Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


SSLoad is a malicious loader or downloader that is used to infiltrate target systems through phishing emails, perform reconnaissance and transmit it back to its operators delivering malicious payloads. To avoid detection, SSLoad employs various encryption methods and delivery techniques highlighting its versatile nature and complexity. It is believed to be a part of Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) operation given its diverse delivery methods and implemented techniques.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2024
First seen
:
|
16 December, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2024
First seen
:
|
16 December, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 876
876
 0
0

 522
522
 0
0

 2816
2816
 0
0
SSLoad is a malware loader known for its complex attack techniques. Its delivery methods and infiltration techniques vary with each deployment, making it challenging for malware hunters to detect.
This loader has been active since January 2024. Recent reports indicate that SSLoad has been used to deploy Cobalt Strike, a popular adversary simulation software often utilized for post-exploitation activities. In one of campaigns, the attackers employed the DLL side-loading technique, involving a decoy Word document that delivers the SSLoad DLL.
Another reported attack utilized an MSI installer distributed via a phishing email that redirected victims to a fake Azure page. From there, a JavaScript script was downloaded, which in turn downloaded the MSI installer, eventually loading the SSLoad payload.
SSLoad’s primary function is to download and execute additional malicious payloads on the compromised system.
Some of the key capabilities of SSLoad malware include:
Early versions of SSLoad malware initially connected to a Telegram channel named "SSLoad" using the first-stage DLL to retrieve an additional URL.
Upon establishing this connection, the malware would download a compressed PE file, utilizing specific User-Agent and Content-Type headers over HTTP. The downloaded file was then decompressed and executed directly in memory, bypassing traditional disk-based detection methods.
Since its inception, SSLoad has undergone several updates, evolving its command-and-control (C2) communication strategies and altering the supporting executables used to load the malware.
Recent versions of SSLoad avoid the first-stage DLL and load the malware directly into the victim’s machine, making detection even more challenging.
Infectious files used by the attackers come in different formats, including compressed archives (e.g., ZIP, RAR), executables (.exe, .bat), documents (e.g., PDF, Microsoft Office files), and scripts such as JavaScript.
Once a user opens, runs, or interacts with one of these malicious files, the infection chain is triggered, leading to the deployment of SSLoad and other associated malware.
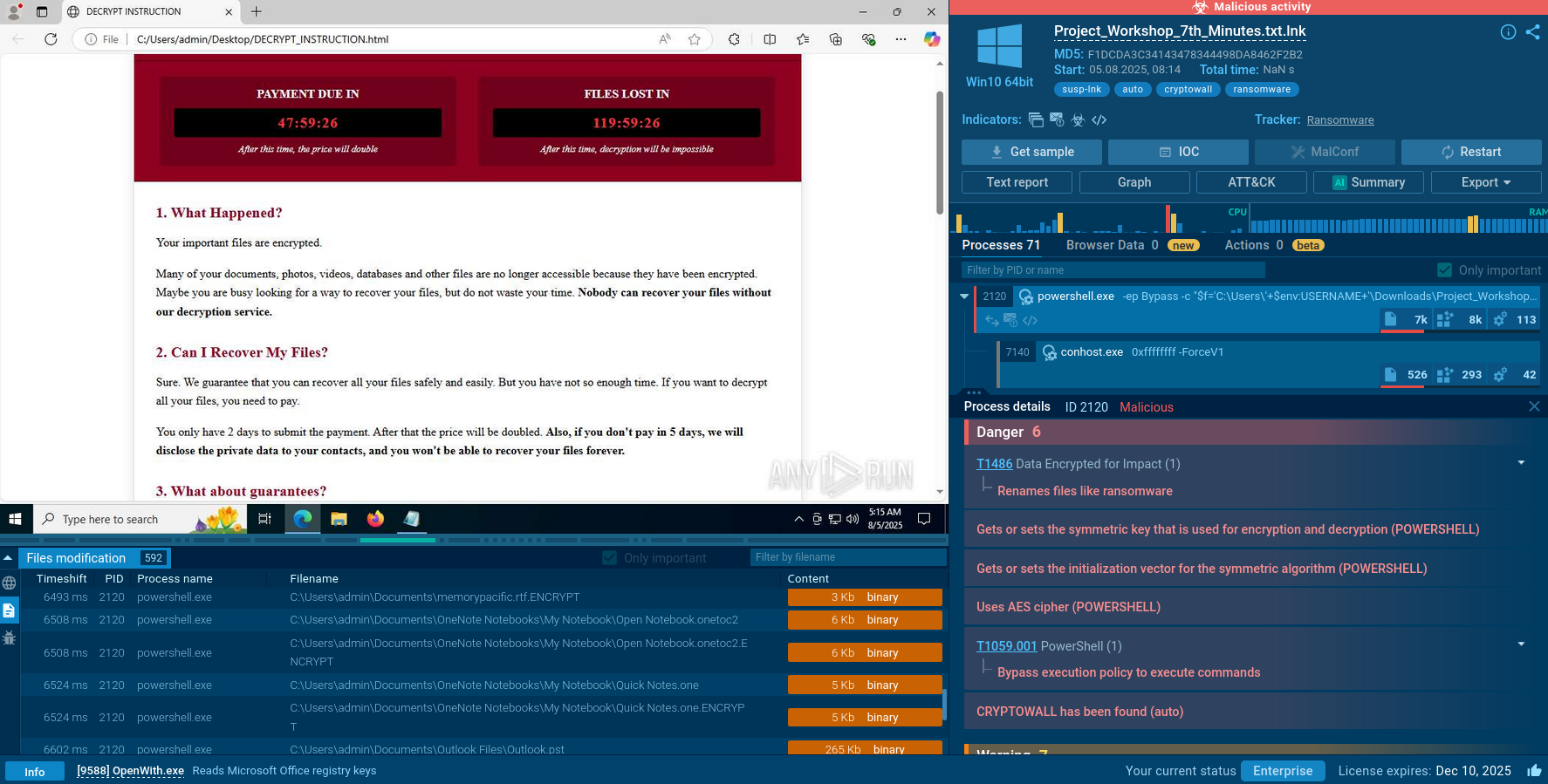
The execution chain of SSLoad malware involves a series of steps designed to infiltrate systems, gather intelligence, and deploy additional payloads. SSLoad is often delivered through phishing emails containing malicious attachments.
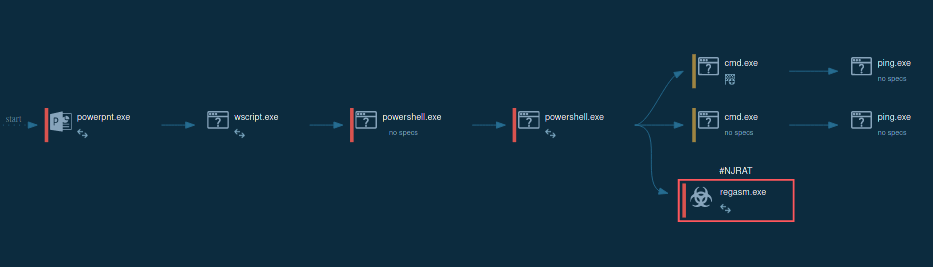
One of the common methods includes a decoy Word document. Let’s run a sample in the ANY.RUN sandbox to observe this method.
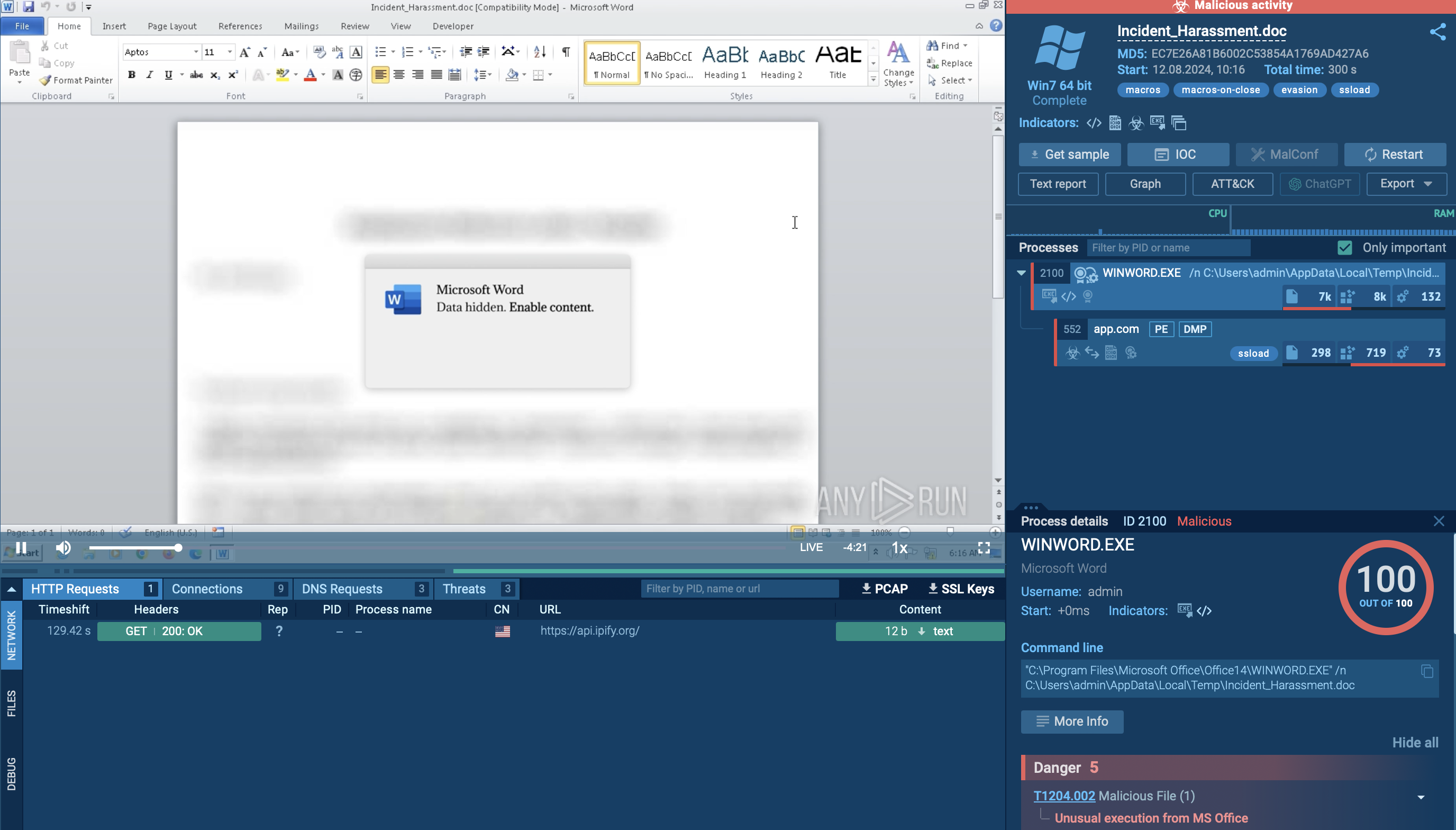 Malicious Word document analyzed in ANY.RUN sandbox
Malicious Word document analyzed in ANY.RUN sandbox
When opened, you can notice how the Word document executes a DLL file associated with SSLoad.
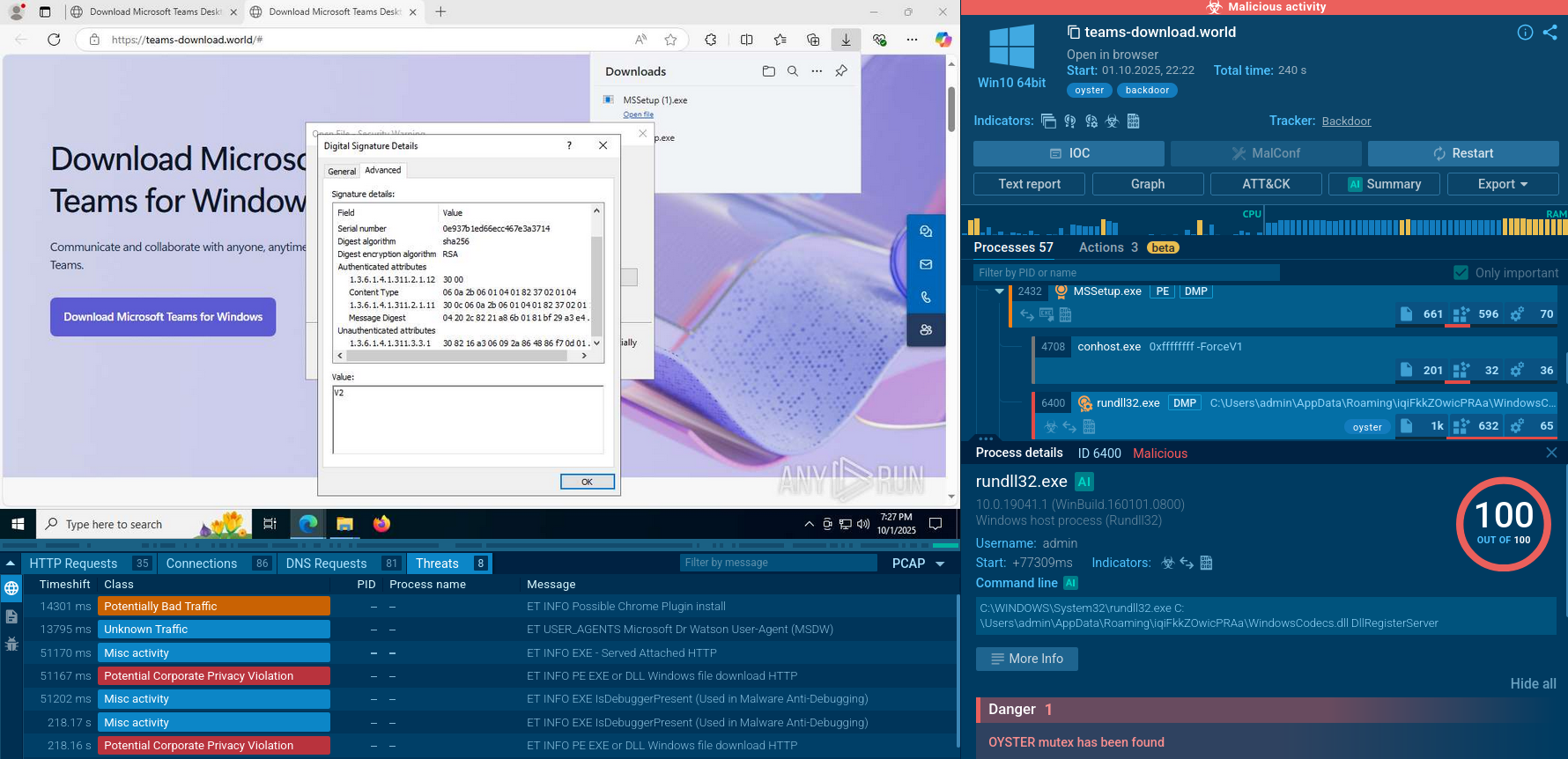
Another approach involves a phishing email that directs users to a fake Azure page, leading to the download of a JavaScript file, which then downloads an MSI installer containing the SSLoad payload.
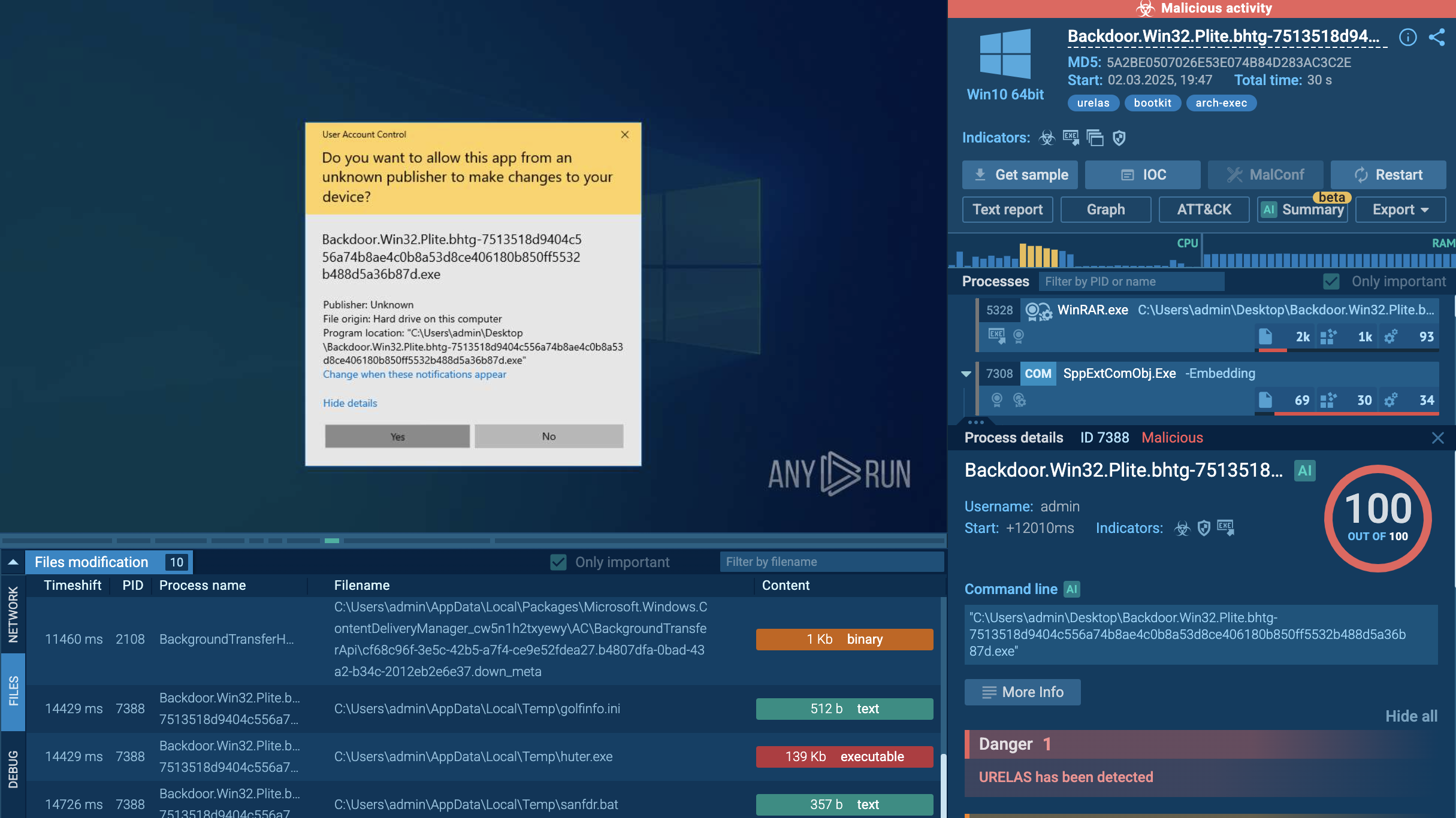
Let’s run another sample of the SSLoad malware in the ANY.RUN sandbox to observe this execution method: MSI installer containing SSLoad malware:
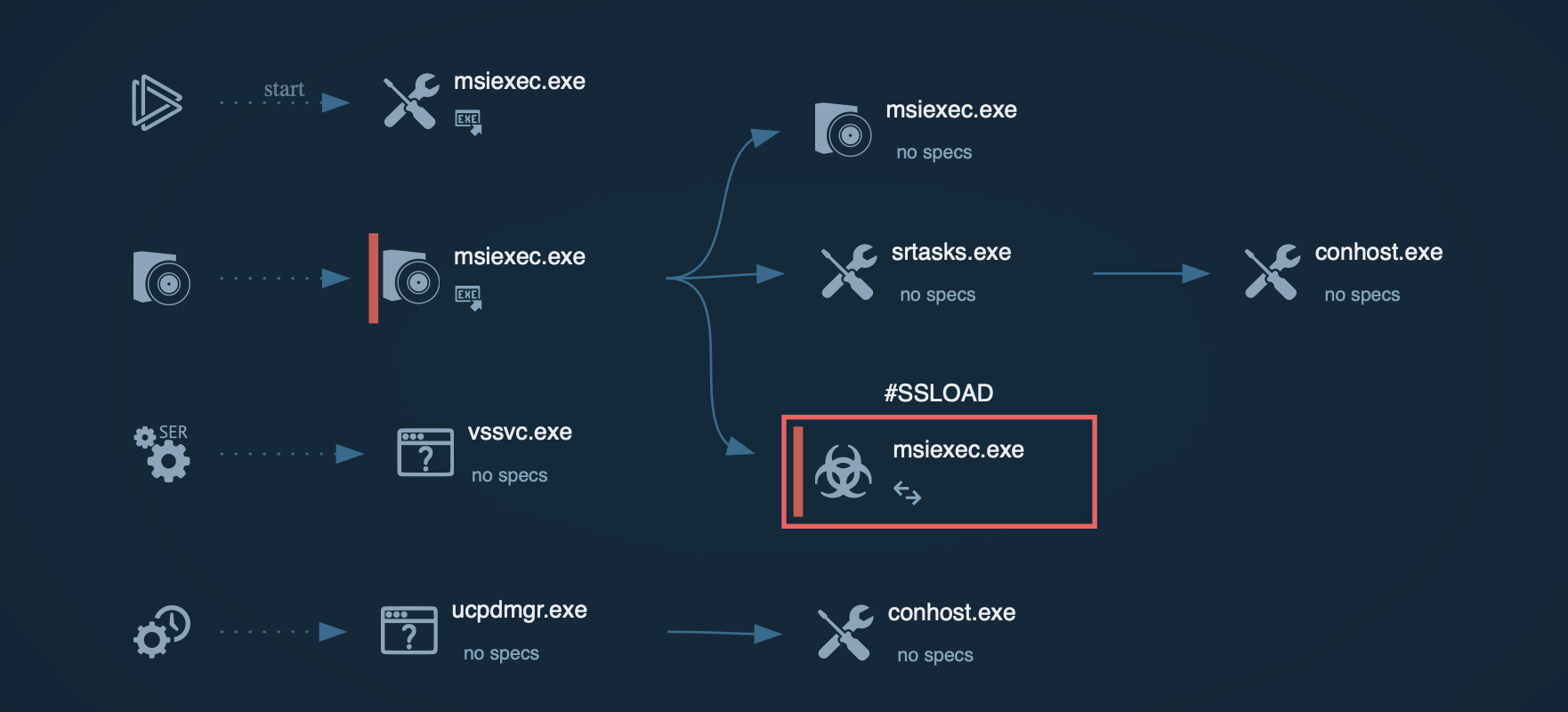 SSLoad process graph with MSI installer in ANY.RUN
SSLoad process graph with MSI installer in ANY.RUN
The MSI installer plays a crucial role in the execution chain. Upon execution, it initiates a series of actions that deploy the SSLoad payload. This installer is designed to execute specific custom actions that facilitate the malware's installation and operation on the victim's machine. Once the MSI installer is run, it extracts and executes the SSLoad payload, typically a Rust-based executable.
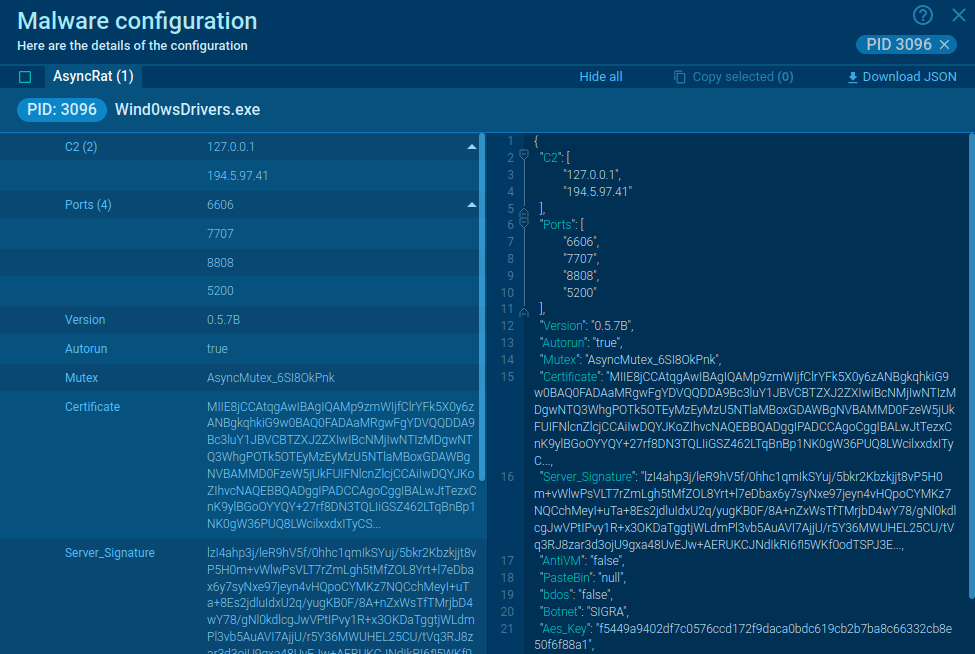
The payload first checks for existing instances of itself on the machine by creating a mutex. If the mutex is found, the malware ceases execution to avoid running multiple instances. After confirming it is the only instance running, SSLoad conducts reconnaissance to gather information about the infected system, transmitting this data back to its operators. SSLoad can deliver further payloads, such as Cobalt Strike, which is used for lateral movement and further exploitation within the network.
SSLoad employs various techniques to evade detection and analysis. For instance, it checks the Process Environment Block (PEB) for the BeingDebugged flag, which indicates if the process is being monitored. If it detects debugging, it can alter its behavior to avoid analysis.
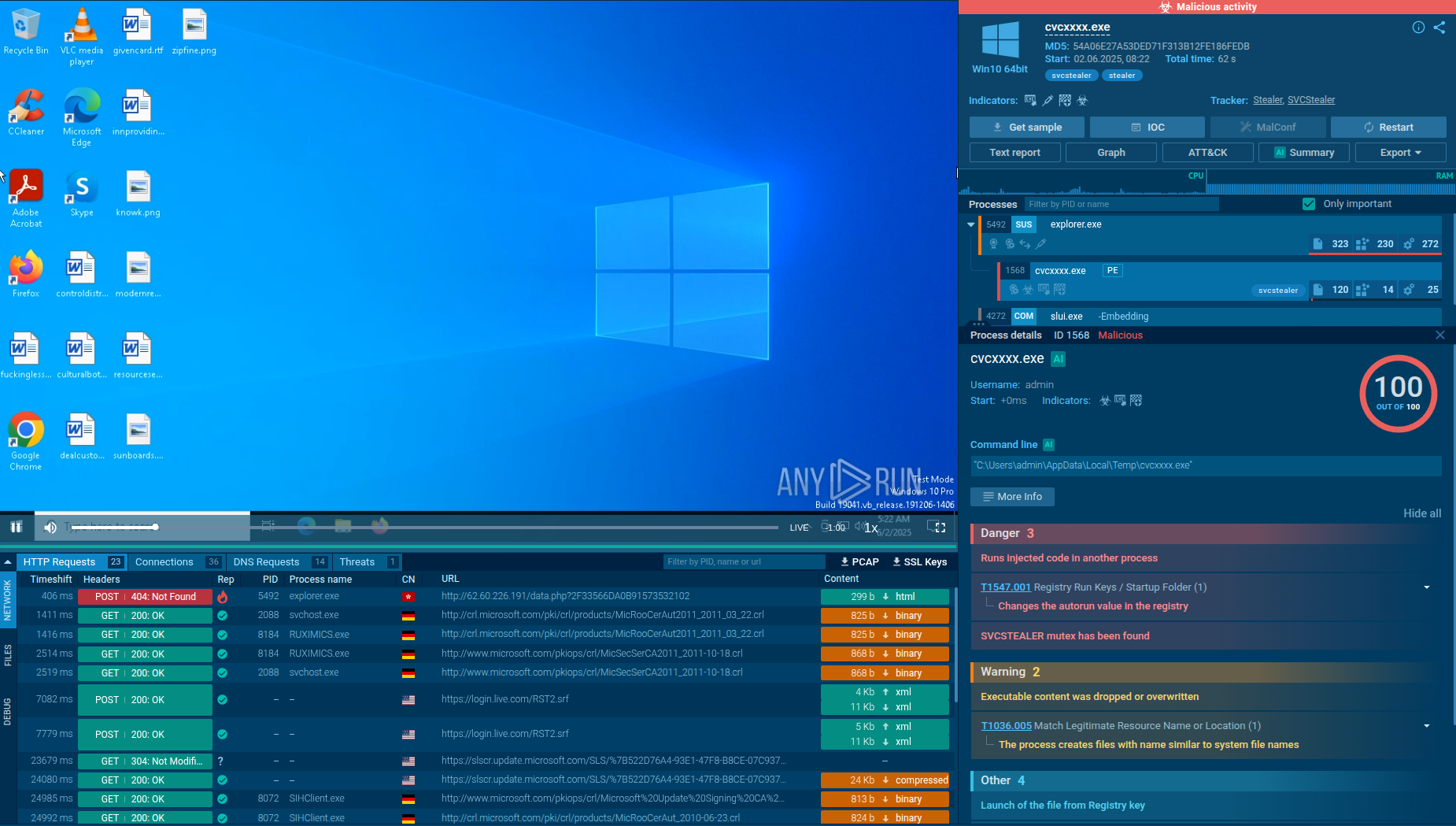
The SSLoad malware may also use the Task Scheduler for time-based evasion, such as delaying execution until a specific time or event. You can run the sample and analyze its behavior here: DLL file execution:
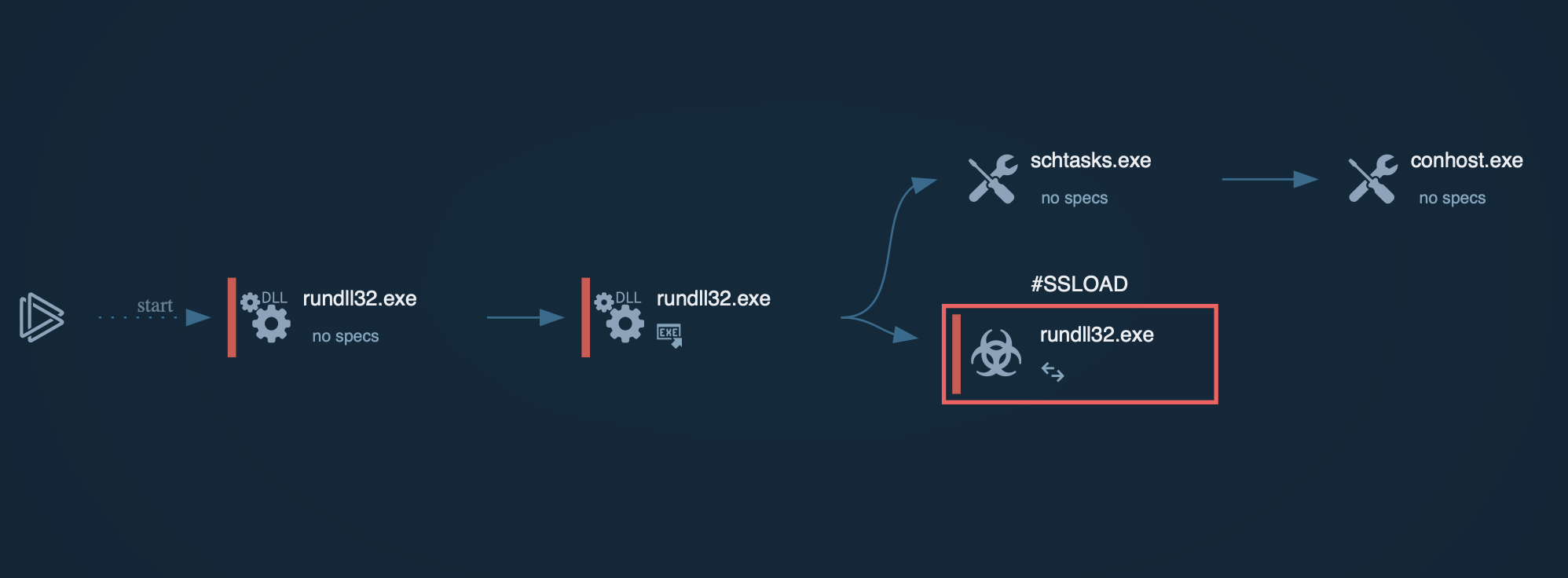 SSLoad process graph with DLL file in ANY.RUN
SSLoad process graph with DLL file in ANY.RUN
Similar to other loaders, like PrivateLoader and GuLoader, cybercriminals may use a variety of methods to spread SSLoad. Phishing and social engineering are the primary tactics, where malware is often disguised as or bundled with seemingly legitimate content to trick users into downloading and executing it.
Key methods include:
SSLoad is a stealthy and malicious loader that poses a significant detection challenge due to its varied distribution methods and sophisticated infiltration techniques.
ANY.RUN is a powerful cloud-based service that enables safe analysis of malicious files, including those infected with SSLoad. It provides a secure environment to observe malware behavior and collect indicators of compromise (IOCs). By using ANY.RUN, you can gain valuable insights into SSLoad’s deployment tactics and strengthen your defenses against it.