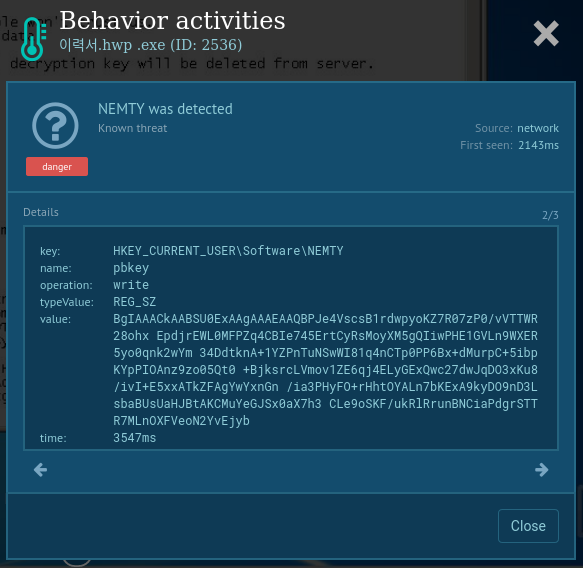
Figure 3: Changes in registry made by Nemty ransomware
The constant evolution of distribution methods, as well as regular updates, prove that this malware is at a stage of active development. First seen in 2019, Nemty is a young threat that already shows signs of sophisticated malware.
Coupled with the potential use of the Ransomware as a Service business model that makes this malware available to many threat actors around the globe, these factors demand that this threat is not taken lightly.
One of the primary dangers of this Ransomware lies in the delivery techniques chosen by the attackers. While mail spam helps to reach millions of potential victims easily, heavy use of exploit kits allows attackers to control every step of the infection.
Thus, it is especially important that security researchers can evaluate this ransomware and continue developing countermeasures and encryptors, like the Avast Nemty. One more tool that can help in this pursuit is the ANY.RUN malware hunting service that will allow studying samples of Nemty in a controlled and safe environment.