Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

GuLoader is an advanced downloader written in shellcode. It’s used by criminals to distribute other malware, notably trojans, on a large scale. It’s infamous for using anti-detection and anti-analysis capabilities.
|
Downloader
Type
:
|
Italy
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2019
First seen
:
|
8 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Downloader
Type
:
|
Italy
Origin
:
|
|
1 December, 2019
First seen
:
|
8 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 452
452
 0
0

 2359
2359
 0
0

 4566
4566
 0
0
Just like the name suggests, GuLoader (sometimes also called CloudEyE and vbdropper) is a first-stage trojan designed to infect a system and drop a final payload. Typically other trojans or RATs. Once the malware makes its way into the victim's system, it attempts to establish a remote connection and download a malicious executable.
This malware is infamous for using advanced anti-detection and obfuscation techniques. It evades network detection, stops executing in virtual environments, and can slip past automatics security systems.
Researchers first observed GuLoader in December 2019, when it was used in a campaign delivering Remcos RAT. Throughout 2020, the trojan kept gaining popularity, at one point accounting for 25% of all packeted samples recorded by Check Point Research. Today, GuLoader remains a highly active threat. It often delivers NanoCore, Agent Tesla, LokiBot, and FormBook.
GuLoader is written in encrypted shellcode wrapped in a Visual Basic 6 (VB6) executable. Notably, it stores second-stage payloads in cloud drive services. Usually, in Google Drive or Microsoft OneDrive. This way, it can establish a connection and download the executable without raising any red flags. The payload is usually encrypted, allowing it to slip past the cloud host’s security measures.
This loader is infamous for its use of anti-analysis techniques:
Like many downloaders, GuLoader is offered as a service. Prices start at $100 per month. It is distributed in the clearnet by a company with a domain name in the .eu zone. The website markets it under the name CloudEye, claiming that this is a security tool intended for protecting applications against cracking. However, the same site contains links to YouTube tutorials that clearly display how to use the software maliciously. They also show how to abuse cloud drives.
Researchers managed to link GuLoader to an Italian-based hacking group by analyzing emails left as contact details in old forum threads. One of the users behind the loader is known under the alias sonykuccio. He advertised a malware variant as far back as 2011 and offered paid services, claiming that he could make other malicious programs harder to detect. That is why GuLoader uses so many intricate anti-evasion techniques.
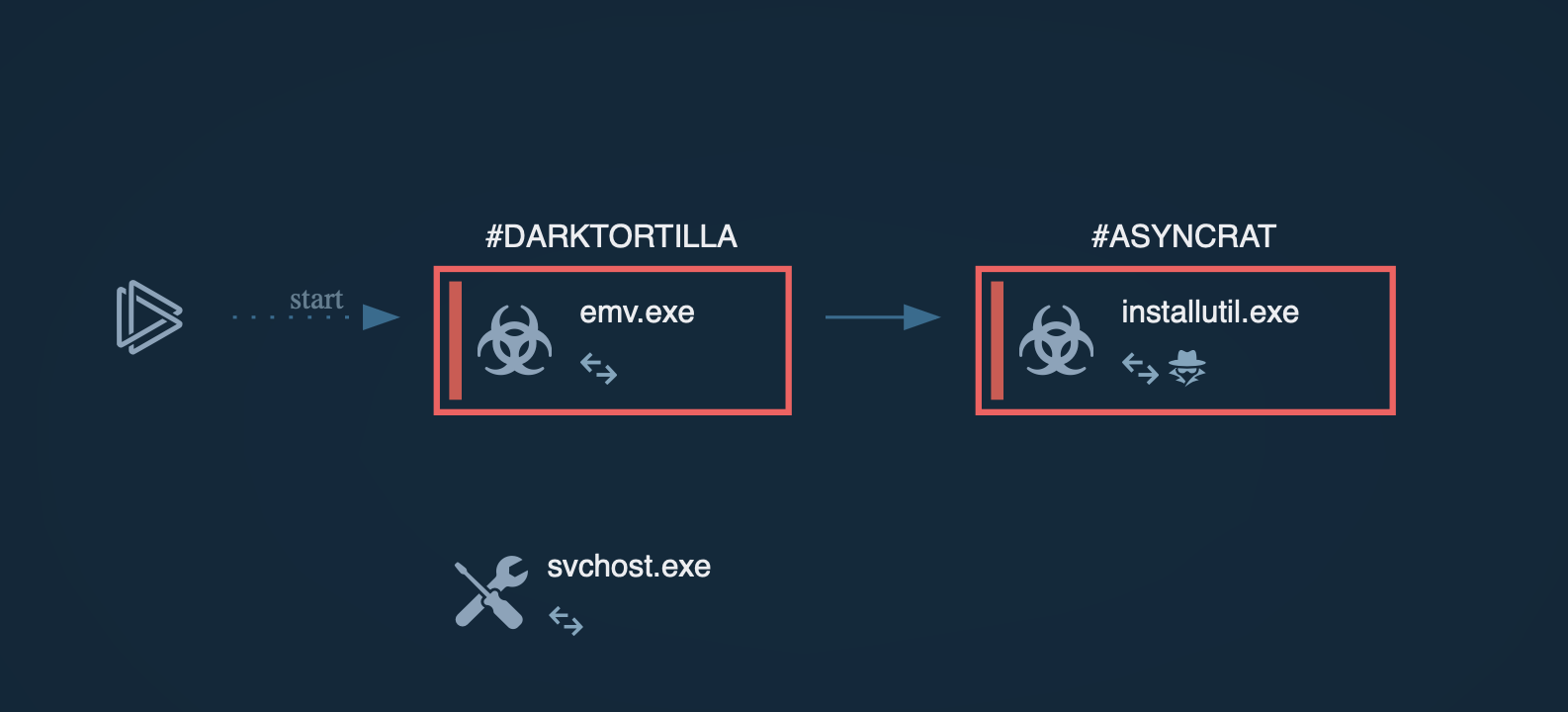
ANY.RUN helps researchers perform malware analysis of GuLoader and track its execution process in an interactive sandbox.
Figure 1: GuLoader text report generated by ANY.RUN
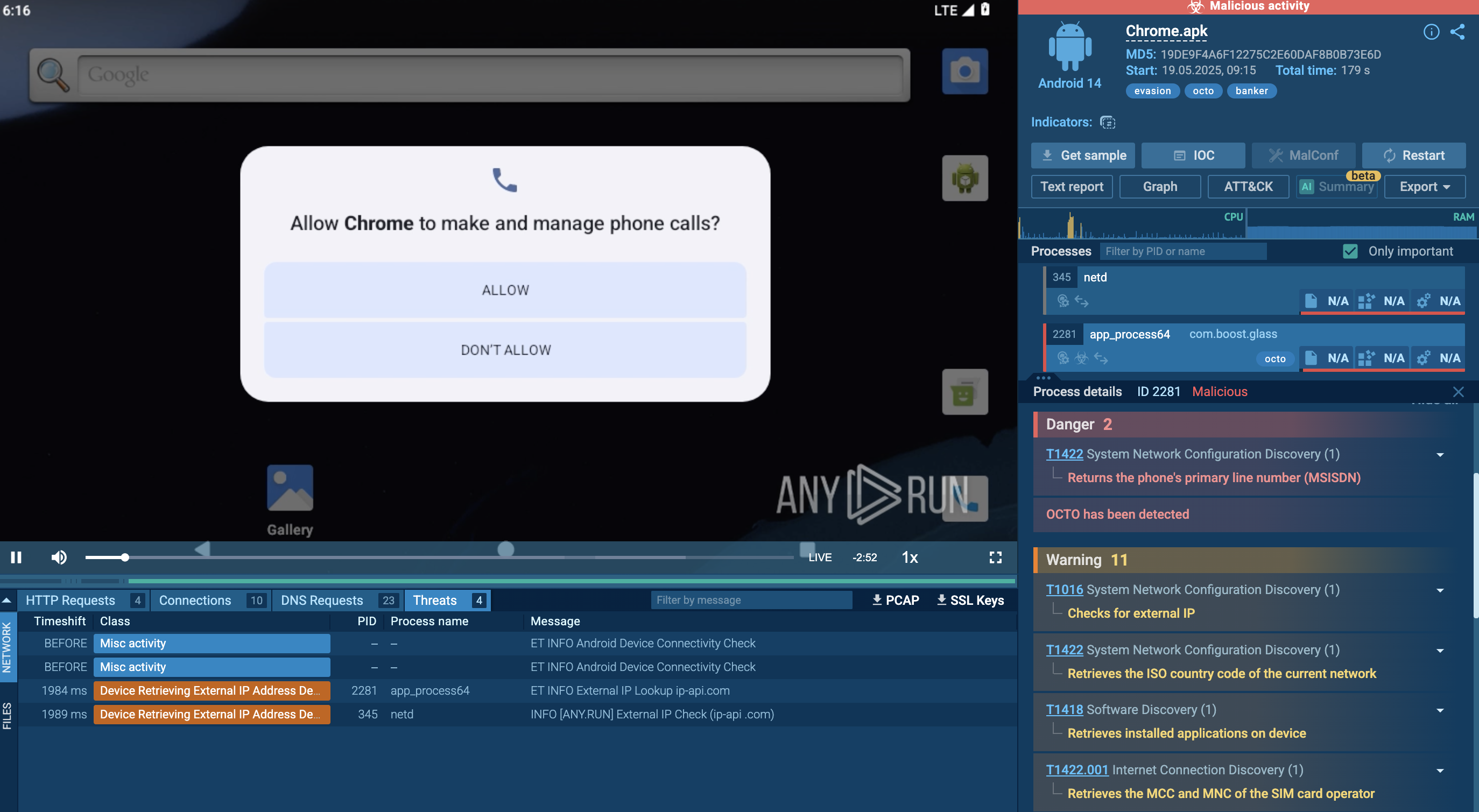
ANY.RUN allows users to save time during analysis and present crucial information extracted from malware immediately. Analysts may take a look inside GuLoader malware configuration 10 second after its process started.
.png)
Figure 2: GuLoader malware configuration
The distribution method of GuLoader has changed over time, but its execution flow has remained fairly straightforward. The main purpose of GuLoader is to download the primary payload to the infected system. Upon starting, it checks whether it is running inside a virtual environment. If the check passes, it establishes a connection and downloads the payload. Once the payload is downloaded and executed, GuLoader stops.
But even if loader didn't connect to C2 during analysis, you always may look in extracted malware configuration to find out from where GuLoader is wants to receive payload!
Read a detailed analysis of GuLoader in our blog.
The distribution method of GuLoader is very typical. The loader is usually delivered as an Office document attachment in spam email campaigns. When downloaded, it uses a macro to install the malicious program. Sometimes it is also delivered as an executable in a .rar archive.
During the pandemic, many campaigns exploited the fear surrounding Covid-19 by mentioning the virus. More recently, attackers have been using fake payment invoices. They will impersonate a bank and use social engineering to trick the victim into downloading an infected file to check “payment details.”
GuLoader is available as a service for a relatively low price, can be easily found in the clearnet, and comes with easy-to-follow instructions. No wonder, then, that creators claim they already have over 5000 clients. Thanks to the combination of advanced anti-evasion tricks and ease of use, we expect its popularity to continue to grow.
Thankfully, GuLoader is easily detectable in ANY.RUN sandbox. It only takes a few minutes to launch an interactive emulation and identify the threat.