Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Laplas Clipper is a crypto-stealing malware that gains unauthorized access to the victim’s clipboard and replaces their crypto addresses to trick them into sending their funds to the attacker’s wallet. This malicious program is offered for sale as a malware-as-a-service (MaaS) and often distributed with the help of loaders, including SmokeLoader.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2022
First seen
:
|
27 June, 2023
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2022
First seen
:
|
27 June, 2023
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
Laplas Clipper is a family of malware that possesses stealer capabilities. Specifically, it works by replacing victims’ cryptocurrency addresses with those of the attacker using the clipboard. As a result, users unknowingly end up sending their virtual coins and tokens to the wallet set up by the threat actor. First observed in late 2022, Laplas Clipper remains in operation to this day and gets regular updates.
Laplas is sold openly via Telegram channels and Darknet forums as a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS). Any user interested in this malicious software can purchase a subscription, starting from one week ($49) and up to one year ($839). As part of the offering, operators receive a web panel that lets them control the entire process of replacing victims’ crypto addresses and get notifications about the malware’s activity.
Phishing campaigns are the most common method employed by threats actors for infecting victims’ computers with Laplas Clipper. Criminals often weaponize .pdf and office-suite format files to conduct multi-stage attacks. In many instances, the malware is being dropped by other malicious software, including SmokeLoader, which penetrates security mechanisms of computers and then downloads Laplas.
Unlike other stealers, such as FormBook and Arkei, Laplas Clipper has a limited functionality, which focuses exclusively on hijacking victims’ cryptocurrency wallets. The capabilities of the malware include:
The malware creates addresses that are almost identical to the original ones. For example, the first three characters after the prefix of the attacker's address will be the same as those of the victim's address. This is often enough for an average user to mistakenly send their cryptocurrency to the wrong address. Apart from generating its own addresses, Laplas Clipper allows operators to use their custom ones.
As for the anti-analysis and anti-detection techniques, some versions of the malware are obfuscated with Babel, a popular obfuscator for .NET, which is capable of renaming symbols and encrypting strings. The malware is also equipped with debugger and virtualization evasion. Read the article “Analyzing a New .NET variant of LaplasClipper: retrieving the config” to learn more about the program’s code and collect its configuration.
Let’s load a sample of Laplas Clipper into ANY.RUN, an interactive malware sandbox, to expose its malicious activities and examine its behavior, as well as to gather up-to-date IOCs.
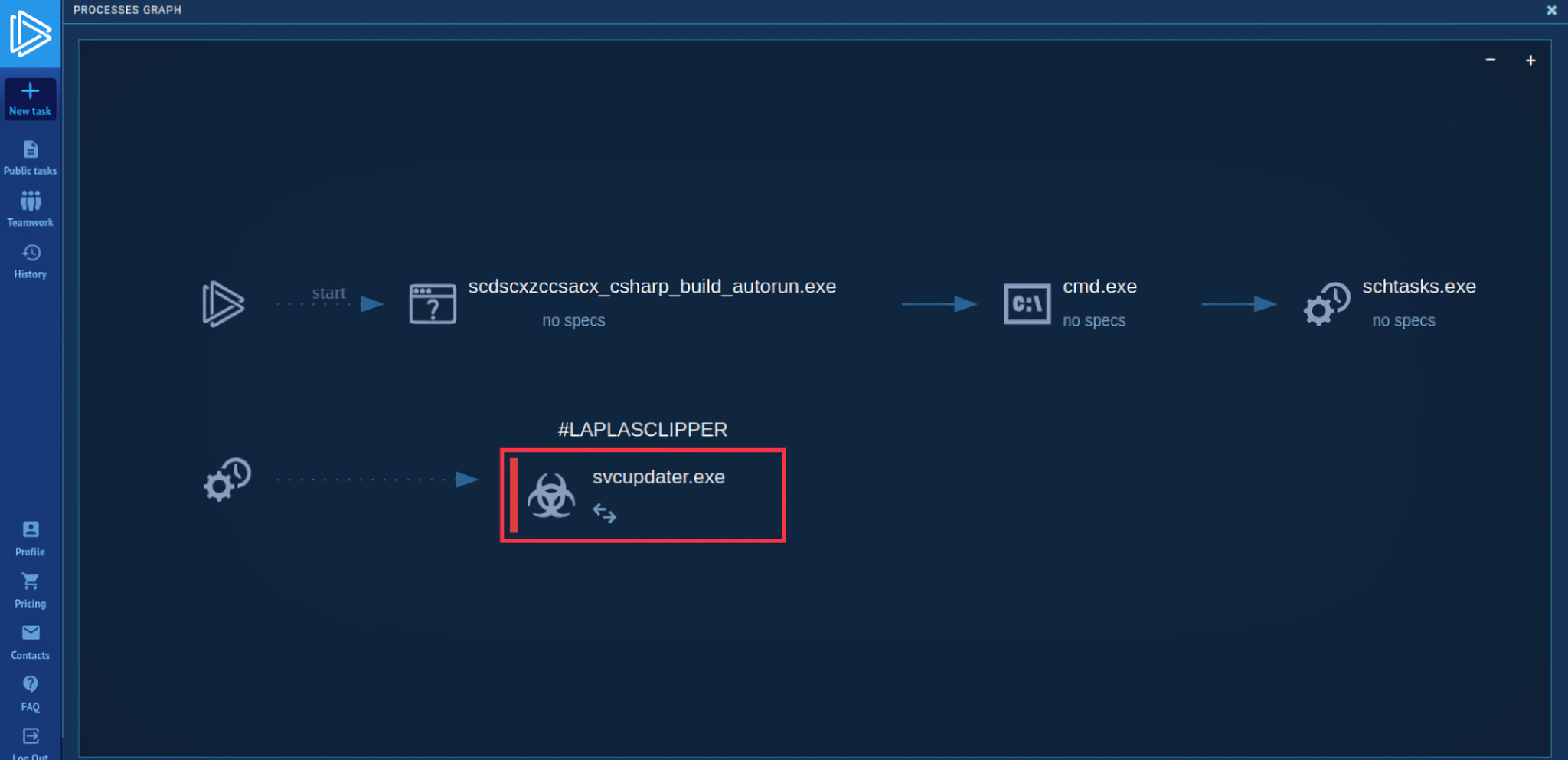 Laplas Clipper's process tree
Laplas Clipper's process tree
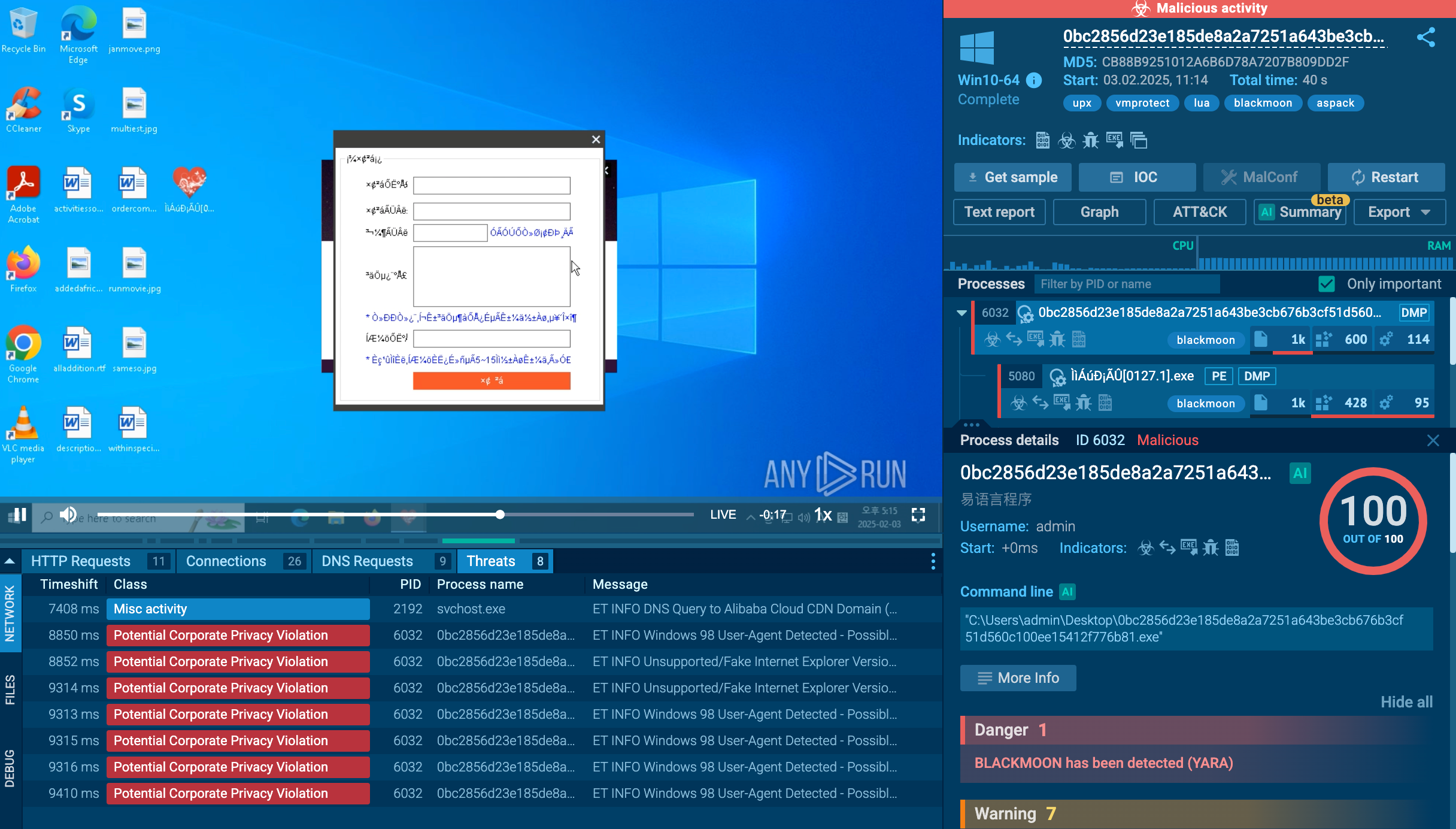
The task starts with the execution of a malicious file with the name "scdscxzccsacx_csharp_build_autorun.exe" located in the temporary folder. What's interesting is that this executable creates a scheduled task called "uAGRIUzbtd", which launches another executable named “svcupdater.exe.” This executable is located in the user's roaming folder stored inside the AppData directory (T1053.005). ANY.RUN shows that the "cmd" process was used to execute the "schtasks" process.
After one minute into the VM operation, the scheduled task starts the "svcupdater.exe" file. This indicates that the malware is attempting to establish persistence on the system by scheduling the execution of a file in the user's roaming folder. This behavior is commonly observed in malware that wants to maintain a presence on the system even after a reboot.
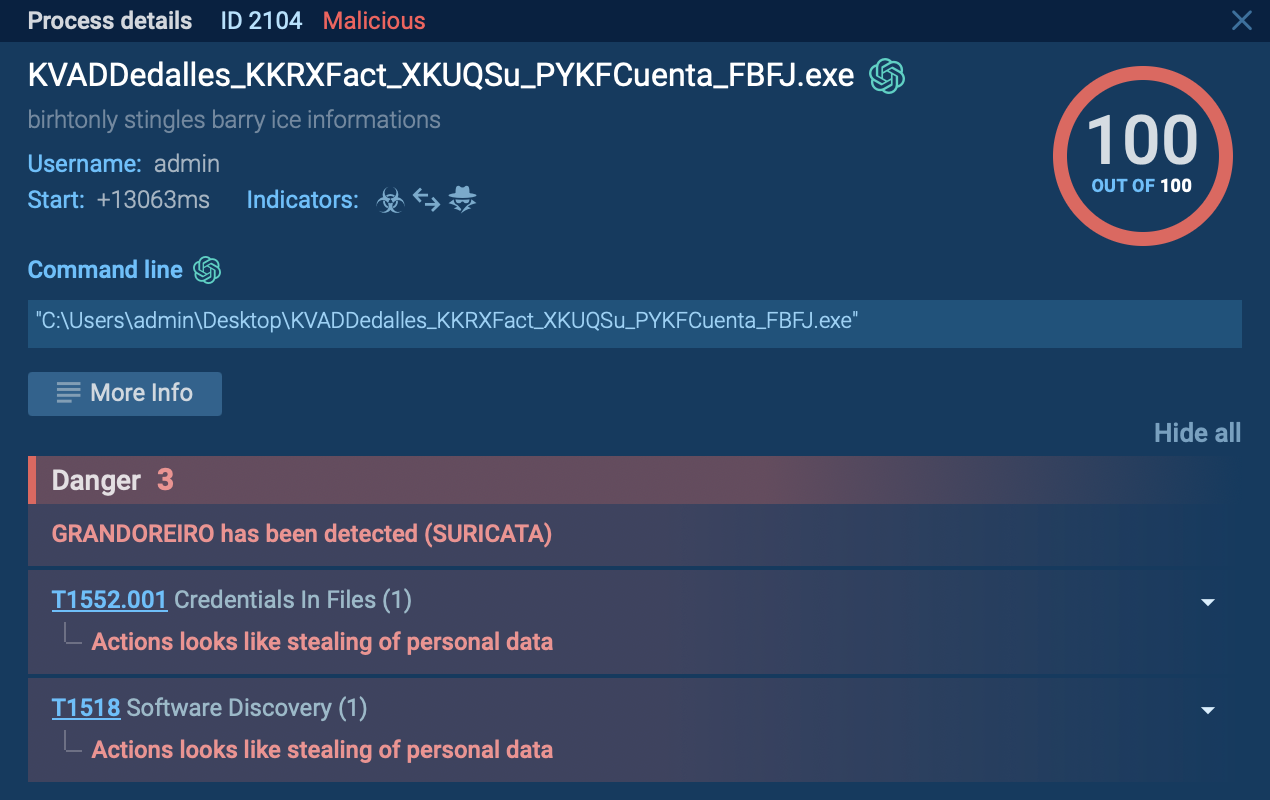
After that, the malware performs its main activity and begins to connect to C2 servers and collect information about the system. In this task, we can not only view the malware configuration by clicking the CFG icon next to the process or the MalConf button, but also download a dump of that process by clicking the DMP icon to perform additional analysis if needed.
Read a detailed analysis of Laplas Clipper in our blog.
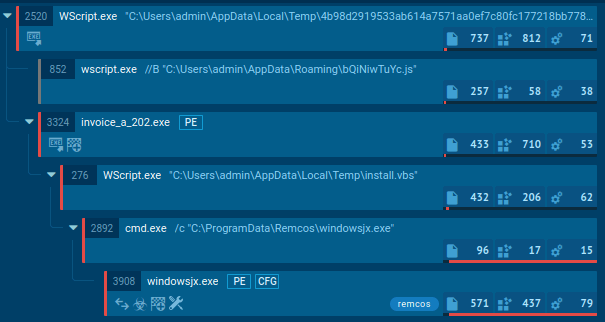
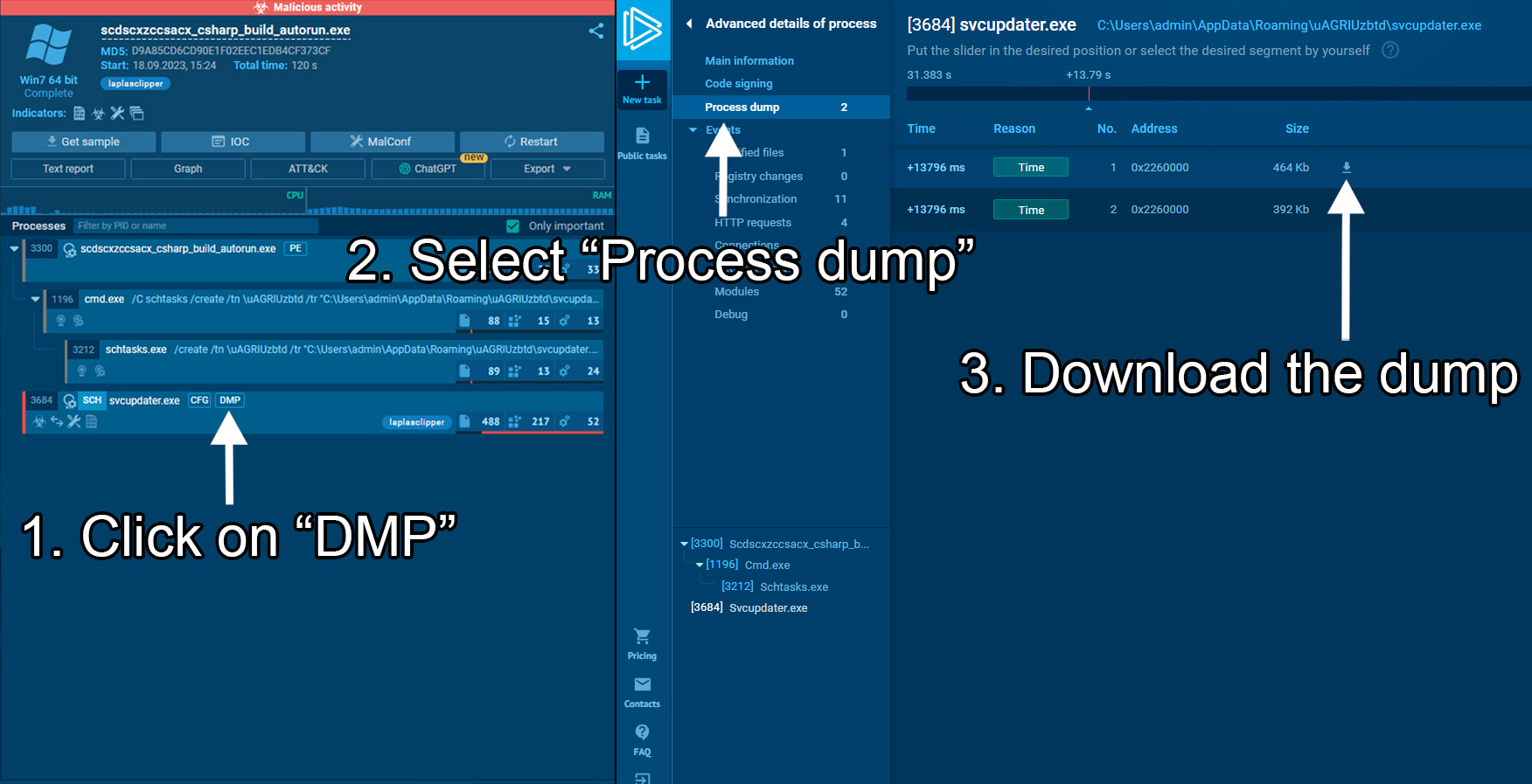 ANY.RUN lets you download a process dump of the analyzed sample
ANY.RUN lets you download a process dump of the analyzed sample
Phishing emails are commonly used by criminals as the first step in multi-stage attacks that ultimately lead to LaplasClipper infection. These attackers often create emails that are misleading and deceive individuals into opening attachments that contain harmful files. For instance, attackers have been observed to pose as CoinPayments, a well-known cryptocurrency payment gateway, and request users to download a .zip folder. By executing the files from the archive, users inadvertently install Laplas Clipper on their systems.
Laplas is a newly developed malware that poses a serious threat to crypto holders worldwide. The malicious actors behind Laplas attacks have been successful in stealing substantial amounts of virtual coins. Therefore, individuals and companies that deal with cryptocurrencies must exercise extra caution when opening email attachments from unknown senders and suspicious files from untrusted sources. To ensure the safety of a document or link, it is recommended to use ANY.RUN. This platform provides conclusive verdicts on the malicious behavior of files and URLs and generates detailed reports, containing IOCs and configs for future detection of the threat.
Try ANY.RUN for free – request a demo!