Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


zgRAT is a malware known for its ability to infect systems and exfiltrate sensitive data to command-and-control (C2) servers. It is primarily distributed through loader malware, as well as phishing emails. zgRAT employs various advanced techniques, including process injection and code obfuscation, to evade detection and maintain persistence on infected systems. The malware can also spread via USB drives and uses popular messaging platforms like Telegram and Discord for data exfiltration.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2021
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2021
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 799
799
 0
0

 484
484
 0
0

 2736
2736
 0
0
zgRAT, a remote access trojan (RAT), has been active in the cybersecurity landscape since its launch in 2021. This malware is designed to infect systems, collect sensitive data, and exfiltrate the stolen information to command-and-control (C2) servers.
zgRAT is primarily distributed through loader malware such as PrivateLoader and SmokeLoader, which act as delivery mechanisms for the RAT. Interestingly, researchers have noted that some samples of zgRAT can be mistaken for PureCrypter due to shared code elements.
With ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox, we can safely execute a zgRAT malware and analyze its behavior on an actual live system.
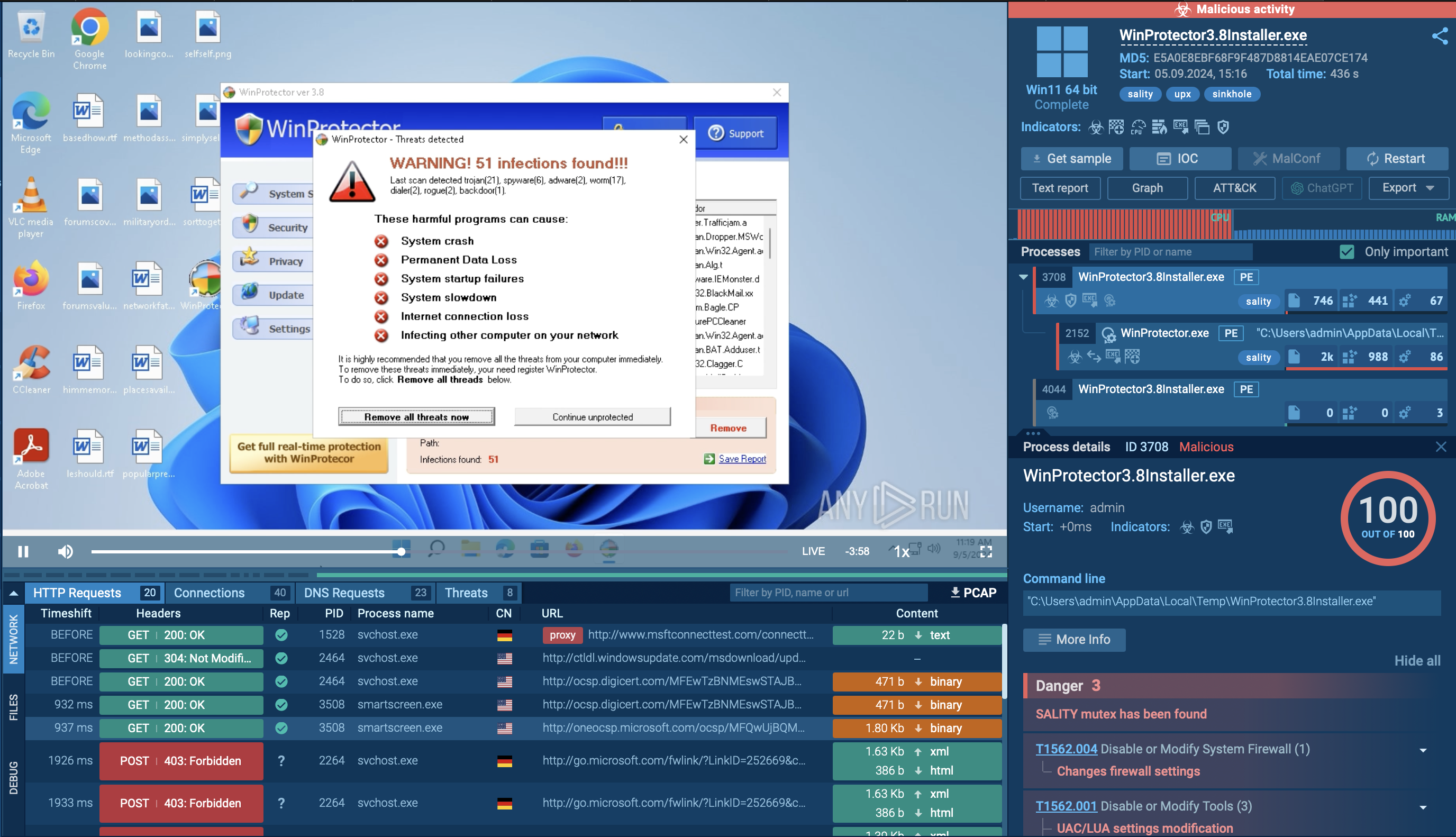
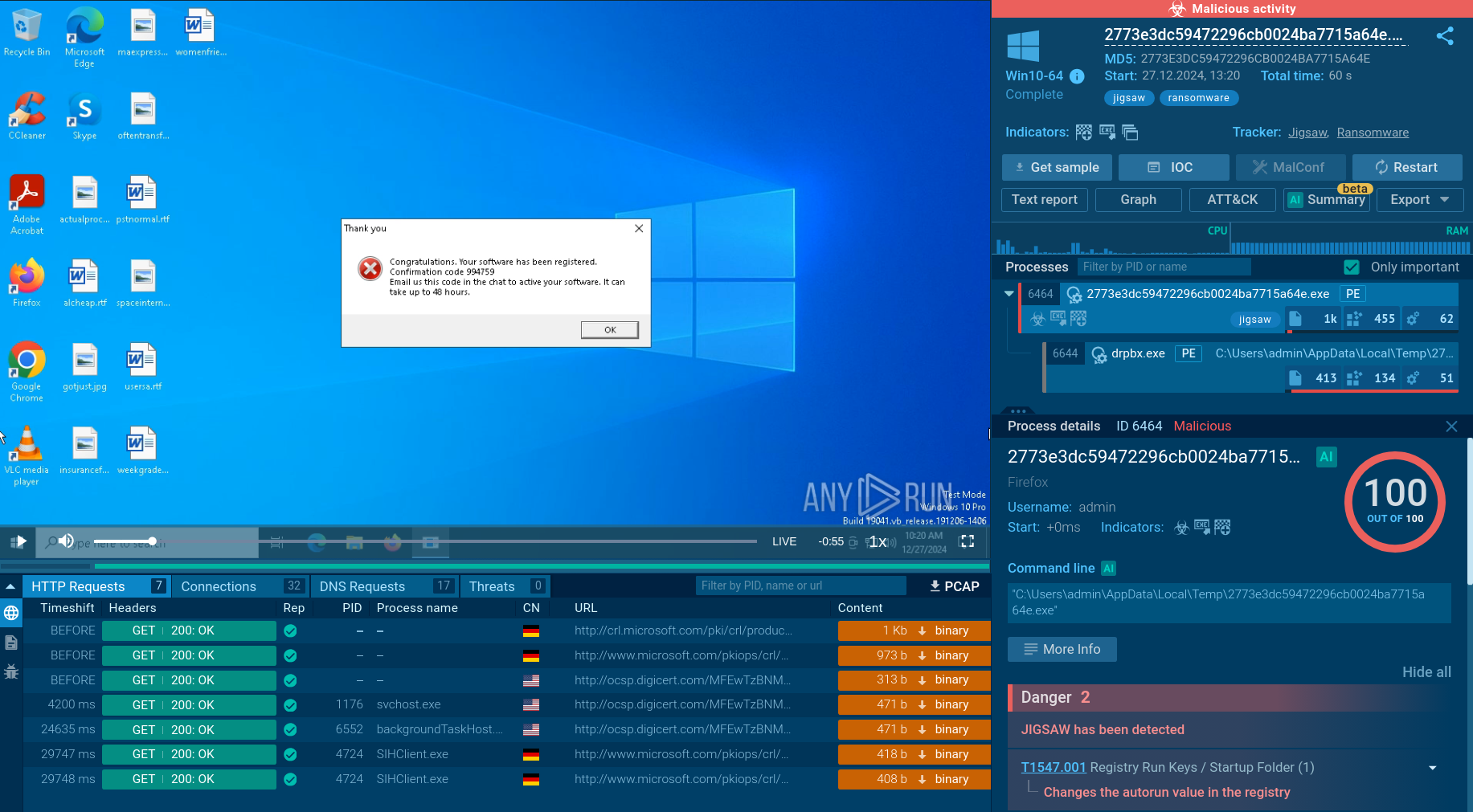
 Analysis of a malicious zgRAT process inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
Analysis of a malicious zgRAT process inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
As observed in this sandbox session, the threat dropped is immediately detected after attempting to gain foothold on the machine.
zgRAT is equipped with advanced capabilities to perform malicious activities on the infected machines, including:
Use ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox to analyze malicious files and URLs. Check out this analysis of a zgRAT sample.
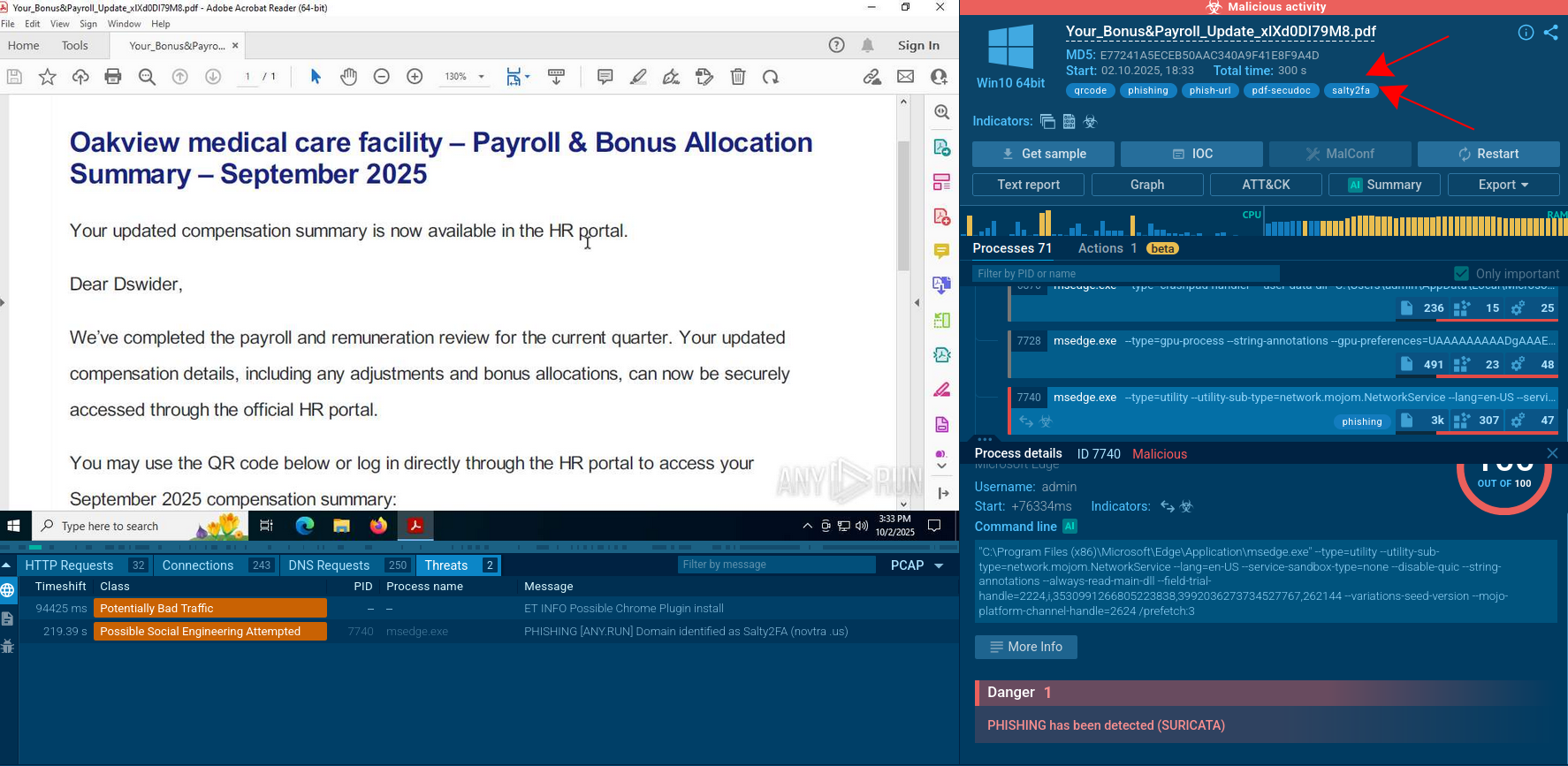
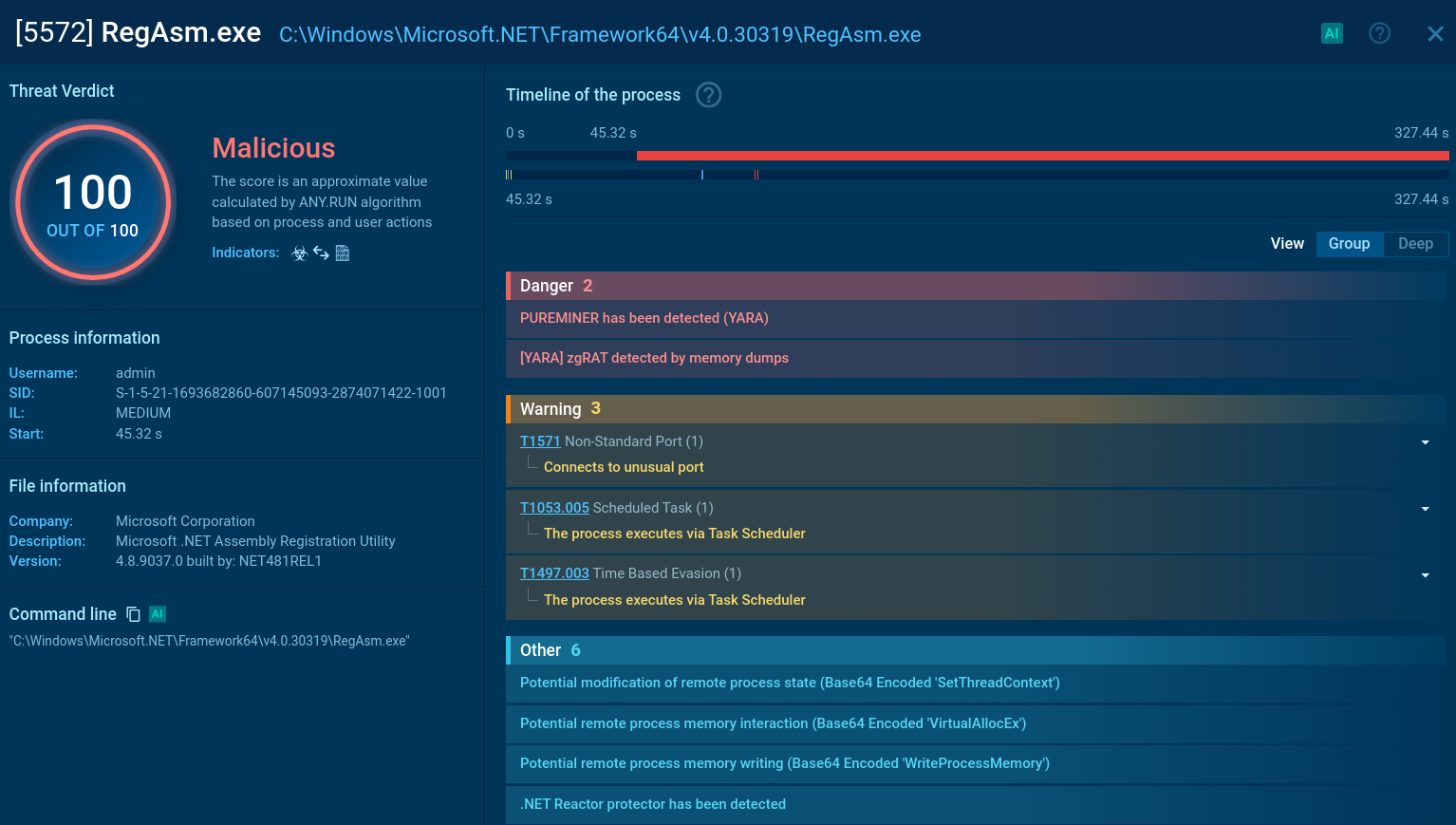
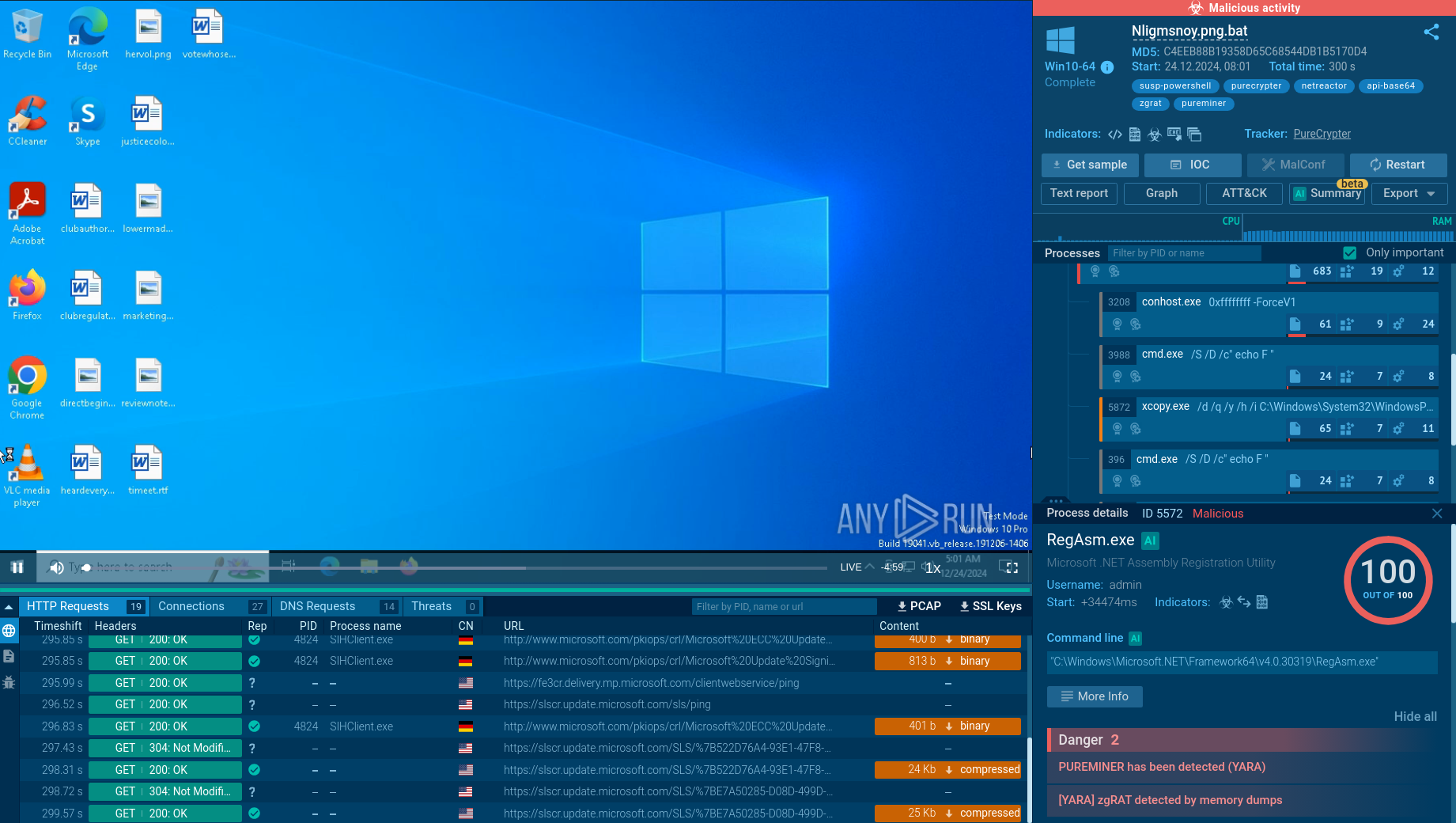 Analysis of a zgRAT sample inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
Analysis of a zgRAT sample inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
zgRAT is often spread through phishing emails containing malicious attachments like Windows Shortcut (LNK) files or Batch scripts (BAT). Opening these attachments triggers a script that drops additional payloads onto the system. The initial script may download and execute a malicious executable, continuing the infection process.
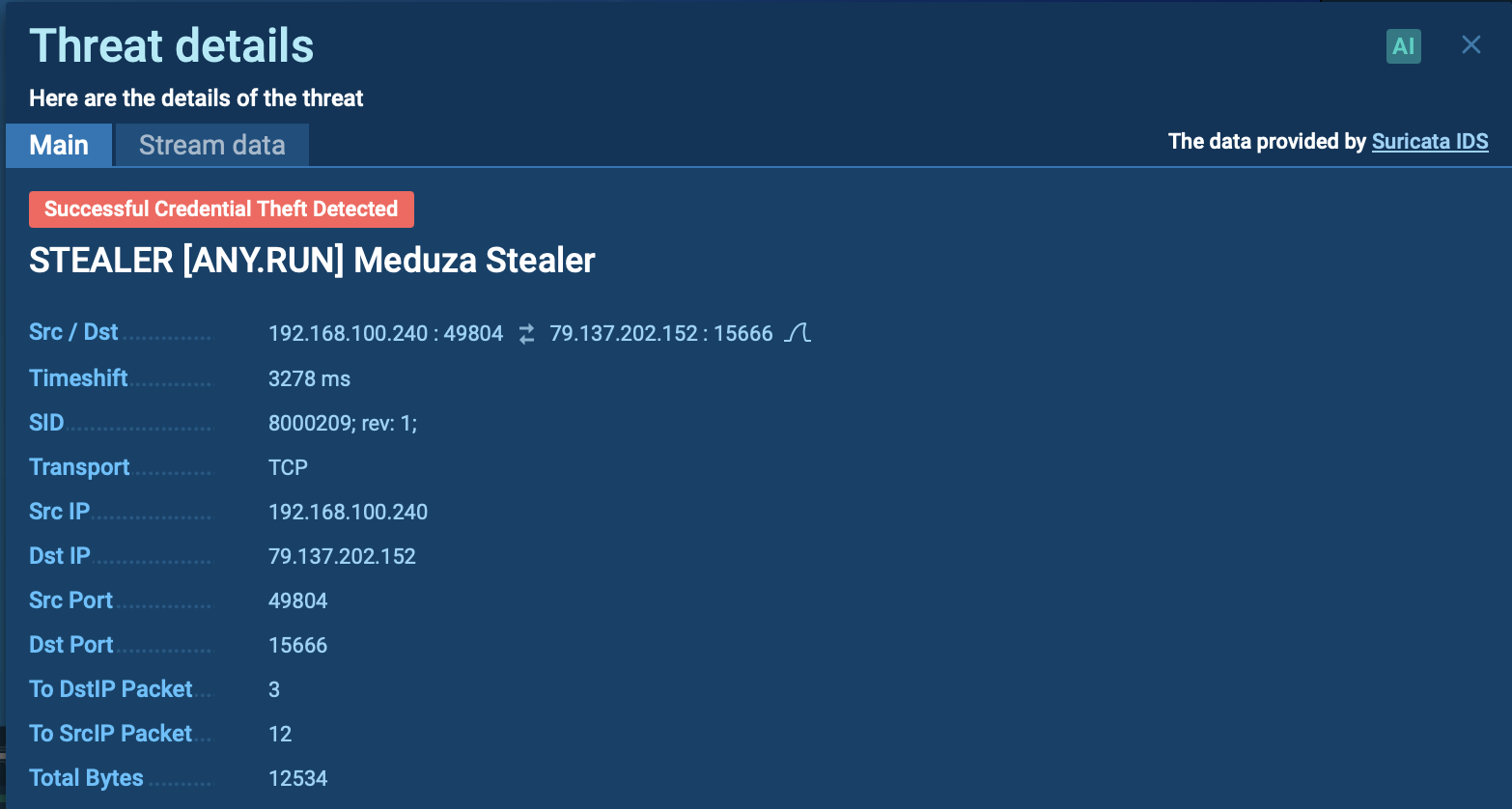
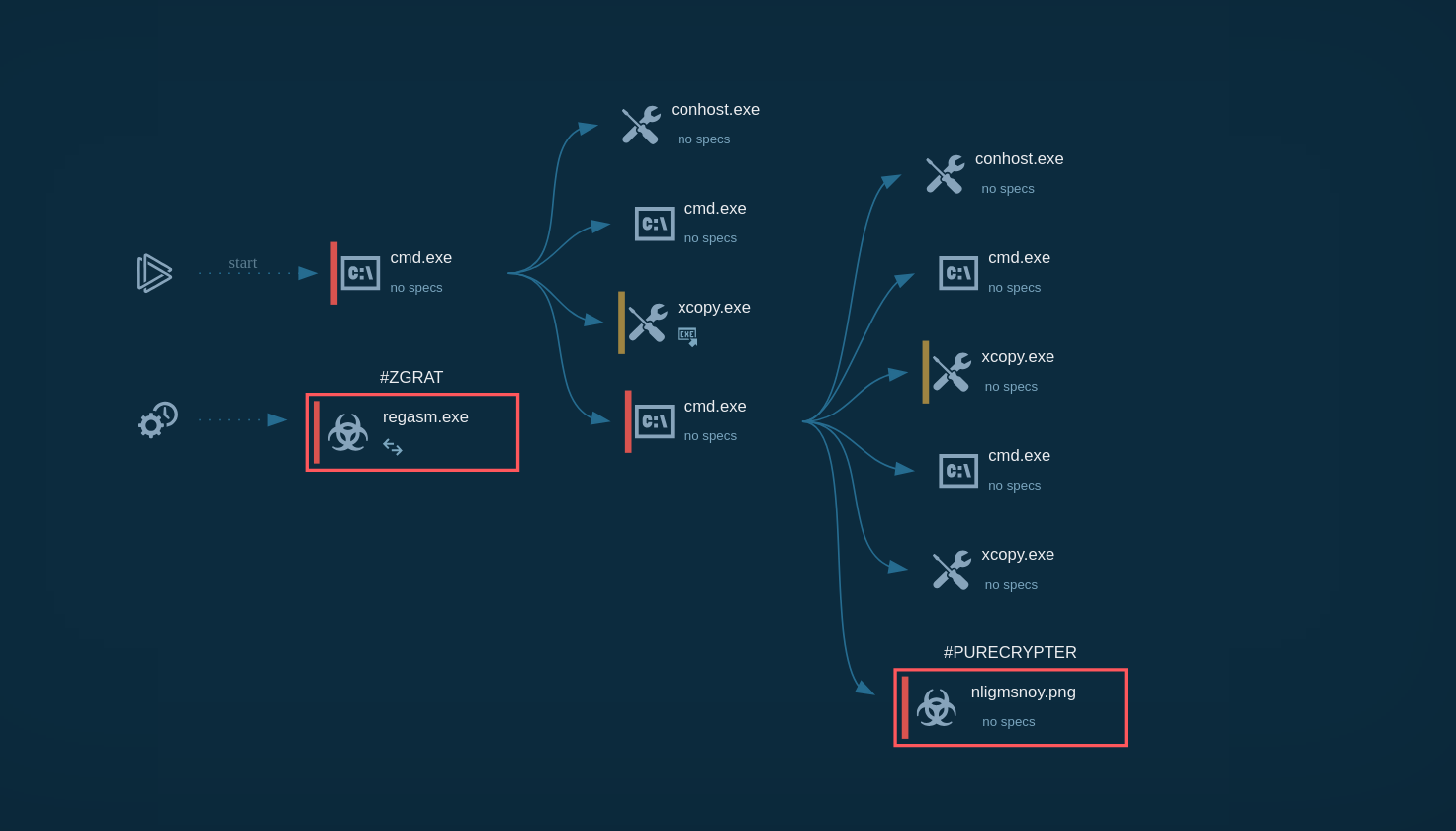 Process graph of a zgRAT execution chain demonstrated by the ANY.RUN sandbox
Process graph of a zgRAT execution chain demonstrated by the ANY.RUN sandbox
To evade detection, zgRAT uses obfuscation techniques such as packing, dynamic code generation, and XOR encryption. It also employs anti-tampering protections similar to ConfuserEx and loads extra DLLs to execute obfuscated methods. The malware complicates static analysis by making dynamic function calls via randomly named wrapper methods.
For persistence, zgRAT modifies registry entries or creates scheduled tasks to run automatically on startup. It creates mutexes to prevent multiple instances and communicates with a command and control (C2) server, allowing attackers to send commands and exfiltrate data. zgRAT can steal sensitive information through keylogging and screen capturing, and as a Remote Access Trojan (RAT), it enables remote control of infected machines, command execution, and file manipulation without user consent.
One of the most common techniques for distributing zgRAT is through phishing emails, which trick users into downloading and executing malicious attachments or clicking on links that lead to the download of malware.
zgRAT is frequently dropped by loader malware that act as intermediaries, ensuring that zgRAT is delivered efficiently to infected systems. Some loaders have also been observed using malvertising techniques, particularly through Google Ads. Malvertising involves malicious advertisements that, when clicked, redirect users to websites that download and install malicious software.
Threat Intelligence Lookup helps security professionals keep up with the latest samples and indicators of zgRAT.
The service provides access to a extensive database containing insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox. With over 40 search parameters, users can find specific data related to threats, including IP addresses, domains, file names, process artifacts, mutexes, etc.
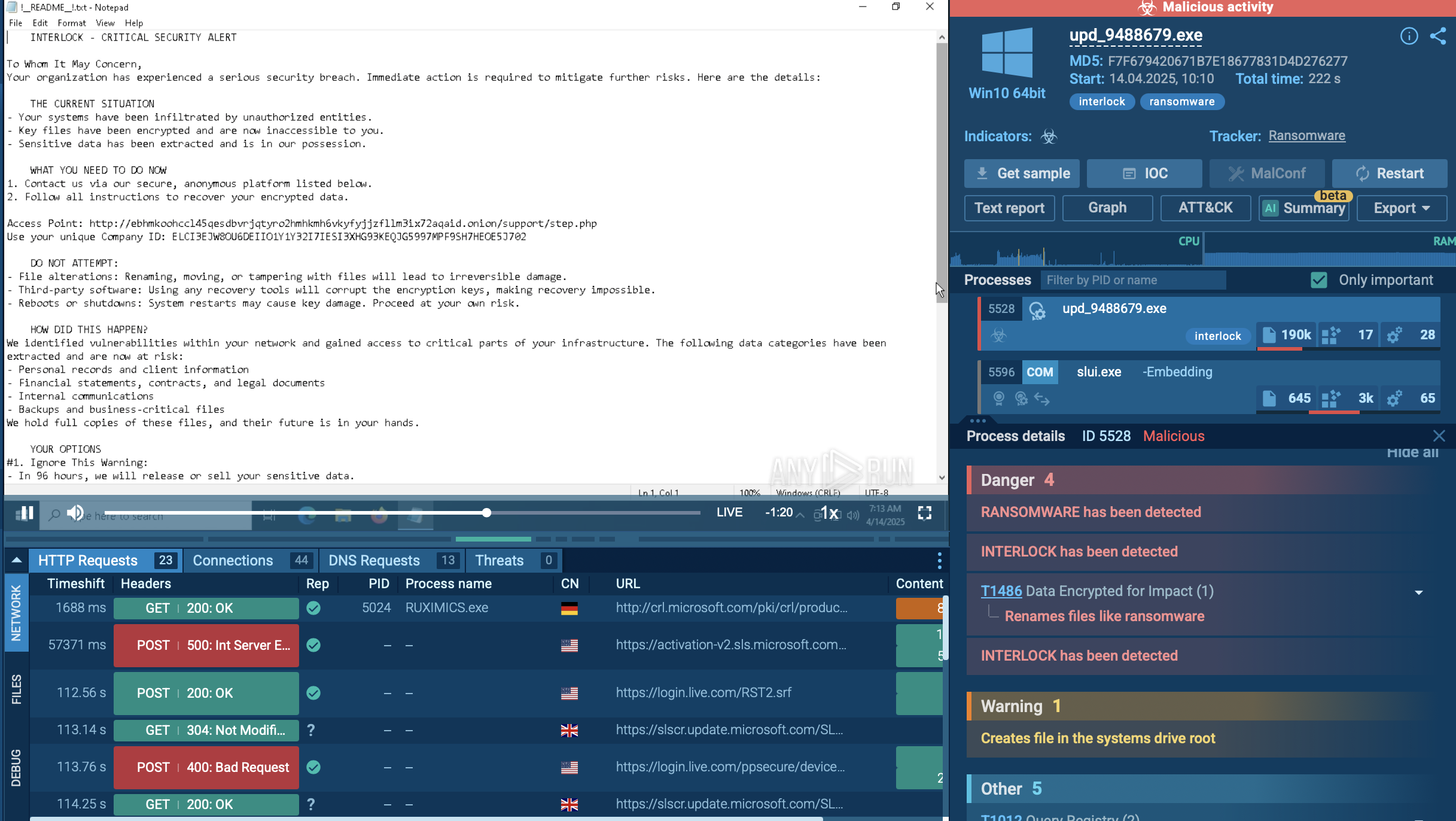
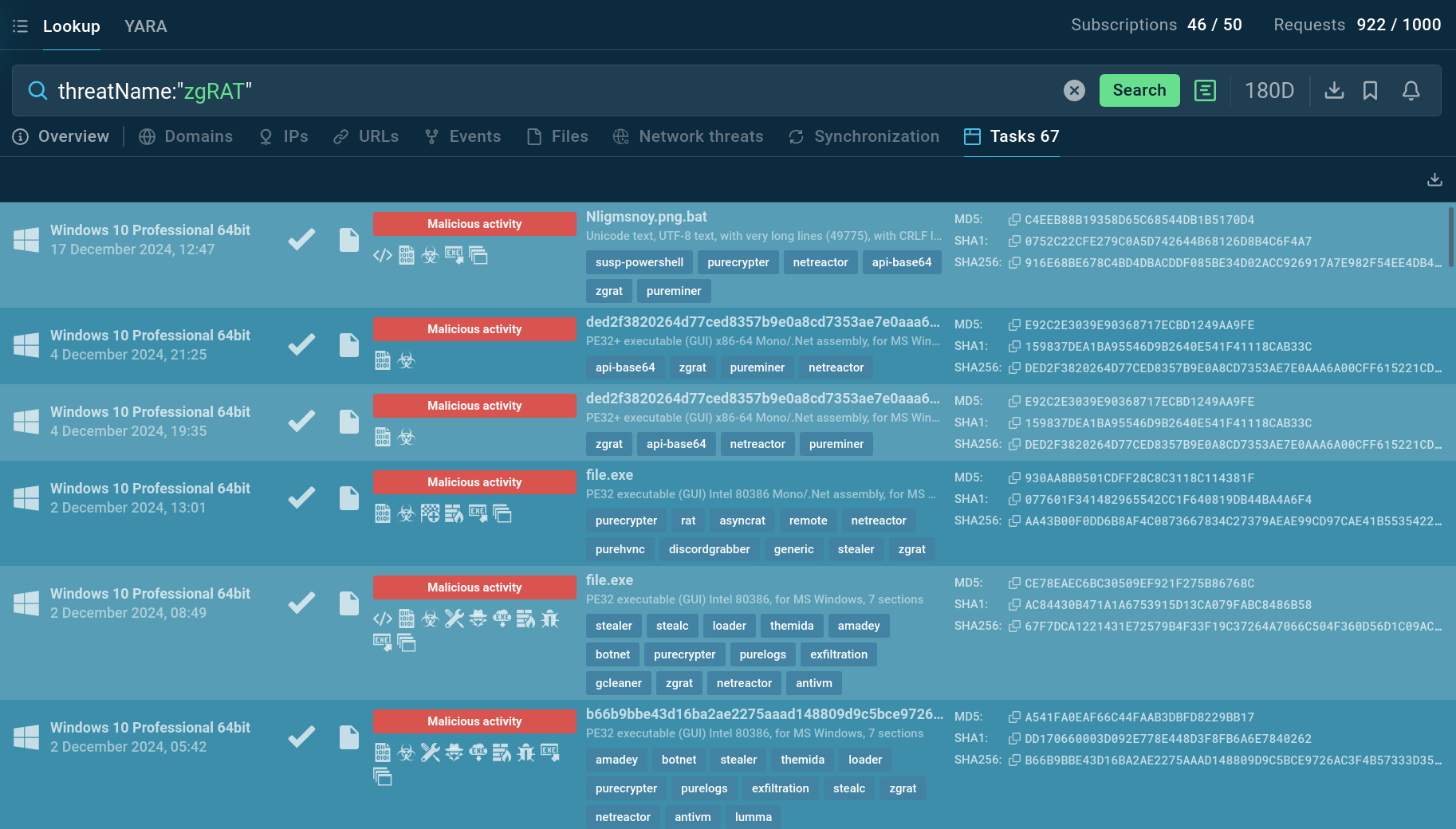 TI Lookup provides a list of sandbox sessions featuring zgRAT malware
TI Lookup provides a list of sandbox sessions featuring zgRAT malware
For instance, important context on zgRAT can be searched by with the query like threatName:"zgRAT". This will return all related samples and sandbox results relevant to this remote access trojan.
zgRAT malware represents a significant threat to businesses, with its advanced capabilities and sophisticated distribution methods. Its ability to steal sensitive data, spread via USB drives, and exfiltrate information through popular messaging platforms makes it a serious security concern.
To ensure proactive identification of malicious content, use ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox that lets you quickly run analysis of any file and URL to determine if it poses a risk.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account to access unlimited cyber threat analysis →