Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


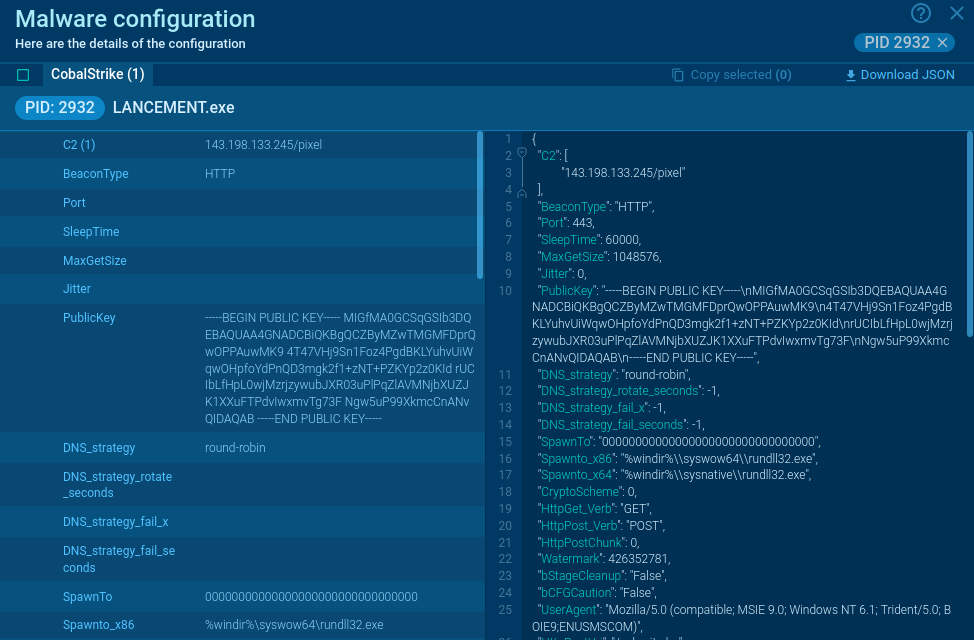
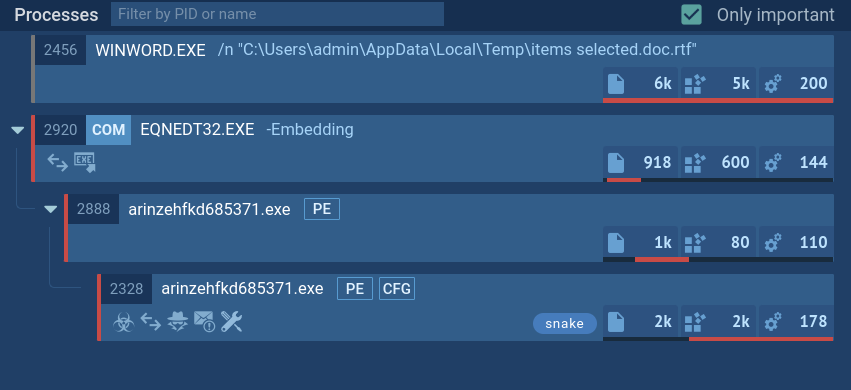
BlueSky ransomware, first identified in June 2022, shares code similarities with other well-known ransomware families like Conti and Babuk. It primarily spreads via phishing emails and malicious links and can propagate through networks using SMB protocols. BlueSky uses advanced evasion techniques, such as hiding its processes from debuggers via the NtSetInformationThread API, making it difficult for analysts to detect and mitigate its attacks.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2022
First seen
:
|
17 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2022
First seen
:
|
17 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 736
736
 0
0

 460
460
 0
0

 2688
2688
 0
0
BlueSky ransomware is a strain of malicious software that encrypts files on a victim's system, rendering them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. First detected in June 2022, it shares similarities with other notorious ransomware families like Conti and Babuk.
BlueSky spreads through methods such as phishing emails, malicious links, and network protocols like SMB (port 445 TCP). Once inside a system, it uses advanced evasion techniques, such as hiding threads from debuggers, to avoid detection. It targets both files and processes, encrypting files with RSA encryption and adding the ".bluesky" extension to them while maintaining operational stability by avoiding critical system processes.
BlueSky ransomware encrypts files on the infected system, spreads through network shares, and uses advanced evasion techniques to avoid detection.
The primary functionalities of BlueSky ransomware include:
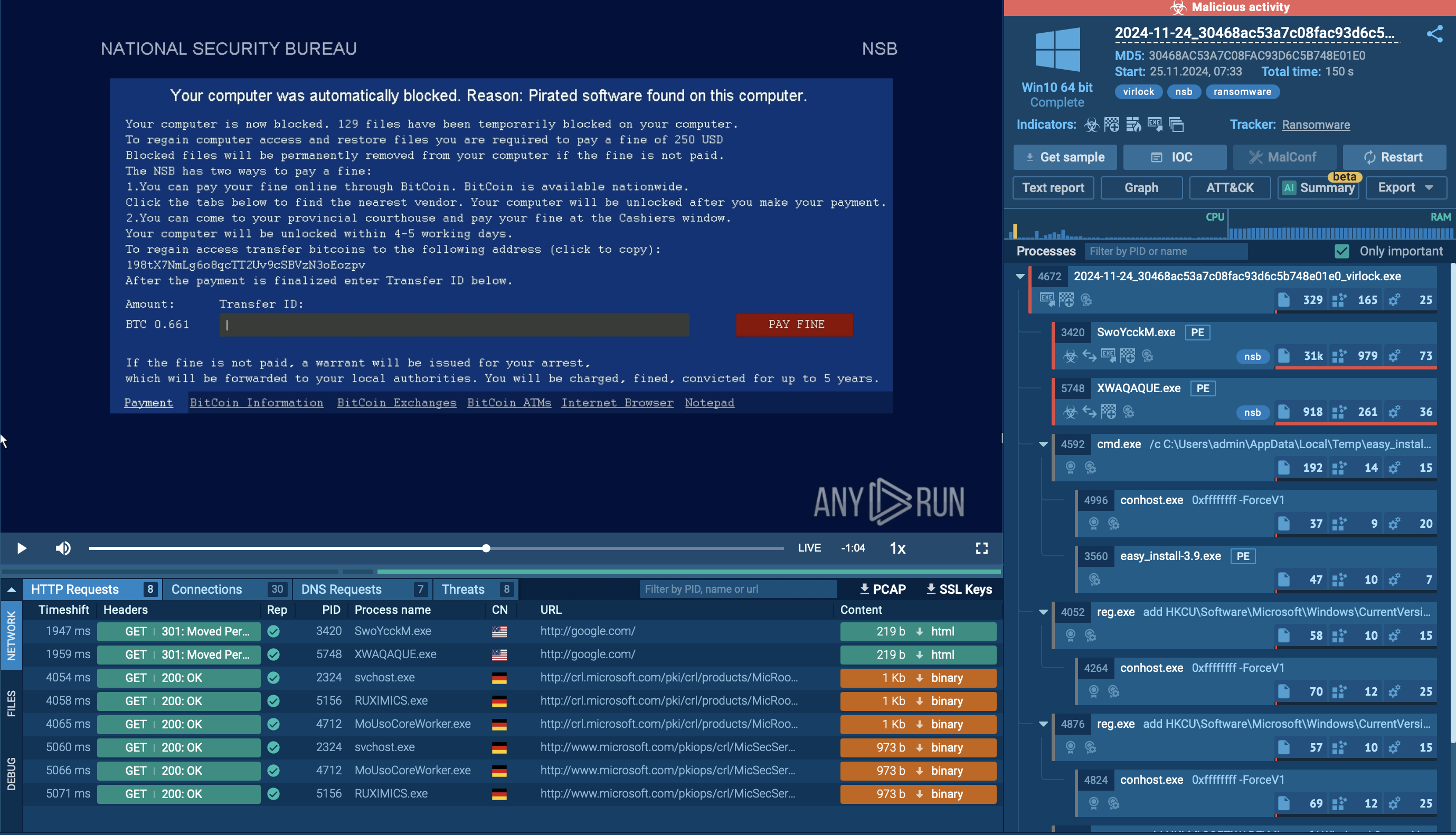
To see how BlueSky operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
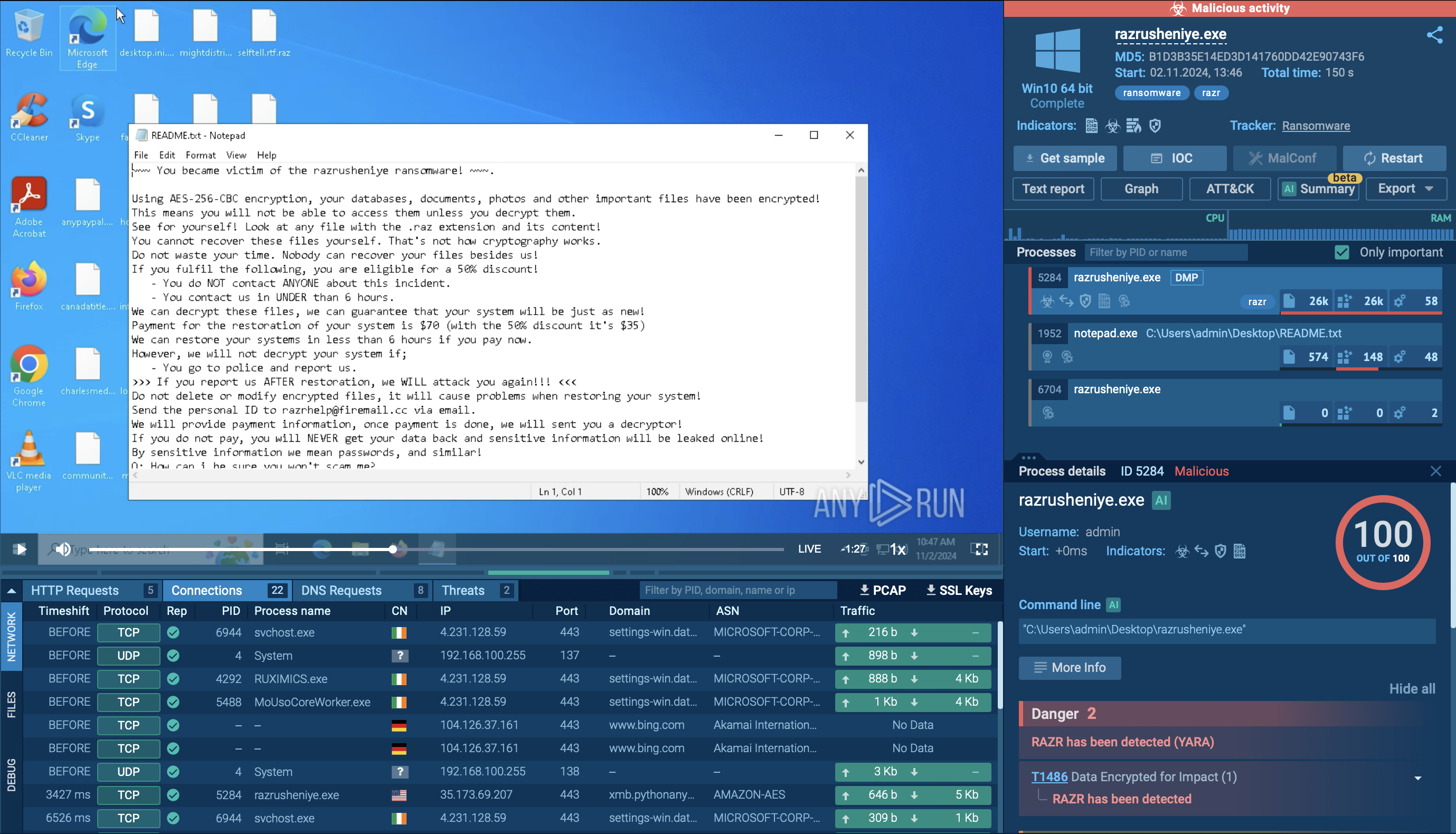
BlueSky ransomware specifically targets files and processes for encryption. However, it strategically avoids critical system processes to prevent system crashes that could halt the encryption process prematurely. This selective targeting allows it to continue encrypting files while the system remains operational.
Encrypted files are marked with the “.bluesky” extension, and a ransom note is left in the directories containing the encrypted files.
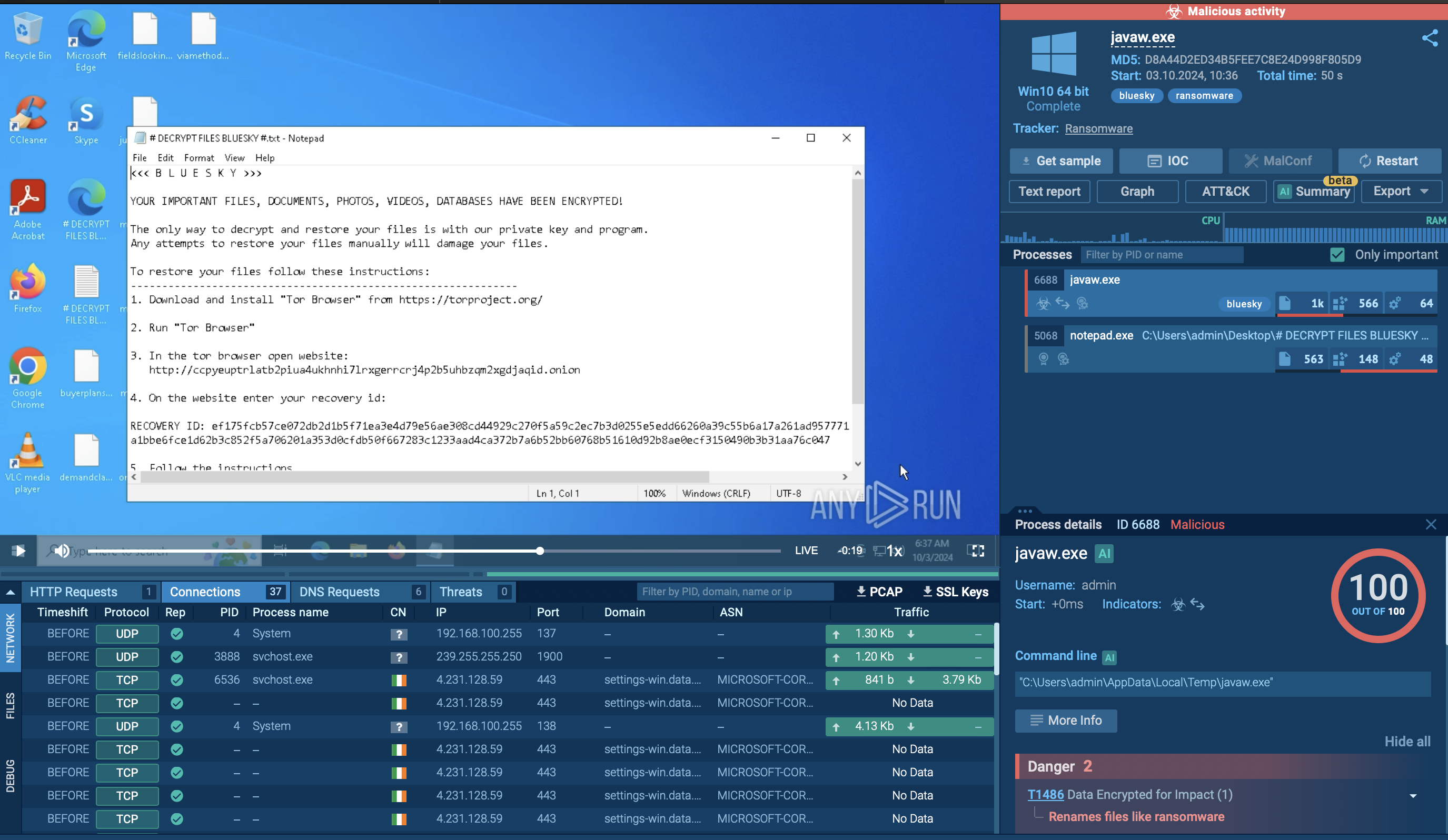 BlueSky ransom note displayed in ANY.RUN’s sandbox
BlueSky ransom note displayed in ANY.RUN’s sandbox
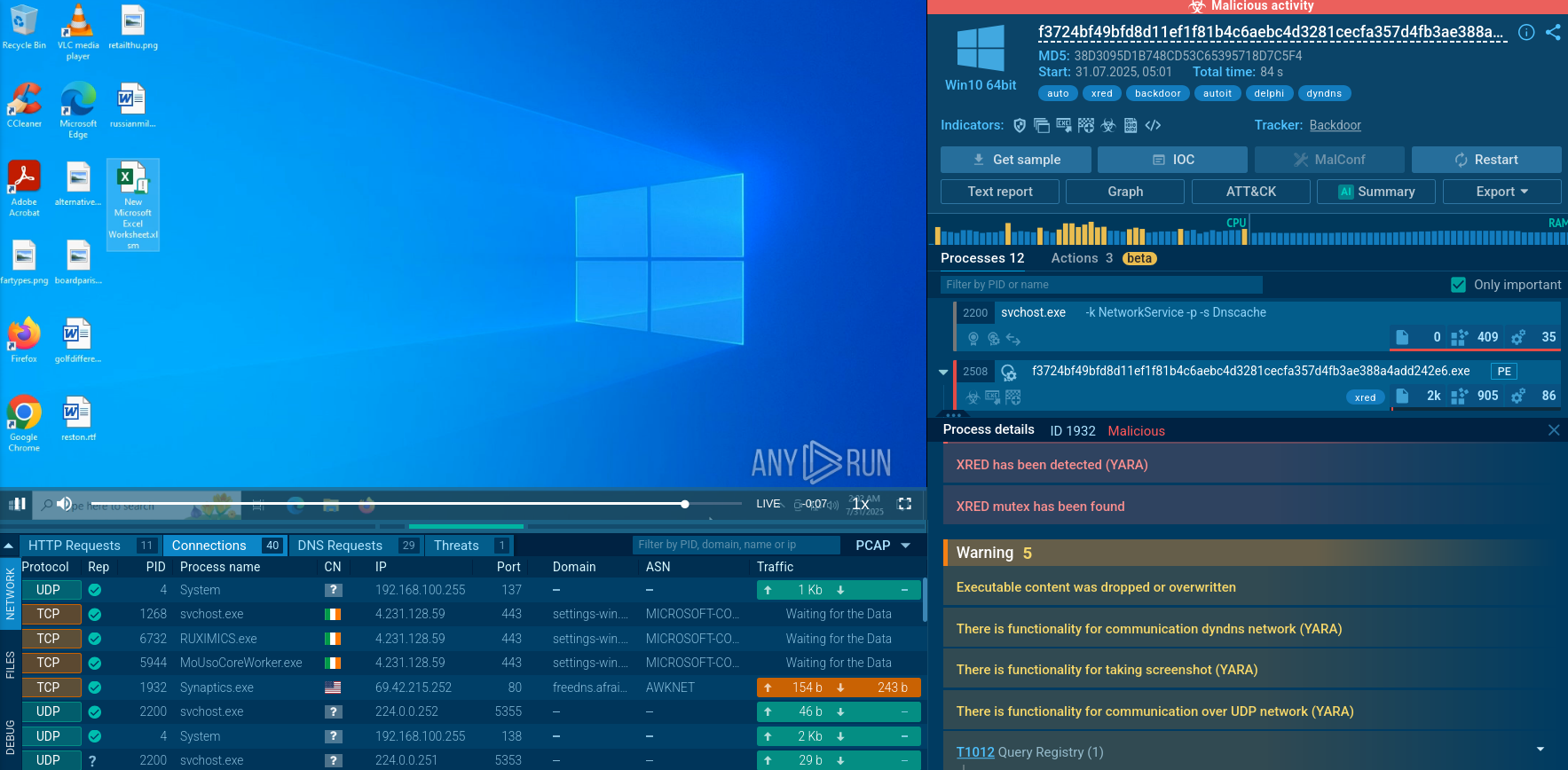
Before the encryption takes place, the ransomware writes critical information to the system’s registry, such as x25519_pub and RECOVERYBLOB. These are used by the attackers to potentially decrypt files if the ransom is paid.
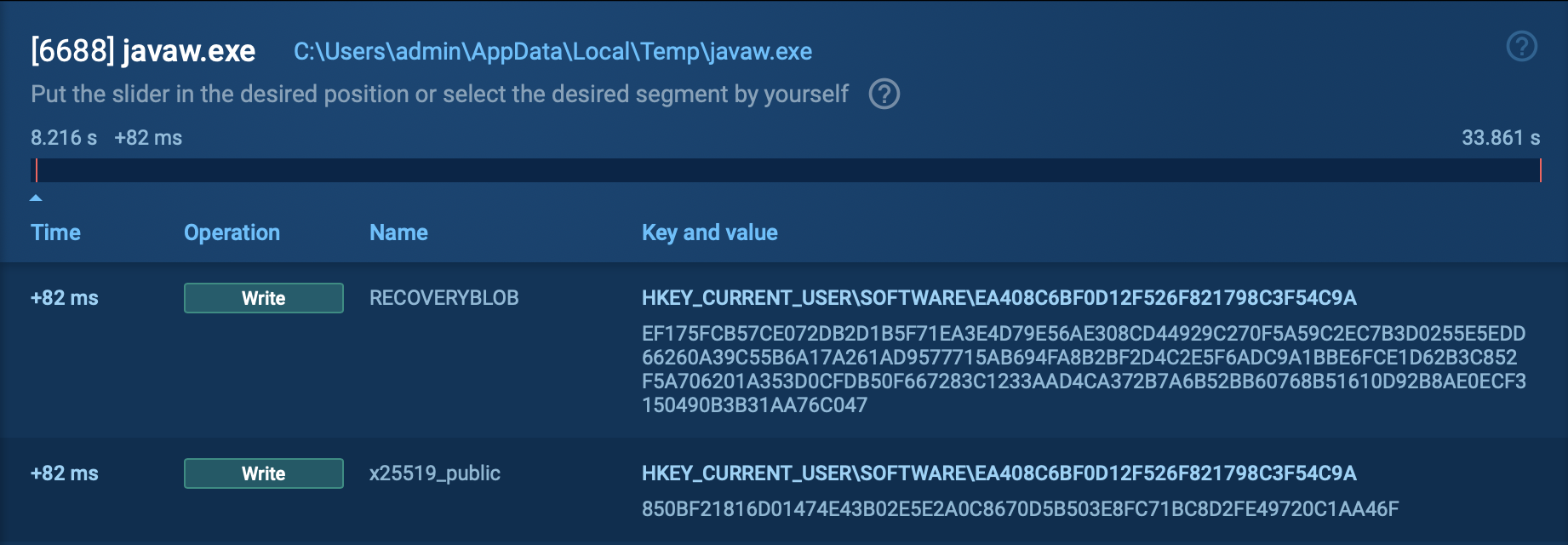 Registry changes displayed by the ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Registry changes displayed by the ANY.RUN’s sandbox
One of BlueSky’s key features is its evasion tactics. It hides execution threads from debuggers using the NtSetInformationThread API, making it difficult for analysts and security tools to track its behavior in real-time. This advanced anti-debugging capability ensures that the malware can run stealthily in a compromised environment, minimizing the chances of detection.
Similar to other malware families like AsyncRAT and Lumma Stealer, BlueSky ransomware is distributed through a variety of methods, making it a versatile and dangerous threat. Here are the primary distribution methods:
To gather up-to-date intelligence on BlueSky ransomware, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service gives you access to a vast database of threat data, built on millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox. It allows you to search using over 40 parameters, such as IPs, file names, domains, and process artifacts.
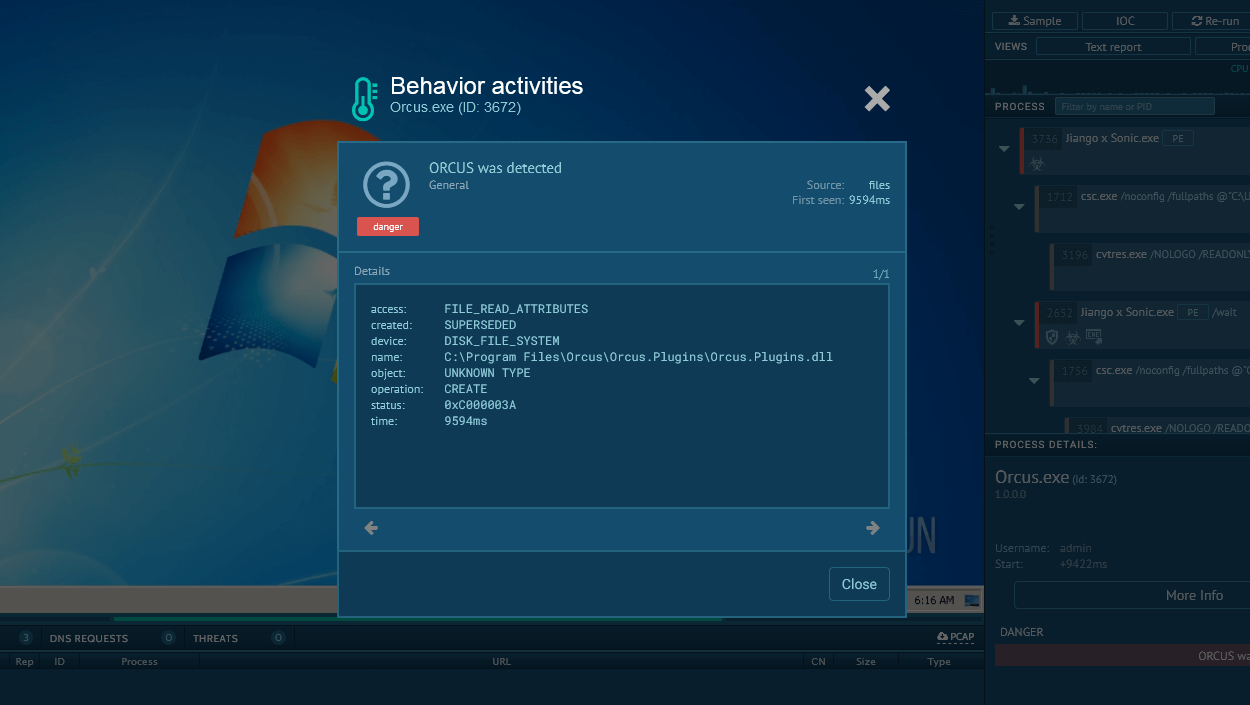
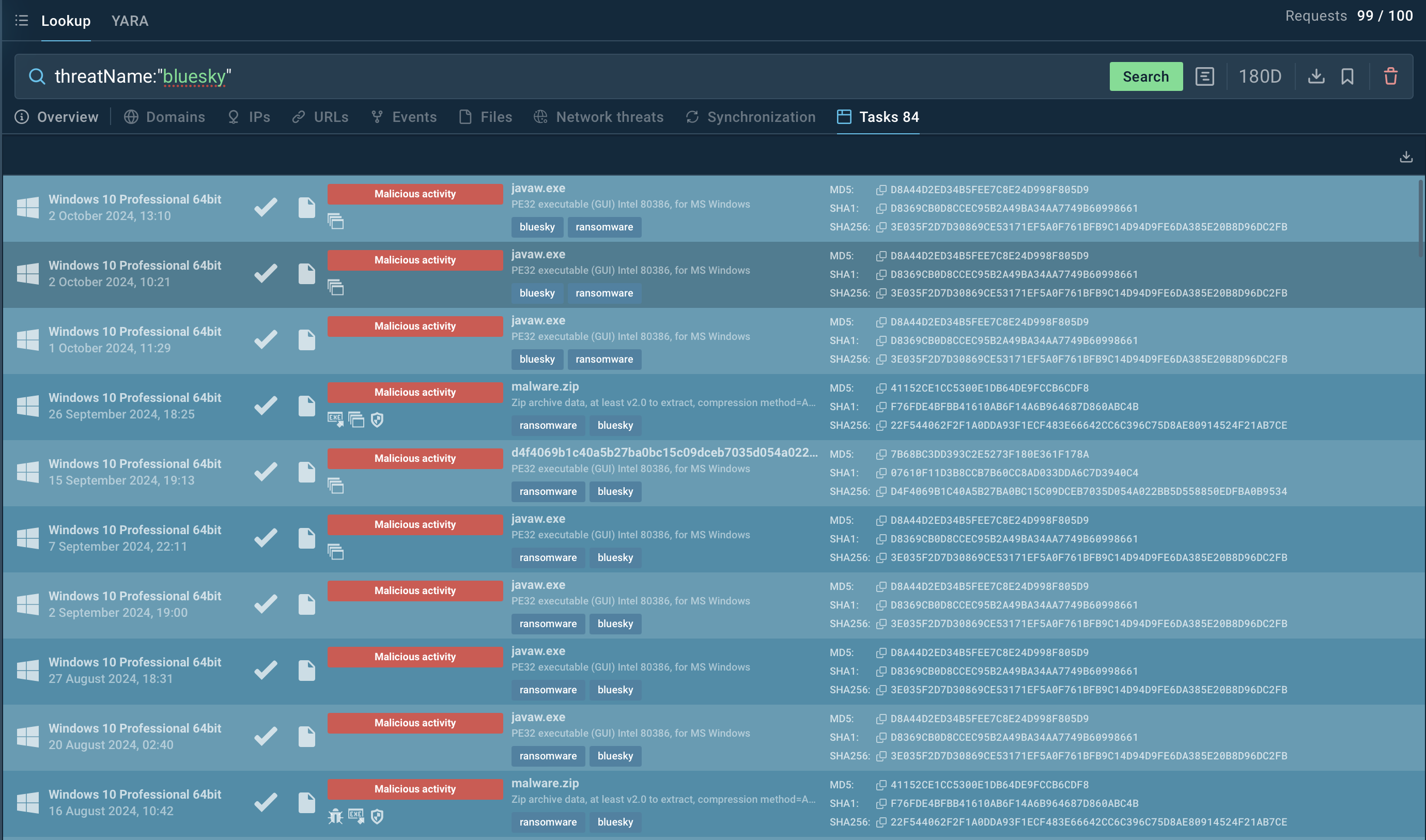 Search query for Bluesky in ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search query for Bluesky in ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup
Searching for BlueSky-related terms, such as threatName:"BlueSky", in TI Lookup brings up results related to this ransomware, including associated samples, network activity, and command-and-control (C2) communication.
Test the capabilities of Threat Intelligence Lookup and the ANY.RUN sandbox.
BlueSky ransomware is a dangerous threat due to its file encryption, network propagation, and advanced evasion techniques. To combat this, it's essential to use tools like ANY.RUN and proactively analyze suspicious files before they cause damage. ANY.RUN provides a real-time malware analysis platform, allowing users to safely investigate and understand malware behavior, while delivering detailed reports for actionable insights.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today to start analyzing threats like BlueSky.