Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Chaos ransomware is a malware family known for its destructive capabilities and diverse variants. It first appeared in 2021 as a ransomware builder and later acted as a wiper. Unlike most ransomware strains that encrypt data to extort payment, early Chaos variants permanently corrupted files, while later versions adopted more conventional encryption techniques.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2021
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2021
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Observed since 2021, Chaos Ransomware has undergone an eventful yet rapid evolution. At its early stage, it branded itself as “Ryuk .Net Ransomware Builder” and mimicked Ryuk ransom notes but actually had little in common with Ryuk. Later it became known as Yashma and was spotted functioning as a wiper, a remote access trojan (RAT) and DDoS botnet (Kaiji variant).
Written in Golang, it targets both Windows and Linux systems across various hardware architectures. Unlike traditional ransomware, Chaos often corrupts files beyond recovery rather than providing a decryption option, making it particularly dangerous.
The malware attacks critical infrastructure sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and energy, but also is a constant menace to SMEs with limited cybersecurity resources since its low-cost deployment via ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) models makes it accessible to less sophisticated cybercriminals.
Chaos ransomware employs common yet effective methods to gain initial access to networks:
Chaos is notable for:
Once inside, Chaos affiliates use tools like AngryIPScanner, Nmap, or PowerShell to map networks and identify high-value targets for encryption or data exfiltration.
Once deployed, Chaos ransomware follows a typical ransomware kill chain. It ensures persistence by leveraging system startup scripts, such as init.d or systemd, to execute malicious files (e.g., /boot/System.img.config) on boot. Then it encrypts files and may exfiltrate sensitive data for double-extortion tactics. A ransom note is generated, demanding payment in cryptocurrency.
The malware may attempt to disable recovery features and security tools and delete shadow copies. Evasion techniques include code obfuscation, packing and encryption, fileless execution in some versions, and use of legitimate certificates in rare cases. Polymorphism is also important: multiple Chaos builds differ in structure and behavior, frustrating signature-based antivirus tools.
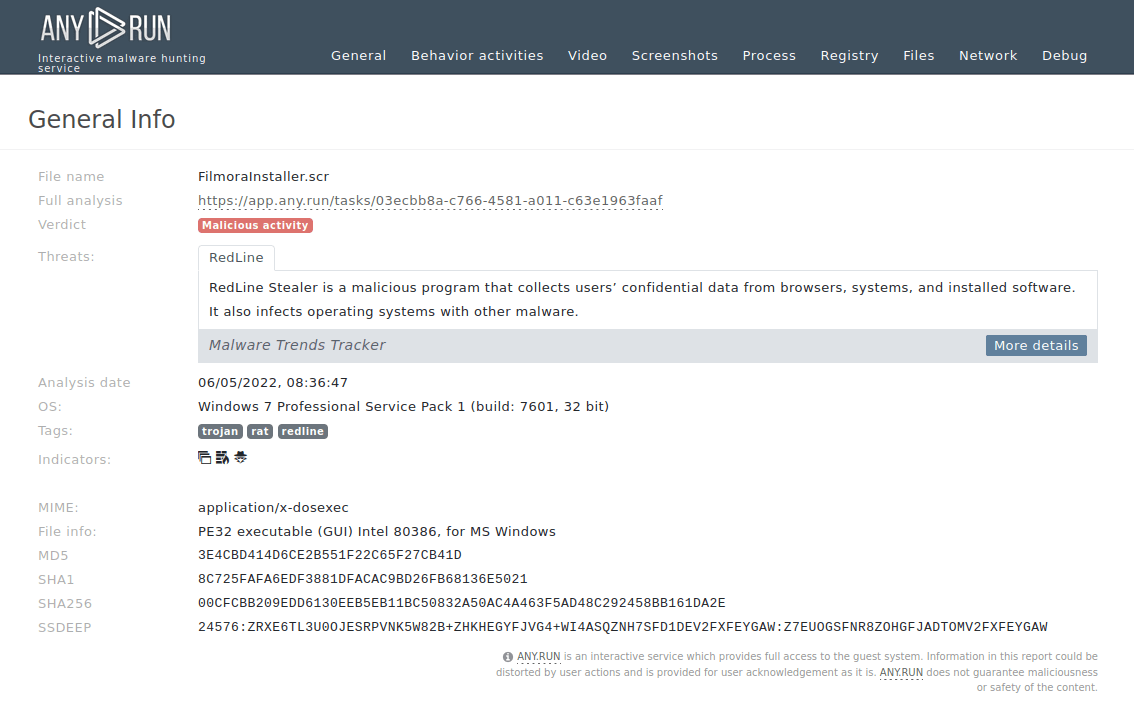
A sample of Chaos ransomware can be thoroughly studied in the safe environment of ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox with its processes, artifacts, and the typical kill chain.
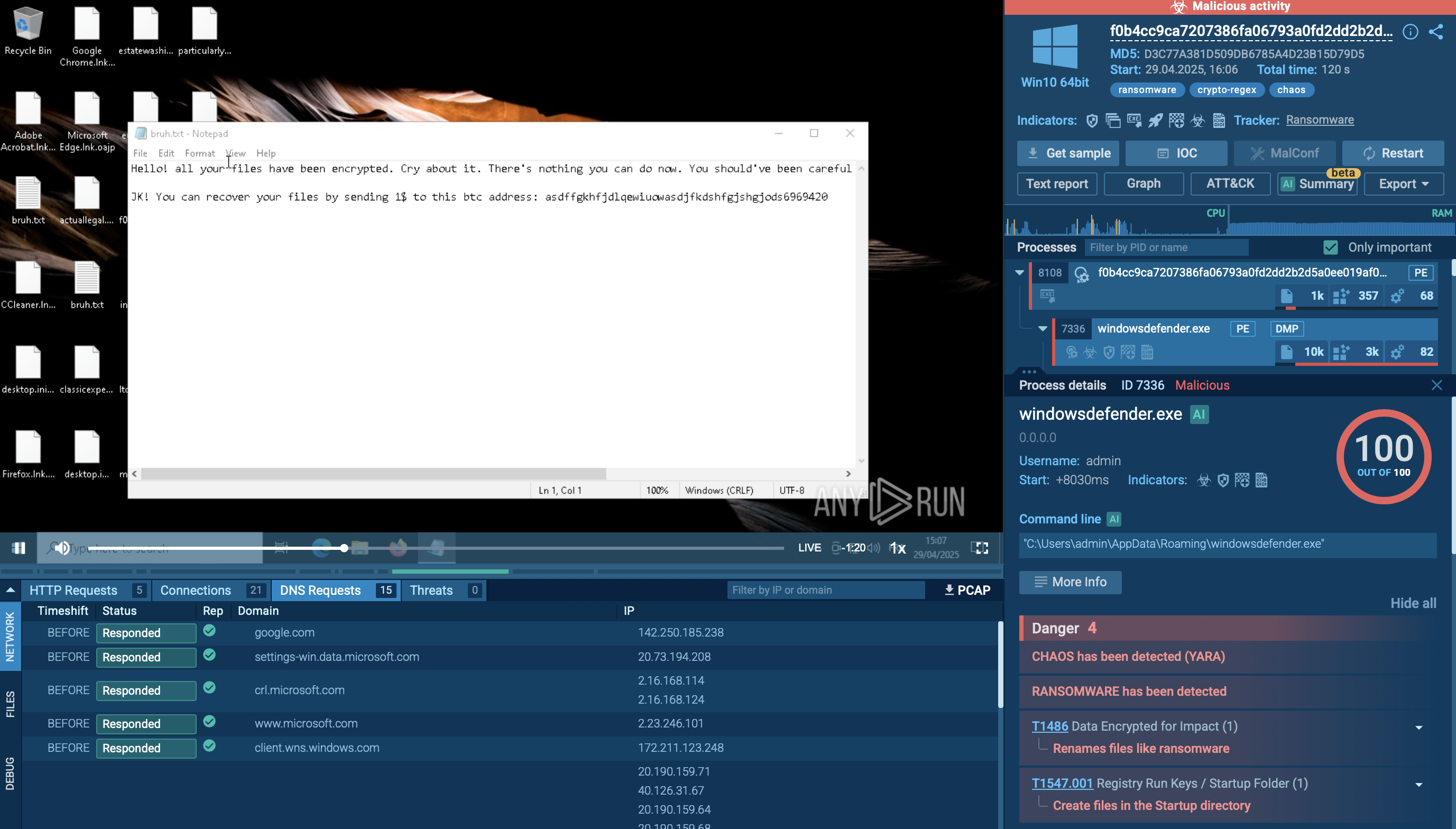 Chaos Ransomware sample in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
Chaos Ransomware sample in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
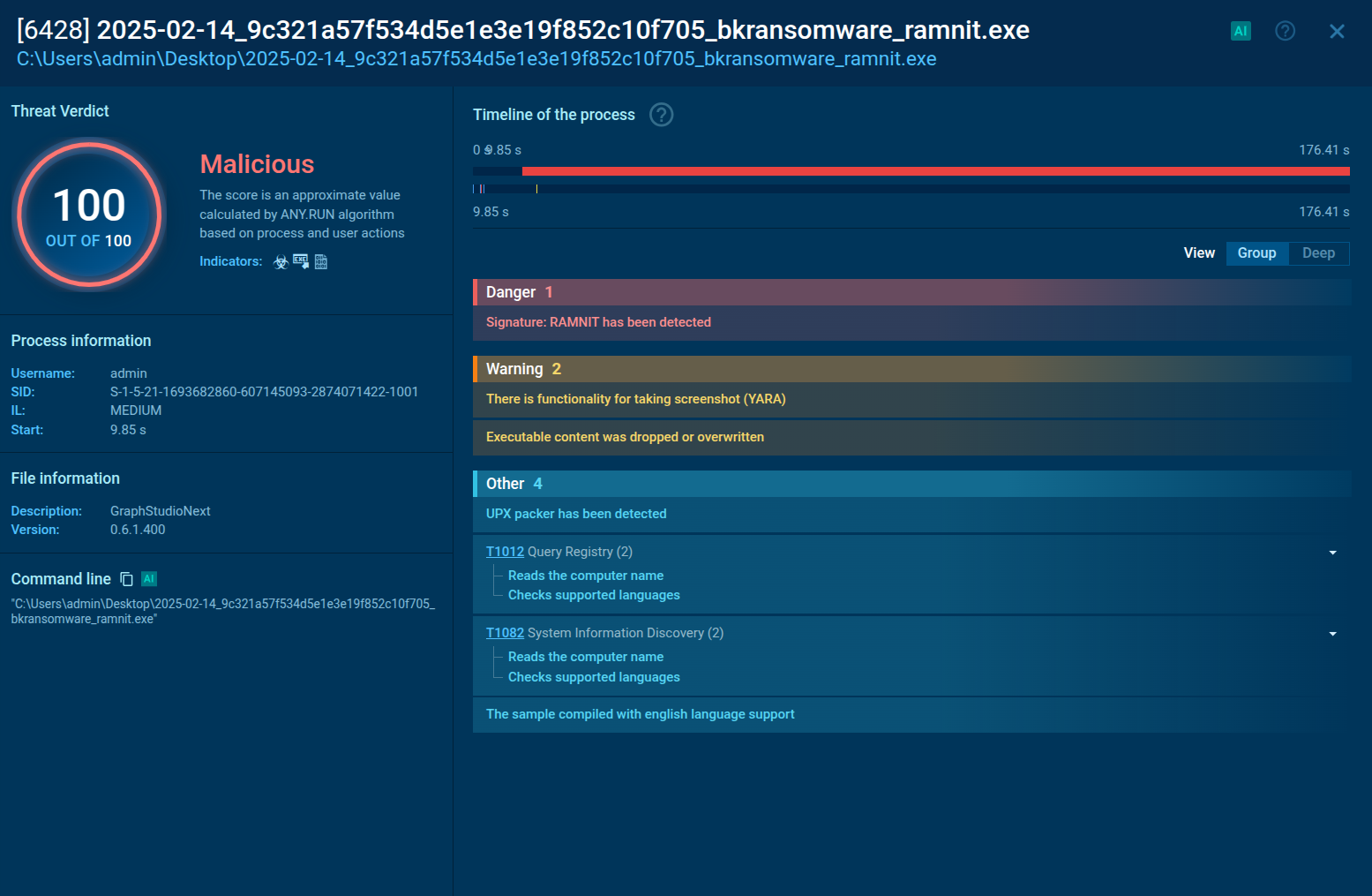
The execution chain of Chaos ransomware typically starts with phishing emails that carry malicious LNK shortcuts. Opening one of these files launches obfuscated PowerShell commands that retrieve a self-extracting archive from a remote server. The archive contains the Chaos ransomware executable together with loaders for additional malware. Once run, Chaos copies itself to a hidden location such as %AppData%\windowsdefender.exe and achieves persistence by placing a shortcut in the Windows Startup folder, guaranteeing execution after every reboot.
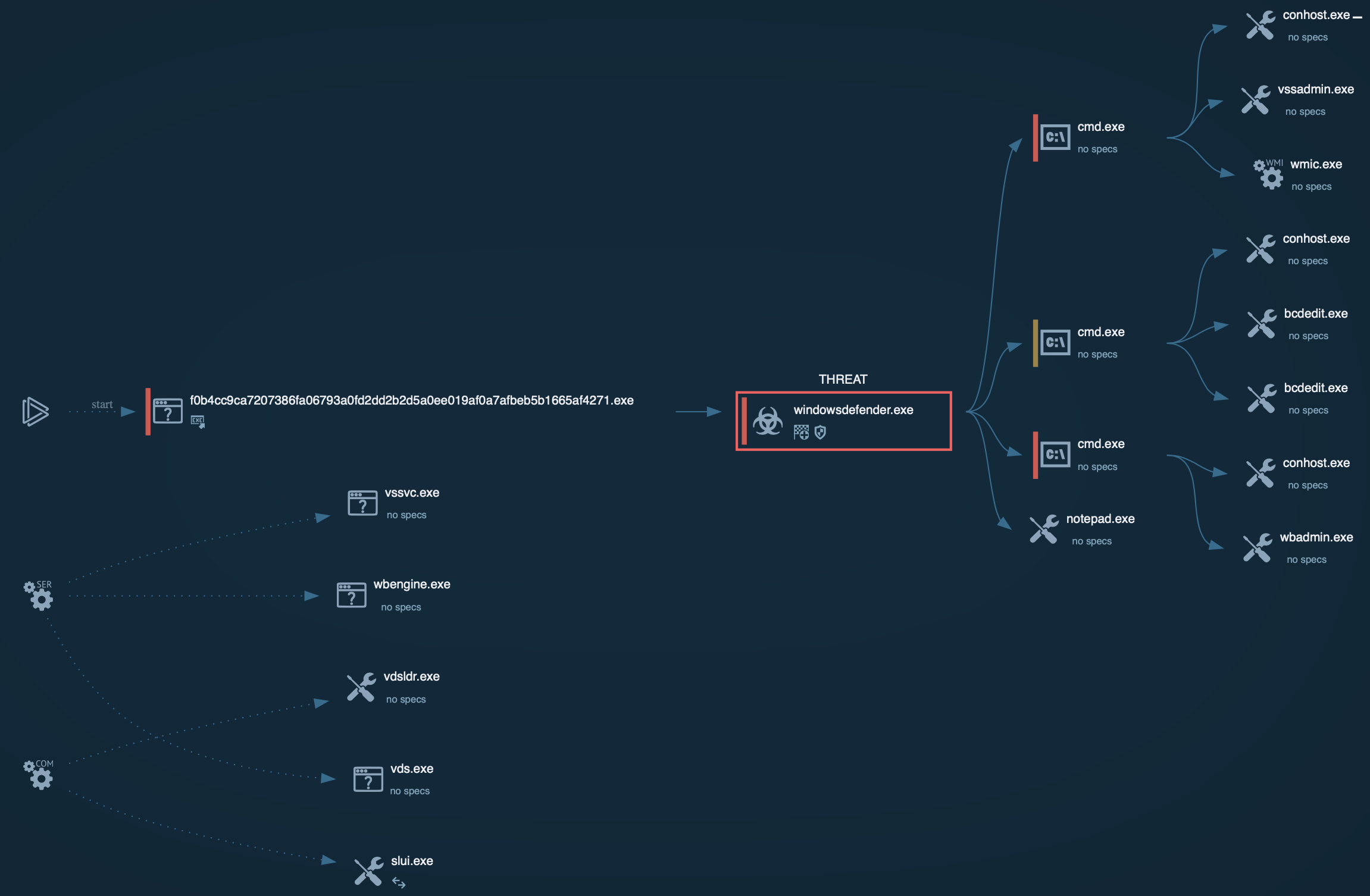 Chaos processes graph
Chaos processes graph
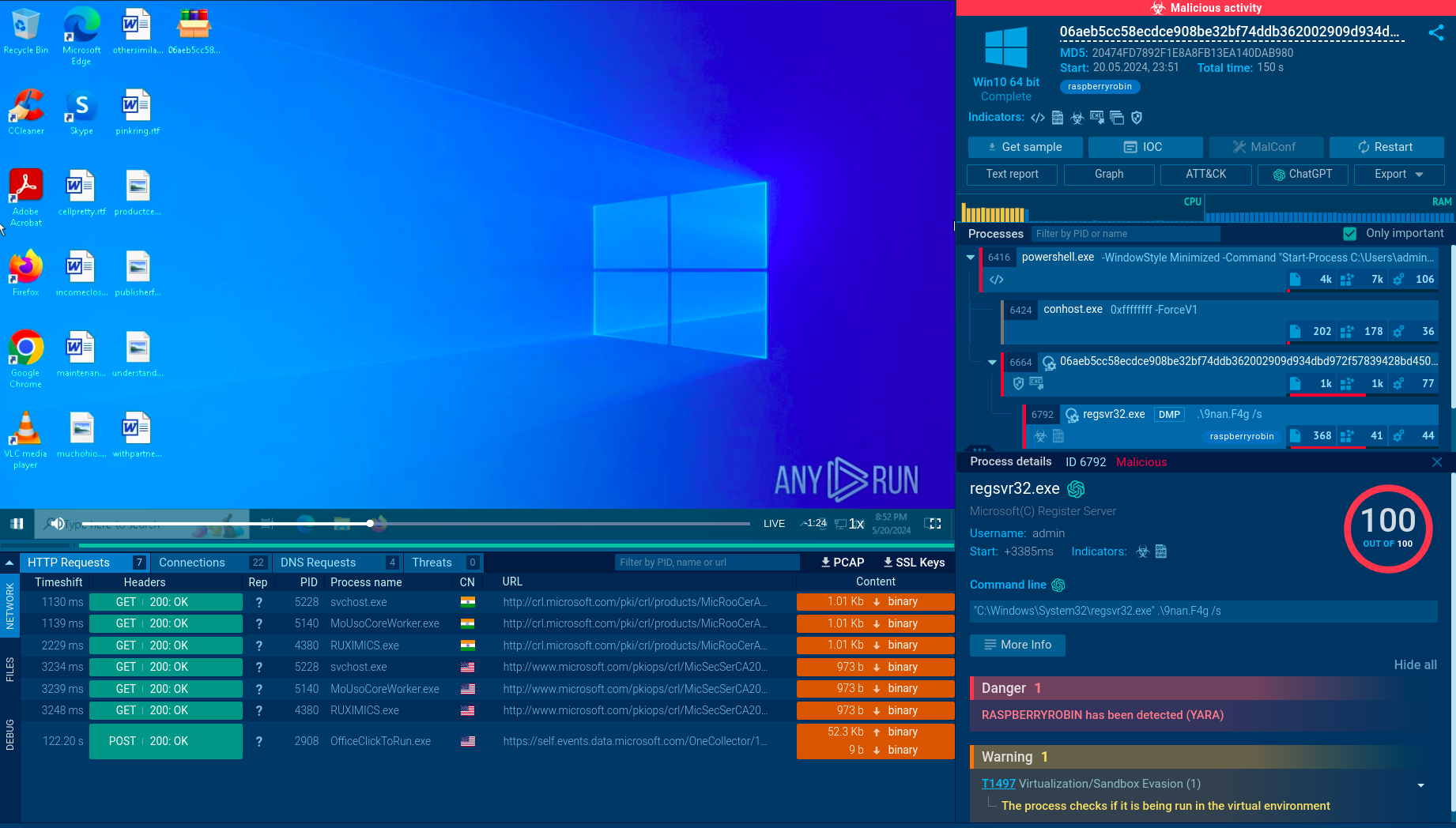
After persistence is in place, Chaos spawns a new process to encrypt the victim’s files. It targets specific extensions to maximize damage and uses vssadmin, WMIC, wbadmin, and bcdedit to delete shadow copies and disable other backup mechanisms. By scanning the file system and encrypting valuable data, it effectively blocks the user’s access. Chaos ransomware also changes the desktop wallpaper on the infected system.
When encryption is complete, Chaos may contact its command-and-control (C2) server to upload encryption keys and system details. This channel also delivers ransom-payment instructions and, if the attackers choose, additional payloads or a decryption key once payment is confirmed. Finally, the victim receives a ransom note outlining the steps required to regain access to their data.
Chaos ransomware is not associated with famous victim names because:
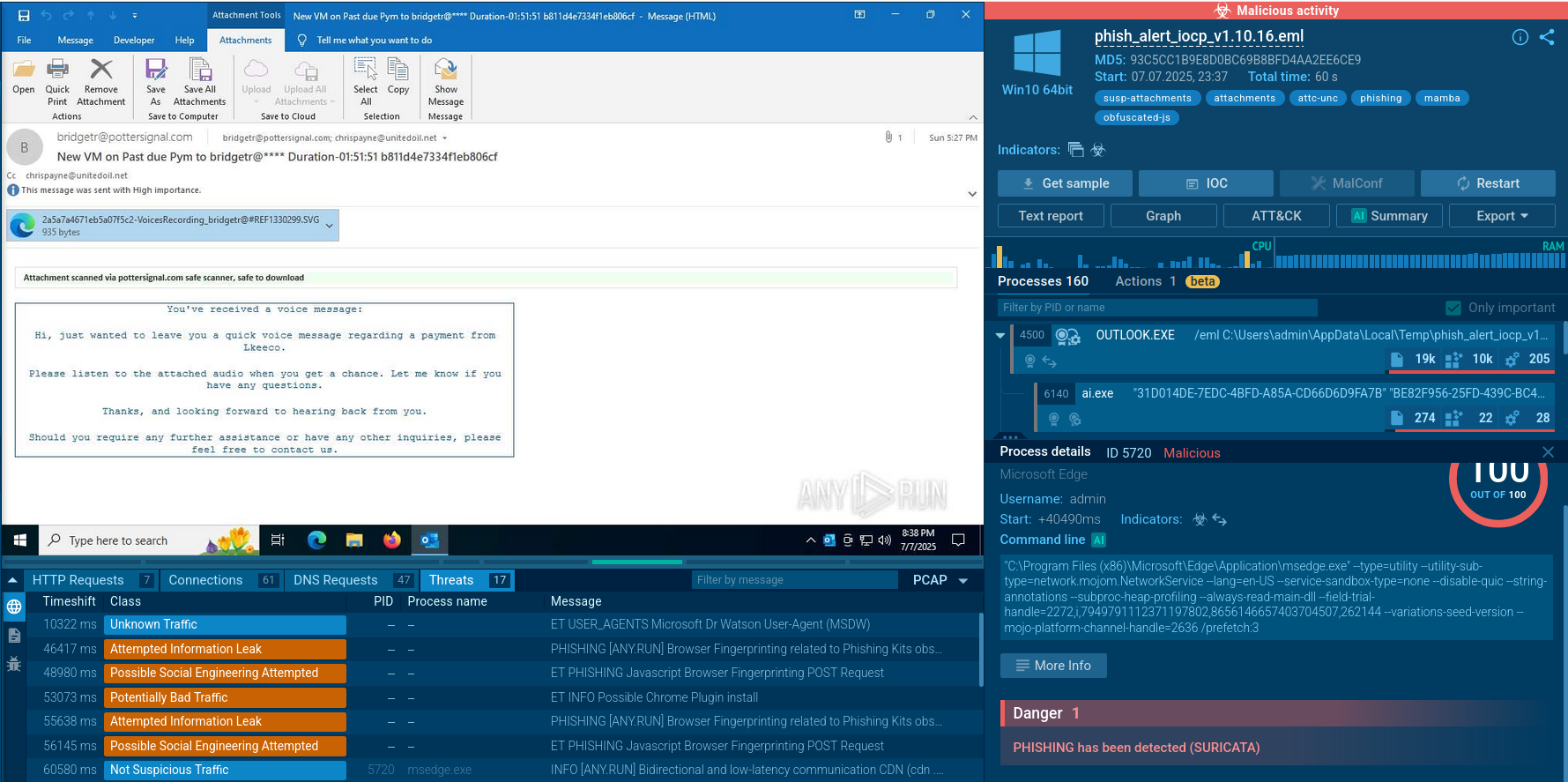
Threat Intelligence plays a key role in detecting and countering Chaos ransomware. IOCs must be gathered to enable monitoring and prevention: IP addresses and domains for C2 servers, file names and hashes.
Start with searching by the malware’s name via Threat Intelligence Lookup to find an assortment of fresh public analyses and harvest IOCs for tuning your security systems.
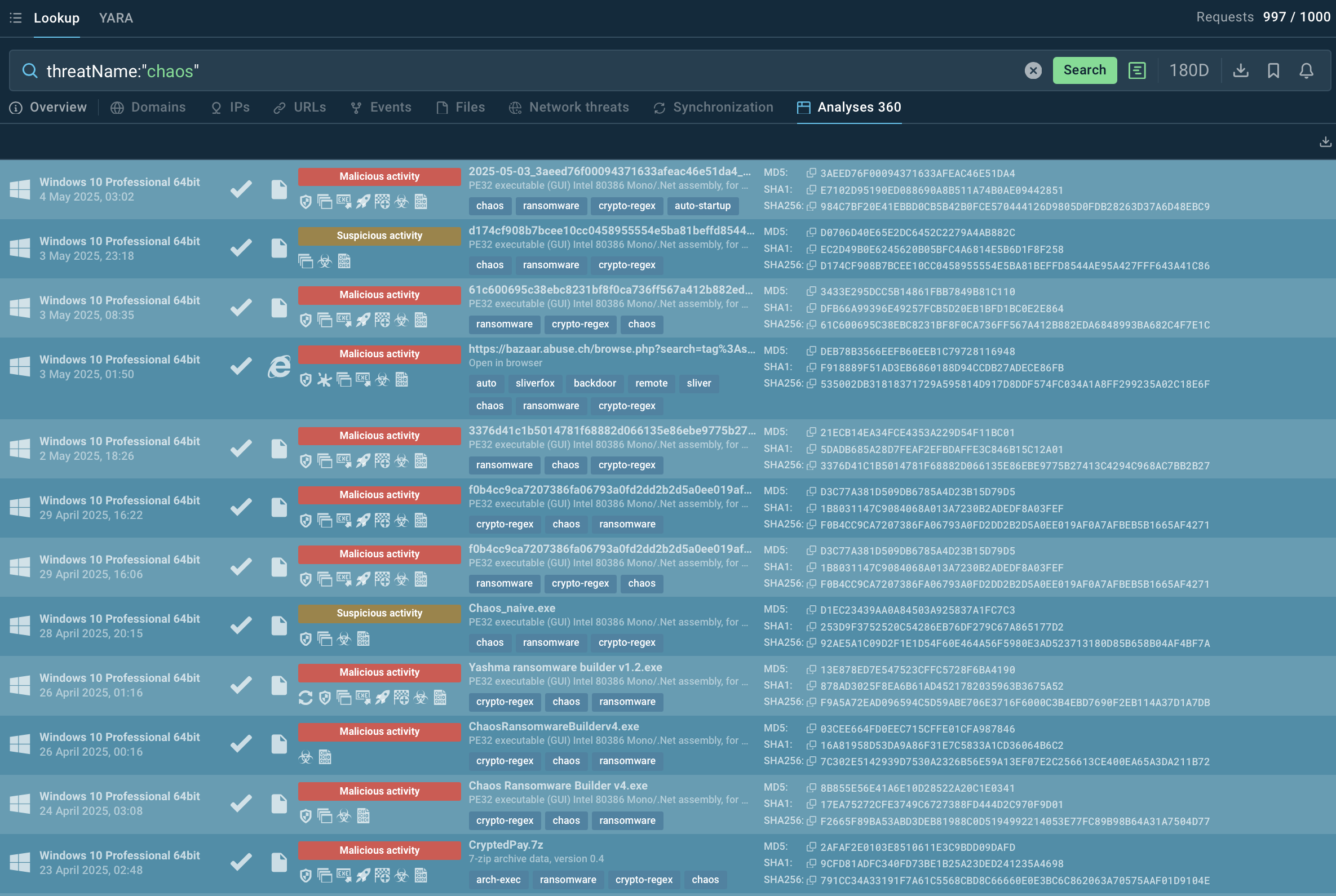 Recent Chaos samples dissected in the sandbox
Recent Chaos samples dissected in the sandbox
TI Lookup also provides sandbox reports containing behavioral analysis of Chaos samples. You'll be able to see how the use of vssadmin, bcdedit, and wbadmin to remove backups, overwriting of small files, unusual PowerShell or script activities trigger detection of Chaos variants.
Chaos ransomware is a multifaceted threat that combines ransomware, RAT, and DDoS capabilities. It is a significant risk to diverse industries, particularly those with unpatched systems or sensitive data. Its ability to infiltrate networks via phishing, exploits, and fake updates, coupled with advanced evasion techniques like port-hopping and binary obfuscation, requires robust detection and response strategies.
By leveraging threat intelligence, anomaly-based detection, and proactive countermeasures like Zero Trust and chaos engineering, organizations can mitigate Chaos’s impact.
Employ Threat Intelligence Lookup to counter Chaos: start with 50 test requests.