Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


StrelaStealer is a malware that targets email clients to steal login credentials, sending them back to the attacker’s command-and-control server. Since its emergence in 2022, it has been involved in numerous large-scale email campaigns, primarily affecting organizations in the EU and U.S. The malware’s tactics continue to evolve, with attackers frequently changing attachment file formats and updating the DLL payload to evade detection.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 November, 2022
First seen
:
|
25 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 November, 2022
First seen
:
|
25 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
StrelaStealer is an information-stealing malware first observed in late 2022, primarily targeting login credentials from popular email clients. This malware is known for its large-scale phishing campaigns, particularly across Europe and the United States, where it has successfully compromised numerous organizations.
The malware is predominantly distributed through phishing emails containing malicious attachments, such as ZIP files or ISO files, which execute the payload once opened.
StrelaStealer employs various obfuscation and anti-analysis techniques to evade detection, including control flow obfuscation and removing PDB strings, making it increasingly difficult for security tools to detect and analyze.
StrelaStealer’s primary function is to steal email login information, which is then transmitted back to the attacker’s command-and-control (C2) server.
This stolen data can be used to conduct further malicious activities, such as sending spam emails, launching spear-phishing attacks, or exfiltrating sensitive information.
Although it is not explicitly marketed as Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS), the ongoing development and frequent updates suggest that it is actively maintained and potentially distributed through cybercriminal networks.
The primary capabilities of the StrelaStealer malware include:
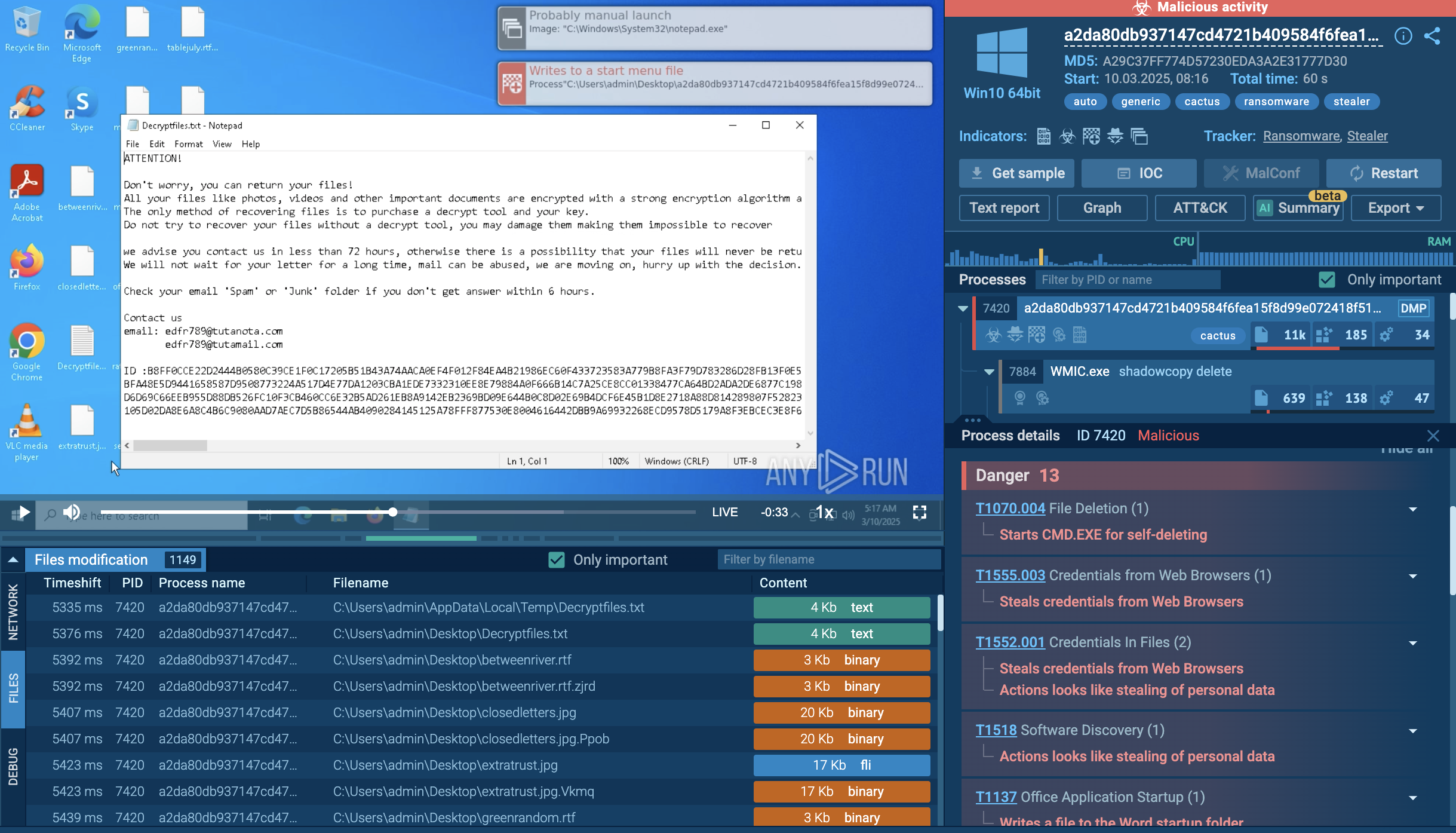
To see how StrelaStealer operates, let’s launch an analysis session using its sample in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
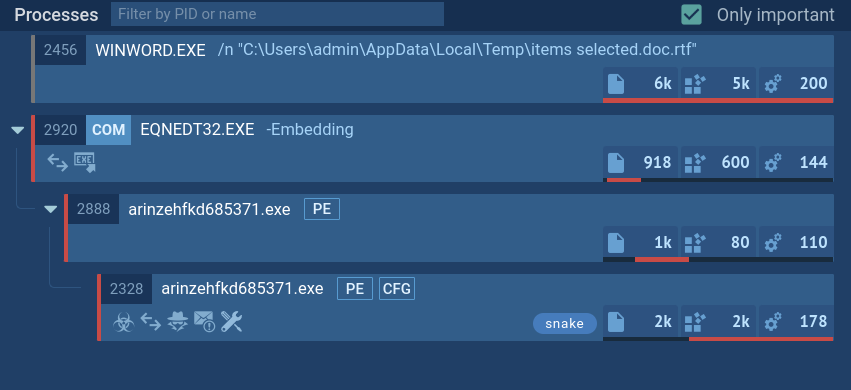
As noted, StrelaStealer is primarily distributed through phishing emails that often contain ZIP file attachments. These emails typically use localized language and subject lines resembling invoices or bills (e.g., "Factura/Rechnung/Invoice###/PO###") to lure victims into opening them. When a victim opens the ZIP file, it contains a JScript file that, upon execution, may drop a base64-encoded file and a batch file onto the system.
The batch file utilizes the certutil -f decode command to decode the base64 file, which creates a Portable Executable (PE) DLL file. The DLL file is then executed using the rundll32.exe or regsvr32.exe process, specifically calling an exported function (often named "hello" in the latest variants) to initiate the malware's operations.
In our sample, the command line contains "davwwwroot" in the path to the downloaded DLL file.
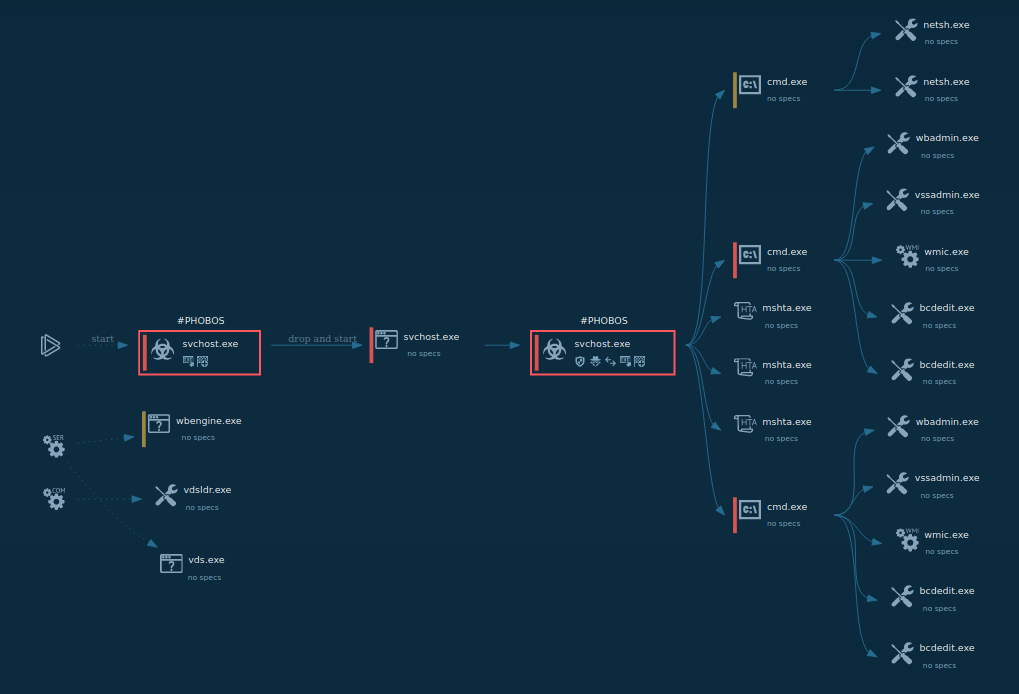
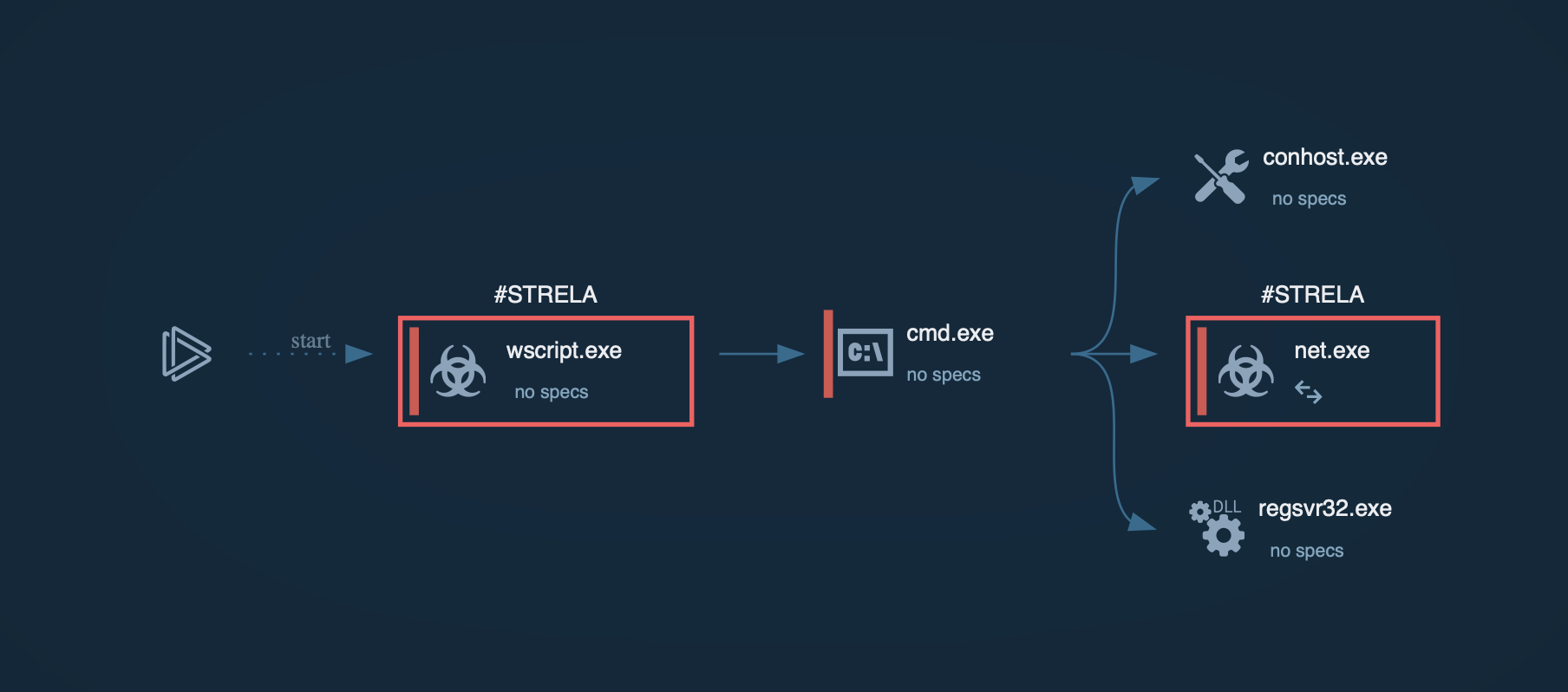 Process graph of StelaStealer displayed by ANY.RUN sandbox
Process graph of StelaStealer displayed by ANY.RUN sandbox
Once executed, StrelaStealer is designed to steal email login credentials from popular email clients such as Outlook and Thunderbird. The stolen credentials are then sent back to the attacker's Command and Control (C2) server for further exploitation.
The latest variants of StrelaStealer employ advanced obfuscation techniques, including control flow obfuscation and the removal of debugging symbols (PDB strings), making it more challenging for security analysts to detect and analyze the malware. The malware's code includes excessively long arithmetic instructions to complicate execution in sandbox environments, potentially causing timeouts during analysis.
Since its emergence in 2022, StrelaStealer has targeted over 100 organizations across the U.S. and Europe, with significant campaigns observed in late 2023 and early 2024. The threat actors continue to adapt their strategies to evade detection while maximizing the impact of their attacks.
StrelaStealer is primarily distributed through:
StrelaStealer is a dangerous malware due to its ability to steal email credentials, evade detection through advanced obfuscation techniques, and spread rapidly via phishing campaigns. Its ongoing development and adaptability make it a persistent threat to organizations.
ANY.RUN is a cloud-based interactive malware analysis platform that enables users to safely analyze and observe the behavior of malicious files in a secure environment. It provides real-time insights, helping security professionals collect indicators of compromise (IOCs) and understand the tactics used by malware like StrelaStealer, ultimately strengthening defenses against such threats.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today and take your cybersecurity to the next level.