Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


The main function of Smoke Loader is dropping other, more destructive malware on infected machines. However, unlike many competing loaders, this one can be extended via plugins to feature destructive, malicious info-stealing functions.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
ex-USSR territory
Origin
:
|
|
30 August, 2011
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR territory
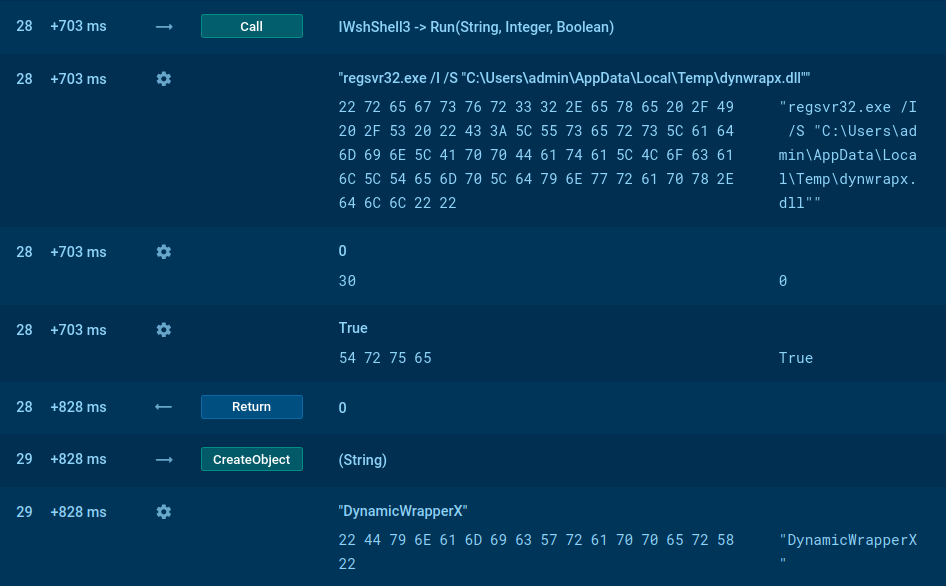
Origin
:
|
|
30 August, 2011
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Smoke Loader, sometimes also called Dofoil, is a modular malware mainly utilized to download other viruses to infected machines. Despite its loader nature, the Smoke Loader bot can be equipped with a variety of malicious functions. Most of these functions are targeted at stealing sensitive data from the victims.
Smoke Loader was first observed in the wild in 2011. It was seen being sold on underground portals grabberz[.]com and xaker[.]name by a member named SmokeLdr. The malware functionality varies from one attack to the other and depends on the choice of modules done by the attackers.
Despite its old age, Smoke Loader continues to be an active threat even to this day. In particular, this malware was featured in RigEK and MalSpam campaigns. It should be noted that after March 2014, Smoke Loader is sold only to Russian-speaking attackers.
The main functions of Smoke Loader include loading up to ten executable files and run them, geo-target the victims to direct attacks at specific countries, load files via URLs, mimic legitimate processes, and provide detailed summaries on installs and launches.
The two optional modules allow Smoke Loader to expand its feature set with information-stealing functions. This allows Dofoil to grab passwords from widely used mail clients, FTP clients, and programs like TeamViewer. The malware can send the data to the C2 for the attacker.
The Smoke Loader virus has been evolving over the years. According to the research of a cybersecurity professional, a late 2018 sample included an array of anti-debugging techniques far more complex than anything present in the early iterations of the malware. For instance, the 2018 Smoke Loader version learned to check if it is being launched in the virtual environment. It also learned to discover and immediately kill any analyzing tools running on the machine. Together, these features make the analysis of the Dofoil malware highly complicated. Dofoil also relies a lot on the process hollowing technique, targeting mostly Explorer.exe.
What’s more, while a lot of malware in the wild need to iterate through a list of processes to find their injection target, thus allowing researchers to discover them, Smoke Loader manages to avoid this behavior and stay hidden by calling the Windows API GetShellWindow to access the shell’s desktop window, and evoke GetWindowThreadProcessId to obtain the process ID of Explorer.exe.
To further confuse security researchers, all Smoke Loader functions contain pointless instructions. At the same time, the library names are encrypted with a hardcoded key. Instructions are not coded in a standard way. Instead, they are mixed with jump instructions. Most of this code reroutes the program flow to create confusion when Dofoil is debugged.
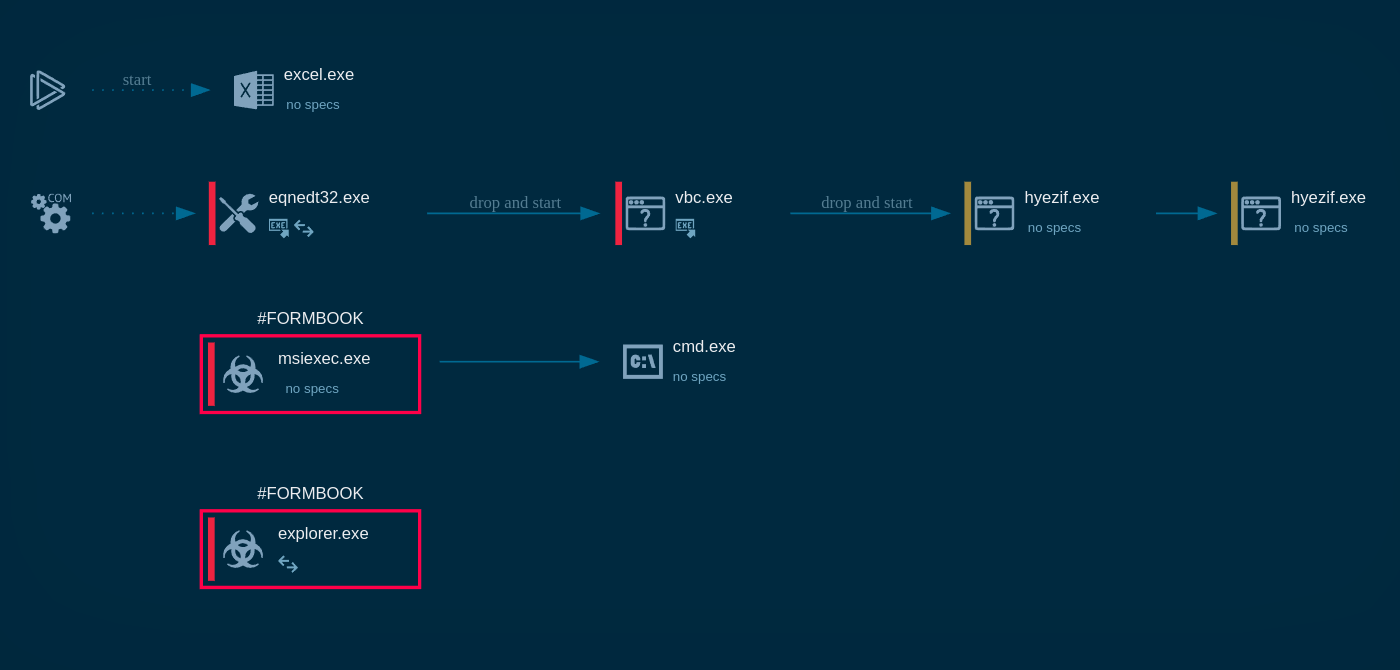
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service displays the execution process of Smoke Loader. It allows examining the malware in a convenient and safe environment.
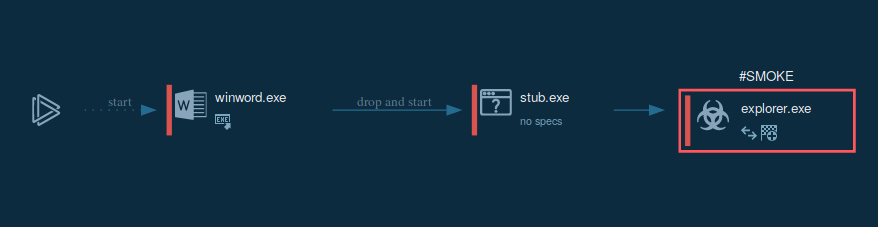
Figure 1: Displays the graph of processes generated by the ANY.RUN malware analyzing service
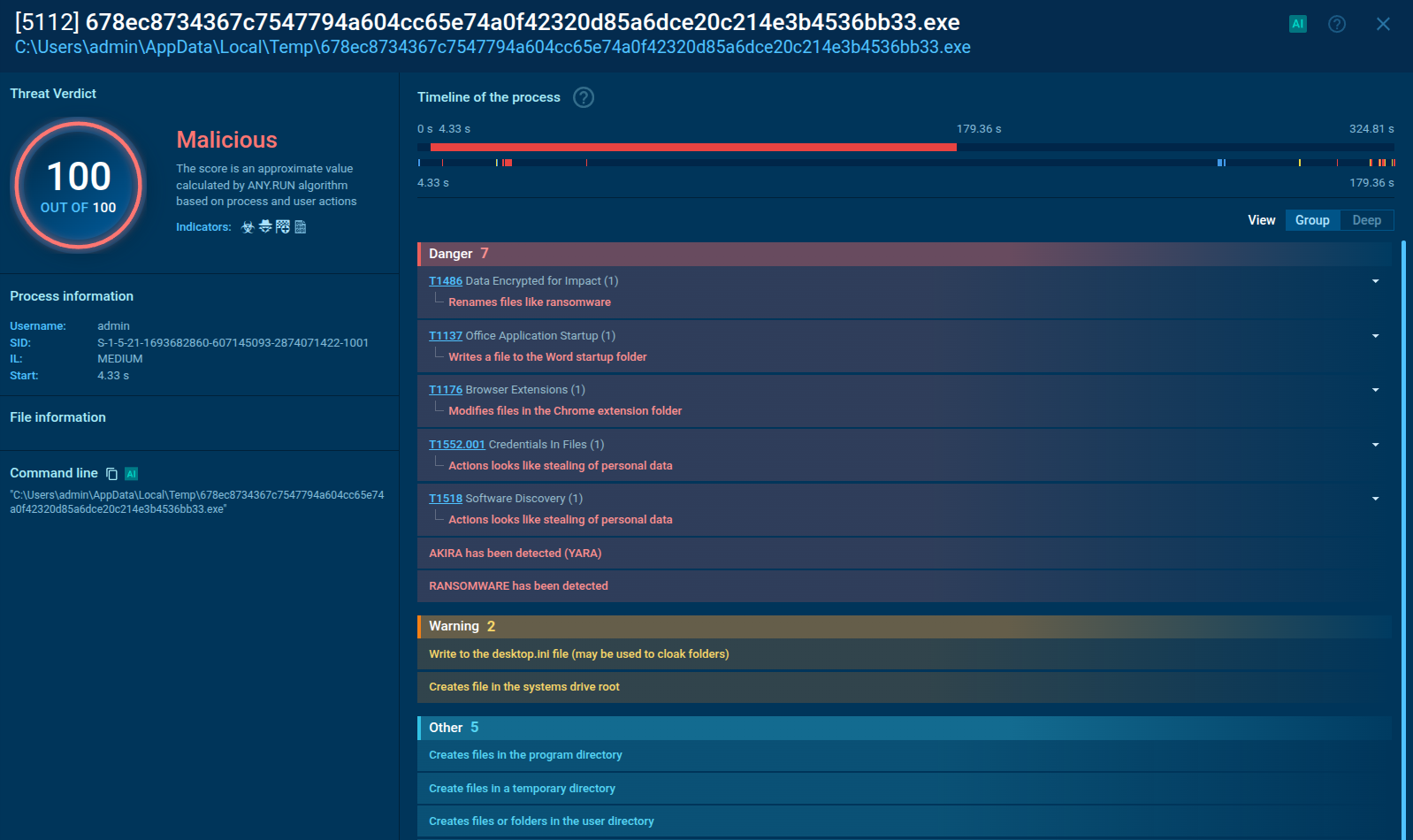
Figure 2: Even more information about the execution of malware can be found in customizable text reports generated by ANY.RUN
So, how does Smoke Loader work? Because the most common vector of attack to infect users' devices are malicious spam campaigns, Smoke Loader trojan mostly gets into devices with Microsoft Office files. Once the user downloads and opens the malicious file, the malware drops to a machine from it.
After that, SmokeLoader injects malicious code into system processes like explorer.exe. An injected process then starts the main malicious activity.
The smoke Loader virus makes its way to machines as a malicious Microsoft Word attachment. It is initially delivered to users in spam email campaigns. Attackers use social engineering to trick potential victims into downloading the attached file and enabling the macros, the same scenario is applied by Ave Maria and Revenge.
This makes contamination prevention fairly simple. Users are advised to stay clear of downloading files from suspicious emails and keep macros disabled. And especially, never enable them if prompted by a downloaded file.
Smoke Loader malware tries to hide its malicious nature. This is done by mixing infrequent requests to legitimate websites into C&C communication. The virus connects to websites such as Microsoft.com and Adobe.com. Despite receiving mainly HTTP 404 in requests, data is still evident in the response body.
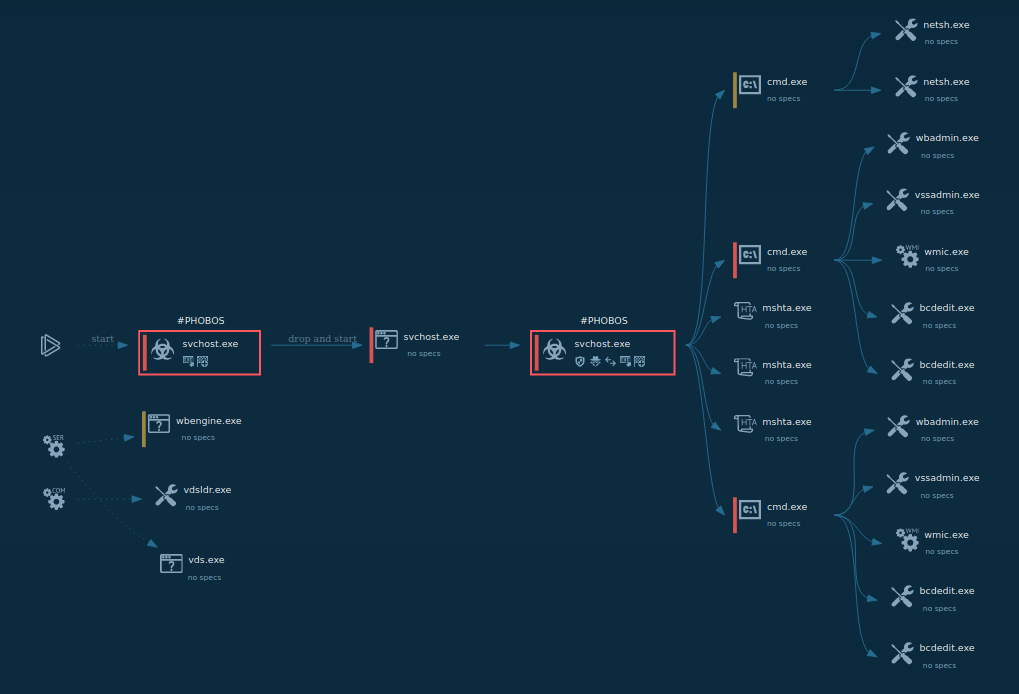
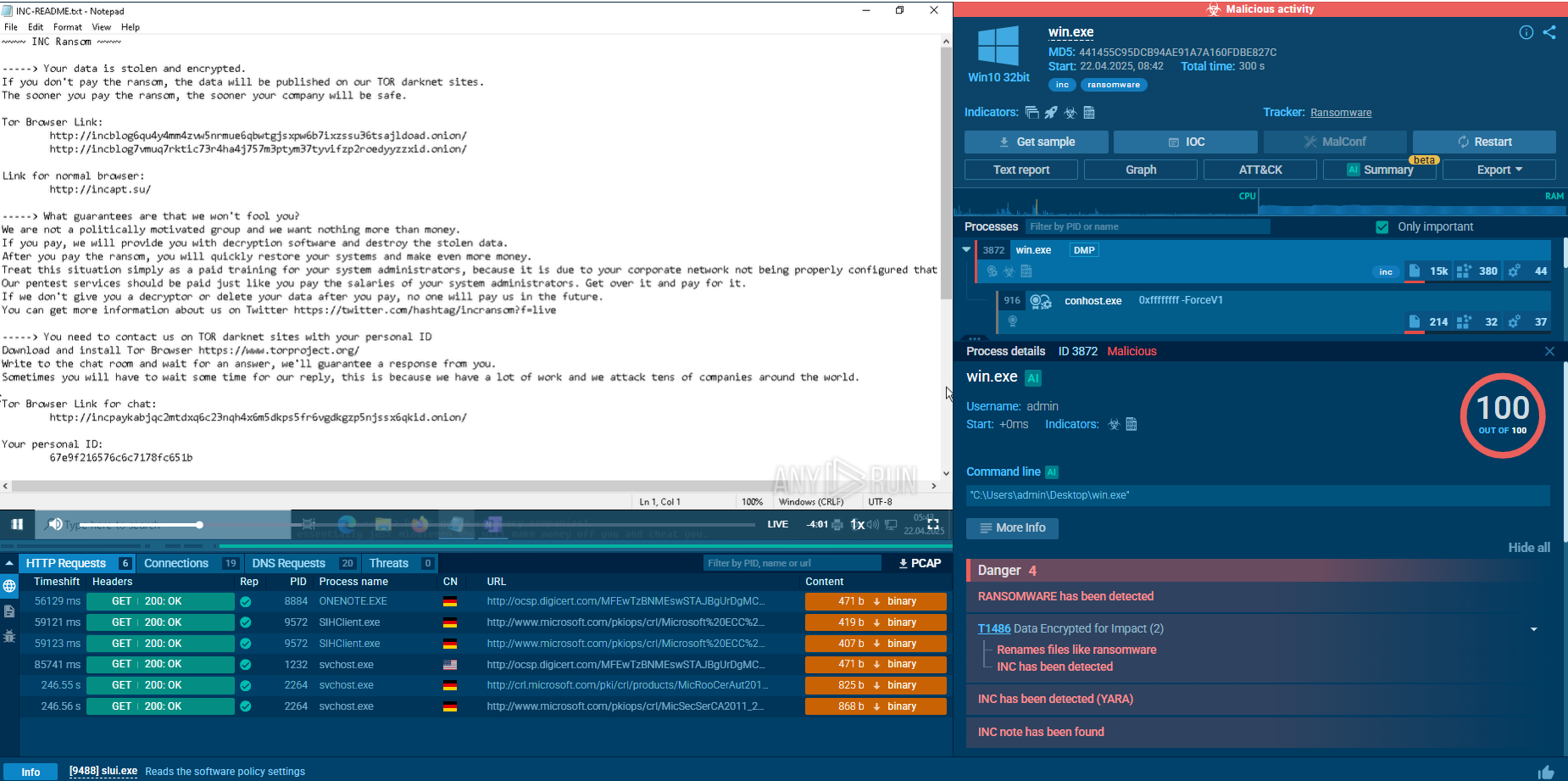
Since SmokeLoader almost always infects systems using similar attack vectors, it can be identified using its execution process. After the executable file, which contains Smoke Loader, has been delivered in the system and launched, it injects its code into the system process like "explorer.exe."
This means that if, after some time following the execution of a sample, an "explorer.exe" process appears, it is time to look into it. To do so, click on the process in the "Process list" section, and in the appeared "Process details" window click the "More info" button. If in the event section you see that previously injected "explorer.exe" create a file named "tesrdgeh.exe," it is a clear indication that you are dealing with Smoke Loader trojan.
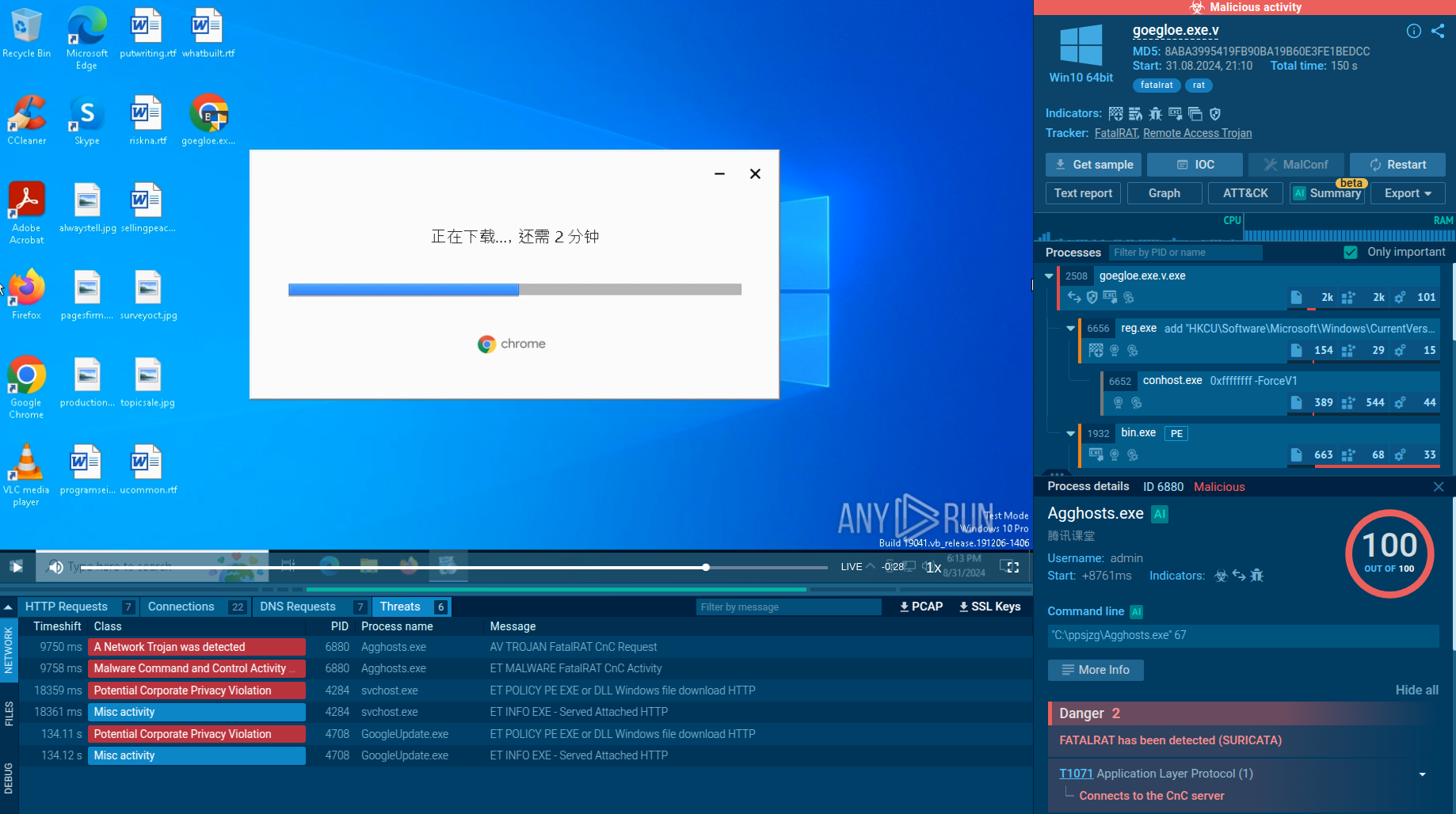
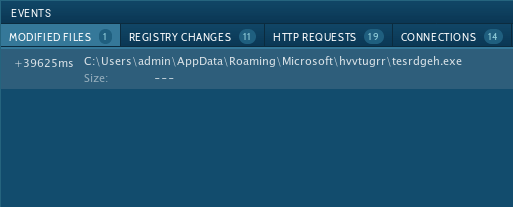 Figure 3: Injected explorer.exe created file tesrdgeh.exe
Figure 3: Injected explorer.exe created file tesrdgeh.exe
Despite being rather old, the Dofoil virus is only gaining popularity. Since its first surfacing in 2011, the malware remains a highly active and elusive threat, not due to its advanced anti-evasion functions. In addition to being used as a loader and installing potentially more dangerous malware.
What’s more, Smoke Loader itself can be used to pull sensitive information from infected machines and conduct destructive, malicious campaigns.
Thankfully, advanced malware hunting services such as ANY.RUN allows us to bypass some of the anti-evasion tricks implemented by the Smoke Loader creators and successfully conduct the analysis of this virus.