Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


PrivateLoader is a malware family that is specifically created to infect computer systems and drop additional malicious programs. It operates using a pay-per-install business model, which means that the individuals behind it are paid for each instance of successful deployment of different types of harmful programs, including trojans, stealers, and other ransomware.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2021
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2021
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
PrivateLoader is a loader, which serves to embed other malware families on compromised systems. The creators of this malicious software, who are likely to be from ex-USSR countries, monetize their activity by charging various threat actors for the installation of their particular type of payload. The services are advertised openly on forums and Telegram channels, making them widely accessible.
The earliest instances of the malware’s activity can be traced to the beginning of 2021. However, researchers were able to spot it for the first time only in 2022, when it gained notoriety as the most widely used loader of the year.
A common vector of infection in the case of PrivateLoader has been through websites offering cracked versions of popular software. Once victims downloaded a file from such sites and ran an alleged software executable, they launched a chain reaction, which led to the installation of PrivateLoader and eventually to a trojan, stealer, or another type of malware being deployed on their system.
Some of the known malware families that have been pushed by PrivateLoader include Redline, DCRAT, Raccoon, and Smokeloader.
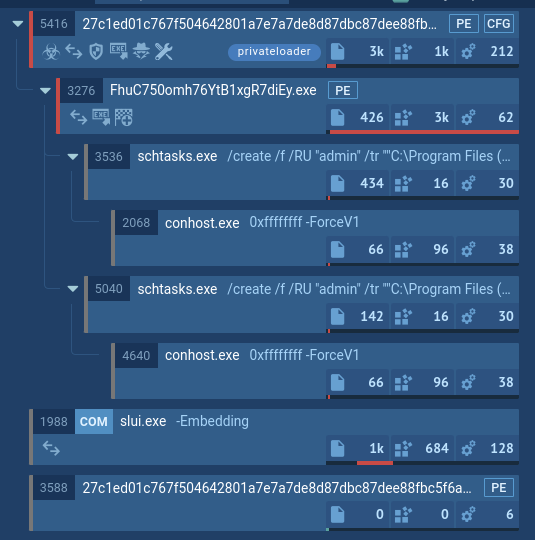
PrivateLoader is written in C++ and has a control panel, allowing operators to manage its activity, including by adding new payload links and tracking the total number of installations.
PrivateLoader is set up to drop payloads depending on the configuration of each victim’s system. For instance, it can distribute malware based on the geo location. It can also scan the machine to determine if there are any crypto wallets installed and see banking credentials. Yet, in most cases, it does not exfiltrate this information.
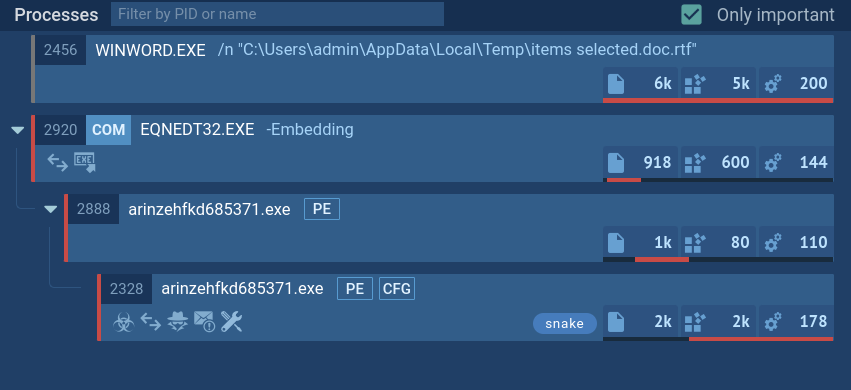
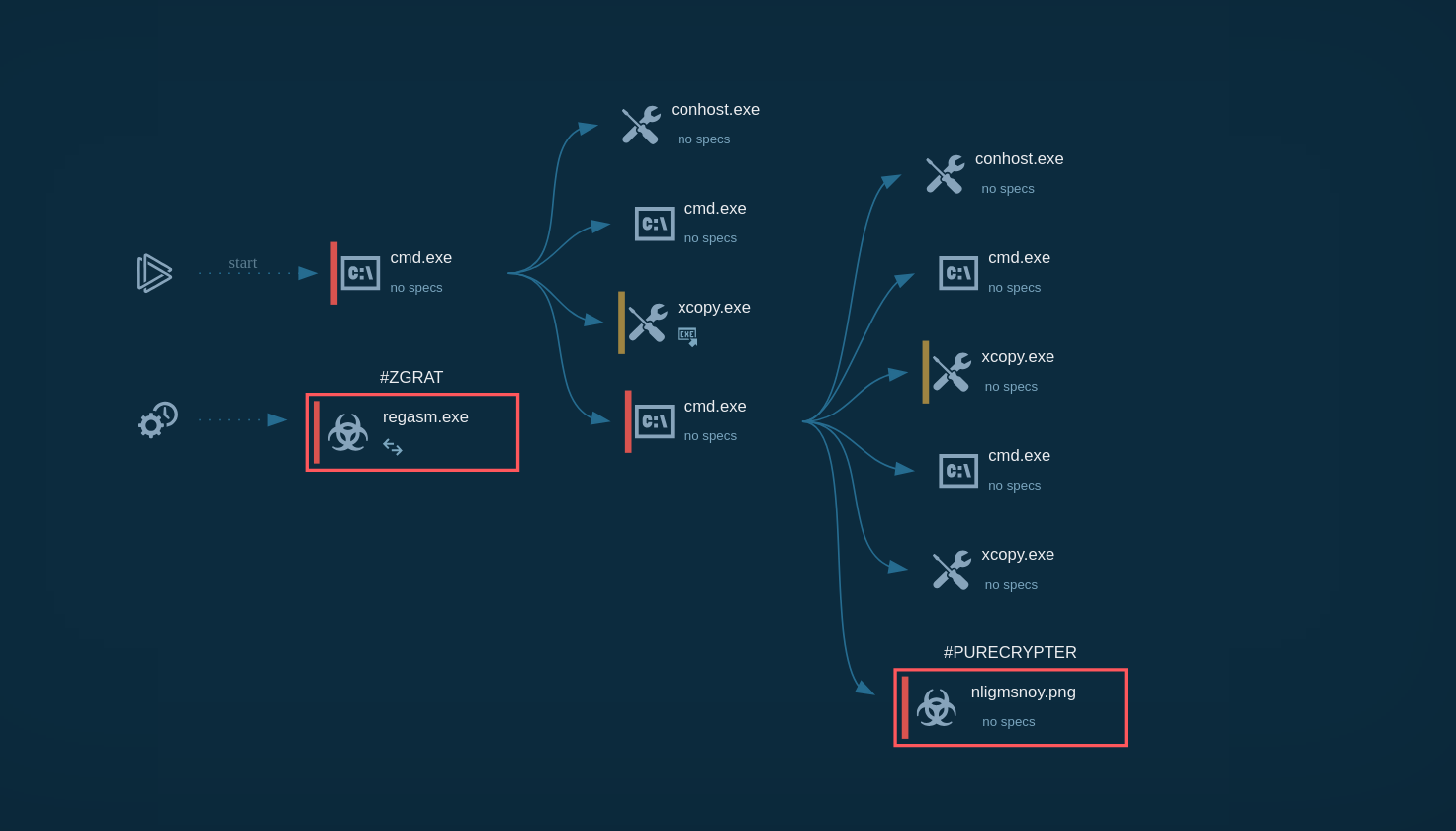
PrivateLoader is a modular threat, consisting of three distinct parts, each with its own purpose. It starts with the Loader module, which is intended for downloading the main Core module. The latter then contacts the command-and-control server (C2) and drops the next-stage threat, as well as the Service module that is regularly updated and responsible for keeping the loader on the victim’s system. In certain instances, PrivateLoader can drop several payloads.
The malware also makes use of the Dead Drop Resolver technique, where it utilizes legitimate services, such as Discord, to host malicious payloads.
PrivateLoader employs various techniques to prevent analysis, including encrypting its important strings and obfuscating the C2 communication.
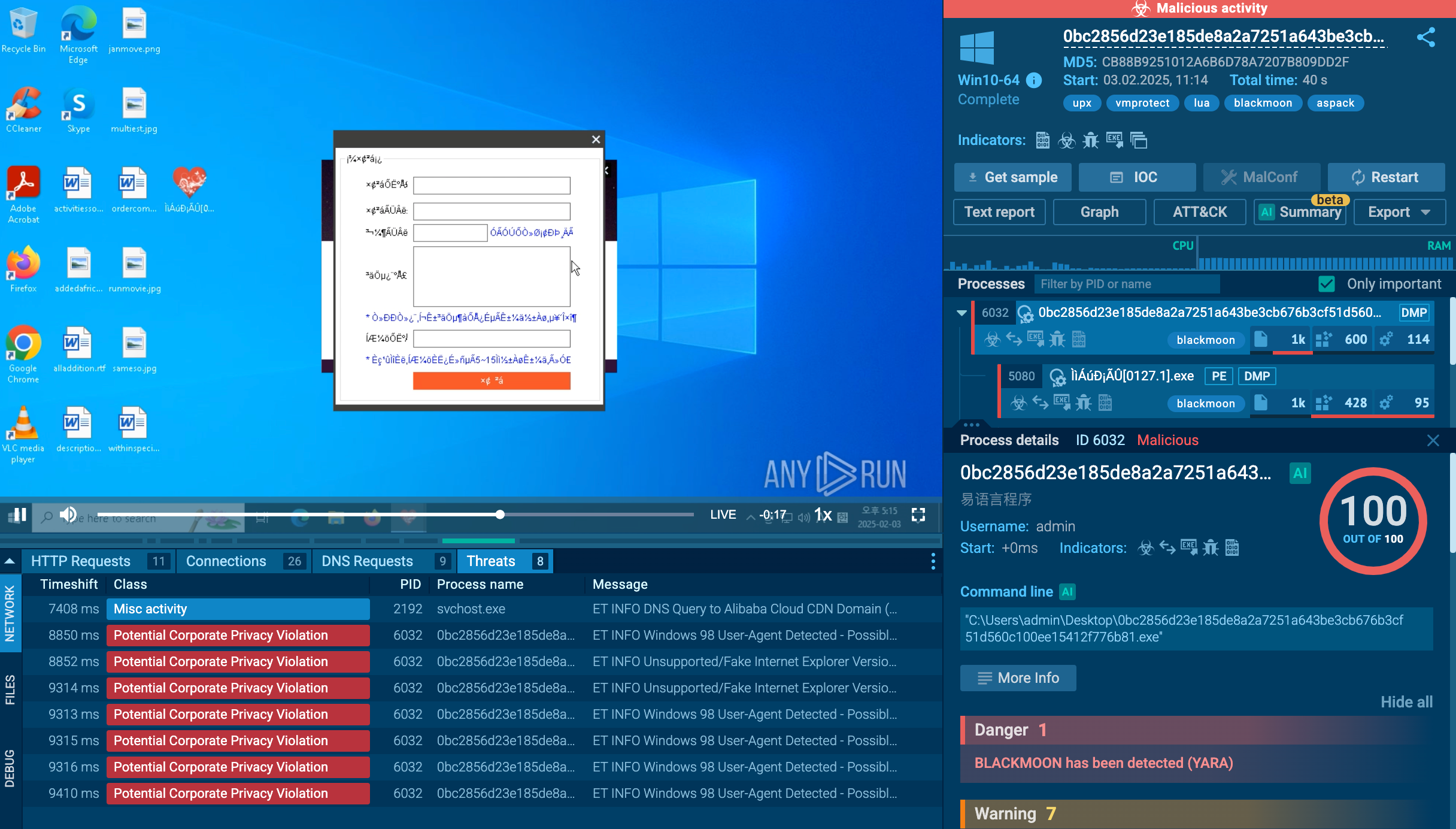
Let’s see how PrivateLoader operates in detail by uploading its sample to ANY.RUN, an interactive sandbox for malware analysis.
The main PrivateLoader process creates a child process whose executable file is located in the user’s “Pictures” directory. The created child process is added to the startup using Task Scheduler. The executable file of the child process was downloaded from the Internet.
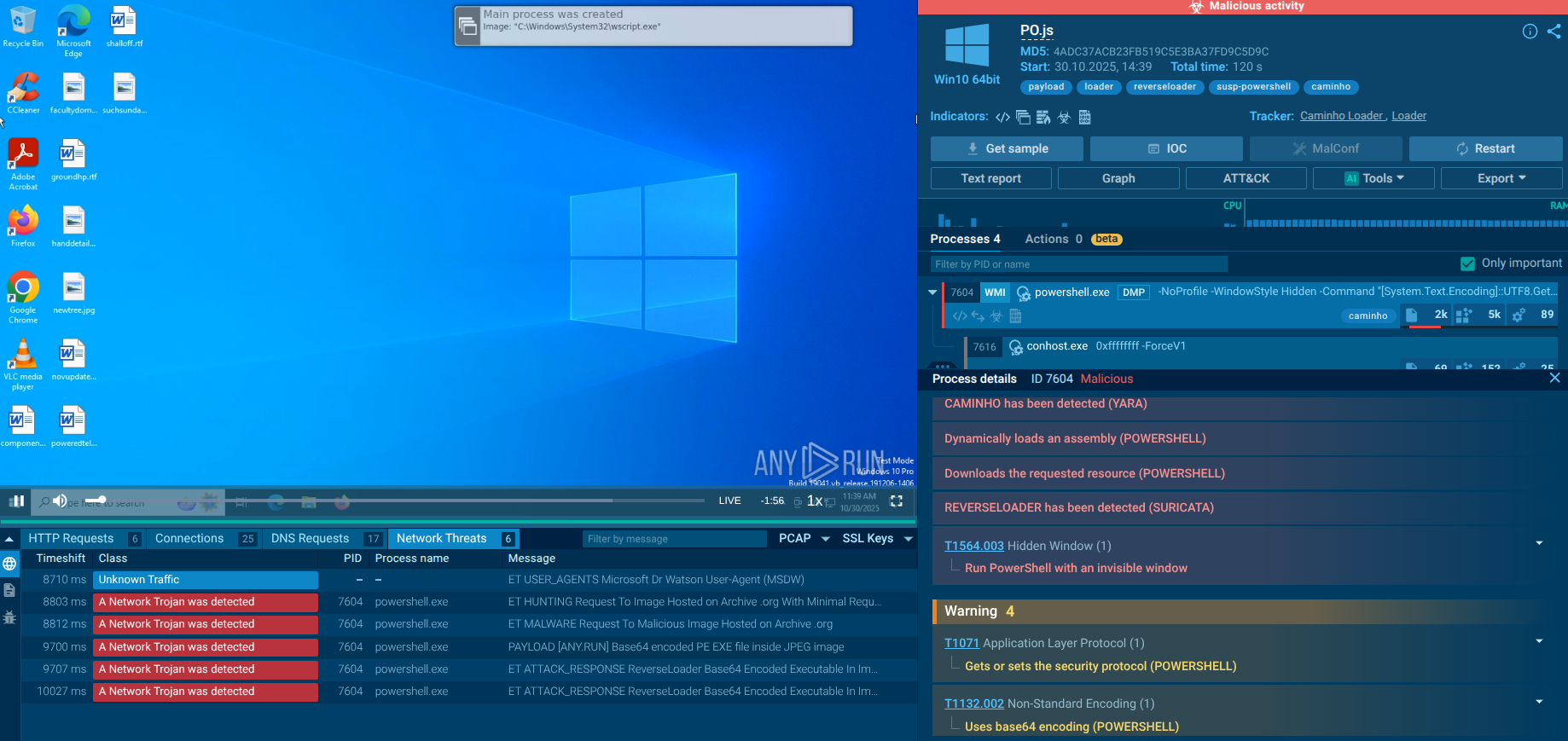
Analyzing the HTTP requests, we can observe connections and data exchanges with the C2 server. The content sent (as well as received) in POST requests consists of BASE64-encoded strings. Moving forward to the indicators, we can see that the malware steals user credentials from browsers.
Read a detailed analysis of PrivateLoader in our blog.
 PrivateLoader’s process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
PrivateLoader’s process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
As mentioned above, the primary way PrivateLoader can infect a computer is via a direct download. Attackers employ SEO poisoning to boost the ranking of their websites. Users visit these links in search of different types of legitimate programs. Yet, after downloading an archive from the website and opening its contents, an infection begins, allowing PrivateLoader to compromise the entire system.
PrivateLoader is a serious threat to organizations and individuals because of the scale of its operation, as it can infect hundreds of thousands of computers in a short period of time. In order to avoid falling victim to this and other malware, it is vital to steer clear of suspicious websites and never download software from unofficial sources.
To determine whether a certain file or link is malicious, use ANY.RUN. It is a malware sandbox that provides users with the ability to interact with the samples at hand in a safe cloud environment. For instance, PrivateLoader usually comes packed into a passworded archive. ANY.RUN lets you easily open it, extract the contents, and run them as if you were using your own computer to expose any harmful behavior and collect IOCs.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!