Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Cobalt Strike is a legitimate penetration software toolkit developed by Forta. But its cracked versions are widely adopted by bad actors, who use it as a C2 system of choice for targeted attacks.
|
Penetration software
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
20 February, 2012
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Penetration software
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
20 February, 2012
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 757
757
 0
0

 467
467
 0
0

 2699
2699
 0
0
Cobalt Strike is a licensed penetration software package developed by Forta (previously Help Systems), that helps red teams simulate an adversary in red-vs-blue games.
While the software itself is completely legal and designed for cybersecurity testing, over the years, many versions of it have been cracked and leaked into the wild. Despite several attempts to stop its abuse — by the developer and the online community — attackers continue to employ it to install multiple payloads after compromising their victims' networks.
Most of these cracked versions were obtained by accessing a trial — which is only given to verified parties, but evidently, hackers found a way to skirt this — and bypass the license check and then trial restrictions. (The trial version of Cobalt Strike has many deliberate giveaways such as the EICAR string embedded in all payloads and a watermark.)
Being a legitimate tool, there is a ton of educational material online, which illustrates what Cobalt Strike can do. Like this official playlist on YouTube. This, of course, lowers the entry threshold and contributes to the popularity of the software among bad actors. One can literally learn how to abuse it directly from its creators.
Cracked Cobalt Strike versions are circulating freely in various underground forums and are sometimes found on clearnet resources, like GitHub. Although most of them are somewhat outdated, they still pose a serious threat — many criminal groups use them to gain initial access and move laterally through victim’s networks.
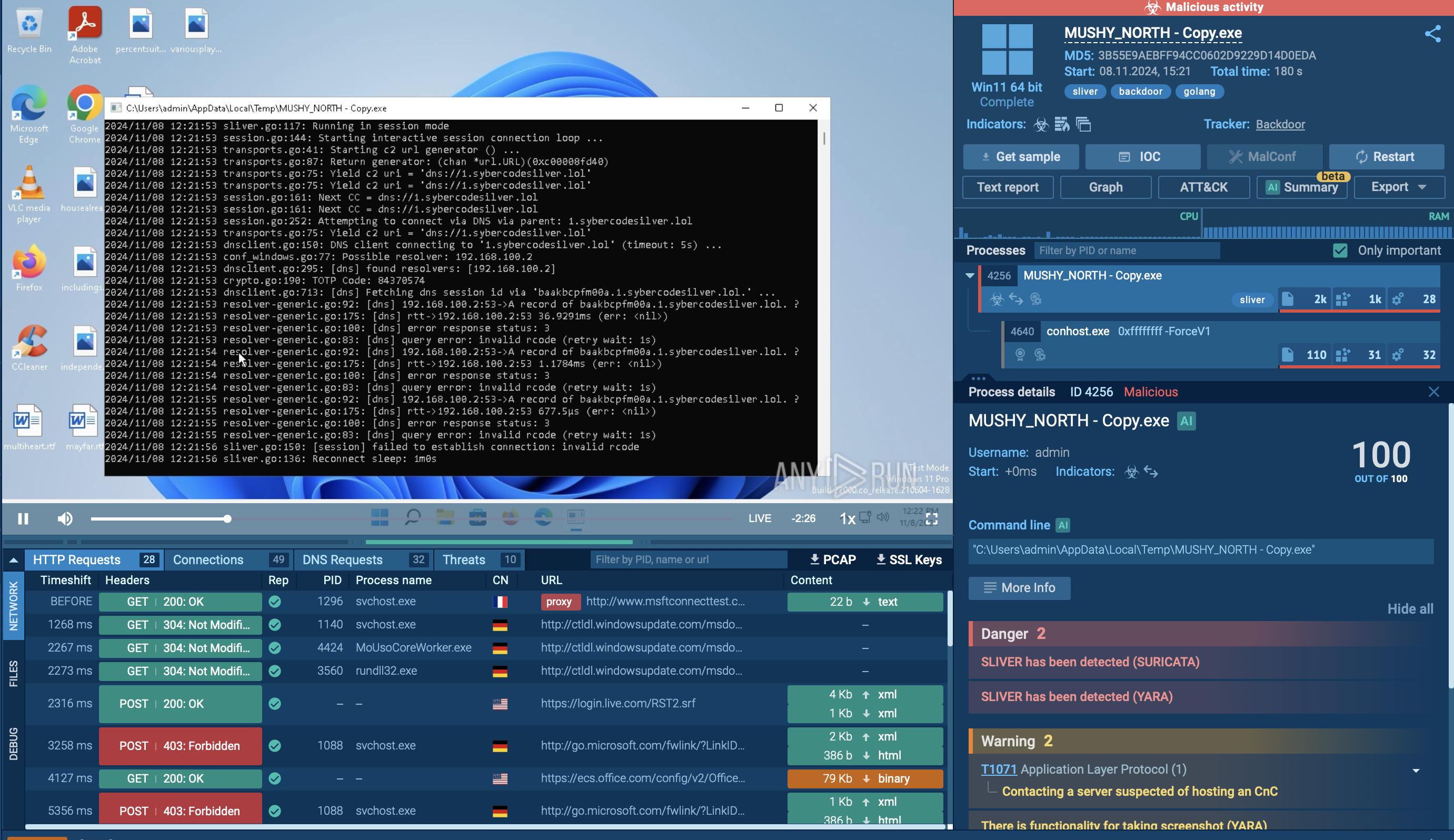
Cobalt Strike consists of multiple components, which together form a comprehensive hacking suit. The central element of the software is the Team Server component — which acts as both the C2 server and a coordinating program that helps multiple adversaries work together and control hijacked devices. To access it, actors use a Client component which serves as the GUI for the Team Server.
Team Server can generate shellcode implants called Stagers. These fileless implants are available as VBA, Javascript and Powershell macro templates. When an attacker infiltrates and injects one of the Stagers into the victim's network, they can contact the Team Server via HTTP/HTTPS, SMB, or DNS to fetch and install the main payload known as the Beacon.
The Beacon is the core binary which allows the attacker to control infected machines remotely. It supports a wide list of malicious operations, and is designed to be configurable and expandable. This feature is often used to deliver and run custom modules, and makes Cobalt Strike's malicious capabilities virtually limitless. What’s more, there are built-in modules that allow attackers to customize the payload to avoid detection: these include the Artifact Kit, Malleable C2 Profiles, and Resource Kit.
Also, it’s important to note that since Cobalt Strike was originally designed for team exercises, the Team Server and Client modules allow criminal gangs to coordinate hacks with multiple attackers acting simultaneously, potentially targeting multiple weak spots.
The payloads usually delivered by Cobalt Strike range from Ransomware to spyware and even Advanced Persistent Threats.
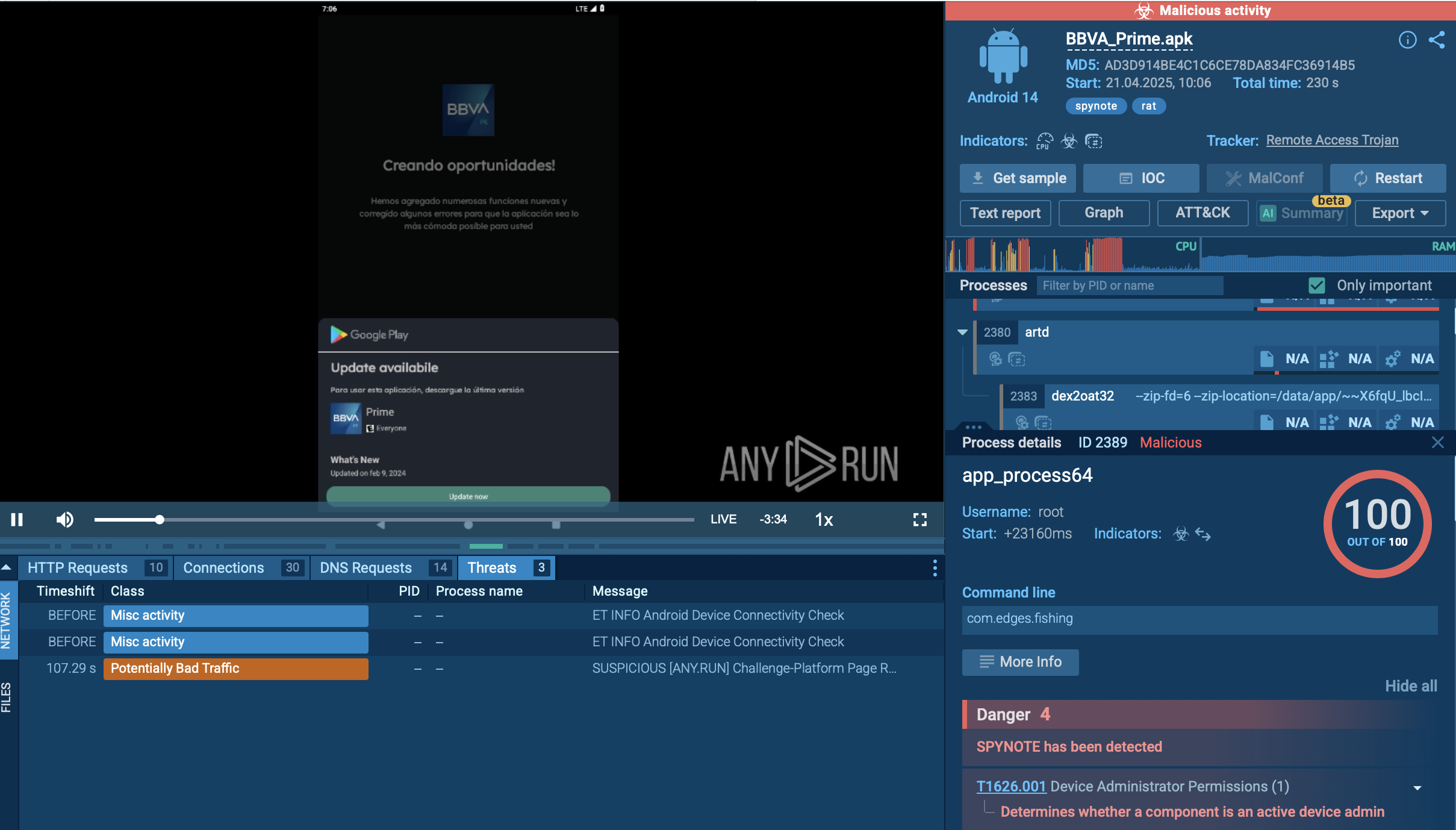
ANY.RUN helps analysts track the execution process of Cobalt Strike in an interactive online sandbox.
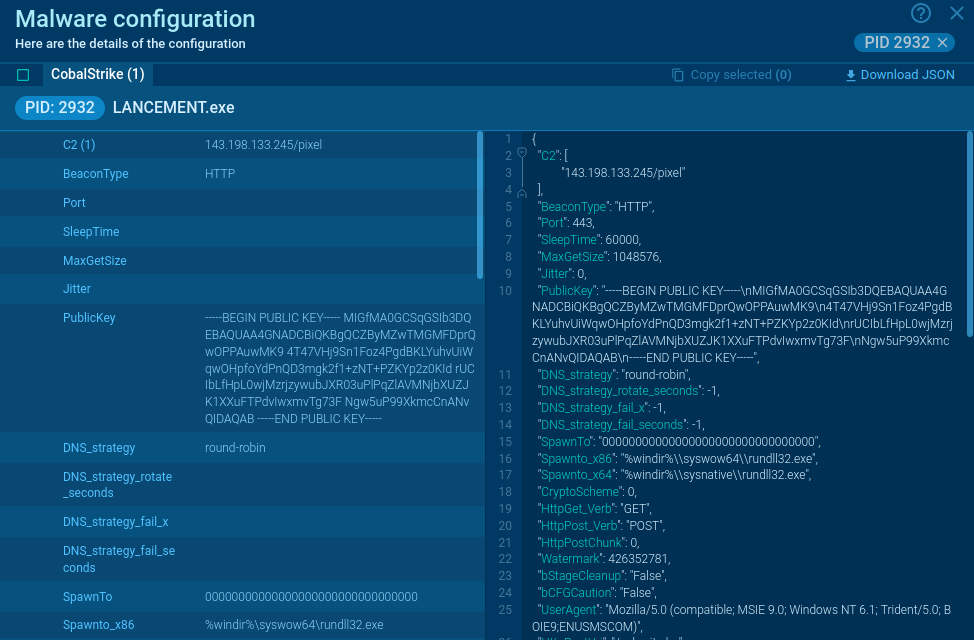
Figure 1: Cobalt Strike malware configuration
ANY.RUN users can access the analysis results 10 seconds after launching the sandbox, which saves crucial time, especially during incident response when every second matters.
The execution of CobaltStike varies greatly from sample to sample. Not only are there lots of iterations of the client, but the program itself is frequently updated by the developers. Besides the common type that uses an executable file, there are also versions that use powershell or JS to dominate the infected system.
In ANY.RUN, users can study the config of CobaltStrike’s utility to better understand how it works.
Unfortunately, the distribution of Cobalt Strike is poorly documented, but it’s believed to be delivered using macros that come with an infected executable embedded in a phishing email. There are few reports of this particular malware, so the conclusion was drawn based on the little information available, and the fact that it is by far the most common attack vector.
Cobalt Strike has gained an excellent reputation among cybercriminals who continue to use it as their Command and Control system of choice to deliver and execute a wide variety of payloads. This is a perfect example of what a legitimate piece of kit can do in the wrong hands. That said, its abuse is a fairly well-researched topic in the community, and there are guides like this one and this one that can help you defend against attacks using this software.
We hope that as the good research continues, and organizations arm themselves against cracked copies of Cobalt Strike, the abuse of this powerful cybersecurity tool will eventually stop.