Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Fog is a ransomware strain that locks and steals sensitive information both on Windows and Linux endpoints. The medial ransom demand is $220,000. The medial payment is $100,000. First spotted in the spring of 2024, it was used to attack educational organizations in the USA, later expanding on other sectors and countries. Main distribution method — compromised VPN credentials.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2024
First seen
:
|
13 October, 2025
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2024
First seen
:
|
13 October, 2025
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Fog is a ransomware that was first noticed in April 2024 actively using compromised virtual private network (VPN) credentials to gain access to organization networks. It started with attacking educational and recreational sectors, later expanding on financial and manufacturing industries.
Fog turned out to be capable of encrypting files with alarming speed: the shortest time observed was 2 hours after appearing in the network. It encrypts data on the device and any mounted shares adding extensions such as .fog, .ffog, .flocked to the affected files.
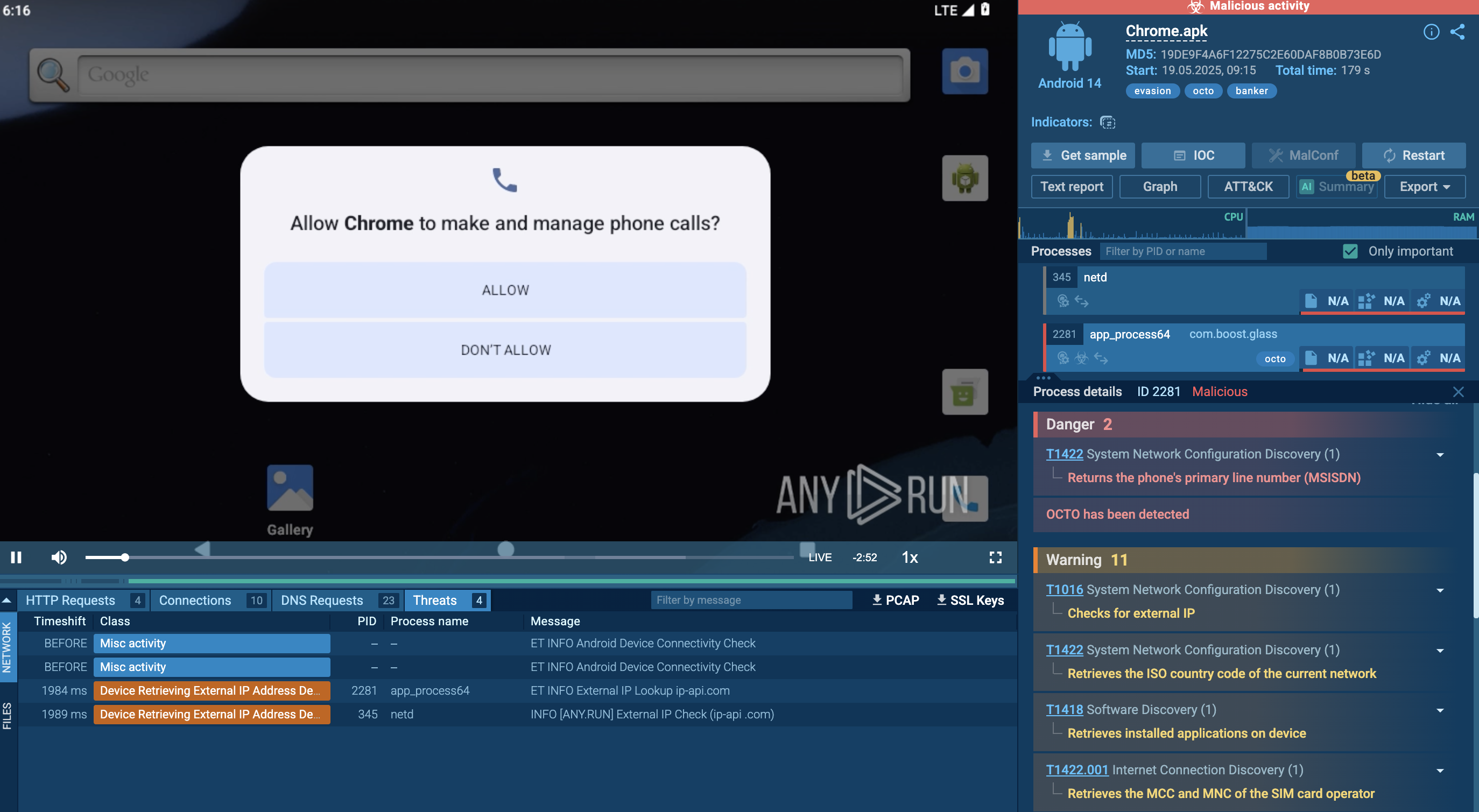
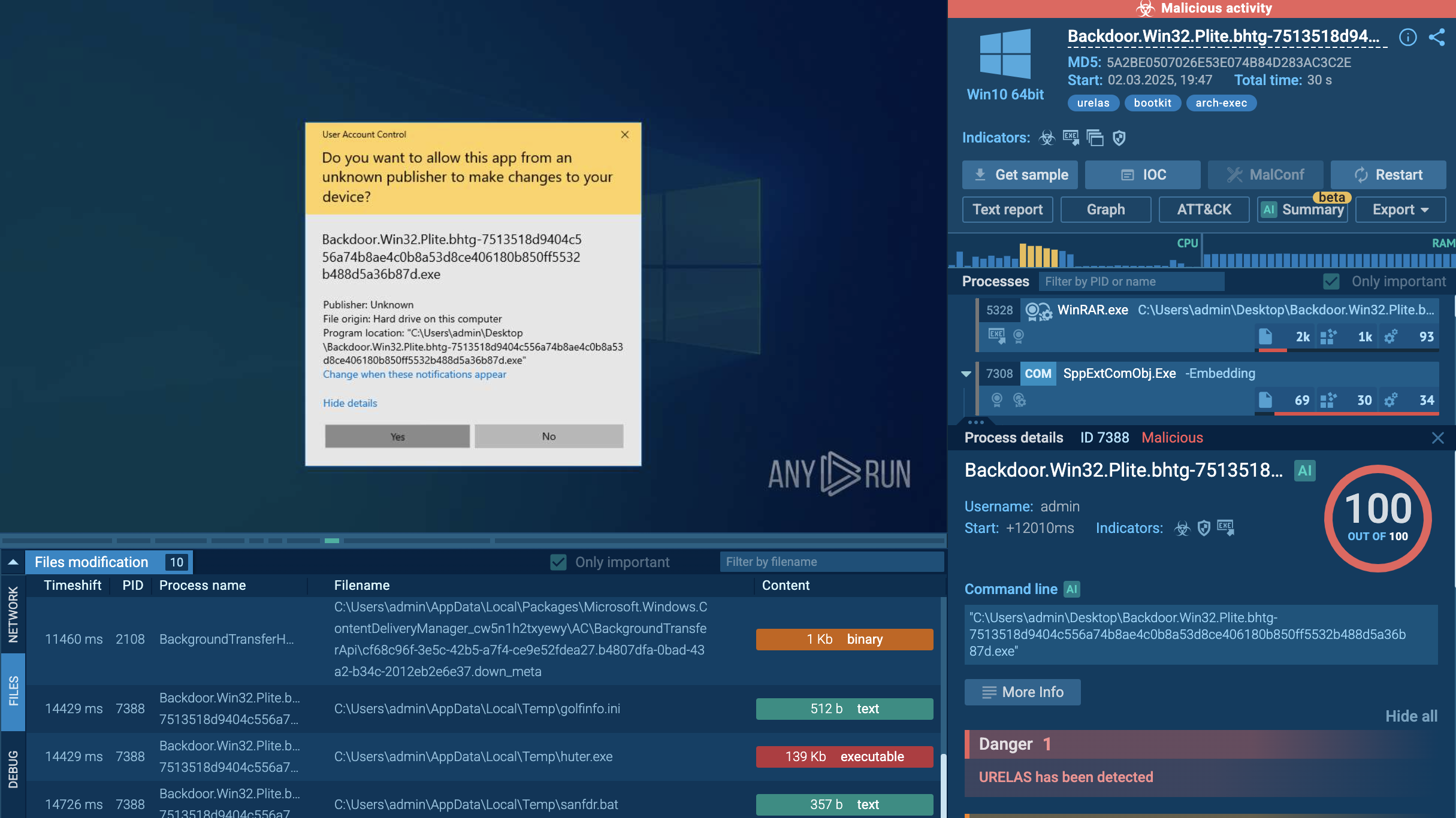
 Fog analysis session the ANY.RUN sandbox and its ransom note
Fog analysis session the ANY.RUN sandbox and its ransom note
After infiltrating a network, Fog explores it to understand its topology and identify critical assets. Further it escalates privileges and moves laterally across the network to establish a strong foothold into it. Before encryption, valuable data gets exfiltrated to be used for double extortion tactics.
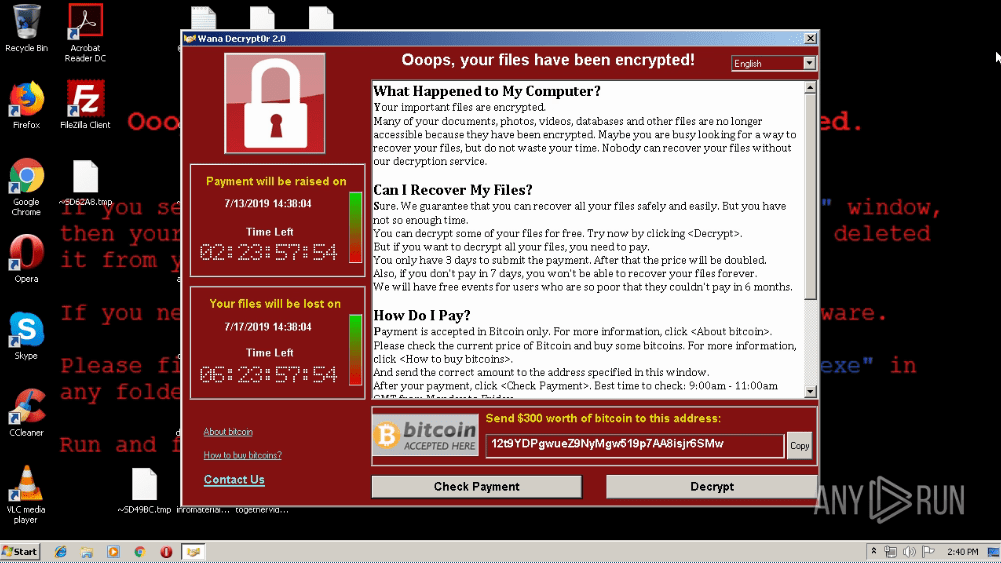
The malware generates a .txt note demanding a ransom for decrypting files and avoiding the publication of sensitive data.
Fog counters recovery efforts, deletes system volume shadow copies, and avoids detection both by security software and by users observing disruptions in the system’s functioning.
Fog is equipped with extensive capabilities:
To see how Fog infects a system, we can upload its sample to ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox, which provides a safe virtual environment for detonating and analyzing malware and phishing threats.
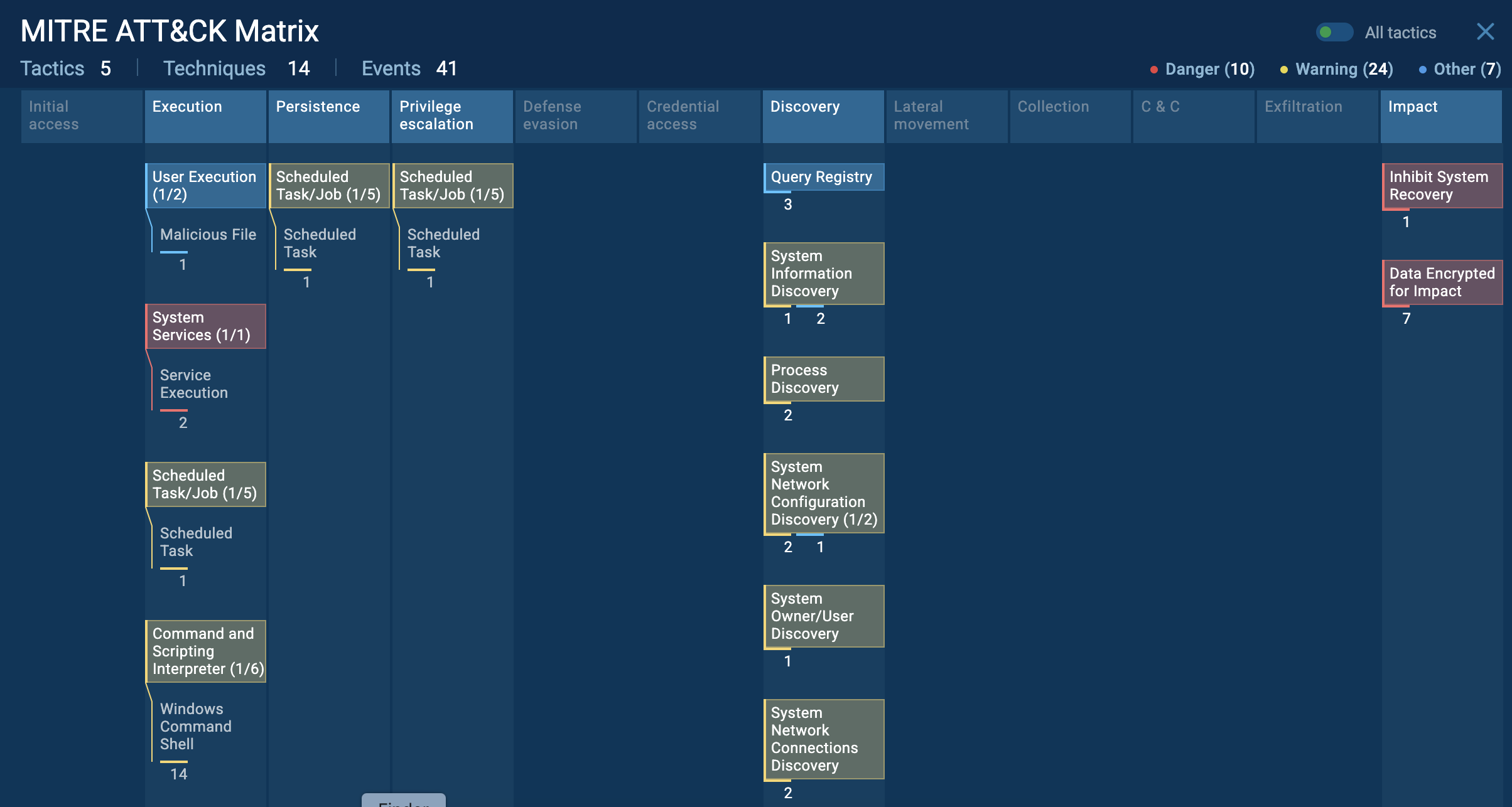 TTP matrix of a Fog attack via Interactive Sandbox
TTP matrix of a Fog attack via Interactive Sandbox
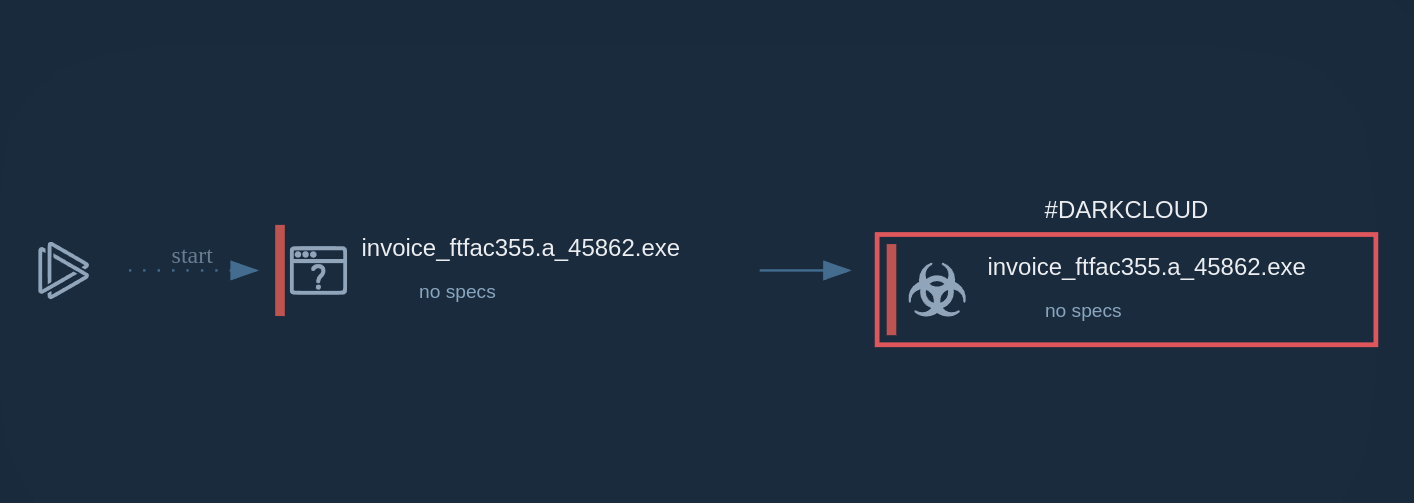
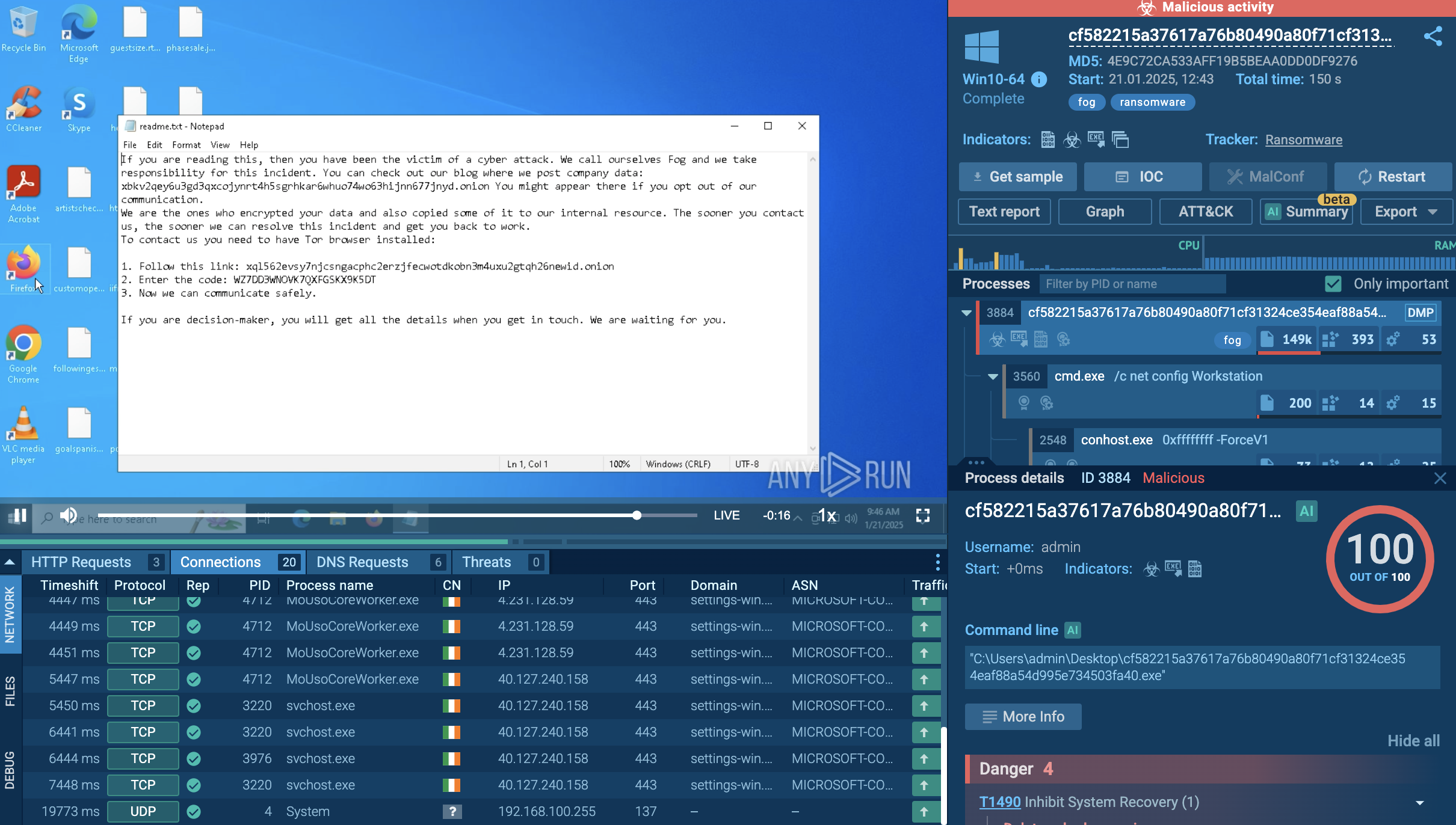
Fog ransomware operates via a sophisticated execution chain that begins with the initial compromise of a target system. Attackers gain access by exploiting known vulnerabilities or purchasing compromised credentials from Initial Access Brokers.
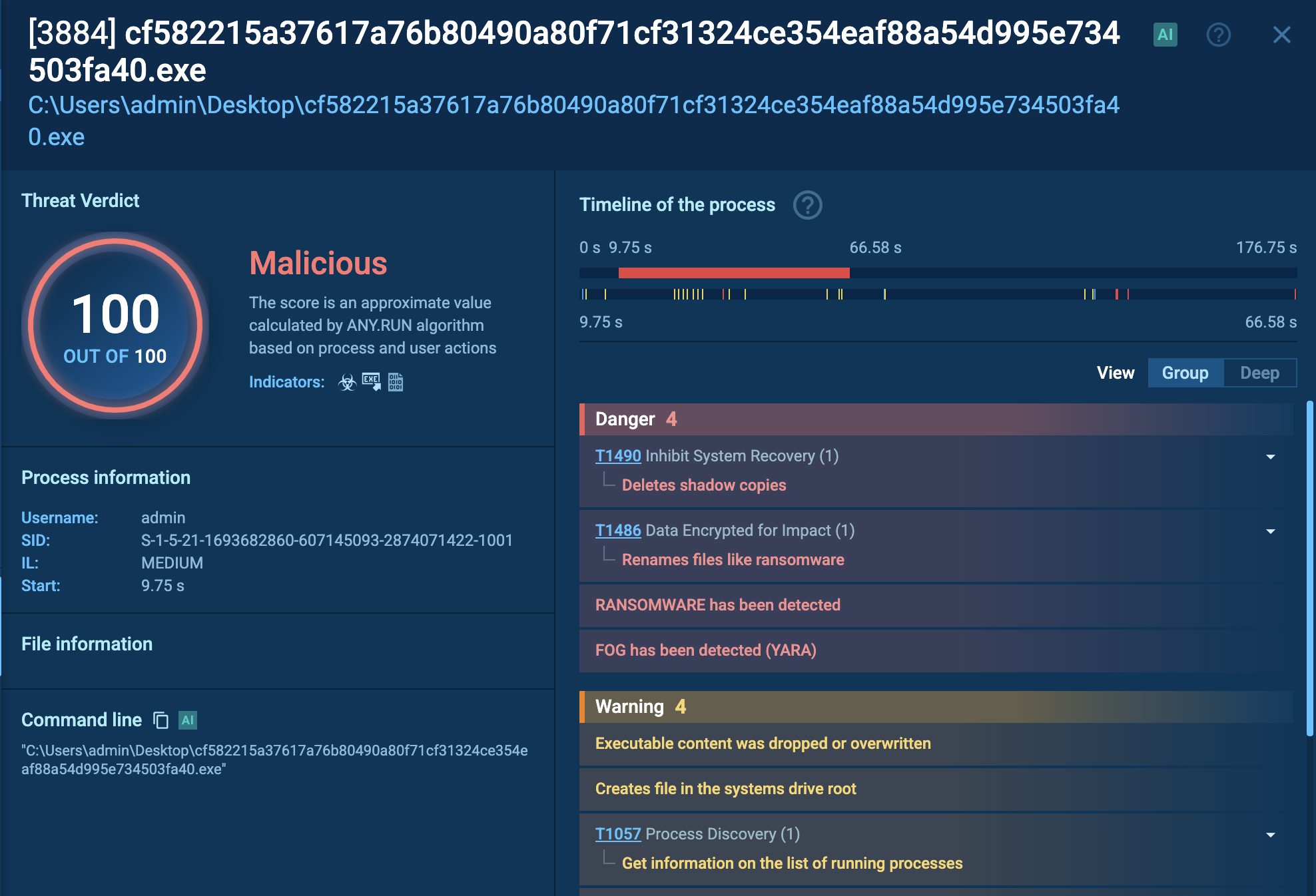 Fog’s malicious process that encrypts data and deletes copies viewed in ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Fog’s malicious process that encrypts data and deletes copies viewed in ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Once inside the network, they conduct reconnaissance, scanning for valuable data and identifying potential encryption targets. This phase is crucial because it allows the attackers to map out the network and establish lateral movement paths to propagate the ransomware effectively.
Once executed, the malware begins encrypting files on both the local system and any mounted shares, appending extensions such as .fog, .ffog, or .flocked, making it evident the files have been compromised.
Additionally, it maintains a whitelist of files and directories to avoid rendering the system unusable, which could alert victims to its presence before it completes encryption. This careful planning allows the attackers to maximize damage while minimizing detection.
As part of its protocol, Fog generates a ransom note named readme.txt, which is distributed across affected systems. This note typically includes an introduction to the Fog group, details about the encryption process, and instructions on how victims can contact the attackers and arrange payment.
The speed at which Fog ransomware can execute its entire chain — from initial access to file encryption — is alarmingly rapid; some reports indicate that the process can occur in as little as two hours.
Gather Fog’s artifacts, IOCs, and TTPs to arm your defenses with fresh data backed by a community of security experts. You can get a list of sandbox reports featuring the most recent analyses of Fog samples.
TI Lookup from ANY.RUN supports over 40 search parameters, including IPs, domains, and file names.
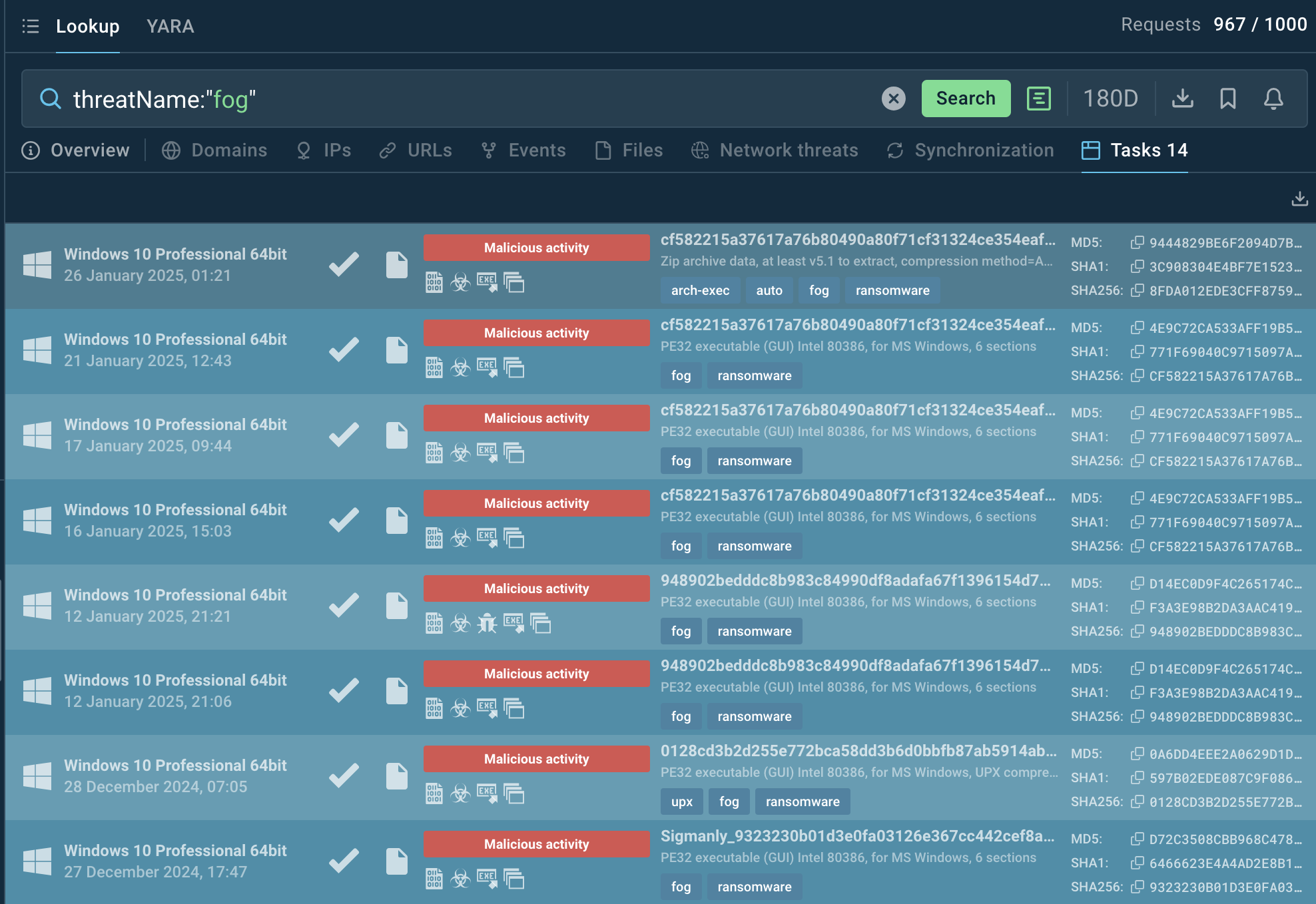 Fog analysis sessions listed by ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup
Fog analysis sessions listed by ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup
Use the threat name or related data like hash values or network connections as search queries to understand the malware's behavior.
For infiltration, it uses compromised VPN credentials leaked from at least two different VPN gateway vendors and bought on the dark market, weak SSH passwords, or misconfigured network services. Brute force attacks against remote desktop protocol (RDP) are also employed.
Use threat intelligence services like TI Lookup by ANY.RUN to gather relevant IOCs for setting up early detection and alerts in your security infrastructure.
Fog is a dangerous and sophisticated ransomware that promises companies operational disruption, financial losses and long-term damages to their business.
It accesses corporate networks by exploiting compromised VPN credentials. Fog strikes rapidly, and preventive measures must be taken to avoid an attack. Keep your security systems up to date and fine-tuned against topical attacks, use tools like ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup and Sandbox to gather threat intelligence and enforce your protection.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account to strengthen your security posture!