Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Xeno RAT is an open-source malware mainly distributed through drive-by downloads. The core capabilities of this threat include remote control, keystroke logging, webcam and microphone access. Equipped with advanced utilities, such as Hidden Virtual Network Computing and Socks5 reverse proxy, Xeno RAT is most frequently used in attacks against individual users.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 799
799
 0
0

 484
484
 0
0

 2736
2736
 0
0
Xeno RAT is an open-source remote access trojan (RAT) distributed openly through GitHub. The creator behind this malicious software states that it was created for educational purposes only. This, however, does not prevent threat actors from leveraging it in their attacks to steal sensitive data and spy on their victims.
Since Xeno RAT is available free-of-charge, there are many amateur and experienced attackers that employ it. Since 2023, the malware has been involved in several campaigns primarily targeting individual users through drive-by downloads.
Xeno RAT is written in C# and is intended to operate on Windows systems. Since the malware is being continuously updated, it poses a serious threat to organizations and users around the world.
Xeno RAT’s range of capabilities is similar to that of other RATs, such as Asyncrat and njRAT. Some of the malicious activities that can be performed using Xeno RAT include:
Out of all features available to the attackers using the Xeno RAT malware, Hidden Virtual Network Computing offers the most extensive functionality for conducting malicious activities. This utility lets criminals not only take full control of the victim’s computer but also do it stealthily and completely without their notice.
The Socks5 reverse proxy feature of Xeno RAT allows attackers to route their network traffic through a compromised computer, effectively hiding it.
Xeno RAT usually achieves persistence on the compromised system using Scheduled Tasks. It has also been observed to leverage process injection to evade detection.
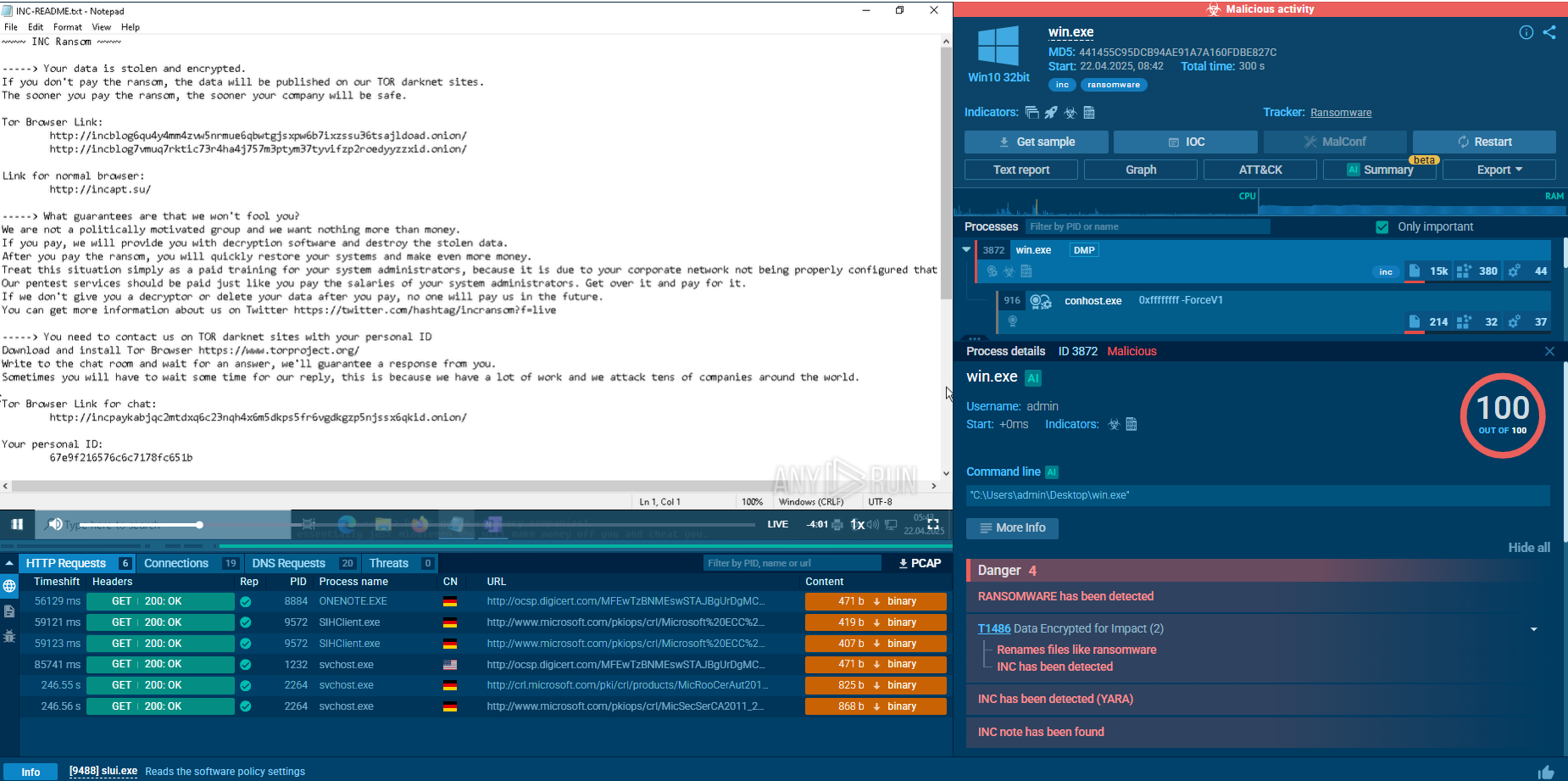
To see how Xeno RAT operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
The execution chain of Xeno RAT may be relatively simple, involving only one or two processes, but it can also become complex with the utilization of multiple processes, including built-in OS tools.
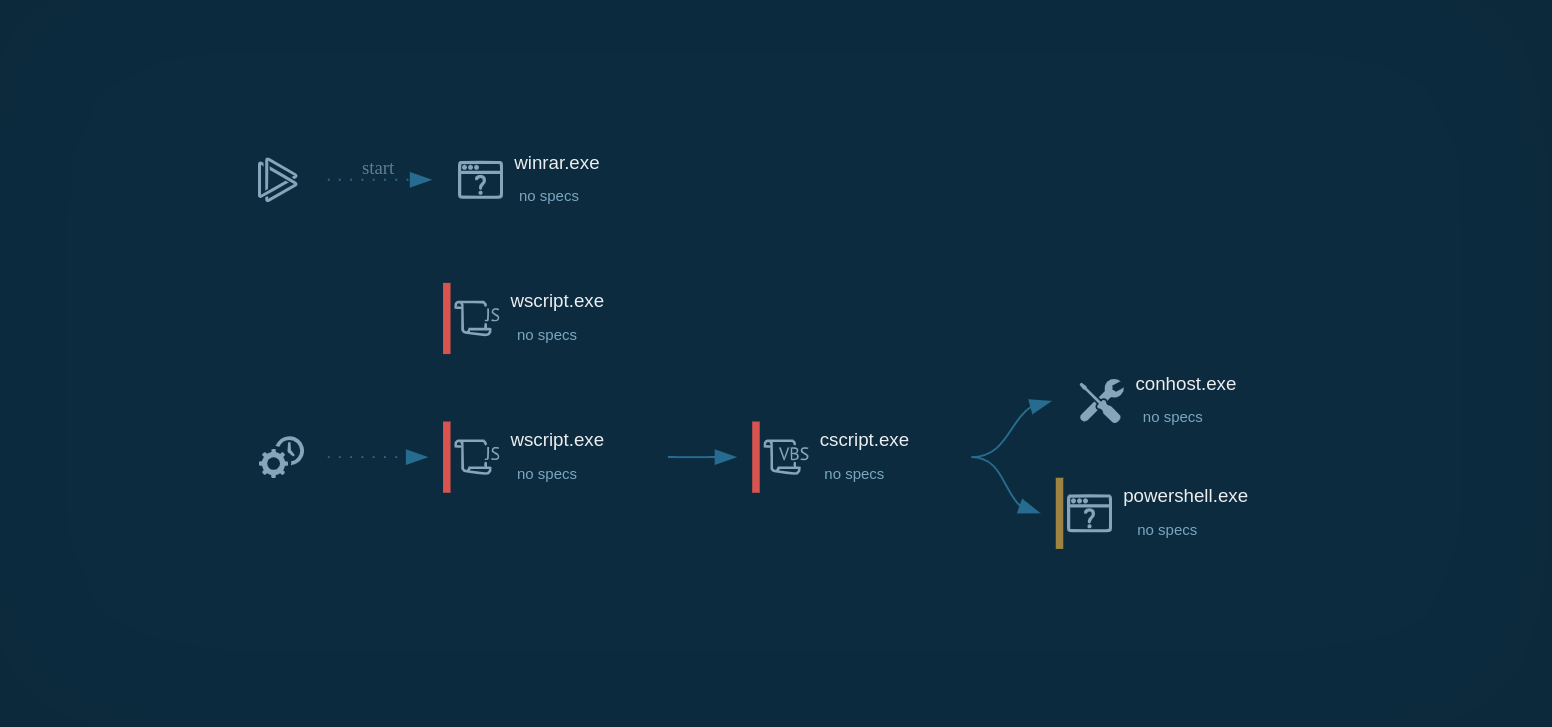
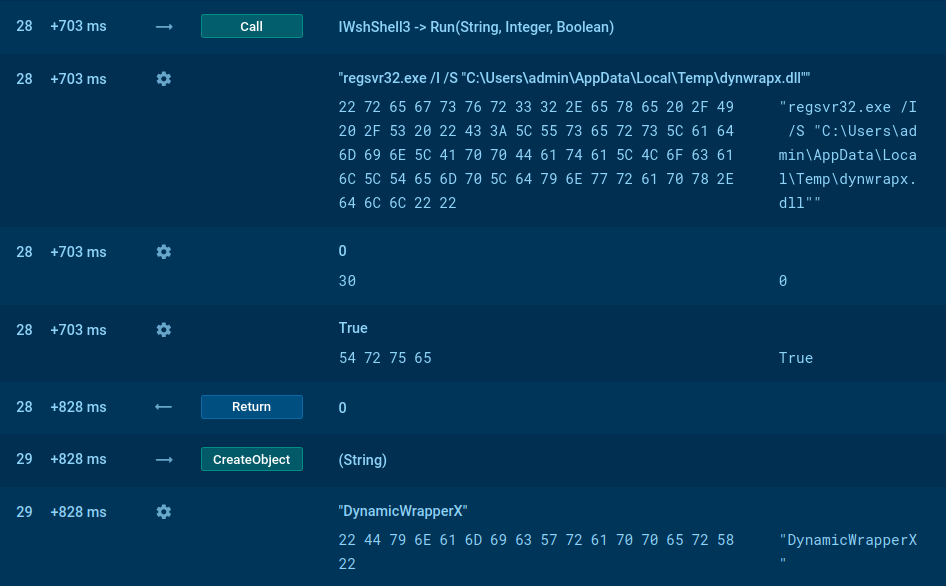 Xeno RAT script analysis in ANY.RUN
Xeno RAT script analysis in ANY.RUN
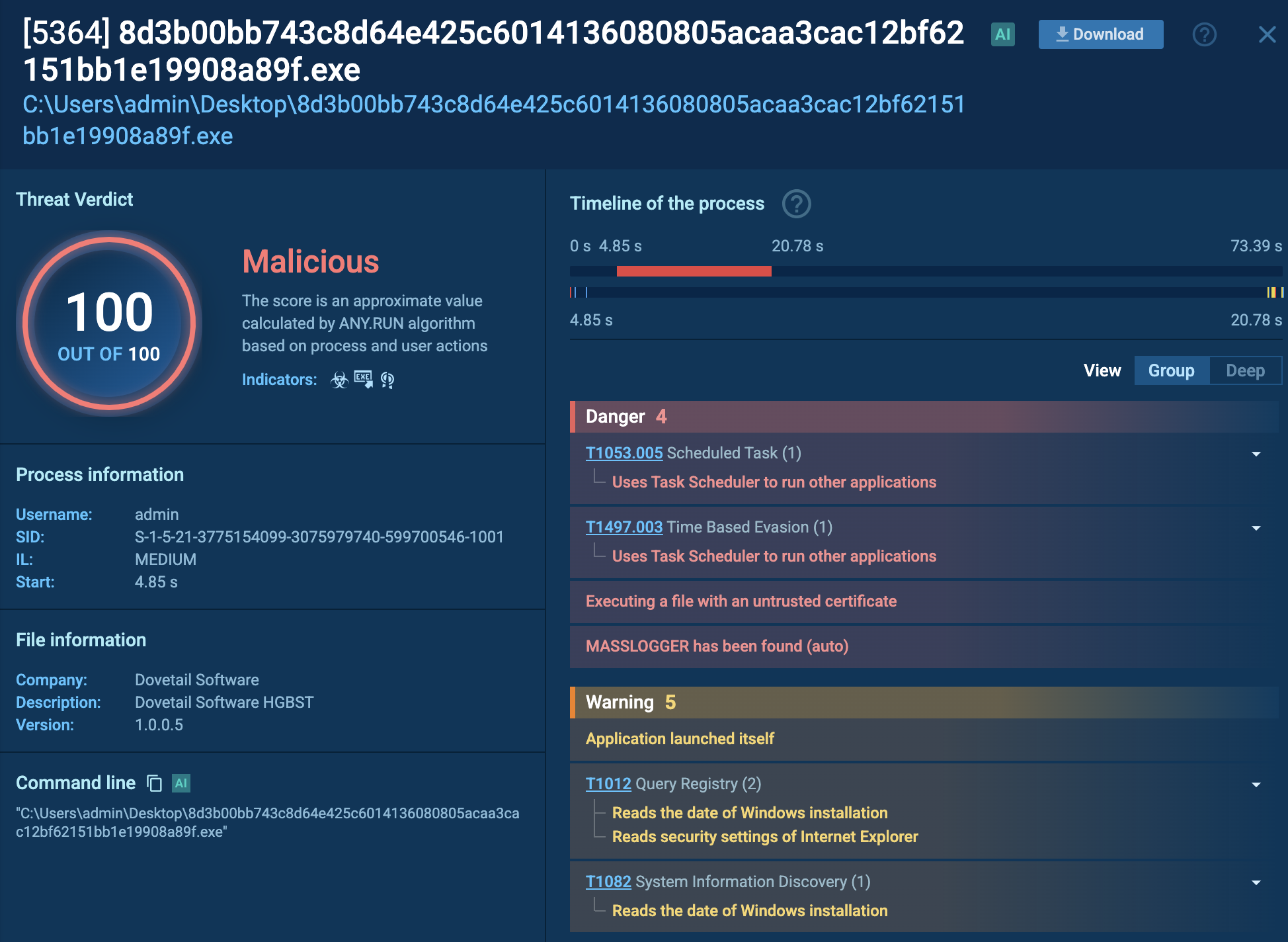
The main malicious activities are carried out by the injected RegAsm process.
In our example, the execution involves multiple processes such as WScript.exe, regsvr32.exe, and RegAsm.exe. The malware creates files in the Startup directory to achieve persistence and loads the dynwrapx.dll (DynamicWrapperX) file. These activities can be monitored using Script Tracer.
For persistence and stealth, XenoRAT can bypass User Account Control (UAC) and maintain its presence even after system reboots using startup functions. It spreads primarily through phishing, exploiting software vulnerabilities, and other typical methods such as downloading from compromised websites or deceptive advertisements.
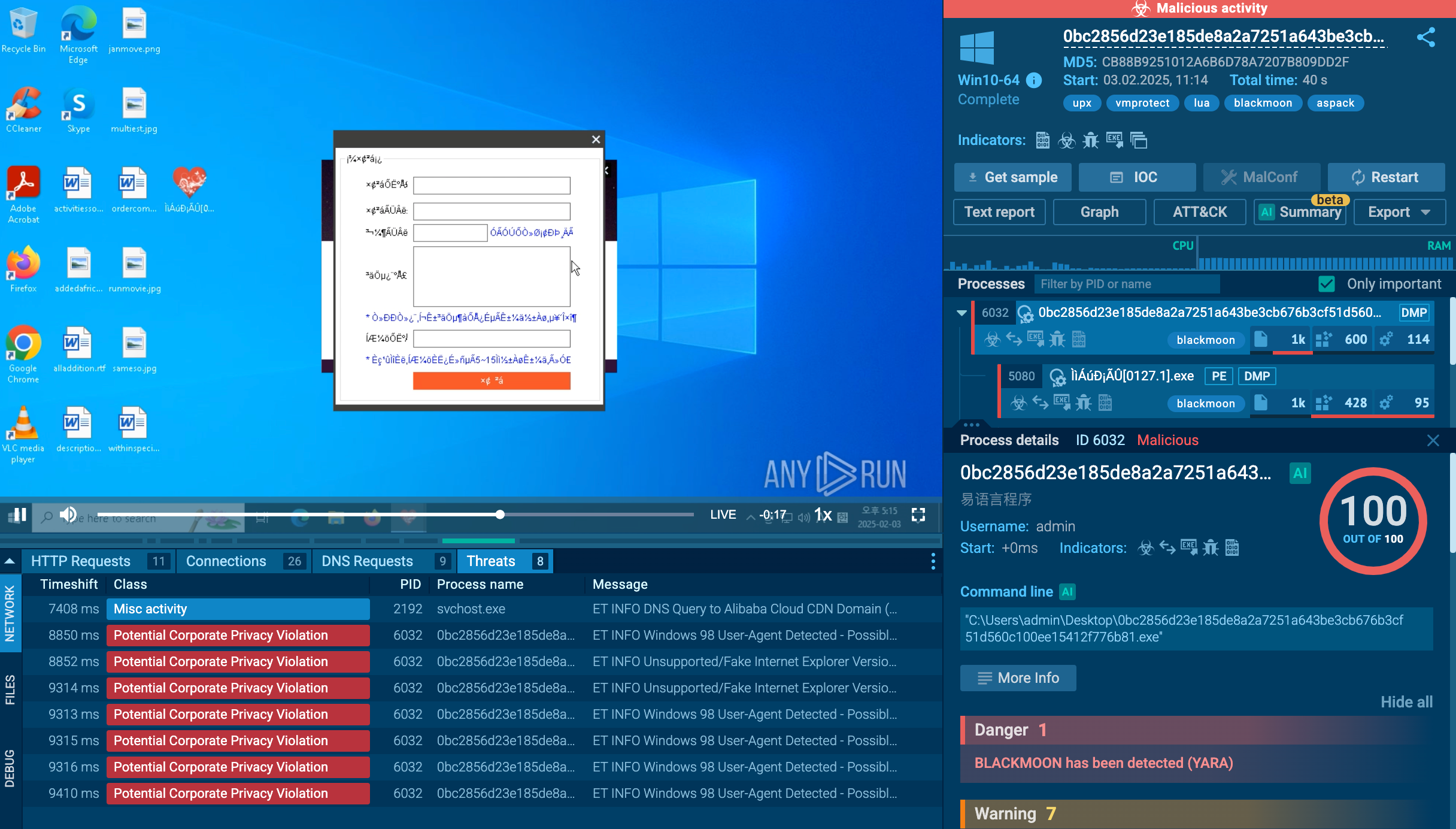
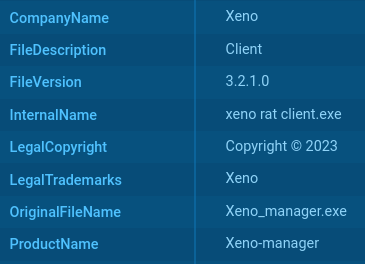 Xeno RAT metadata in ANY.RUN
Xeno RAT metadata in ANY.RUN
Sometimes, Xeno RAT builds may inadvertently reveal themselves by naming directories after the malware, such as "xeno rat client" or "XenoManager," or by embedding its name in PE metadata, for instance, as the company name or product name.
As for the most common delivery methods, drive-by downloads constitute the main vector of Xeno RAT attacks. Individual users are the primary target of these. As a result, to trick their victims into downloading and running the malicious software, threat actors may disguise it as video games or software updates.
Xeno RAT’s wide range of features and capabilities, including HVNC, make it a versatile tool for conducting cyber attacks. The open-source nature of this threat highlights the importance of having proper security measures in place to prevent potential attacks.
Using a sandbox like ANY.RUN to analyze suspicious files and URLs should one of such measures. The cloud-based service allows you to detonate any malicious file in a safe and secure environment, while also having the ability to interact with the system just like on your own computer. Use ANY.RUN to study the behavior of malware, understand its TTPs, and collect indicators of compromise.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!