Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


MassLogger is a credential stealer and keylogger first identified in April 2020. It has been actively used in cyber campaigns to exfiltrate sensitive information from compromised systems. It is designed for easy use by less tech-savvy actors and is prominent for the capability of spreading via USB drives. It targets both individuals and organizations in various industries, mostly in Europe and the USA.
|
Keylogger
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
4 January, 2020
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
4 January, 2020
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 850
850
 0
0

 505
505
 0
0

 2783
2783
 0
0
MassLogger is a sophisticated .NET-based malware classified as a credential stealer and keylogger observed from April 2020. It has since evolved with regular updates from its creator, known as NYANxCAT, who is also linked to other malware like LimeRAT and AsyncRAT.
Its high configurability, evasion techniques, and broad targeting capabilities, as well as the price of approximately $100, made it a popular item on dark web forums. It affects both individual users and organizations, with campaigns targeting industries like manufacturing, banking, and logistics across regions such as Europe (Turkey, Latvia, Italy, etc.), the U.S., and beyond.
MassLogger typically infiltrates networks through social engineering tactics, most often via phishing emails. They may target business users and masquerade as legitimate correspondence, such as procurement requests, shipping notices (e.g., referencing companies like Maersk), or other professional communications.
It can also spread via USB drives by injecting itself into files, infecting new systems when those files are opened.
In some campaigns, MassLogger has been distributed via compiled HTML files (.chm), which, when opened, execute embedded JavaScript to initiate the infection chain.
The infection chain is often multi-staged, involving scripting languages like PowerShell and .NET assemblies, making it harder to trace back to the initial vector.
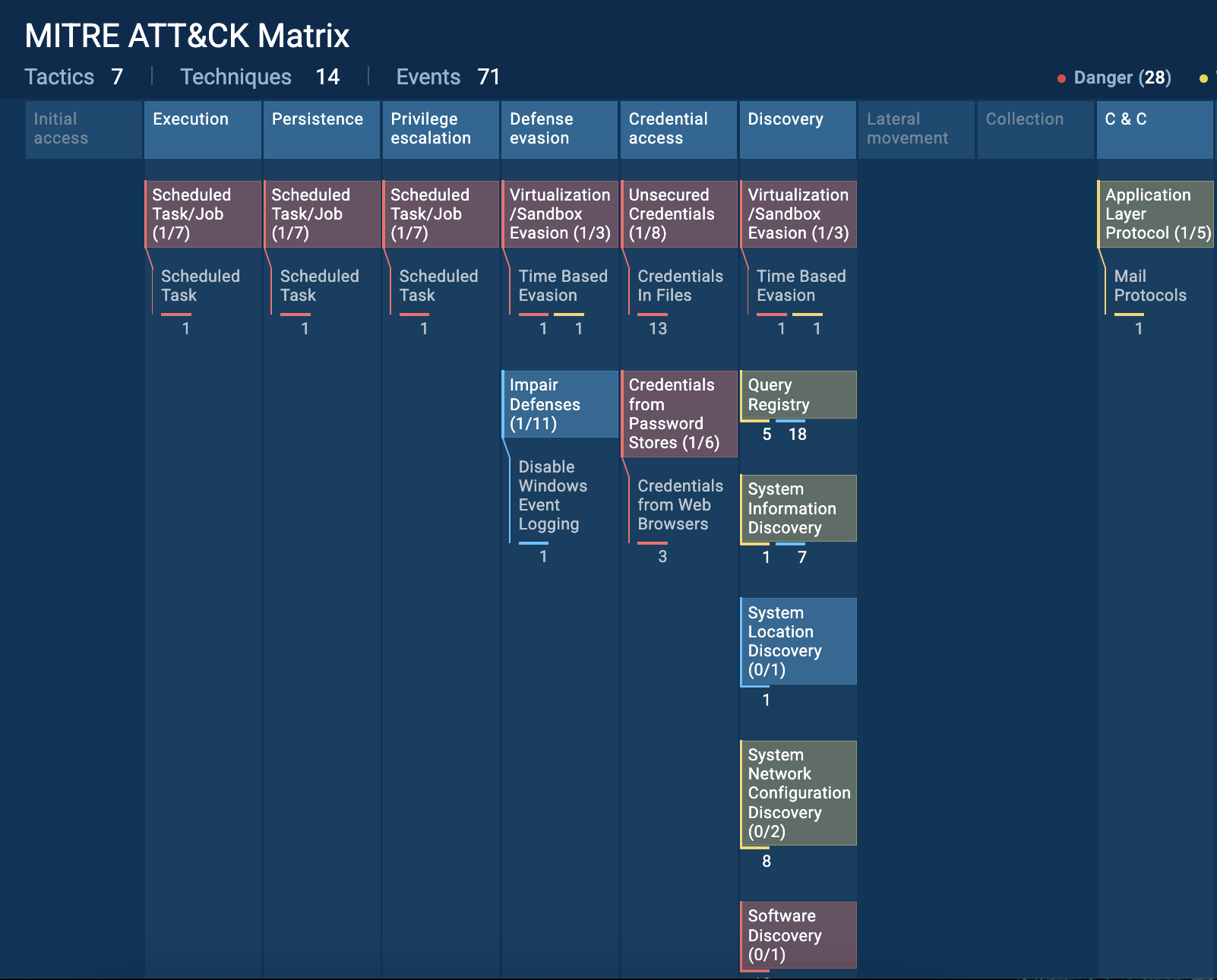 MassLogger tactics and techniques via MITRE ATT&CK Matrix
MassLogger tactics and techniques via MITRE ATT&CK Matrix
MassLogger is highly efficient at collecting and exfiltrating data. It extracts credentials from a wide range of applications, including web browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge), email clients (Outlook, Thunderbird, Foxmail), messaging apps (Discord, Telegram, Pidgin), VPN services (NordVPN), and FTP clients (FileZilla). It can also extract cryptocurrency wallet data.
Besides, it engages keylogging, clipboard monitoring, screen capturing, gathering system info via WMI queries.
All the variety of MassLogger’s vicious ways is illustrated by fresh malware samples and analyses in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox. Let’s view one of the recent analysis sessions.
See MassLogger’s sample in action
The intrusion often begins with a phishing email containing a malicious attachment — typically a RAR-compressed archive with an unusual filename extension, such as .chm or .pif — used to bypass email filters. In the past, Microsoft Office files were also commonly used.
The main payload is a variant of the MassLogger Trojan, designed to retrieve and exfiltrate user credentials from various applications, including web browsers, email clients, and VPNs. After the payload is decrypted, MassLogger parses its configuration to target specific applications.
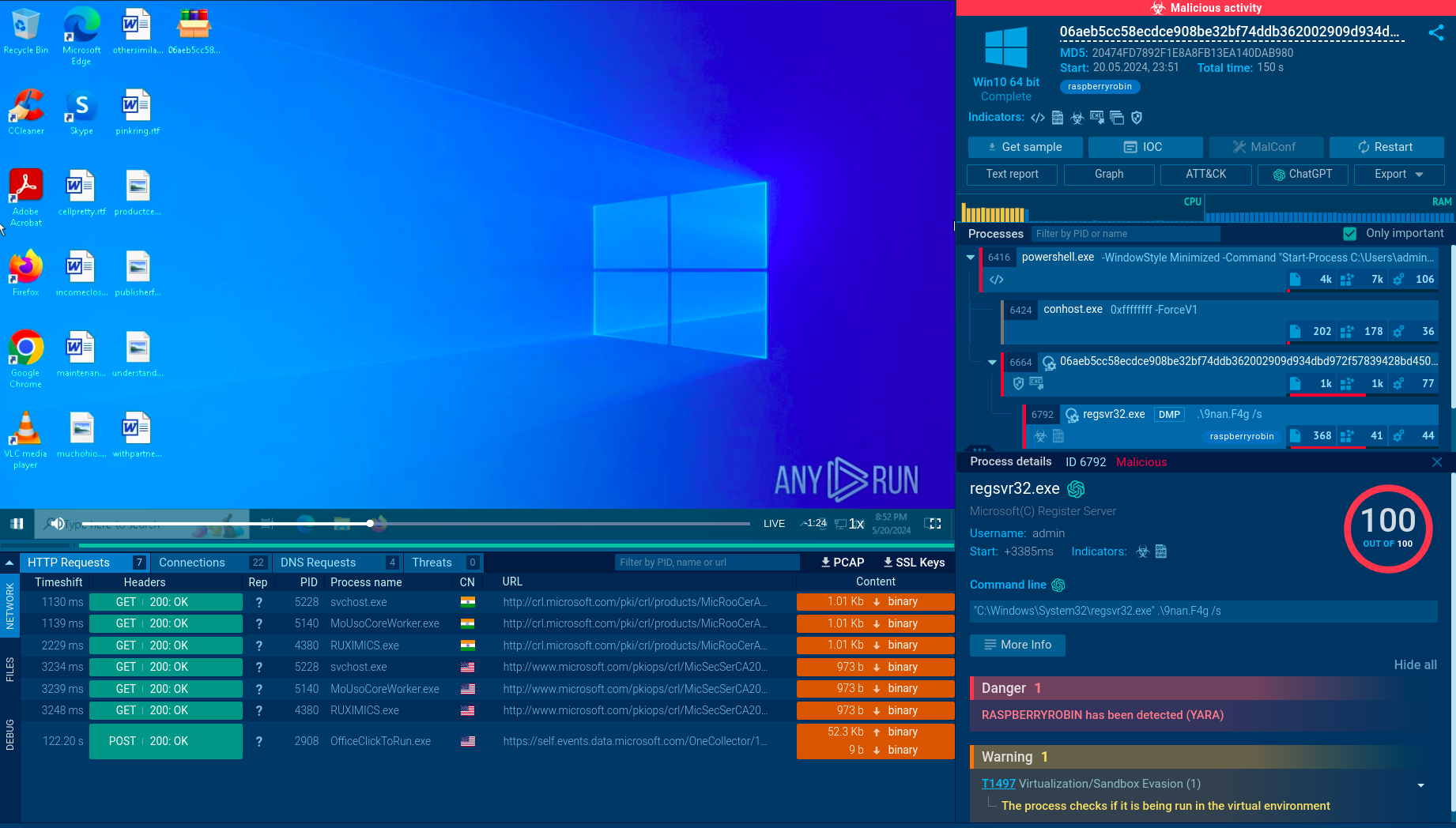
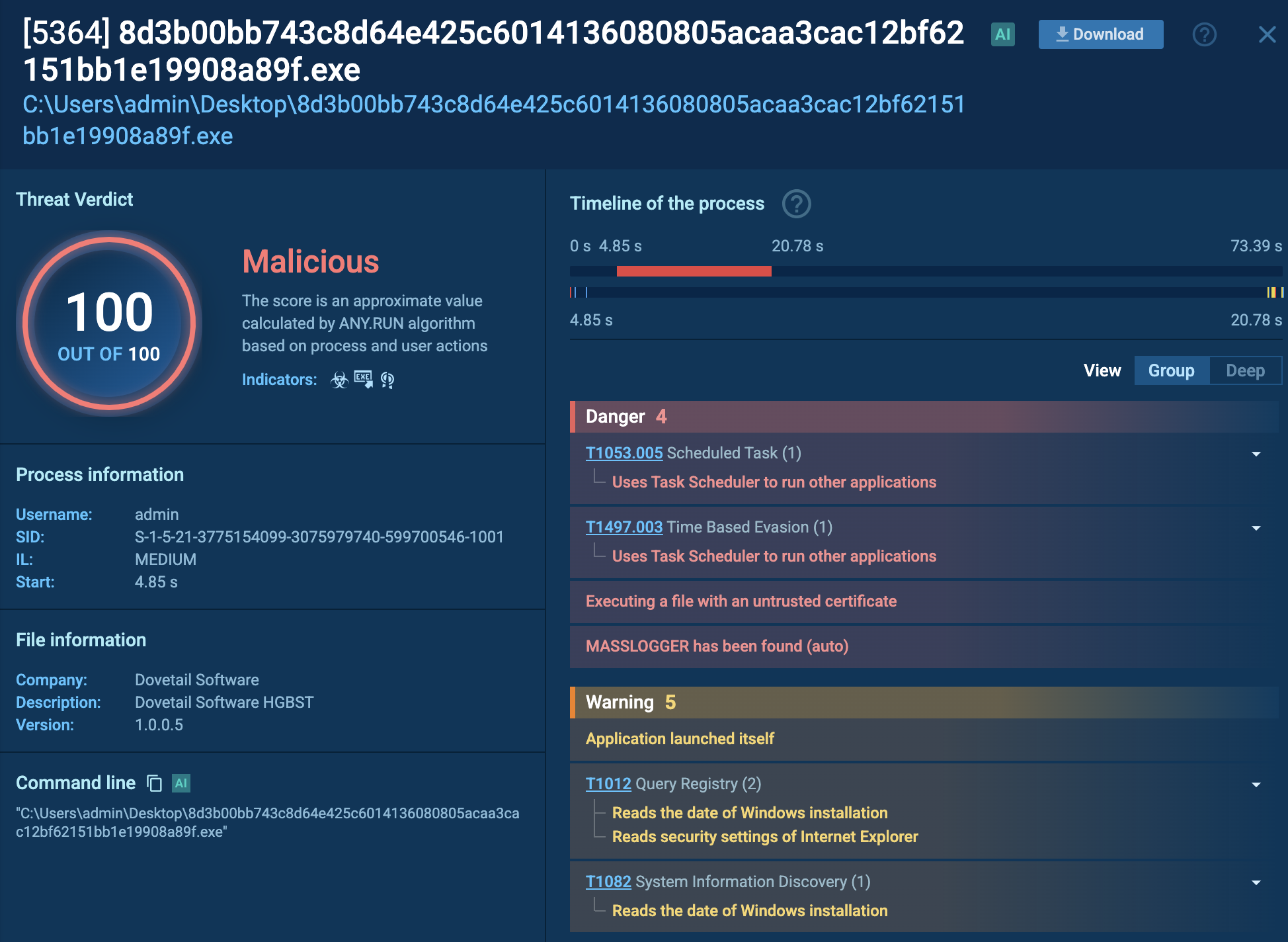 MassLogger acting in the system, malicious process detected by the sandbox
MassLogger acting in the system, malicious process detected by the sandbox
In some cases, it may be configured as a keylogger, though this functionality is often disabled depending on the campaign. The malware collects credentials from targeted applications and stores them in a log file — typically named Log.txt — in a temporary directory within %APPDATA%. Sometimes, it sends stolen information directly from memory without writing it to disk.
The stolen credentials are exfiltrated using methods such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol). In certain scenarios, the data is sent via email to a compromised mailbox, encoded in Base64. MassLogger generally does not persist on the system after execution, meaning it does not install components that would automatically restart upon a system reboot. It also does not request updates from the threat actor over time, making it a relatively straightforward yet effective credential-stealing tool.
MassLogger employs several advanced evasion techniques:
These tactics make MassLogger a "noisy" yet stealthy stealer, balancing aggressive data theft with efforts to remain undetected.
These campaigns highlight MassLogger’s key strengths: its configurability, low entry cost, and evasion tactics like obfuscation, fileless execution, and anti-analysis checks. Unlike headline-grabbing ransomware attacks, MassLogger’s impact is often quieter but insidious, focusing on credential theft that can lead to downstream breaches.
Threat intelligence is of much help in proactive defending against MassLogger. Use ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup to gather IOCs, study attackers’ TTPs, preempt incidents by blocking known C2 infrastructure.
Start by searching MassLogger in TI Lookup by the name and explore malicious samples that the cybersecurity community using ANY.RUN’s tools have encountered.
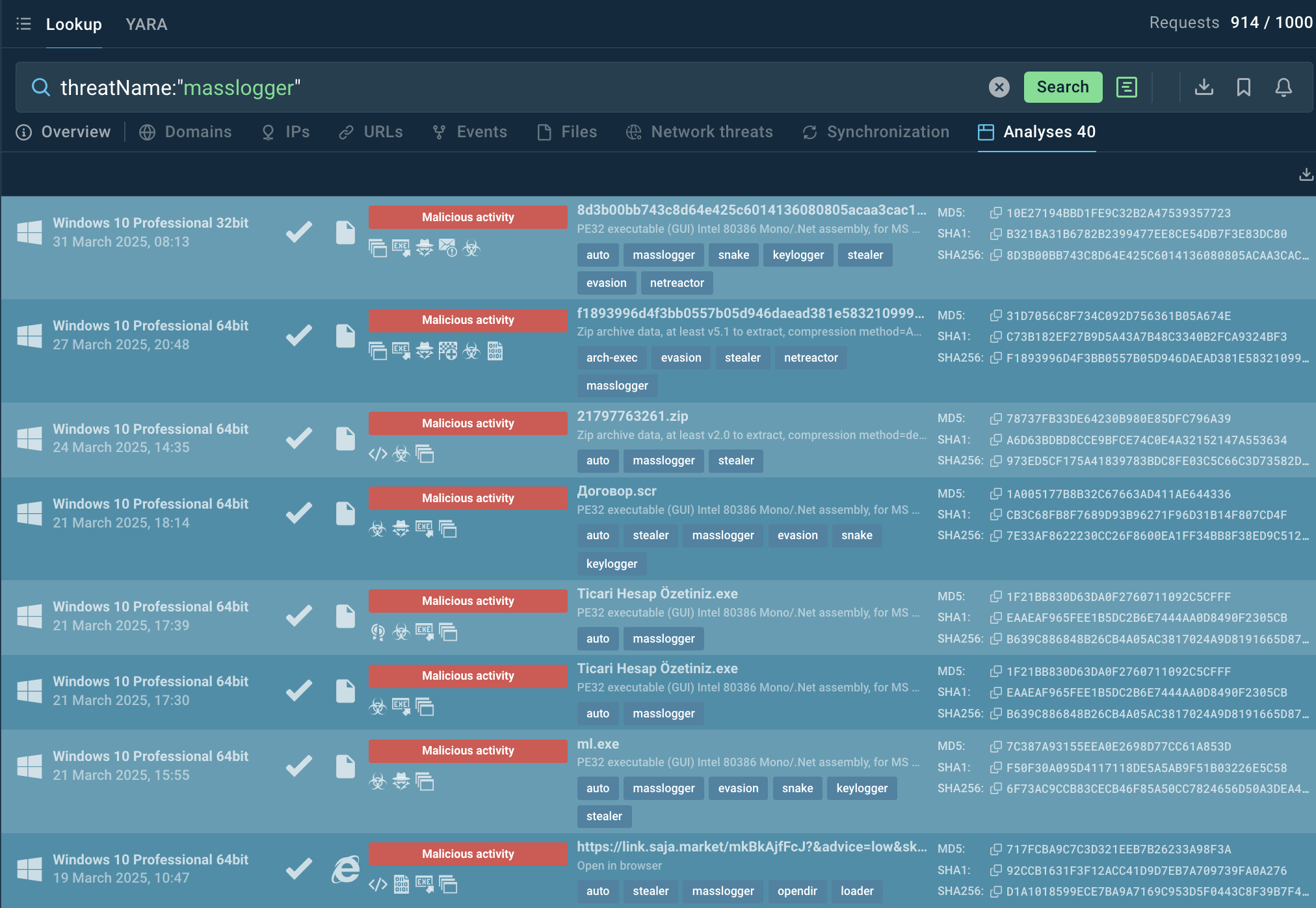 MassLogger samples submitted in the Sandbox and filtered via TI Lookup
MassLogger samples submitted in the Sandbox and filtered via TI Lookup
Explore each session to collect new IOCs and use them for further research. Enrich your monitoring and detection systems with the harvested indicators.
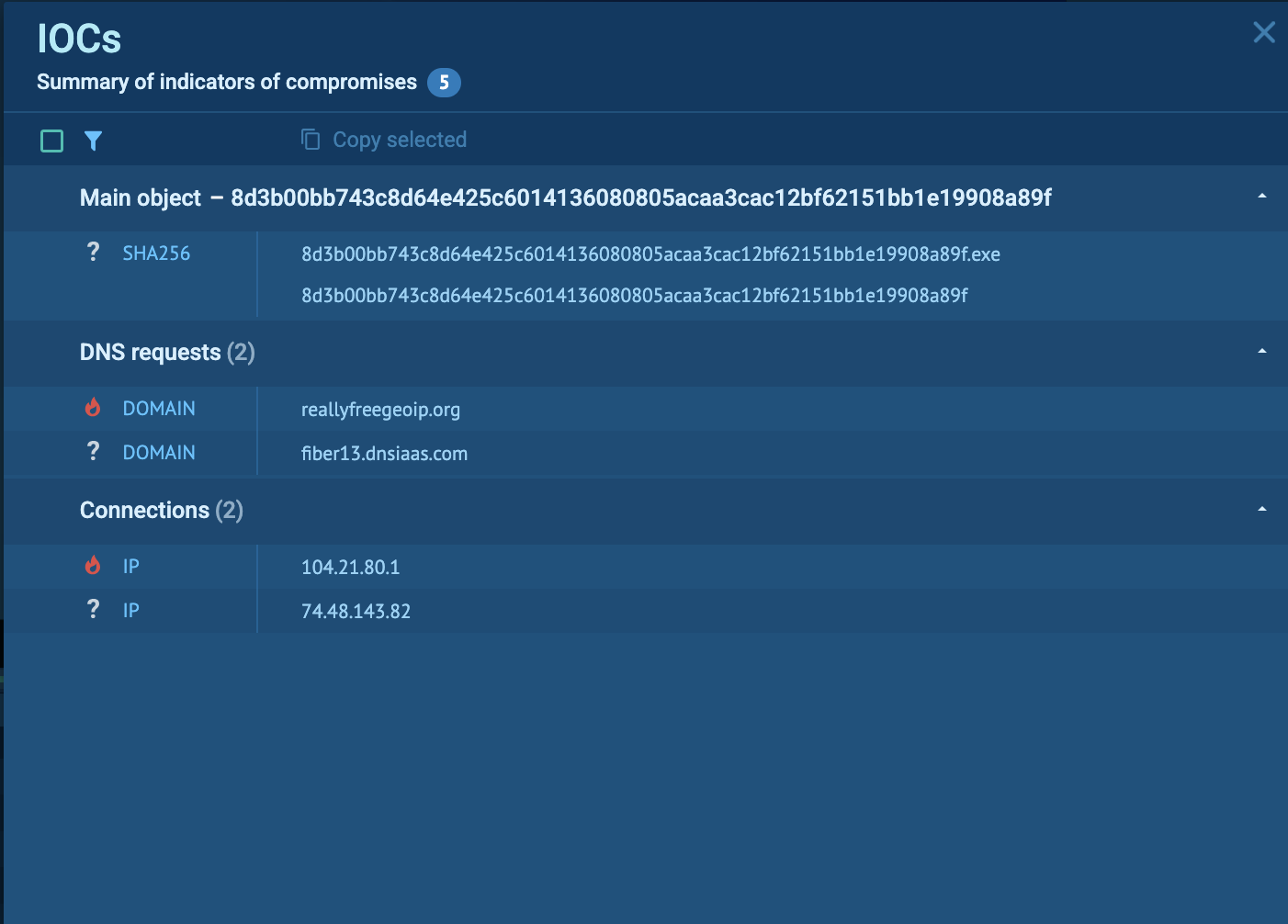 Click the IOC button in the top right block of the analysis view interface in the Sandbox
Click the IOC button in the top right block of the analysis view interface in the Sandbox
MassLogger’s combination of accessibility, evasion tactics, and broad data theft capabilities makes it a formidable threat. Its reliance on phishing and fileless execution demands robust email security and endpoint protection, while its stealth requires advanced threat intelligence to stay ahead of evolving campaigns.
By combining behavioral detection, network monitoring, and proactive intelligence-driven countermeasures, organizations can effectively mitigate its risks.
Start building your defenses against MassLogger with 50 requests in TI Lookup