Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

MetaStealer is an info-stealing malware primarily targeting sensitive data like login credentials, payment details, and browser history. It typically infects systems via phishing emails or malicious downloads and can exfiltrate data to a command and control (C2) server. MetaStealer is known for its stealthy techniques, including evasion and persistence mechanisms, which make it difficult to detect. This malware has been actively used in various cyberattacks, particularly for financial theft and credential harvesting from individuals and organizations.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2022
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 March, 2022
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 779
779
 0
0

 476
476
 0
0

 2720
2720
 0
0
MetaStealer is an information-stealing malware first observed in 2022. Initially announced on underground forums, MetaStealer is available as a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) for a subscription price of $125 per month or $1,000 for lifetime use.
Based on the RedLine stealer codebase, it includes several improvements, making it a more effective tool for credential theft and data exfiltration.
This malware has been distributed mainly through malspam campaigns, often using phishing emails to drop the malicious payload into the victim's machine.
MetaStealer has been observed in malvertising campaigns and cracked software distributed through compromised YouTube accounts. Its ability to steal login credentials, cryptocurrency wallet information, and browser-stored data has made it a popular choice among cybercriminals.
The primary functionality of MetaStealer malware is to exfiltrate sensitive data from infected systems. Its key features include:
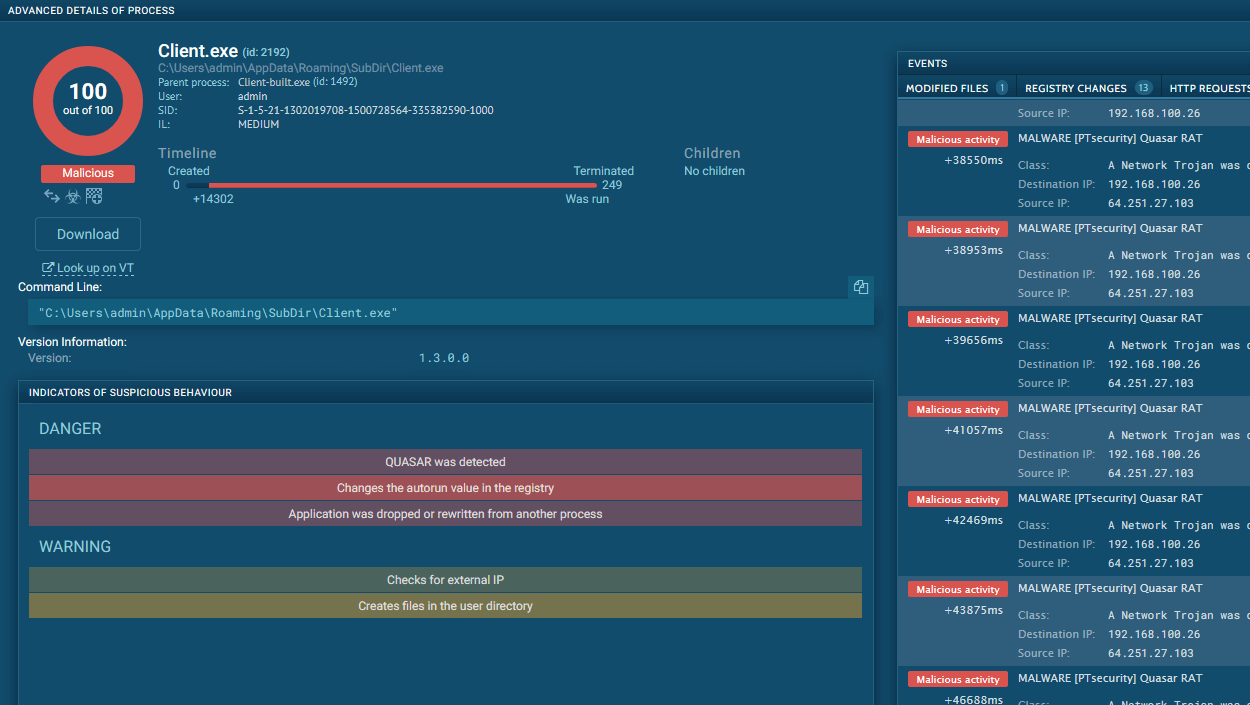
Once executed, MetaStealer is capable of establishing persistence on the infected system by modifying registry keys, making sure that it can reinfect the machine after a reboot. This persistence mechanism helps attackers maintain prolonged access to compromised systems.
MetaStealer's focus on browser exploitation is particularly dangerous, as it targets saved login credentials, autofill data, cookies, and other session information stored in web browsers. This gives attackers the ability to access a wide range of online accounts, from social media to financial services, without needing direct interaction from the victim.
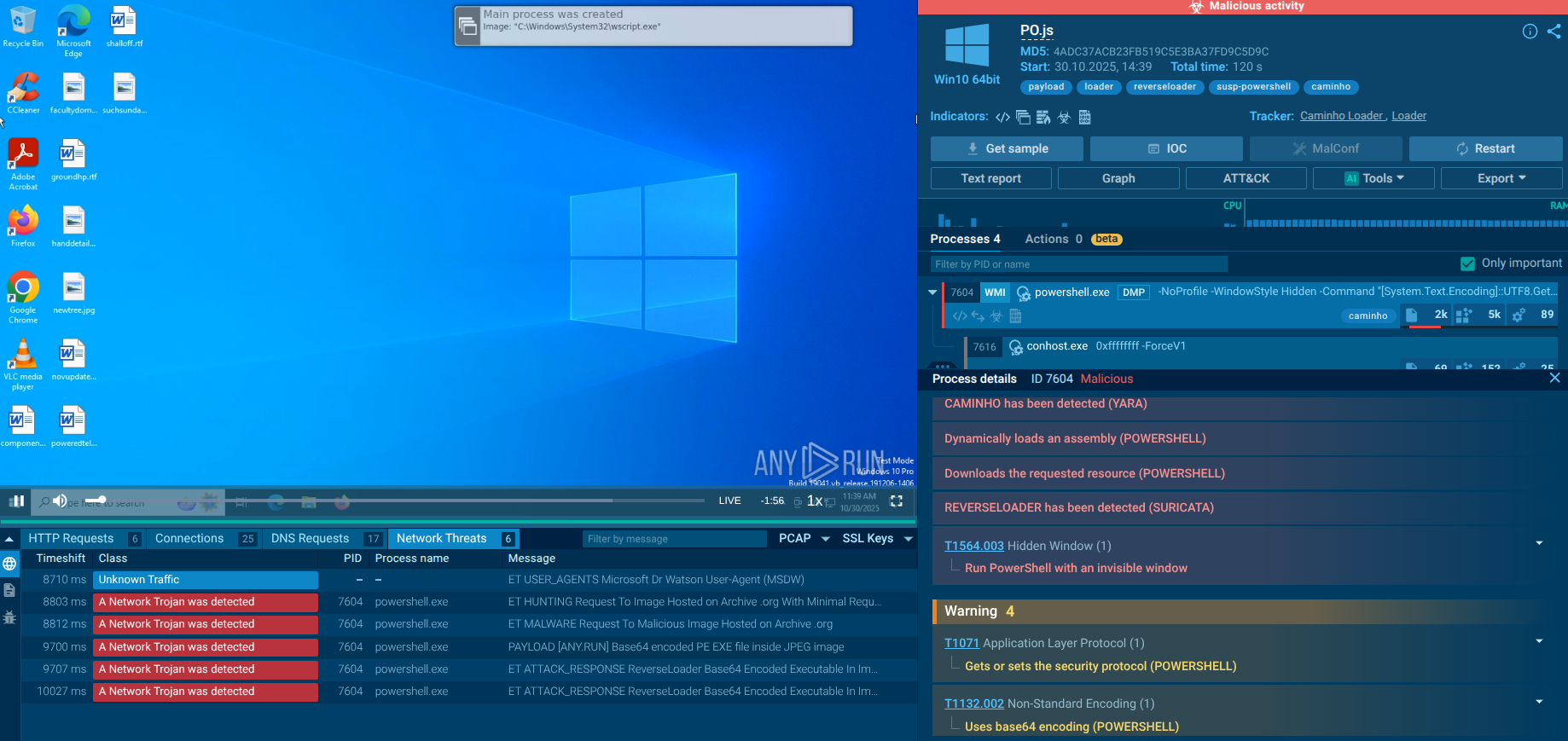
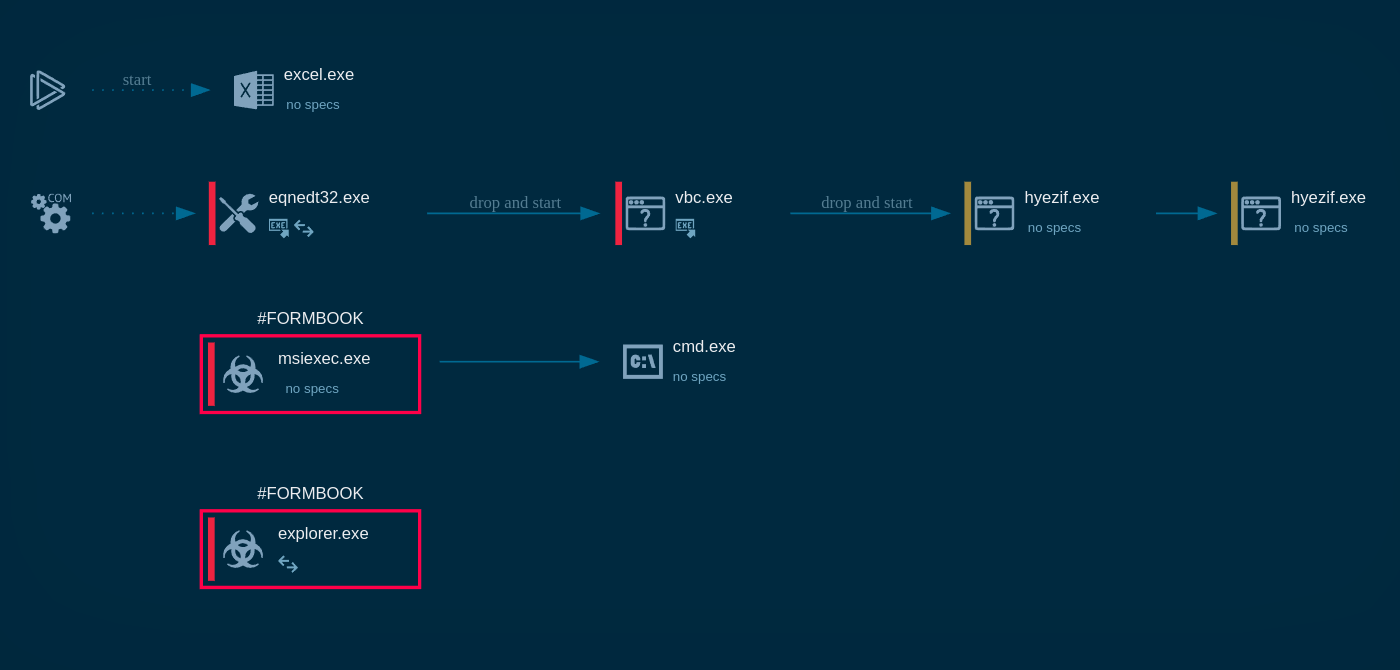
To see how MetaStealer operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
 Metastealer process graph shown in ANY.RUN sandbox
Metastealer process graph shown in ANY.RUN sandbox
Upon execution, MetaStealer may retrieve information about the operating system using winver.exe. It then duplicates itself, creating a copy that is placed in the local application data directory (%localappdata%\Microsoft\windows) and executed to maintain persistence.
To evade detection by Windows Defender, the malware may employ a PowerShell command to add exclusions for certain file types, allowing it to execute without triggering antivirus alerts. This command specifically targets executable files, facilitating the malware's operation without hindrance.
MetaStealer then collects extensive system details by executing systeminfo.exe.
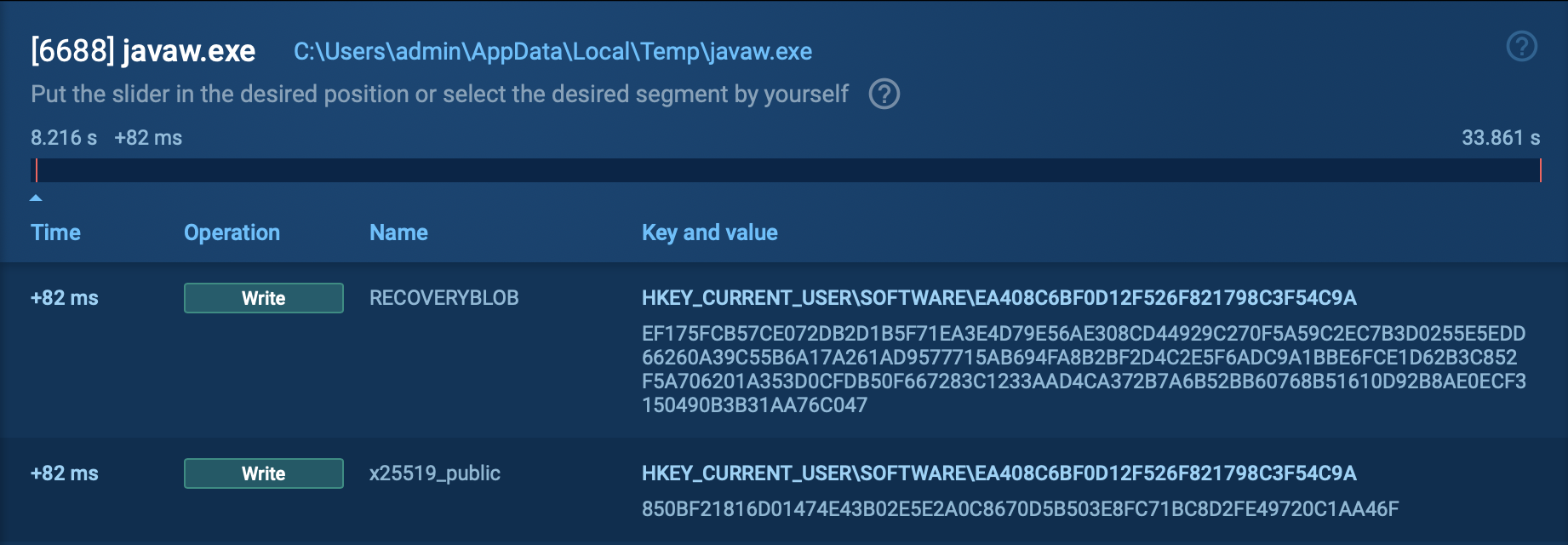
Following this, it focuses on extracting sensitive information from installed web browsers, such as autofill data, cookies, and login credentials. This information is crucial for attackers as it can provide access to various online accounts and services.
After gathering the necessary information, MetaStealer prepares to send the stolen data back to the attackers, typically by establishing a connection to remote servers where the collected information is transmitted.
The exact mechanisms for exfiltration can vary but often involve HTTP POST requests to predefined command and control (C&C) servers.
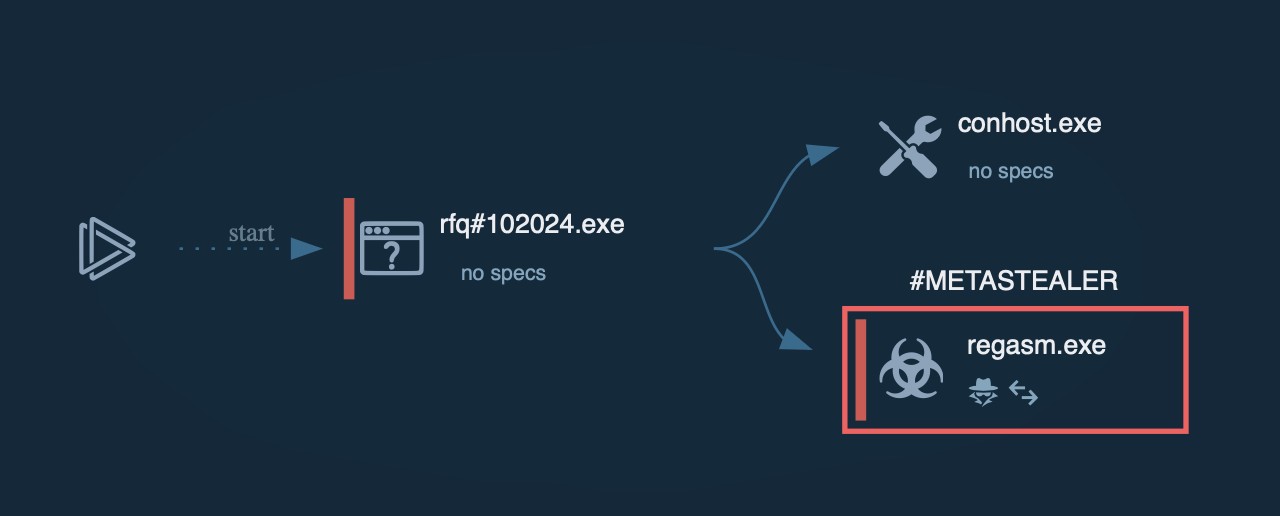
In our example task, MetaStealer injects itself into the RegAsm system process to evade process-based defenses and possibly elevate privileges. The injected process attempted to connect to the C2 server, triggering a Suricata rule.
In some cases, the malware may arrive on the system alongside legitimate software, masquerading to avoid suspicion.
MetaStealer is distributed through various methods, with attackers using different tactics to target victims. Some of the key distribution methods include:
To collect up-to-date intelligence on MetaStealer, use Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service provides access to a large database filled with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox. With more than 40 customizable search parameters, you can find relevant data on threats including elements like IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts.
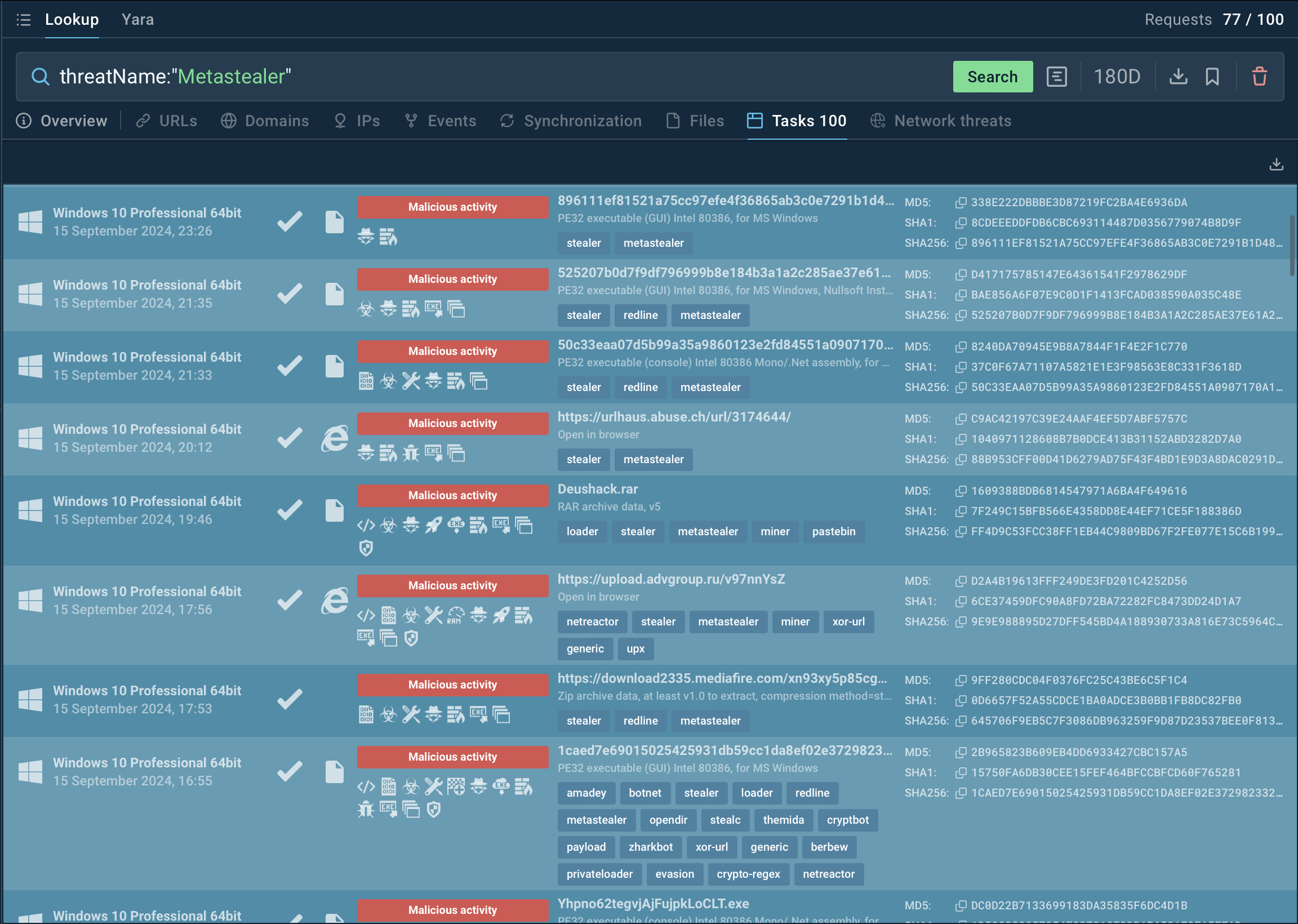 Search results for Metastealer in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Metastealer in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, to gather intelligence on MetaStealer, you can search directly for its threat name or use a related artifact. By submitting a query like threatName:"MetaStealer", TI Lookup will bring up all associated samples and sandbox results relevant to this malware.
Get a 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup along with the ANY.RUN sandbox
MetaStealer poses a significant threat due to its ability to steal credentials and spread through various distribution methods. It’s crucial to proactively analyze suspicious files and URLs to protect against this and similar malware.
ANY.RUN offers real-time threat analysis, letting users investigate suspicious files, track malware behavior, and collect actionable intelligence to improve security defenses.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today and start analyzing emerging threats with no limits!