Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


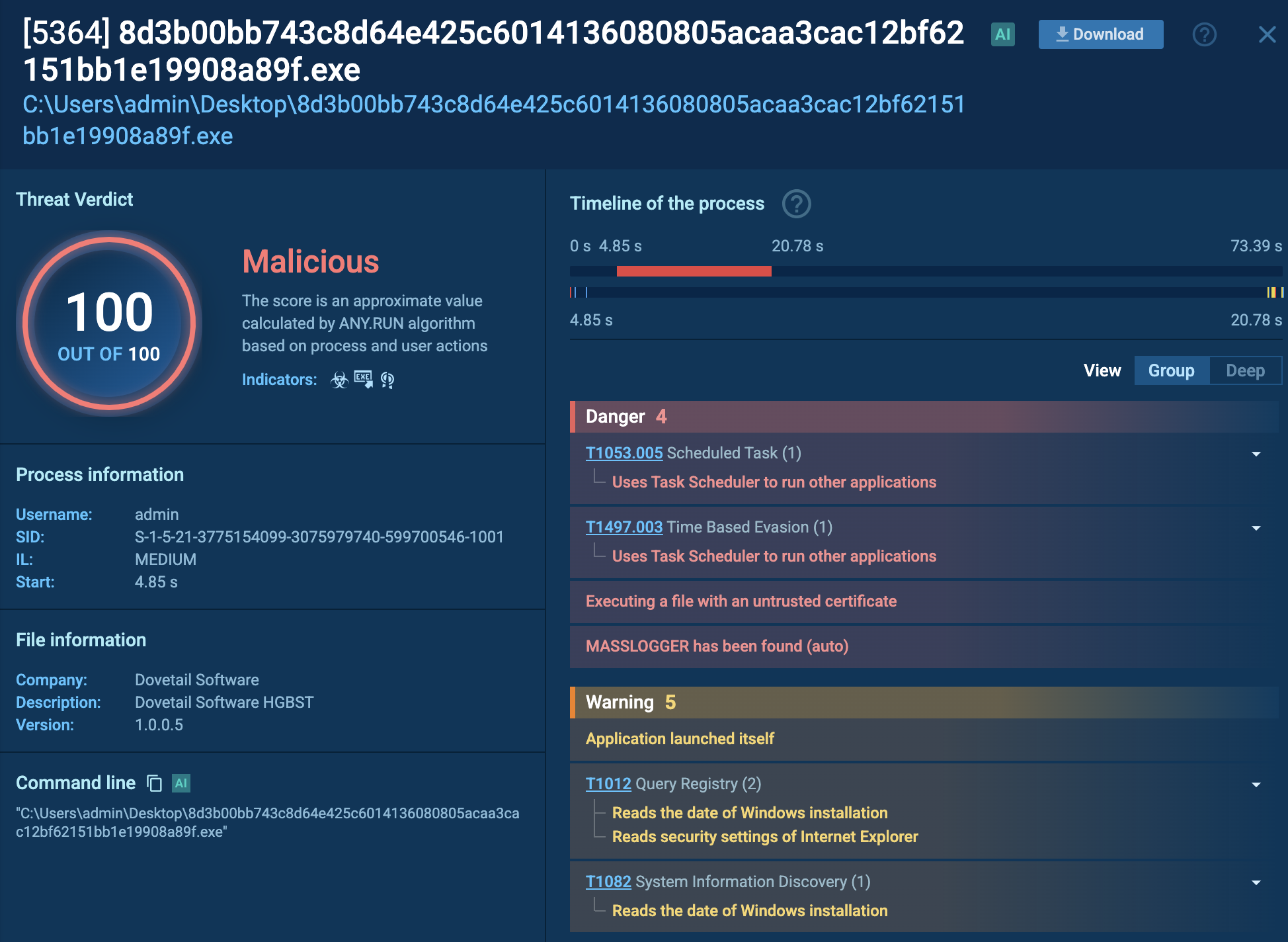
DeerStealer is an information-stealing malware discovered in 2024 by ANY.RUN, primarily targeting sensitive data such as login credentials, browser history, and cryptocurrency wallet details. It is often distributed through phishing campaigns and fake Google ads that mimic legitimate platforms like Google Authenticator. Once installed, it exfiltrates the stolen data to a remote command and control (C2) server. DeerStealer’s ability to disguise itself as legitimate downloads makes it particularly dangerous for unsuspecting users.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2024
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2024
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 779
779
 0
0

 476
476
 0
0

 2720
2720
 0
0
DeerStealer is a relatively new info-stealing malware that emerged in 2024, targeting sensitive data like login credentials, browser history, and cryptocurrency wallet details.
Unlike more established stealers, DeerStealer has quickly gained attention due to its innovative distribution methods, including fake websites mimicking legitimate services like Google Authenticator. These sites trick users into downloading malware under the guise of security software.
The malware has been linked to malicious campaigns that target individual users as well as organizations, and it’s speculated to share similarities with other stealer malware like XFiles.
In addition to exfiltrating data, DeerStealer persists on infected systems by modifying registry keys, enabling it to survive reboots and remain active.
This persistence, combined with its focus on browser exploitation and cryptocurrency theft, makes DeerStealer a significant risk, particularly to users managing sensitive online accounts and assets.
The primary functionality and features of DeerStealer malware include:
In some DeerStealer campaigns, attackers use a Telegram bot to send information about infected systems, such as IP addresses and country.
When victims land on a fake website (like a Google Authenticator download page), their IP address and country are sent to a Telegram bot. This bot, named "Tuc-tuc," helps attackers track the locations of infected users and coordinate further actions.
Telegram serves as a secure and anonymous medium for logging victim data, making it easier for the attackers to monitor their phishing campaigns without detection.
To see how DeerStealer operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
DeerStealer is commonly distributed via fake websites that mimic legitimate services, such as Google Authenticator. When users attempt to download the application from these sites, their information, such as IP address and country, is sent to a Telegram bot.
The malware itself is hosted on platforms like GitHub and is designed to run directly in memory without leaving traces on disk.
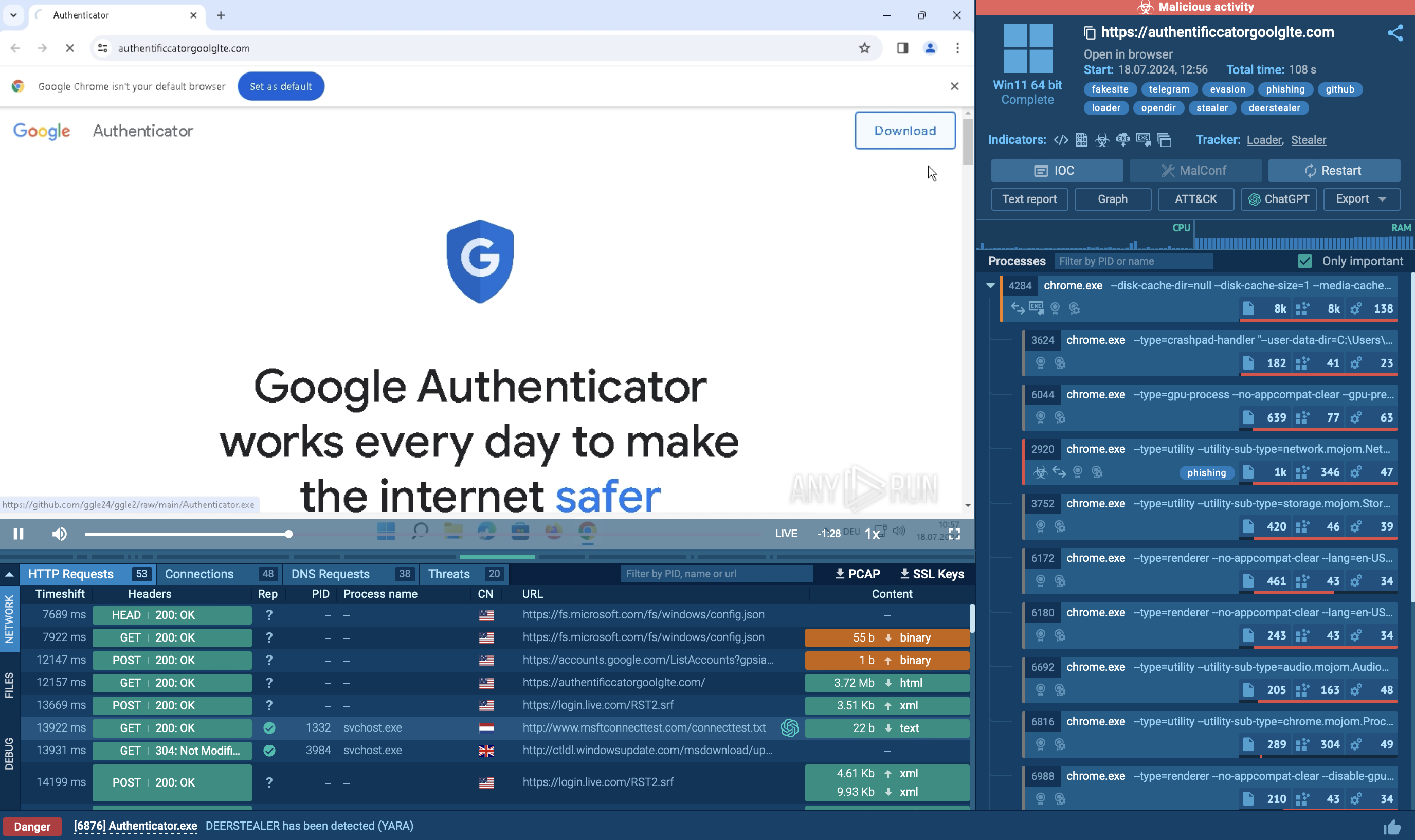 Fake website mimicking Google Authenticator analyzed inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Fake website mimicking Google Authenticator analyzed inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Upon execution, it launches a Delphi-based application that serves as a launcher for the final payload.
To evade detection, the payload employs obfuscation techniques and runs entirely in memory, making it difficult for traditional antivirus solutions to identify.
Before initiating its malicious activities, DeerStealer performs checks to confirm it's not operating in a sandbox or virtual environment. It collects hardware identifiers (HWID) and transmits them to its command and control (C2) server. If the checks are passed, the malware retrieves a list of target applications and keywords from the server.
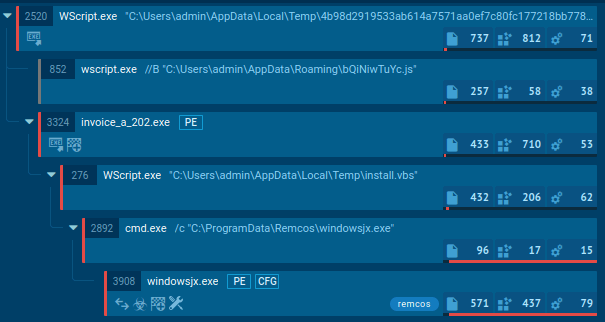
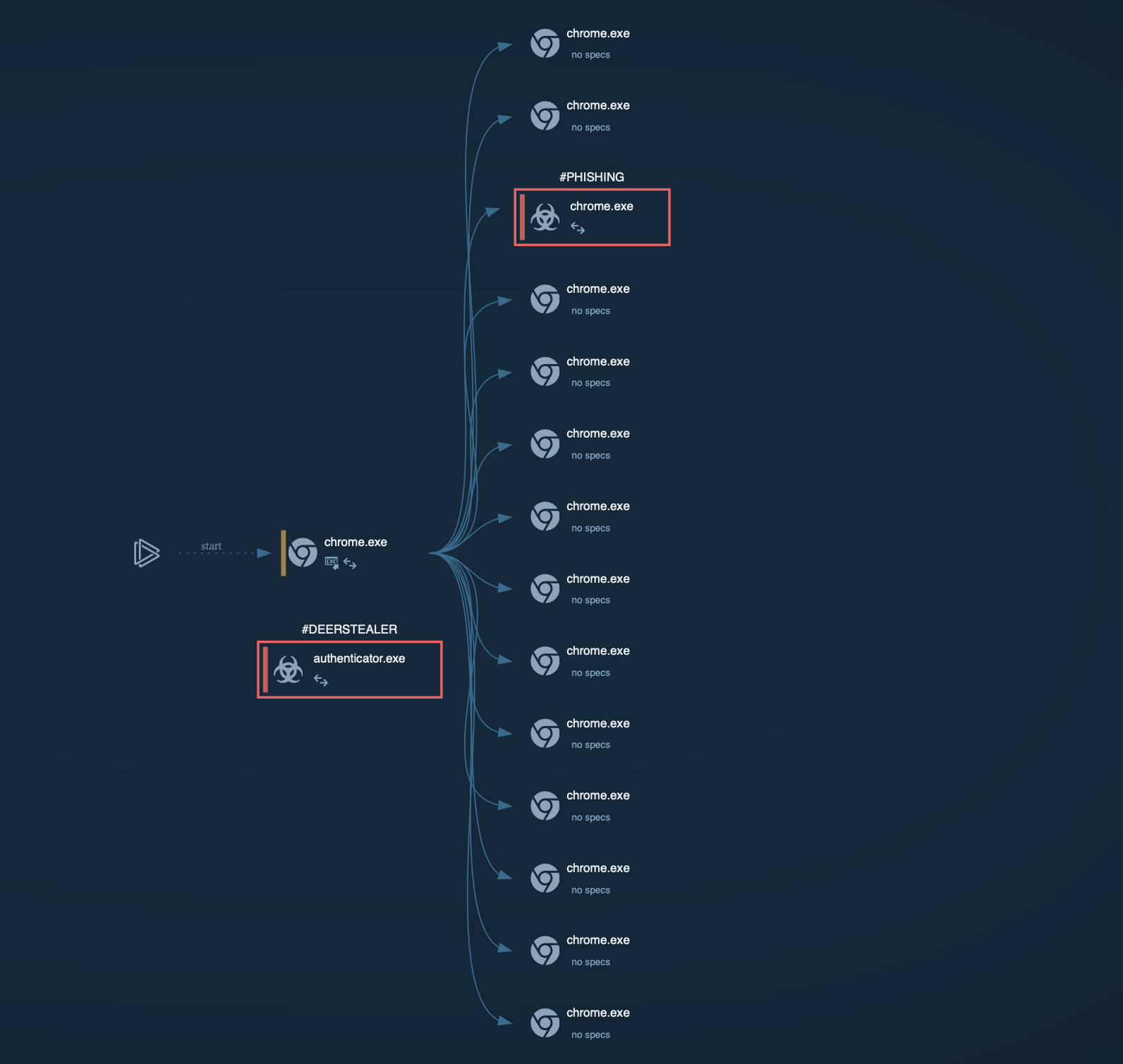 DeerStealer process graph displayed in the ANY.RUN sandbox
DeerStealer process graph displayed in the ANY.RUN sandbox
DeerStealer scans the infected system for sensitive information, such as cryptocurrency wallet credentials, browser-stored passwords, and other personal data. The stolen data is organized into a structured format, often JSON, before being exfiltrated.
The exfiltration occurs through POST requests, typically sent over encrypted channels to bypass network monitoring tools. To maintain persistence, DeerStealer may establish scheduled tasks or modify startup configurations, enabling it to execute automatically upon system reboot.
DeerStealer is primarily distributed through various deceptive techniques that aim to trick users into downloading malware. Some of the key distribution methods include:
To collect up-to-date intelligence on DeerStealer, you can utilize Threat Intelligence Lookup from ANY.RUN.
This tool gives access to a comprehensive database filled with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions. Using over 40 customizable search parameters, such as IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts, it allows you to uncover important details about threats like DeerStealer.
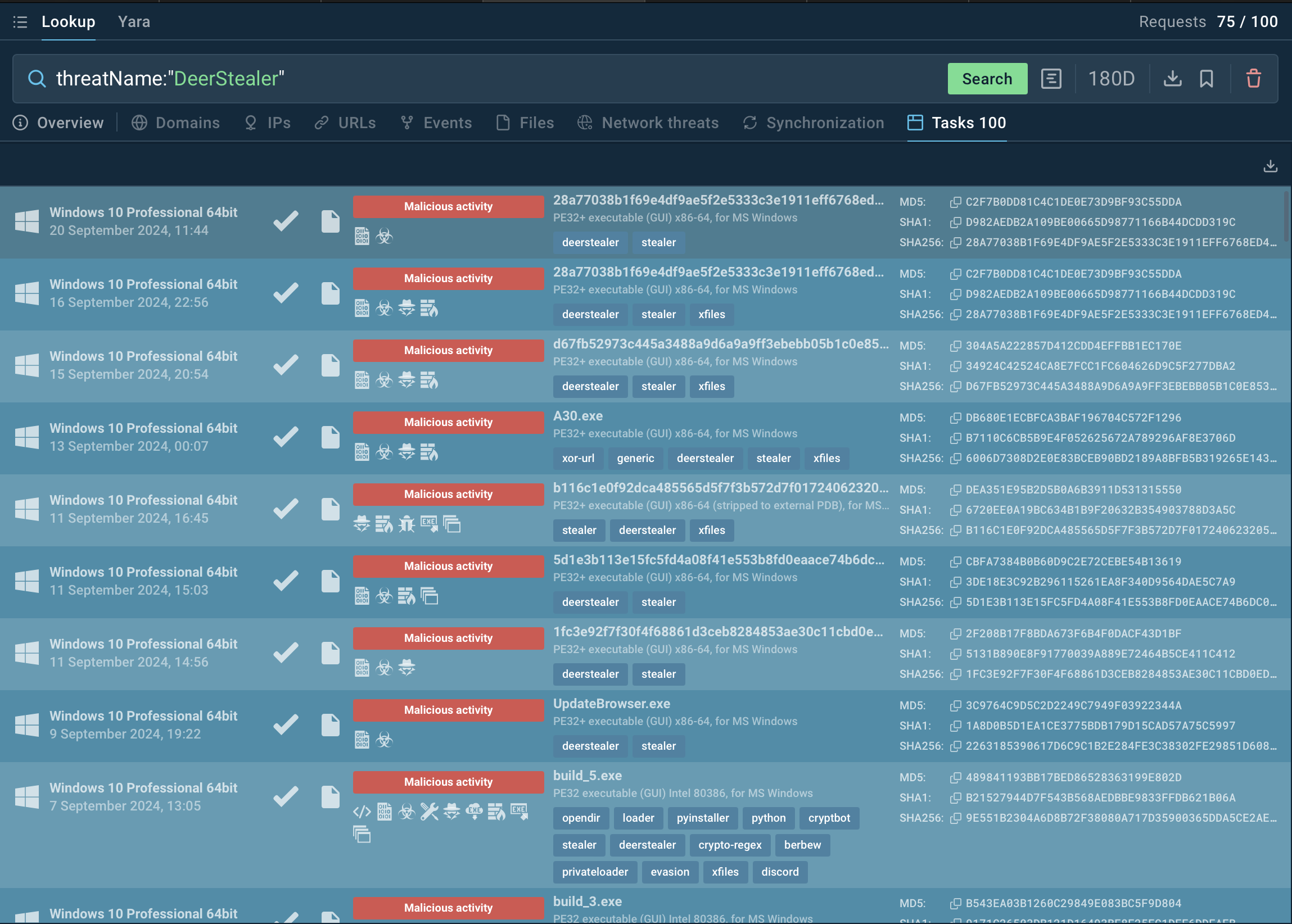 Search results for DeerStealer in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for DeerStealer in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For instance, by searching for DeerStealer’s name or using a related indicator, such as a domain or process artifact (threatName:"DeerStealer", Threat Intelligence Lookup will display all relevant samples and sandbox results associated with the malware.
Get your 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup along with the ANY.RUN sandbox.
DeerStealer is a serious threat, capable of stealing login credentials, browser data, and cryptocurrency information. Its distribution through fake websites makes it difficult to detect. It’s important to analyze suspicious files and URLs to protect against DeerStealer and similar malware.
ANY.RUN provides a real-time sandbox for analyzing malware behavior and allows its users to quickly identify threats, gathering key indicators of compromise (IOCs)
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today and start analyzing all the emerging threats with no limits!