Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Stealc is a stealer malware that targets victims’ sensitive data, which it exfiltrates from browsers, messaging apps, and other software. The malware is equipped with advanced features, including fingerprinting, control panel, evasion mechanisms, string obfuscation, etc. Stealc establishes persistence and communicates with its C2 server through HTTP POST requests.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2023
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 779
779
 0
0

 476
476
 0
0

 2720
2720
 0
0
Stealc is an infostealer written in C that has been promoted and sold on DarkWeb forums since the beginning of 2023. This malware is primarily used to steal sensitive data from programs, such as web browsers, email clients and messengers. Some examples of such software include Discord, Telegram, and Outlook. This malicious software also has the capability to grab files from infected systems and drop additional malware on them.
According to an interview conducted by threat researcher g0njxa with the developers of the malware, the unique feature of Stealc is the provision of a PHP control panel that has to be hosted on the operator's own server, which gives them more privacy.
Stealc has a range of functions that make it a serious threat. Here are some of its notable features:
Stealc requires external DLLs that are not embedded in the PE but rather downloaded from a specific URL hosted by the C2. The downloaded DLLs include sqlite3.dll, freebl3.dll, mozglue.dll, etc. These DLLs provide additional functionality to the malware, such as interacting with SQLite databases, encrypting data, and interacting with Mozilla-based applications.
After establishing persistence, Stealc begins its communication with the C2 server, first requesting its configuration and then exfiltrating stolen data with the help of HTTP POST requests.
In summary, Stealc is a sophisticated malware that can steal sensitive data, evade detection, establish persistence, and communicate with a C2 server. Its unique features and capabilities make it a significant threat to cybersecurity. It is crucial for individuals and organizations to take proactive measures to protect themselves from such threats.
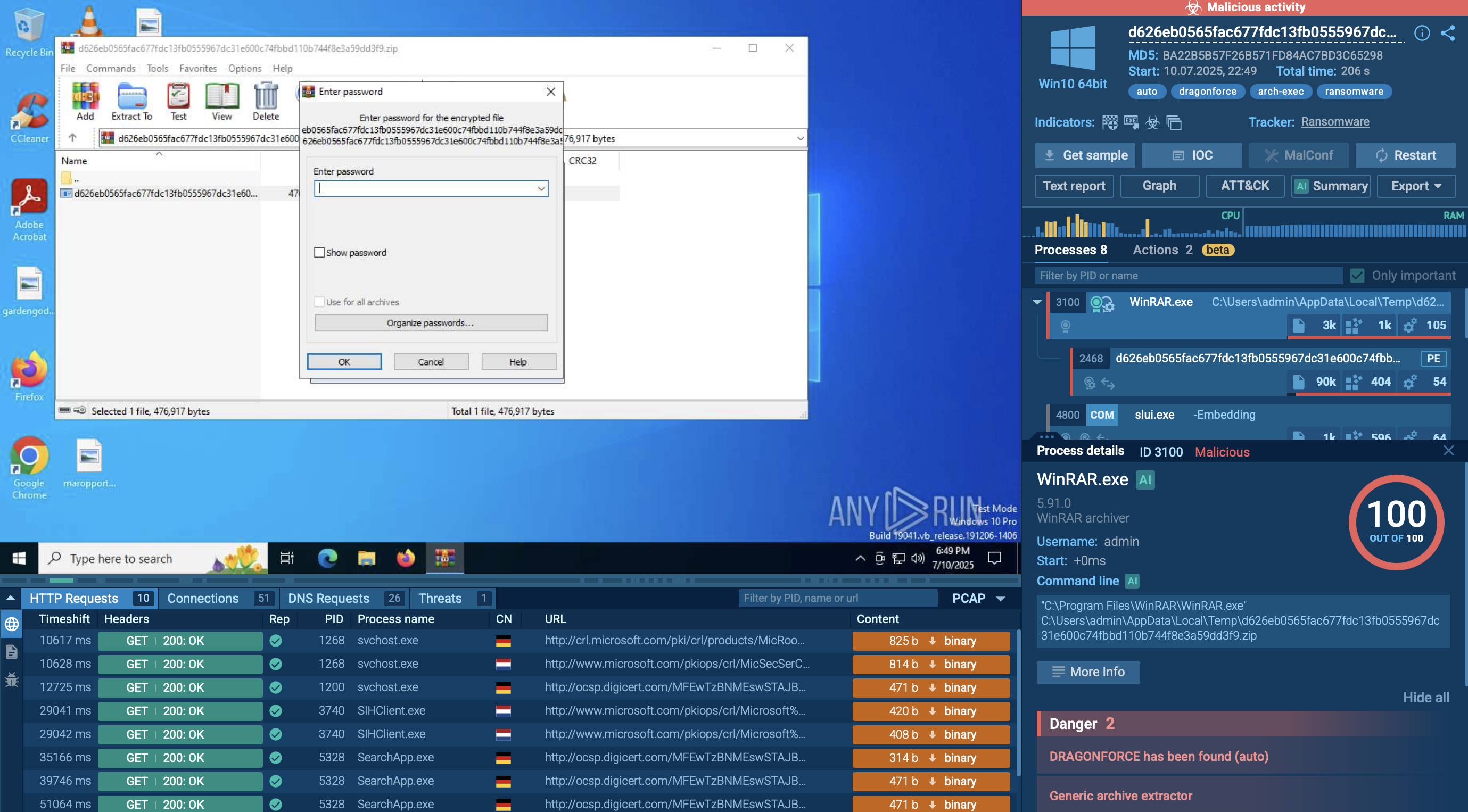
To analyze Stealc, we can upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox for detailed analysis.
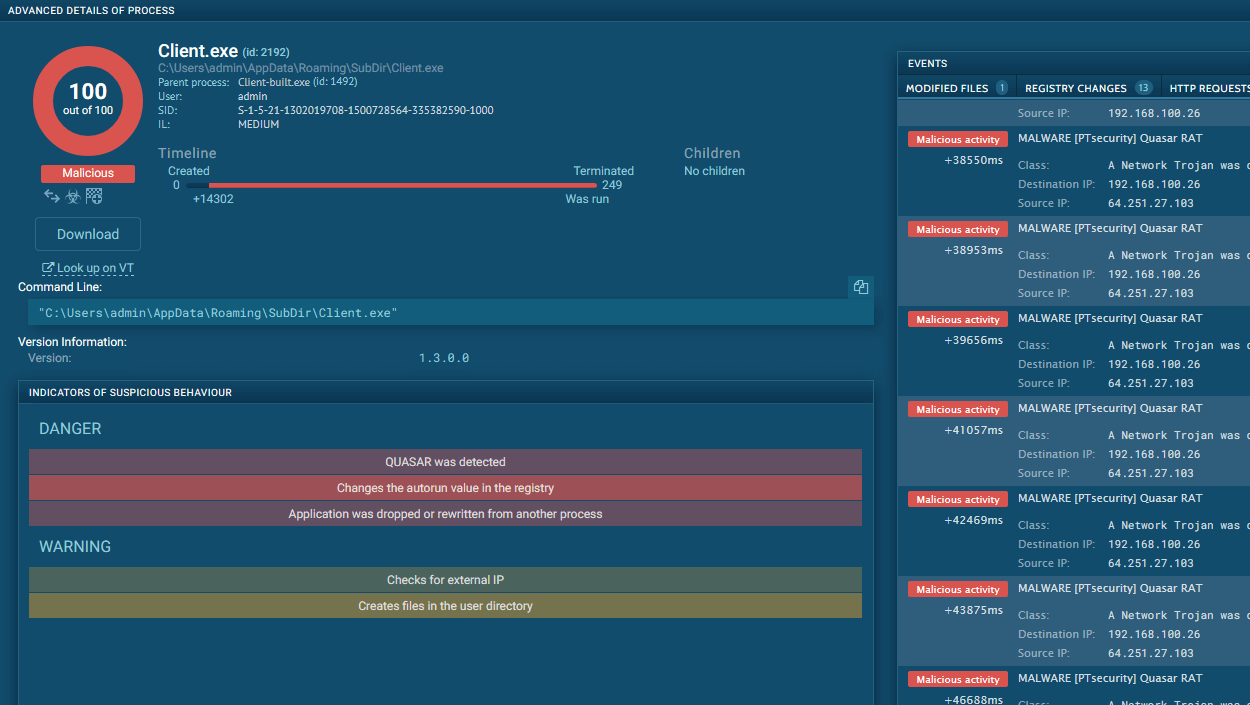
Stealc malware typically operates through a multi-stage execution chain to compromise systems and steal sensitive information. Initially, it may infiltrate a target system through various means such as phishing emails, malicious downloads, or exploiting software vulnerabilities. Once inside, it may establish persistence mechanisms to ensure its continued operation even after system reboots. Stealc then proceeds to escalate its privileges to gain deeper access to the system and evade detection.
It often employs techniques like code injection or hooking to hide its presence from security software. Finally, the malware executes its primary function of stealing data, such as login credentials, financial information, or personal documents, and exfiltrates it to remote servers controlled by the attackers. Throughout this process, Stealc may employ encryption and obfuscation techniques to further mask its activities and evade detection by security measures.
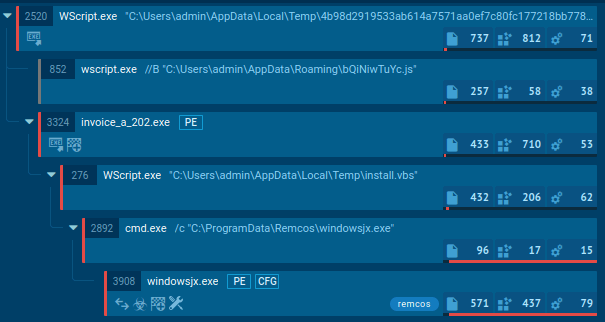
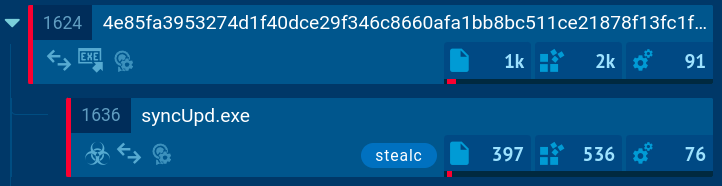 Stealc process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
Stealc process tree demonstrated in ANY.RUN
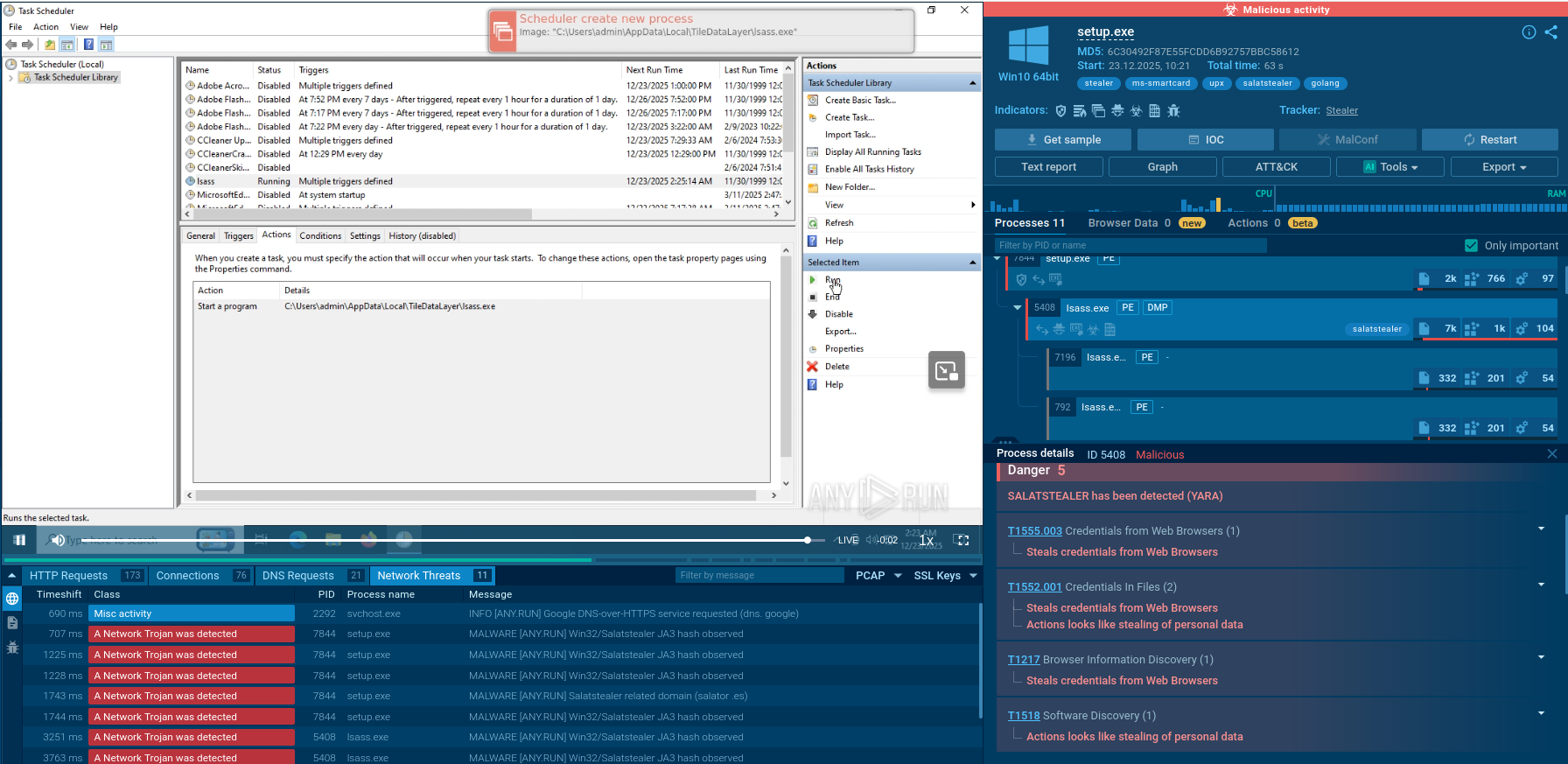
In the example, the malware checks the operating system language and creates a scheduled task through the Windows Task Scheduler to repeatedly execute malicious code. However, the execution chain of Stealc often consists of a single process that performs all malicious activities.
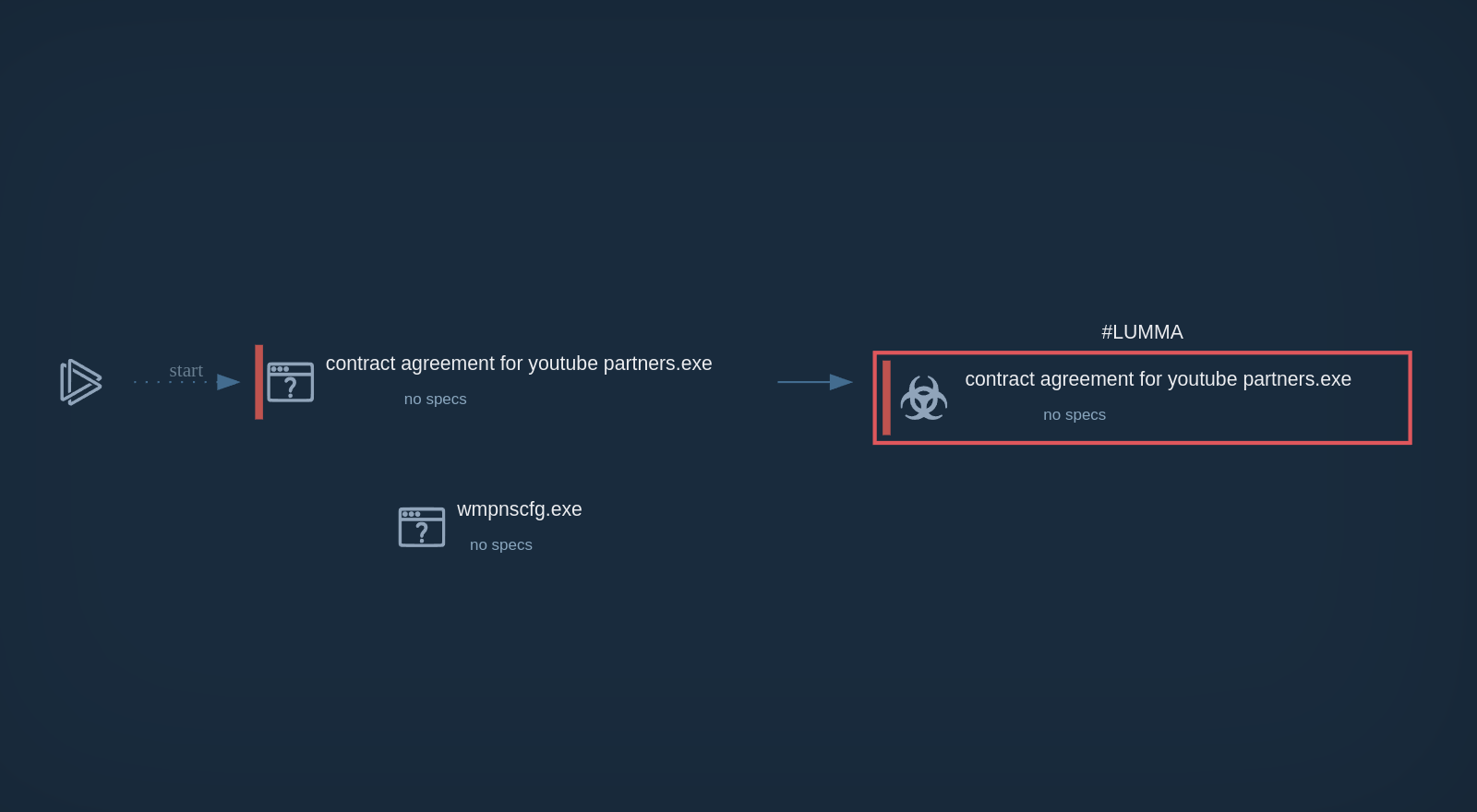
Attackers employ various methods to distribute Stealc malware. One of the most common methods is the use of fake websites offering legitimate software for download. Users are tricked into downloading Stealc instead of the program they were looking for.
Another distribution method is through malicious email attachments. Attackers send phishing emails with malicious attachments, such as Microsoft Office documents or PDF files, that contain the Stealc payload.
Stealc can also be dropped by loaders, malicious programs that are designed to download and install other malware onto a compromised system. One example is CrackedCantil, which is a loader that has been observed dropping Stealc, as well as other ones, such as Lumma, RisePro, and RedLine.
Stealc is an advanced malware that can steal sensitive data, evade detection, and maintain persistence on compromised devices. To safeguard against such threats, individuals and organizations need to take proactive measures. ANY.RUN is an online sandbox that provides an effective solution for this purpose.
ANY.RUN's sandbox provides a secure and isolated environment for running and analyzing malware samples. This allows users to observe the behavior of the malware without putting their systems at risk. The detailed technical reports generated by ANY.RUN provide insights into the malware's functionality, communication patterns, and other important characteristics.
Create your ANY.RUN account – it’s free!