Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Ramnit is a highly modular banking trojan and worm that evolved from a file-infecting virus into a powerful cybercrime tool. It specializes in financial fraud, credential theft, remote access, and malware delivery, being a serious threat to businesses and individuals. First spotted in 2010, Ramnit became popular after the 2014 takedown of the GameOver Zeus botnet, as cybercriminals sought alternatives for banking fraud.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2010
First seen
:
|
20 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 May, 2010
First seen
:
|
20 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 857
857
 0
0

 508
508
 0
0

 2788
2788
 0
0
Ramnit emerged in 2010 as a computer virus, initially infecting Windows executable files (EXE, DLL), HTML files, and later expanding to target other file types. Over time, it has evolved to include the functions of a banking trojan, inter alia by incorporating elements from the Zeus banking trojan's source code in 2011.
Now it focuses on financial data theft and is used for financial fraud, credential theft, remote access, and botnet operations. Besides banking credentials, it is able to steal information for various online accounts.
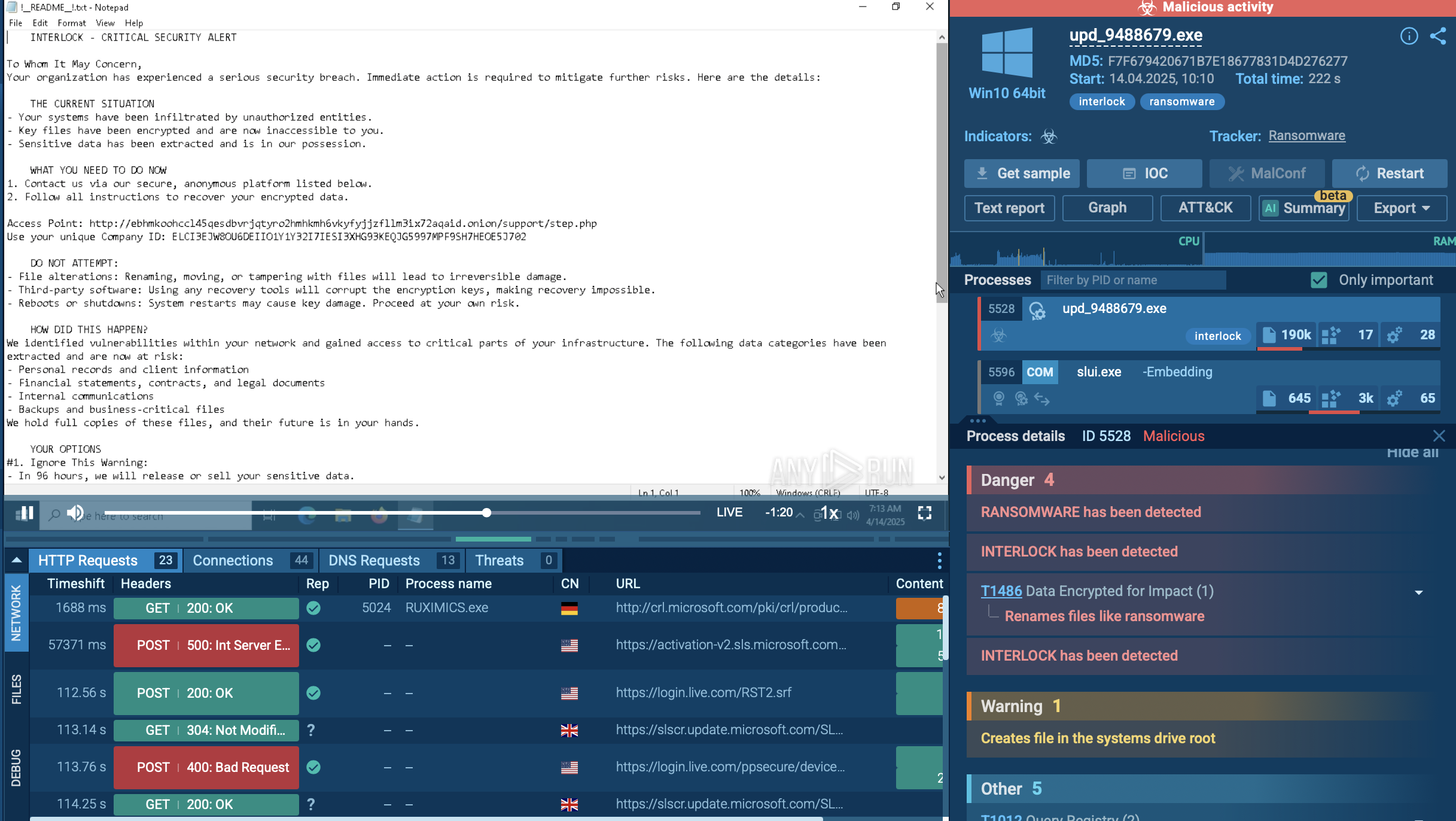
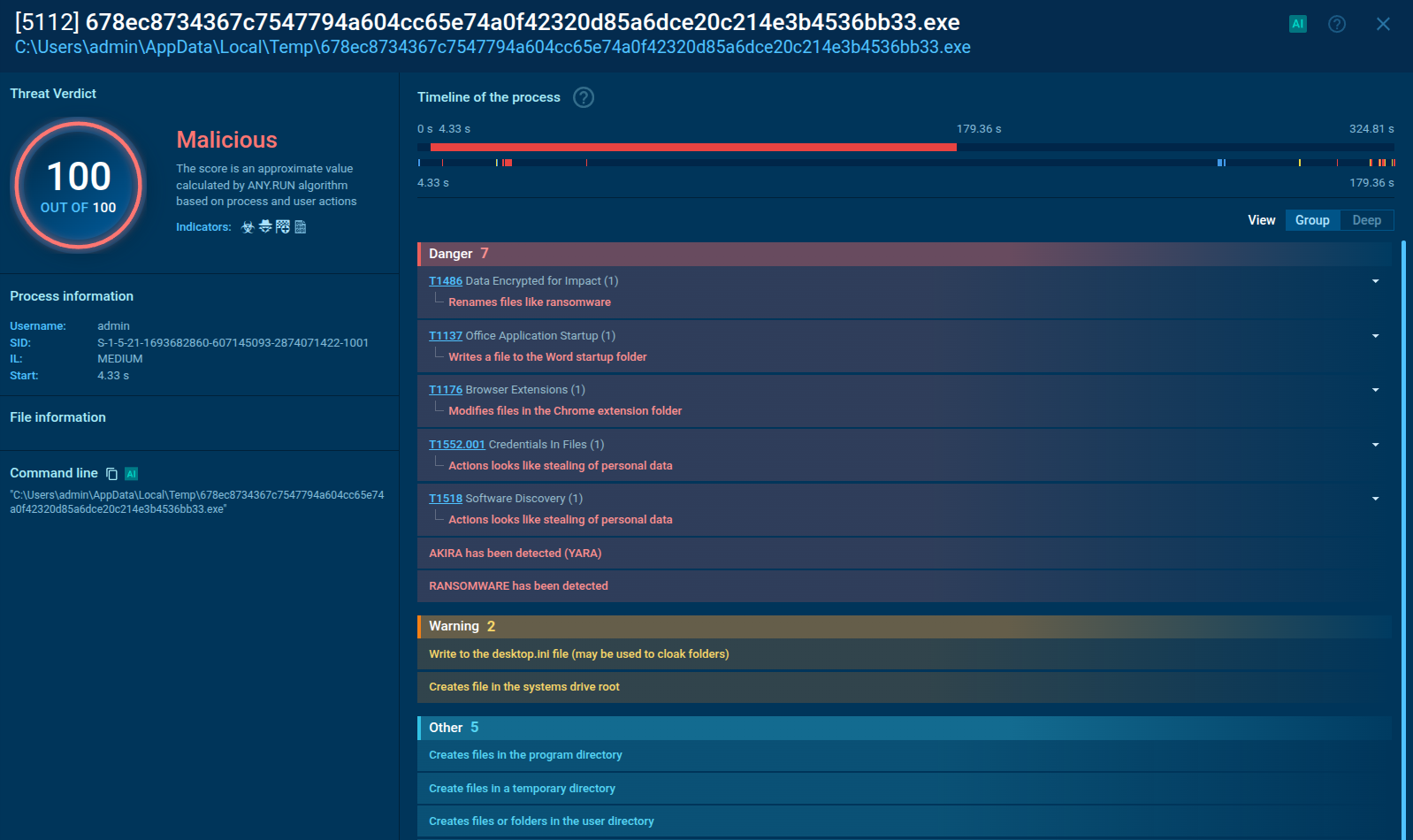
 Analysis of Ramnit malware in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Analysis of Ramnit malware in the ANY.RUN sandbox
View Ramnit analysis inside ANY.RUN's Interactive sandbox
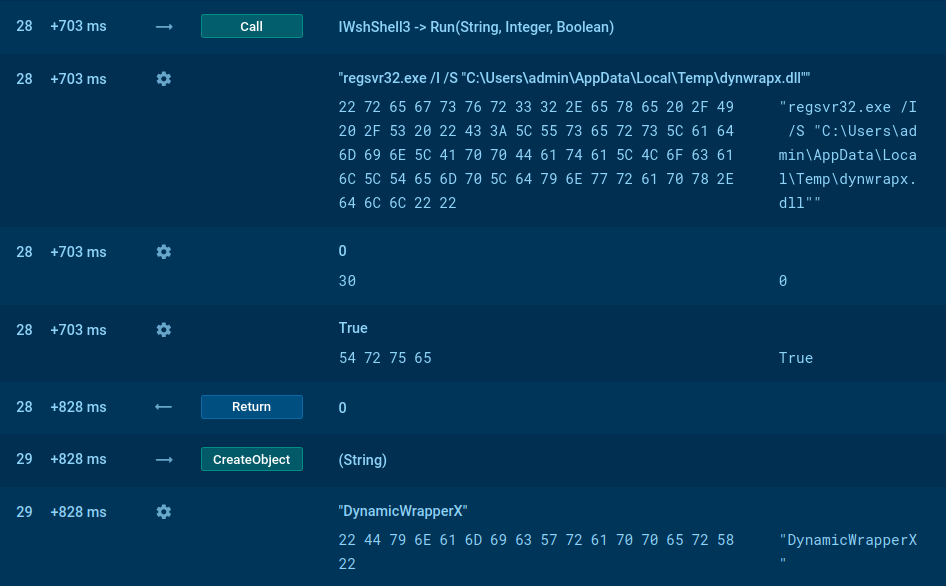
Ramnit infects and modifies files such as .dll, .exe, and .html on a system to spread itself and establishes backdoors for other malware, providing remote access to attackers. The infected endpoints are added to a botnet for coordinated attacks or further distribution of malware.
Ramnit allows attackers full system control over a device and further propagates through networks, escalating from a single machine infection to an organizational one.
Ramnit is equipped with extensive malicious capabilities:
Ramnit employs advanced evasion tactics to bypass detection: modifies its code to change its signature with each infection (polymorphism); runs within legitimate system processes (e.g., explorer.exe, svchost.exe); detects virtual machines; encrypts C2 traffic to avoid network detection; continuously generates new C2 domains.
To observe Ramnit’s activities in real time, we can detonate it in the safe environment of ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox.
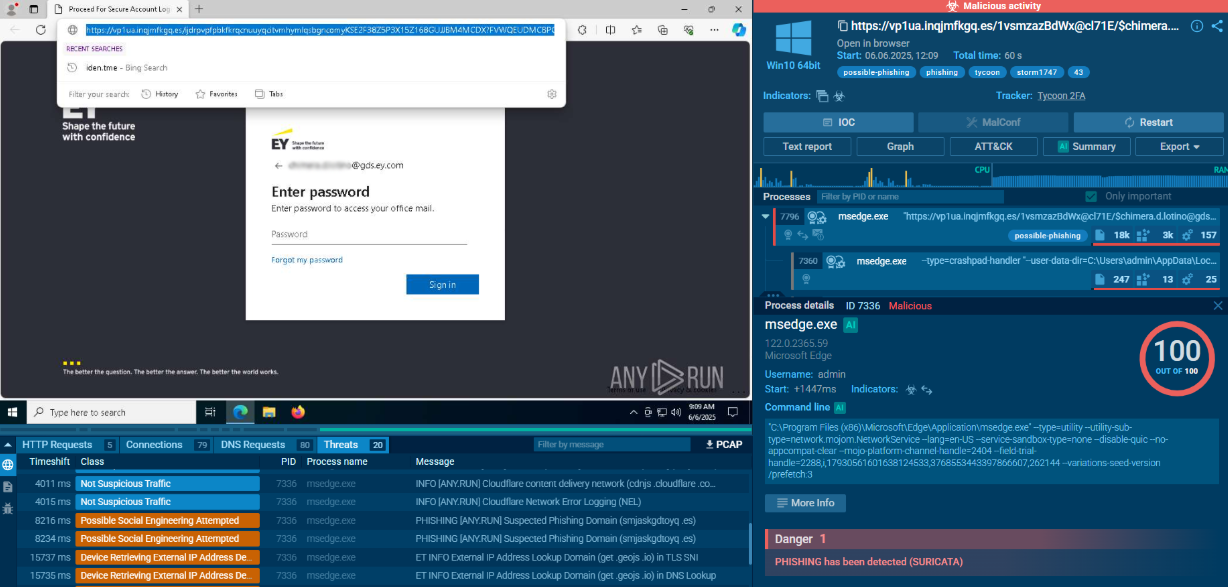
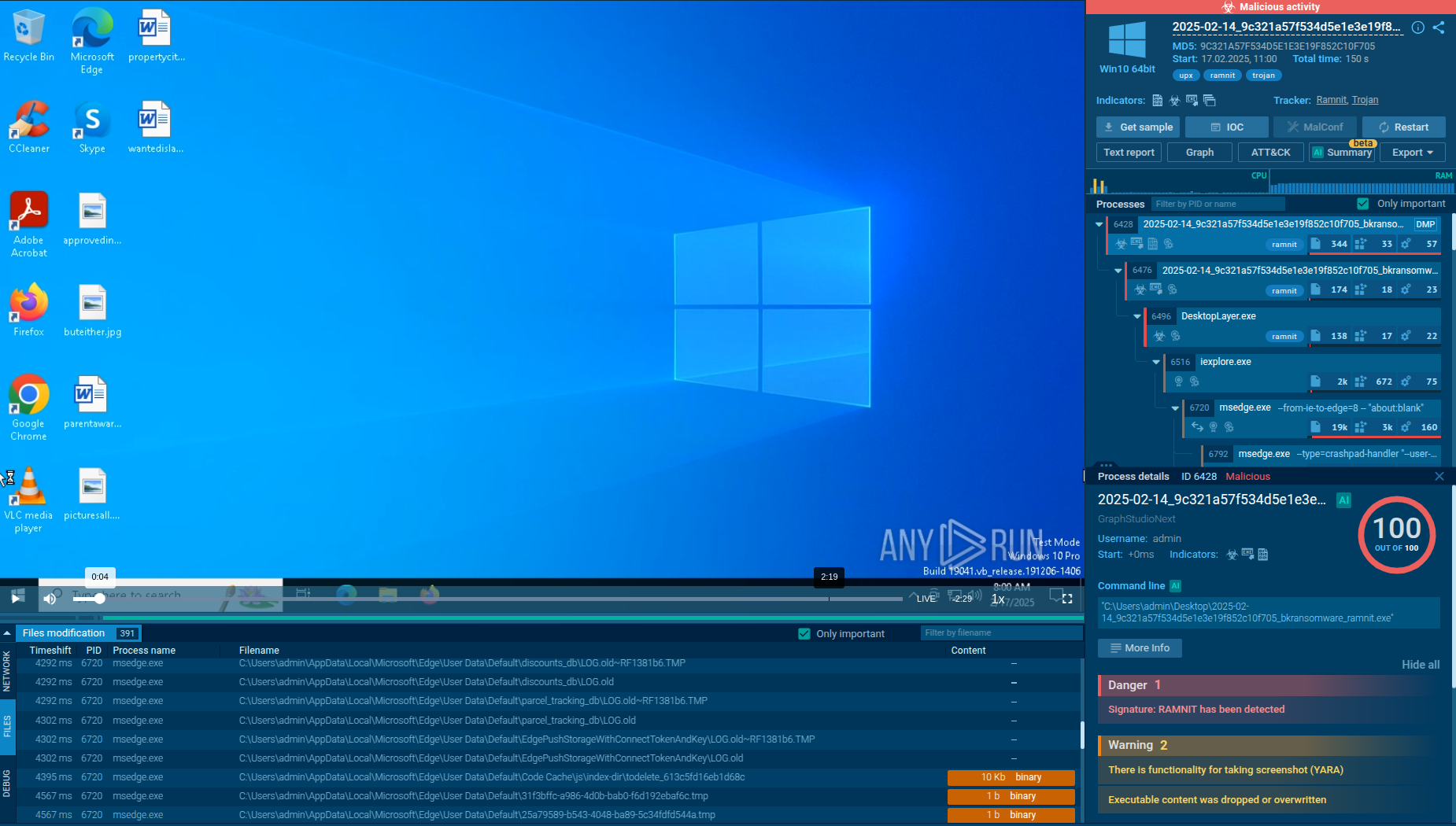
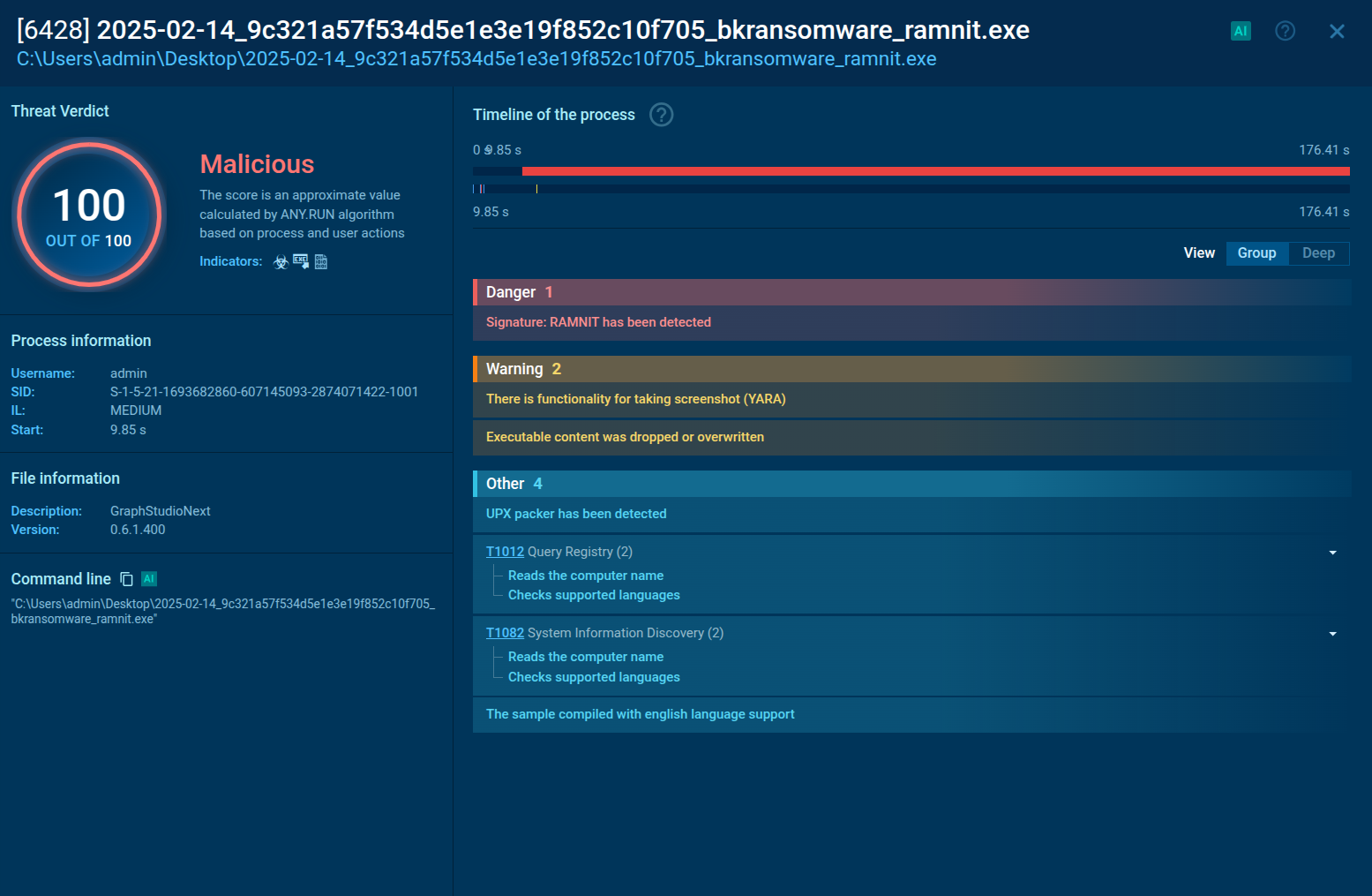 Analysis of a Ramnit process in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Analysis of a Ramnit process in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Ramnit typically spreads via phishing campaigns that use multi-stage malware. When a victim opens the initial payload, it downloads additional components and installs the Trojan. Once active, Ramnit harvests financial credentials and other sensitive data (e.g., social media and email).
After installation, Ramnit connects to its command and control (C&C) servers and often uses a domain generation algorithm (DGA), which creates random domain names to evade DNS blocklists. The C&C server uses the same DGA to register and manage these domains, making Ramnit harder to disrupt.
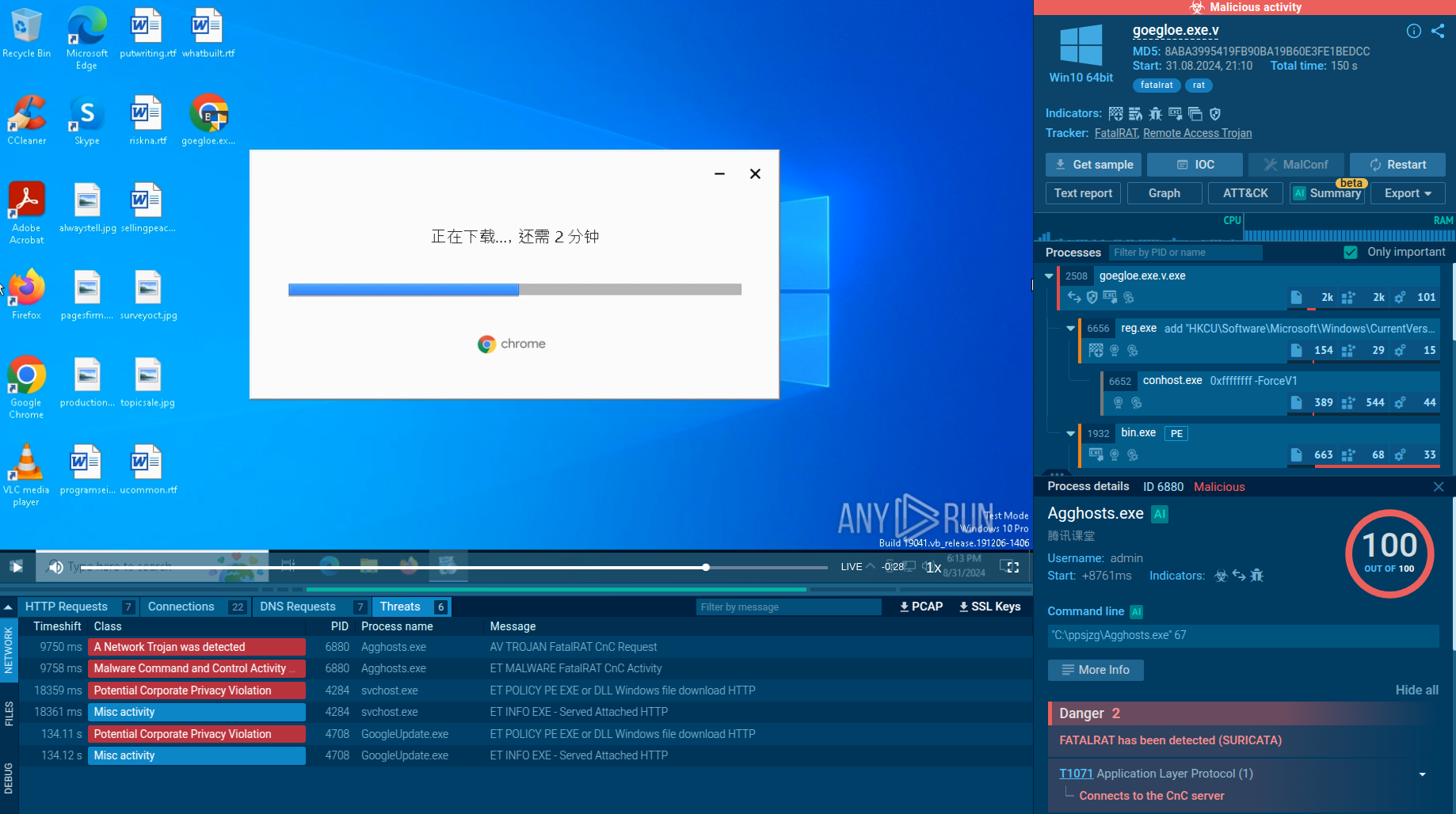
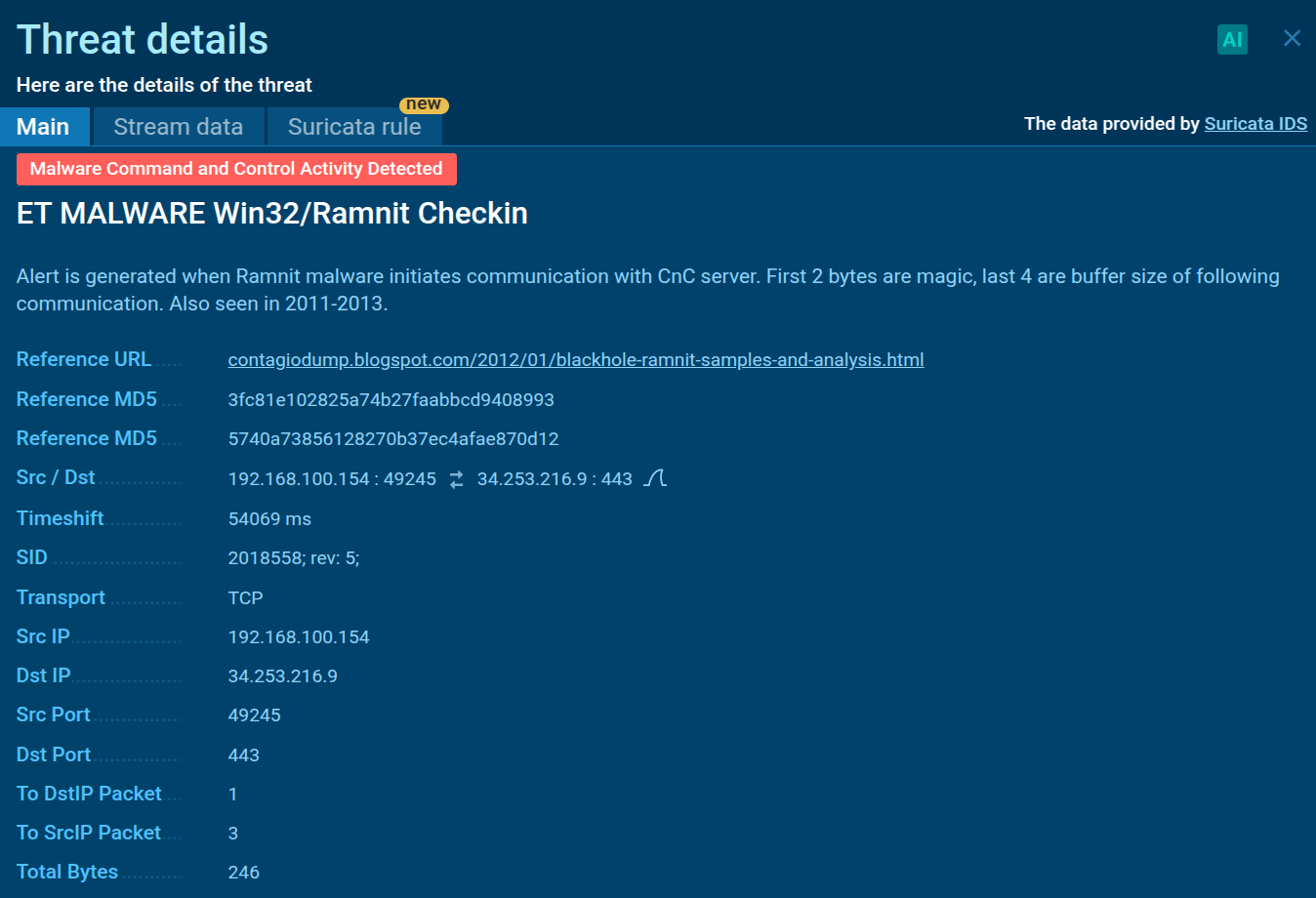 Detection of Ramnit network connection in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Detection of Ramnit network connection in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Ramnit’s modular design lets it download extra modules as needed. It can inject malicious code into browsers—often during online banking sessions — to steal data in real time. To evade detection, it uses techniques like process hollowing, injecting code into legitimate processes like “msiexec.exe” and “explorer.exe.” It can also fetch a VNC module for remote access.
Finally, Ramnit creates a proxy network of infected machines, relaying malicious traffic through multiple hosts to hide attacker activity. Overall, its execution chain relies on phishing-based distribution, DGA-powered C&C communication, modular expansion, and proxy networks to evade detection and facilitate broader attacks.
Use Threat Intelligence Lookup to get a comprehensive picture of recent Ramnit activity and collect up-to-date indicators of the threat for setting up preemptive defenses. With over 40 search parameters, including IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts, you can extract data from Ramnit malware samples analyzed in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox by a huge community of security experts.
Leverage TI feeds to track C2 infrastructure, malware hashes, keep a watch over evolving tactics of Ramnit via MITRE ATT&CK mappings, and protect your business from financial and reputational loss.
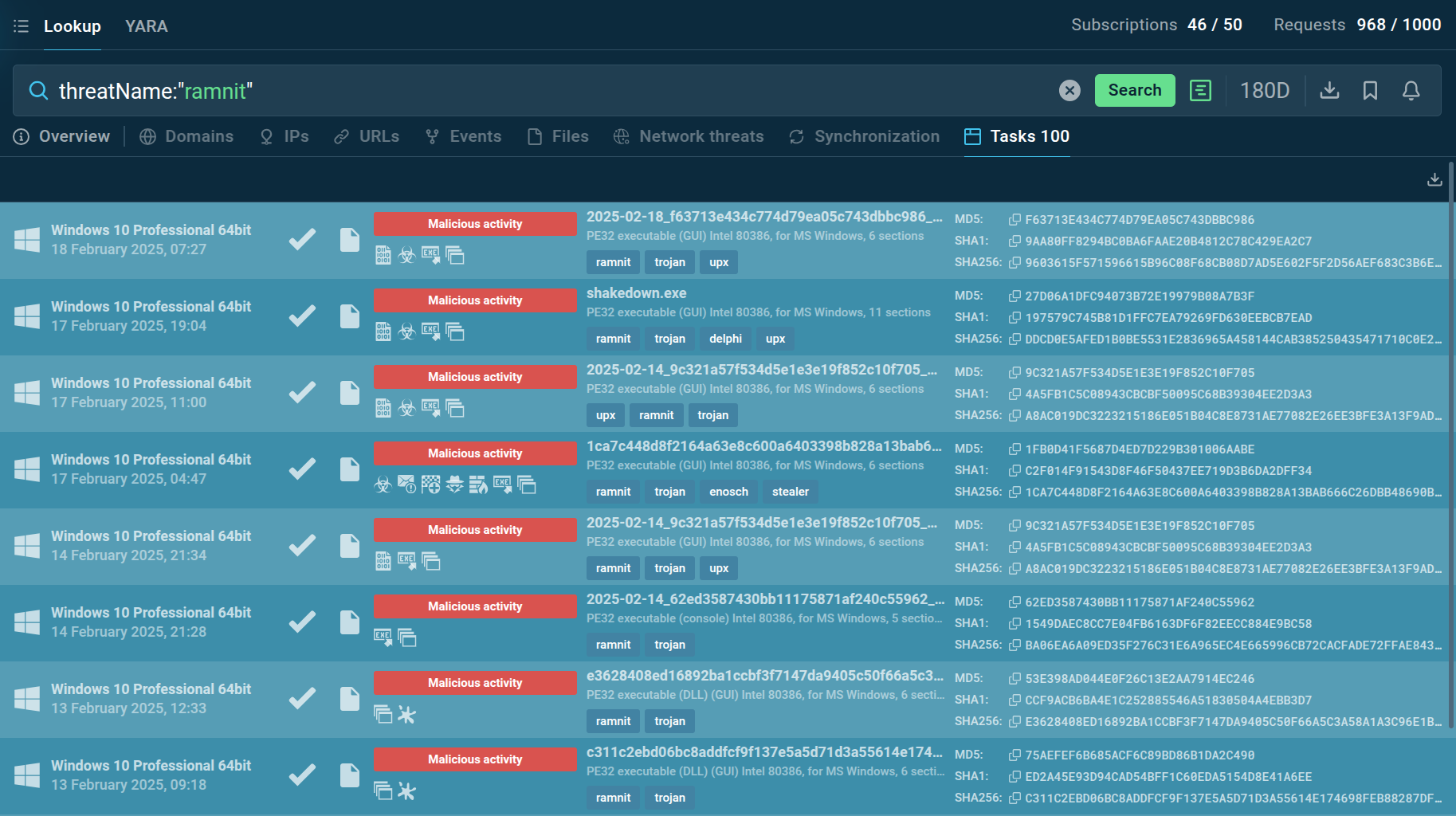 Recent Ramnit samples in ANY.RUN's TI Lookup
Recent Ramnit samples in ANY.RUN's TI Lookup
For example, submitting the query threaName:"ramnit" will provide you with the latest public sandbox reports on Ramnit samples.
Ramnit spreads through multiple infection vectors, making it highly persistent and difficult to eradicate. It is delivered via phishing emails containing malicious Word, Excel, or PDF documents with embedded macros or exploit code. Users are infected when visiting compromised websites that host exploit kits targeting browser vulnerabilities.
Besides, Ramnit has been dropped by other malware families, including Emotet and Dridex, to expand its botnet.
It also can spread via USB drives, SMB shares, and network infections, bypassing internet defenses.
Hybrid capabilities of Ramnit make it an especially serious threat to organizations worldwide. It can function as a banking trojan, worm, RAT, and credential stealer simultaneously. To avoid suffering from Ramnit infection, make sure to introduce proper preventive security measures.
One of the essentials tools to help you identify Ramnit early is a malware sandbox. ANY.RUN provides an interactive malware sandbox that lets you safely detonate suspicious files and URLs in a fully functional virtual environment. The service helps you quickly detect cyber threats and collect critical data needed to prevent them from affecting your infrastructure.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account now to try advanced malware analysis.