Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Mallox is a ransomware strain that emerged in 2021, known for its ability to encrypt files and target database servers using vulnerabilities like RDP. Often distributed through phishing campaigns and exploiting exposed SQL servers, it locks victims' data and demands a ransom. Mallox operates as a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS), making it accessible to affiliates who use it to conduct attacks.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2021
First seen
:
|
29 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2021
First seen
:
|
29 January, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
Mallox is a ransomware strain that emerged in 2021 and has since become a known threat, particularly targeting organizations with vulnerable SQL servers and RDP configurations.
Its method of operation involves encrypting victims' files and appending unique extensions like ".mallox" to the encrypted data, effectively making the files inaccessible. Victims are then presented with a ransom note demanding payment, usually in cryptocurrency, in exchange for the decryption key.
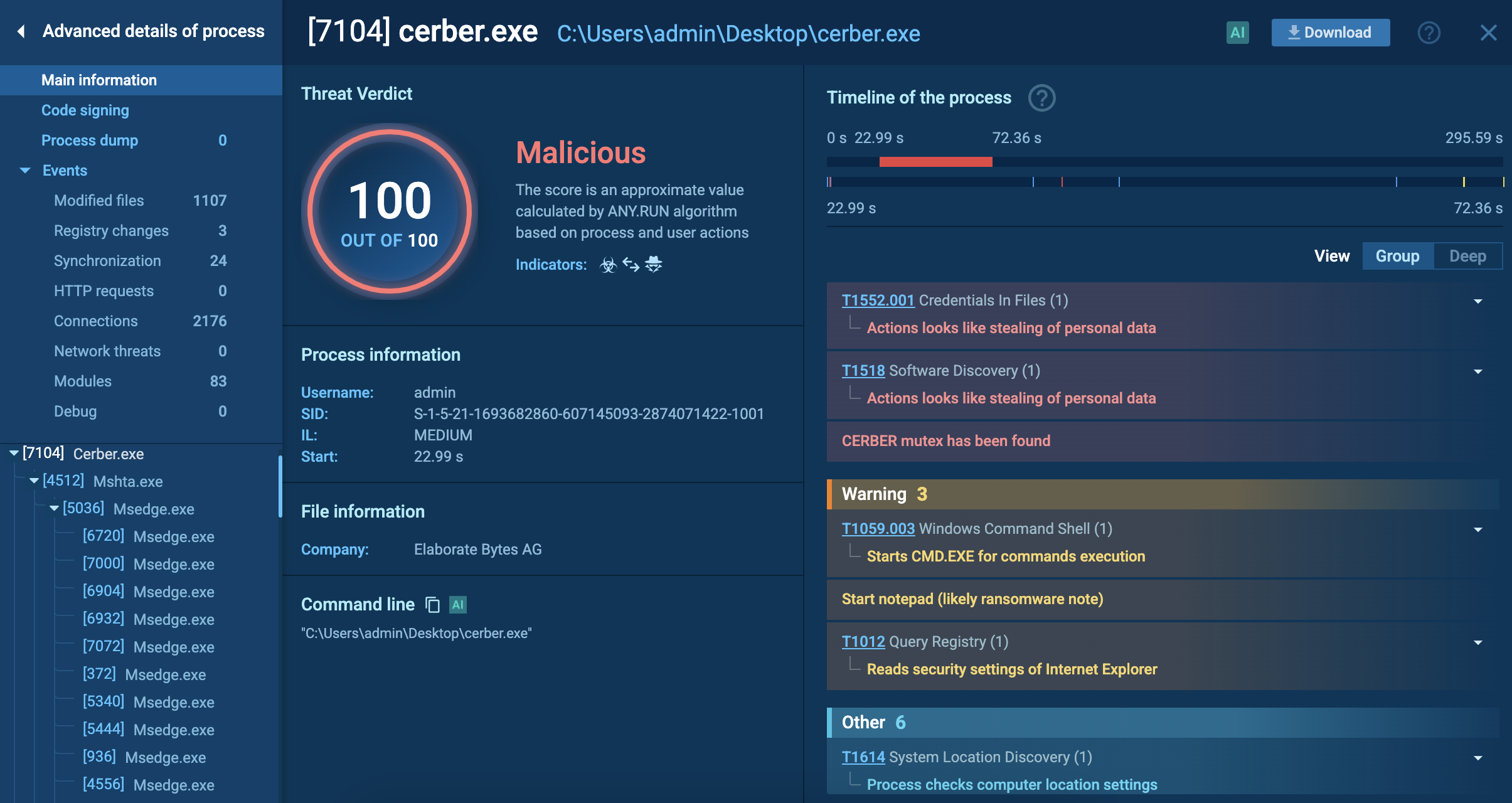
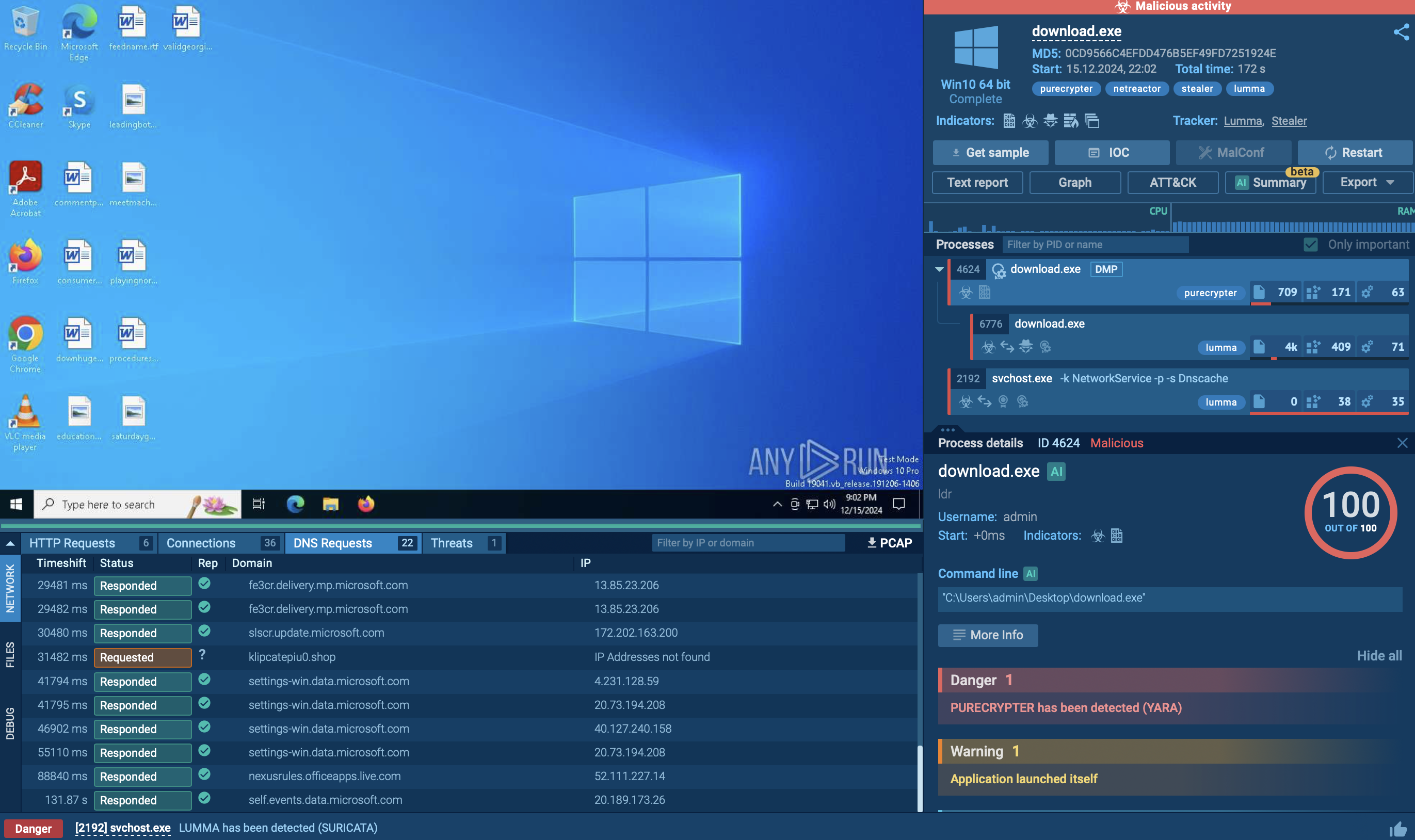
When analyzing the Mallox ransomware inside the ANY.RUN’s sandbox, we can see the whole process of its attack chain, including the displayed ransom note:
 Analysis of Mallox inside ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox showing a ransom note
Analysis of Mallox inside ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox showing a ransom note
Mallox operates through a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, making it accessible to various threat actors who can customize and distribute the ransomware. It employs advanced techniques like modifying boot configurations, disabling Windows recovery options, and using PowerShell scripts for downloading and executing payloads.
The primary functionalities of Mallox ransomware include:
This ransomware collects detailed system data, such as total disk space, operating system version, computer name, locale settings, and the architecture of the processor. It then sends this information to its command-and-control (C2) server to aid in managing the infection.
Additionally, it uses an external API, like api.ipify.org, to determine and retrieve the device's public IP address, allowing the attackers to gain further insight into the network environment.
This action can be observed in ANY.RUN’s sandbox when detected by Suricata rules.
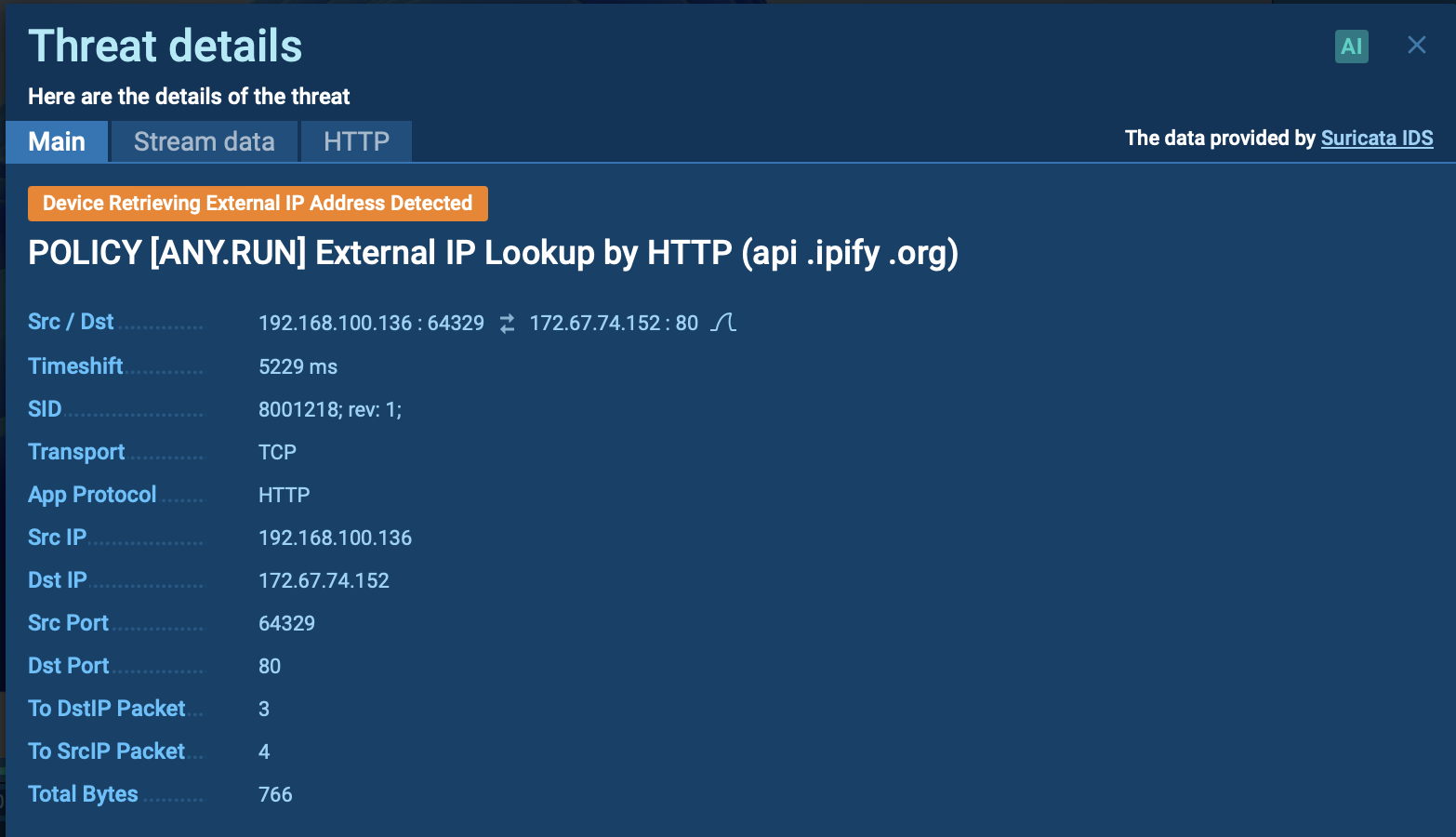 External IP address retrieval detected inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
External IP address retrieval detected inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
To see how Mallox ransomware operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
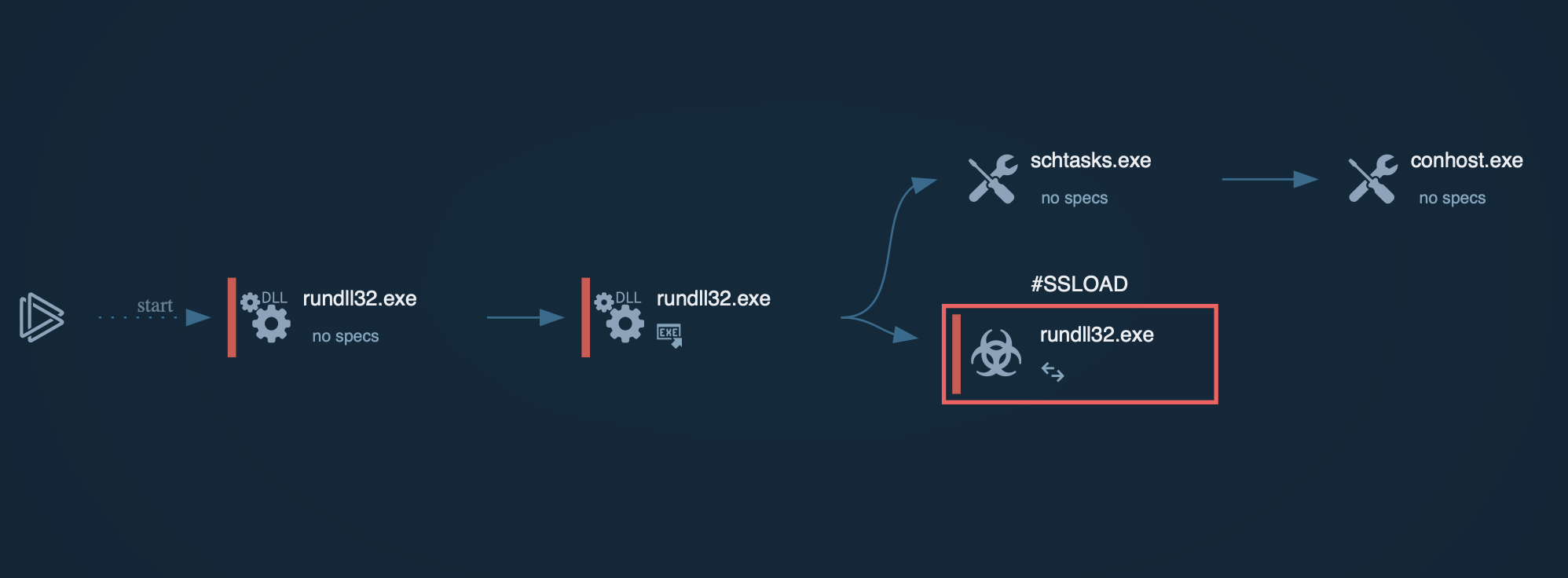
Mallox ransomware employs a sophisticated attack chain, sometimes beginning with initial access through brute-force attacks on unsecured Microsoft SQL servers.
Once inside, the ransomware executes various commands and scripts to facilitate its malicious activities, culminating in file encryption and ransom demands.
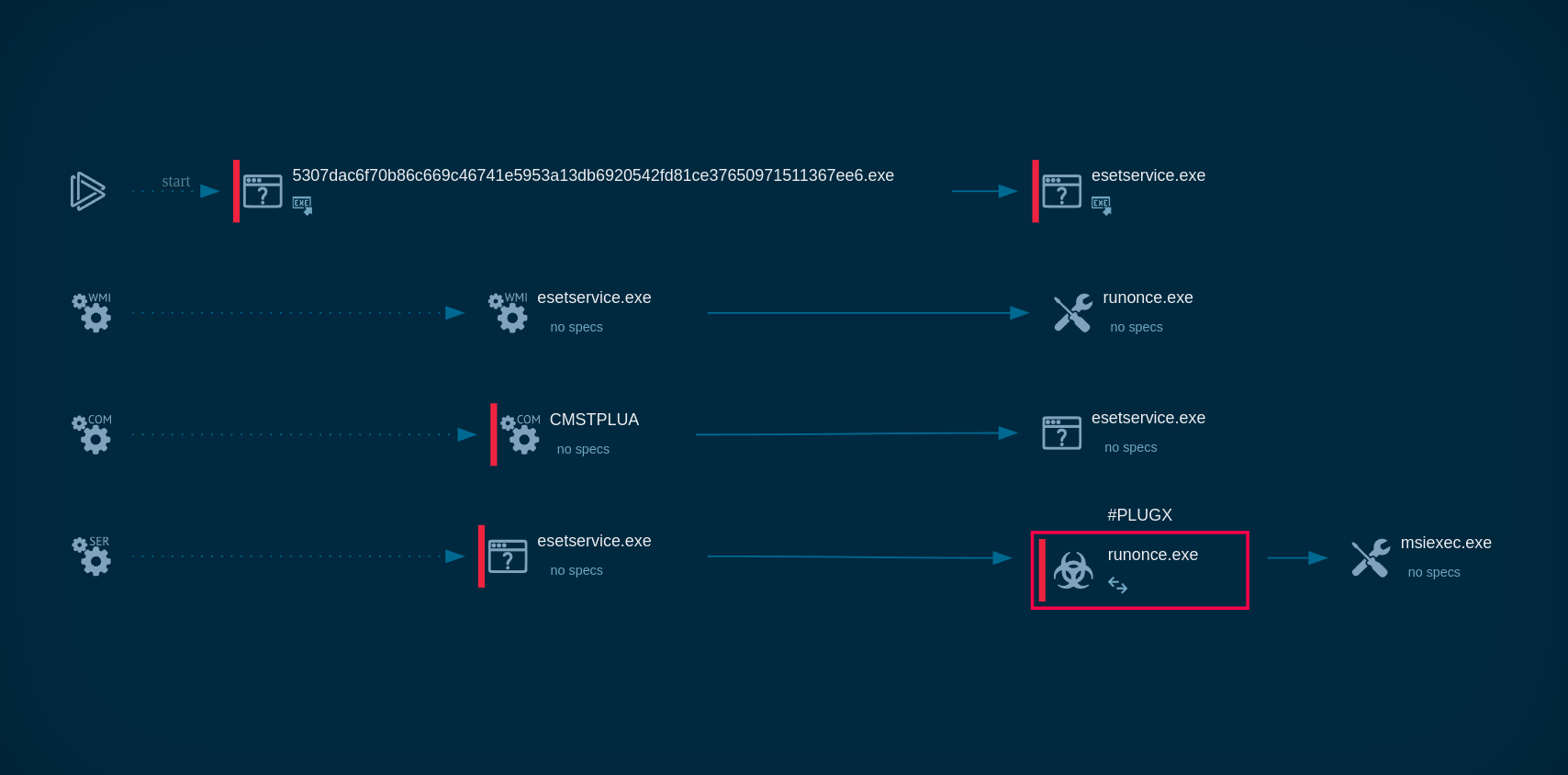
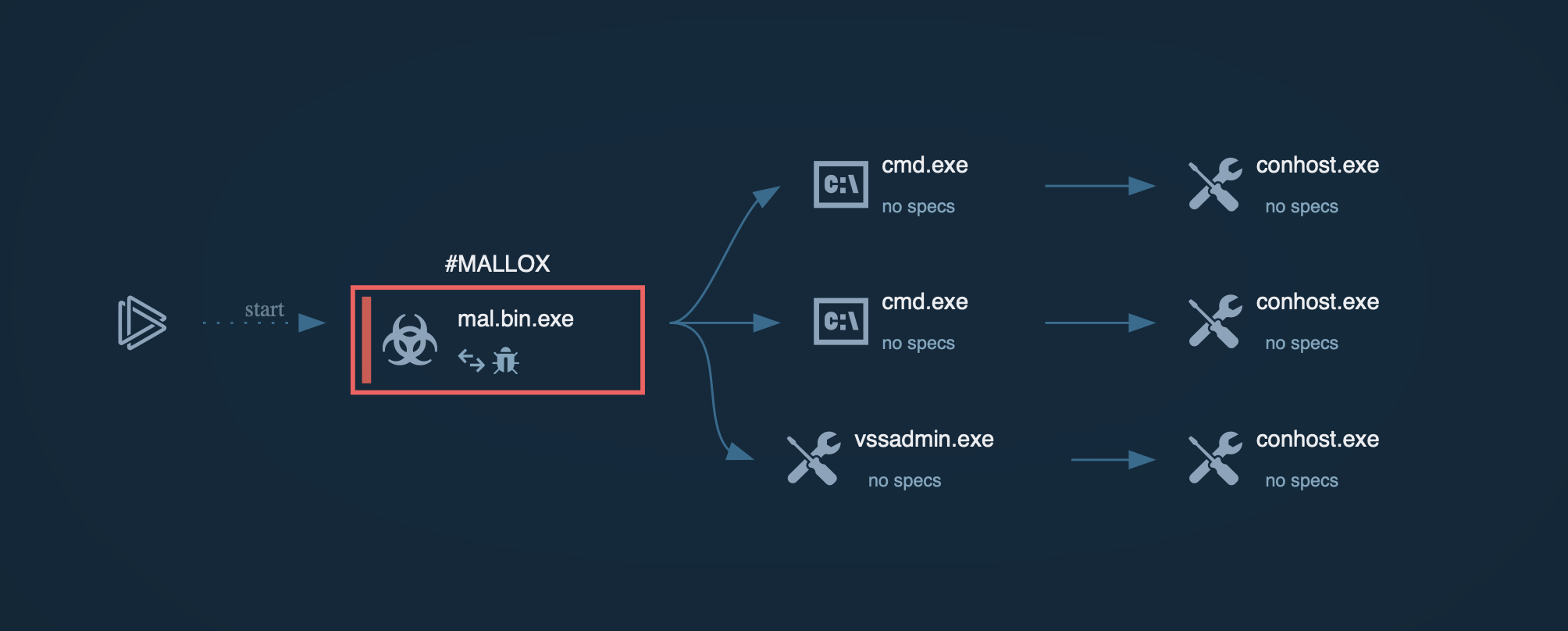 Process graph of Mallox ransomware displayed inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Process graph of Mallox ransomware displayed inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Mallox primarily targets unsecured Microsoft SQL servers by using dictionary brute-force attacks to gain access to the victim's network. After compromising the SQL server, the attackers utilize command-line tools and PowerShell scripts to download the ransomware payload from a remote server.
The downloaded payload may inject itself into legitimate processes (e.g., Aspnet_Compiler.exe) using techniques like process hollowing, allowing it to evade detection by traditional antivirus software.
Upon execution, Mallox modifies Boot Configuration Data (BCD) settings to disable recovery options, making it harder for users to restore their systems post-infection.
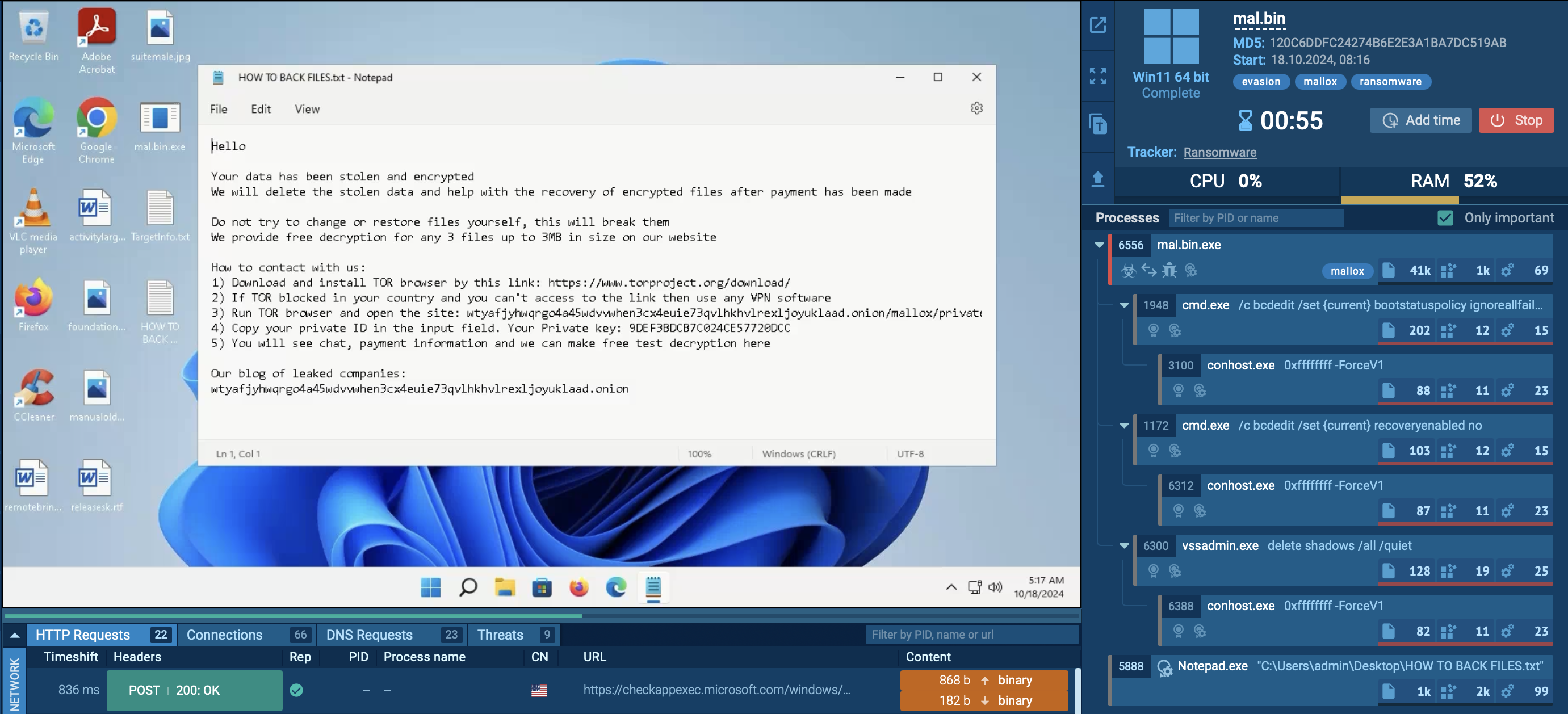
The ransomware encrypts files on the infected system, appending a ".mallox" extension to the encrypted files. It also generates ransom notes named “HOW TO BACK FILES.TXT” in each folder containing encrypted files.
Before encryption, Mallox may exfiltrate sensitive data from the system, which is later used against victims who refuse to pay the ransom.
Victims are instructed to contact the attackers via TOR or email, with unique identifiers (private ID in our sample) provided for negotiation purposes. The ransom notes often threaten to expose the stolen data if demands are not met.
Besides this, the ransomware modifies Windows registry settings to disable shutdown, restart, and sign-out options, effectively locking users out of their systems to prevent interruption of the encryption process.
If users attempt to shut down or reboot their systems, Mallox displays warnings about potential data loss, further pressuring victims to comply with ransom demands.
Mallox ransomware is typically distributed through a few primary methods, making it a significant threat to targeted systems:
To collect the latest intelligence on Mallox ransomware, you can utilize Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service offers access to an extensive database with insights from numerous malware analysis sessions conducted within the ANY.RUN sandbox. It includes over 40 search parameters, enabling you to explore specific details like IP addresses, domains, file names, and various process artifacts.
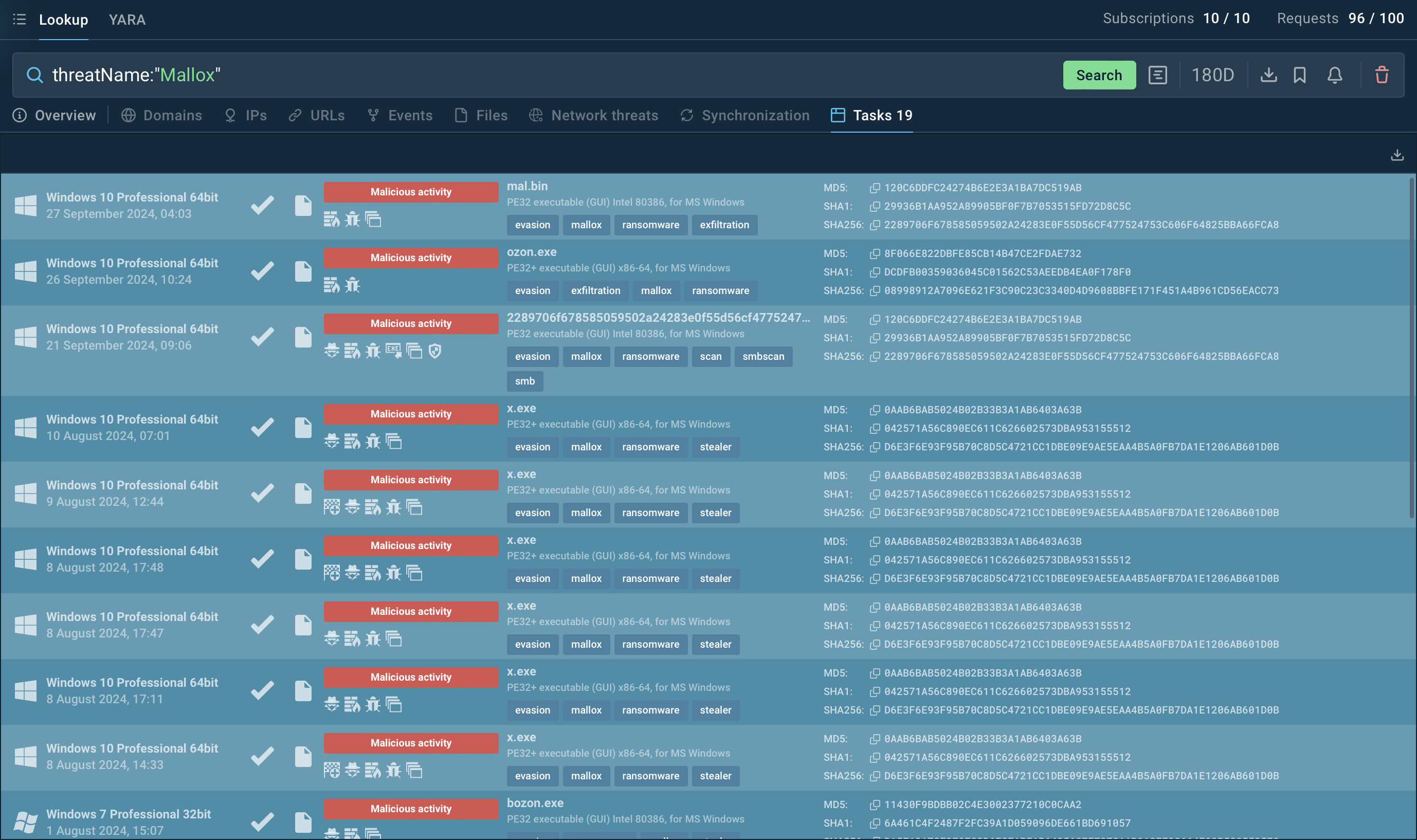 Search results for Mallox in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Mallox in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Using Threat Intelligence Lookup, you can search directly for a threat name or use a related artifact. For instance, by entering a query like threatName:"mallox" AND domainName:"", you can quickly access Mallox threat data along with sandbox sessions that you can explore in detail to gain comprehensive insights into this malware’s behavior.
Get a 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup along with the ANY.RUN sandbox.
Mallox ransomware poses a significant threat due to its ability to encrypt critical files, exfiltrate sensitive data, and disable recovery mechanisms. To mitigate such threats, integrating tools like ANY.RUN is crucial for proactively analyzing suspicious files and URLs before they cause harm.
ANY.RUN offers a real-time threat analysis with detailed process graphs, in-depth network traffic analysis, and a user-friendly interface that allows analysts to simulate real-world threat scenarios effectively.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today and enhance your malware analysis capabilities.