Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


CryptBot is an advanced Windows-targeting infostealer delivered via pirate sites with "cracked" software. It has been first observed in the wild in 2019.
|
Infostealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
20 December, 2019
First seen
:
|
1 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Infostealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
20 December, 2019
First seen
:
|
1 March, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 966
966
 0
0

 568
568
 0
0

 2918
2918
 0
0
CryptBot, initially detected in 2019, is an information stealer designed to compromise Windows operating systems.
Its primary purpose is to exfiltrate confidential data from infected machines, such us:
The primary distribution channels for CryptBot involve spearphishing emails and illicit software cracks.
CryptoBot is a relatively modern malware. However, it’s authors are constantly evolving the threat, making it harder to detect. Around February 2022 researchers began noticing that threat actors simplified CryptBot’s functionality, making it lighter, leaner, and less likely to be detected.
This saw them remove features such as the anti-sandbox evasion, redundant second C2 connection, second exfiltration folder, screenshot function, and the option to collect data on TXT files on the desktop.
At the same time, post 2022 samples have gained targeted additions and improvements that make them more potent. Previously, the malware could only exfiltrate data from Chrome versions between 81 and 95. Now, CryptBot searches all file paths and exfiltrates user data, regardless of the Chrome version in use. This improvement allows CryptBot to be effective against a wider range of targets.
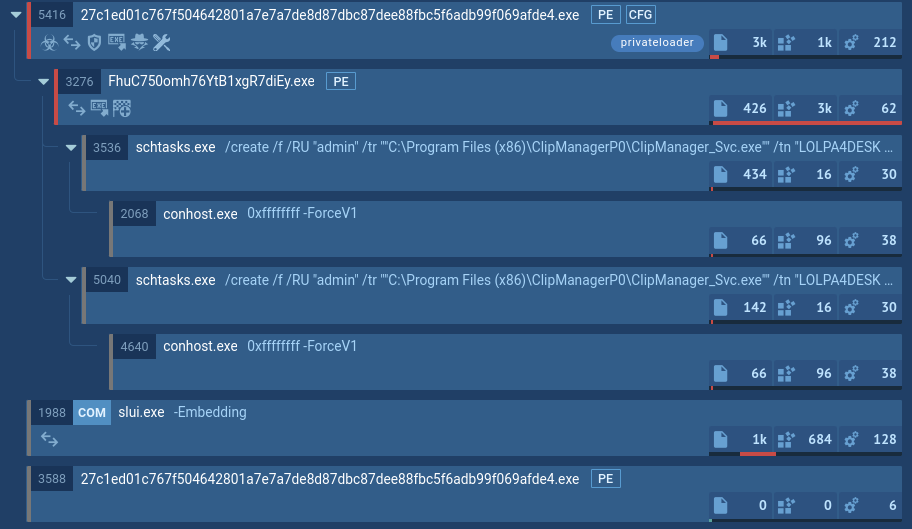
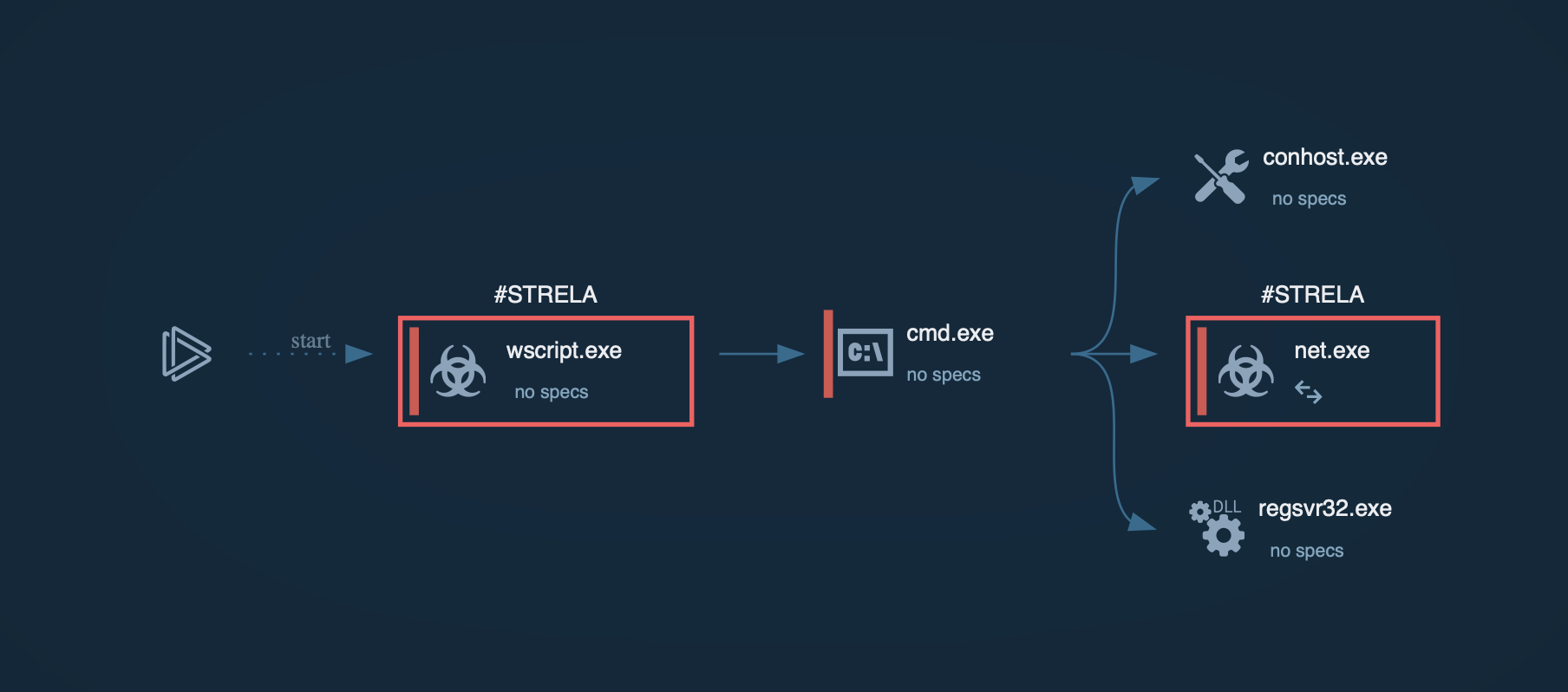
Initiation of the CryptBot attack sequence typically occurs when an unsuspecting user visits a compromised webpage and is lured into downloading what appears to be a legitimate file, such as an SFX file posing as software like Adobe Photoshop. Once the user downloads the file, a malicious SFX file is placed on their computer. When executed, a folder is created in the user's %Temp% directory, containing several files that enable the subsequent stage of the attack.
The folder might contain an authentic Windows DLL, a BAT script, a concealed AutoIT script, and an AutoIT v3 compiler for executables. Some files might be disguised as image, audio, or video files to hide their actual purpose. The specific file extensions used can vary across different CryptBot versions.
The AutoIT interpreter tool, which is frequently exploited by numerous malware families, plays a role in the attack process. The BAT script examines the victim's system for certain antivirus products and uses a "sleep" function to avoid detection if any are found. It is also in charge of decrypting the highly obfuscated AutoIT script and transferring it to the virtual memory area for execution.
In the end, the AutoIT compiler for executables runs the harmful script, initiating an AutoIT process and loading the CryptBot binary into the system's memory.
At ANY.RUN, you can securely execute CryptBot and conduct dynamic analysis within a completely interactive cloud-based sandbox environment. Our platform automatically gathers and presents rich execution data in easy-to-read formats.
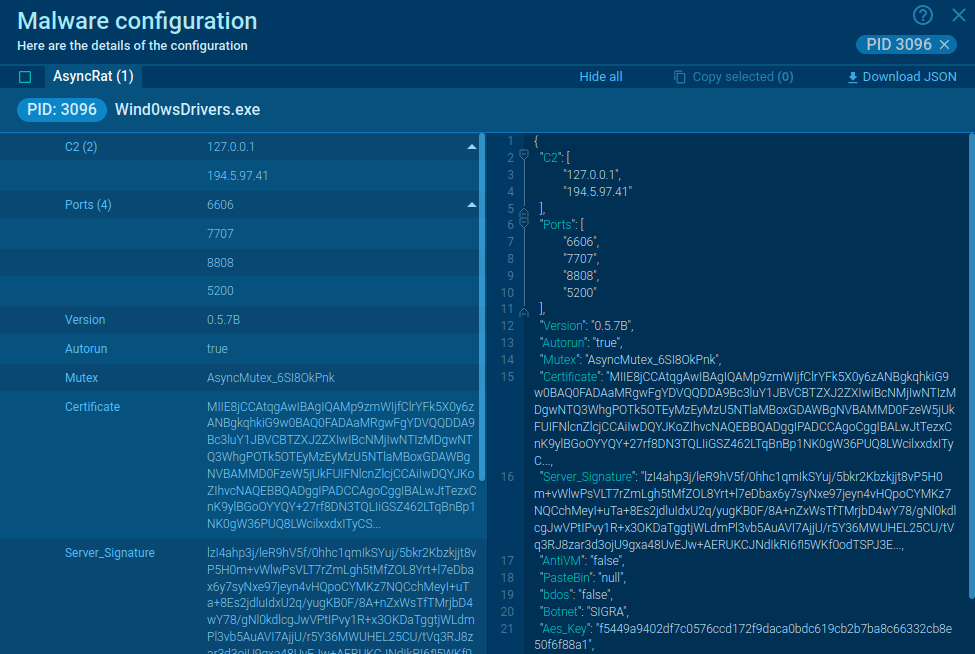
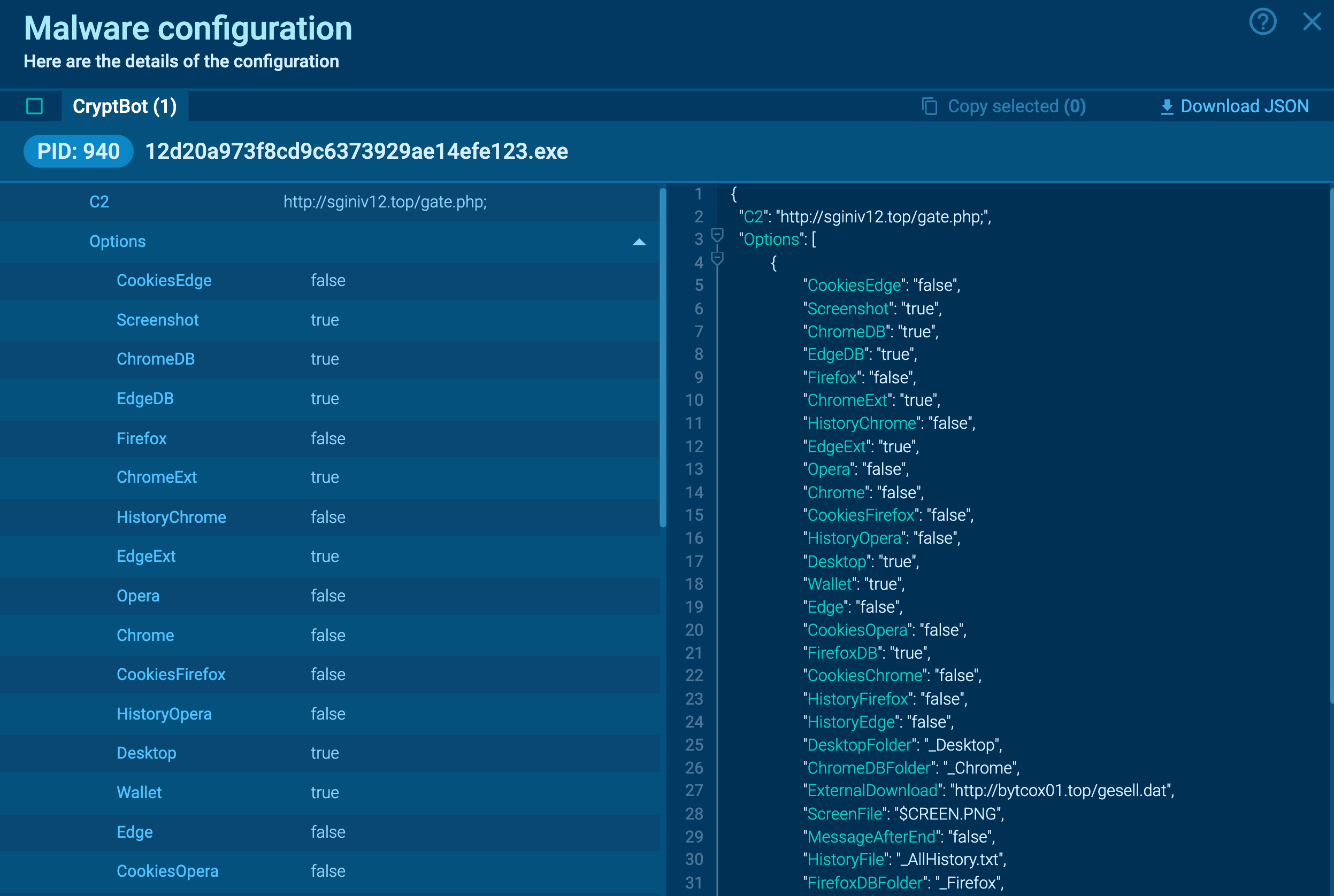 Figure 1: CryptBot’s configuration automatically extracted by ANY.RUN
Figure 1: CryptBot’s configuration automatically extracted by ANY.RUN
You can collect more info about the analyzed sample by looking at extracted malware configuration. A PCAP file for later analysis is also available for download.
Upon initiating the initial payload, the execution flow of CryptBot can be variable. Cryptbot might sometimes employ the "compile after delivery" technique for defense evasion or release and execute a second file.
Then, the malware gathers data about the infected system, the software installed, and pilfers credentials. For data exfiltration, the stealer often establishes a connection with the C2 domain, with the ** .top** extension. It's noteworthy that it consistently sends requests to a page named gate.php. After completing these actions, the malware may implement a file deletion technique, deleting itself.
Read a detailed analysis of CryptBot in our blog.
In addition to utilizing phishing and spearphishing techniques with infected documents, starting around February 2022, CryptBot has expanded its distribution methods by leveraging cracked software lures to target potential victims.
The strategy involves creating websites that masquerade as providers of software cracks, key generators, pirated games, or other utilities. Then, search engine optimization (SEO) techniques are used to rank the malware distribution sites at the top of Google search results.
The malicious websites undergo frequent updates, employing various lures to attract users. Visitors are taken through a series of redirections before reaching the delivery page, which may be hosted on a compromised legitimate site for SEO poisoning attacks.
CryptBot's primary targets are individuals searching for software cracks, warez, and other methods of bypassing copyright protection. To avoid infection by CryptBot and other similar malware, users should refrain from downloading such tools.
By staying informed about CryptBot's distribution methods and recent changes, malware analysts and security researchers can better understand this threat and develop effective countermeasures.
Speed up your workflow by analyzing CryptBot in ANY.RUN. Create an account using your business email and try our interactive cloud sandbox for free.