Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases

Arkei is a stealer type malware capable of collecting passwords, autosaved forms, cryptocurrency wallet credentials, and files.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
21 May, 2018
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
21 May, 2018
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 435
435
 0
0

 2295
2295
 0
0

 4454
4454
 0
0
Arkei is a stealer designed to exfiltrate information from infected systems. Typical for this malware type, it is distributed using Malware-as-a-Service (MaaL) model, which means that anyone can use the malware with minimal technical knowledge — all you need is to purchase access to a control pane from a website that sells the service.
This malware — which is written in C++ — targets Windows systems and is considered a medium impact and medium risk threat.
Having been around since 2018, Arkei has become popular among adversaries: not only is it widely used, but it has spawned several forks including Mars, Oski, and Vidar stealer, which we have covered before in the ANY.RUN trends trackers.
Arkei is capable of retrieving a variety of information from infected machines, including:
Cryptocurrency owners are at the highest risk and are the main targets of Arkei. It can extract data from around 40 crypto wallet extensions, including MetaMask that accounts for over 80% of web3 wallet usage.
The stealer also targets more than 30 web browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Opera, Brave, and TOR.
Arkei can also target 2FA extensions, a capability it has had roughly since the beginning of 2022. It's unclear how attackers are planning to use this data, but it's certain that this development could pose new risks for both corporate and private users.
The specific data types that the malware targets depend on its configuration file — a Base64-encoded file with the .PHP extensions — and will vary from campaign to campaign. The attacker can use it to set Arkei's behavior with custom rules, and target specific information.
It is important to note that Arkei terminates execution on machines from the ex-USSR regions.
The stealer identifies the region by accessing the language identifier of the Region Format setting. This behavior is typical for malware originating from the ex-USSR territories, which gives an insight into Arkei’s origin.
Arkei is equipped with multiple evasion techniques that help it avoid detection. For example, it checks that the computer name is not set to “”HAL9TH”” and the username to “”JohnDoe” — these are the default settings of the Windows Defender emulator. It also checks if several DLLs are loaded in a process against a list of antivirus and emulation software.
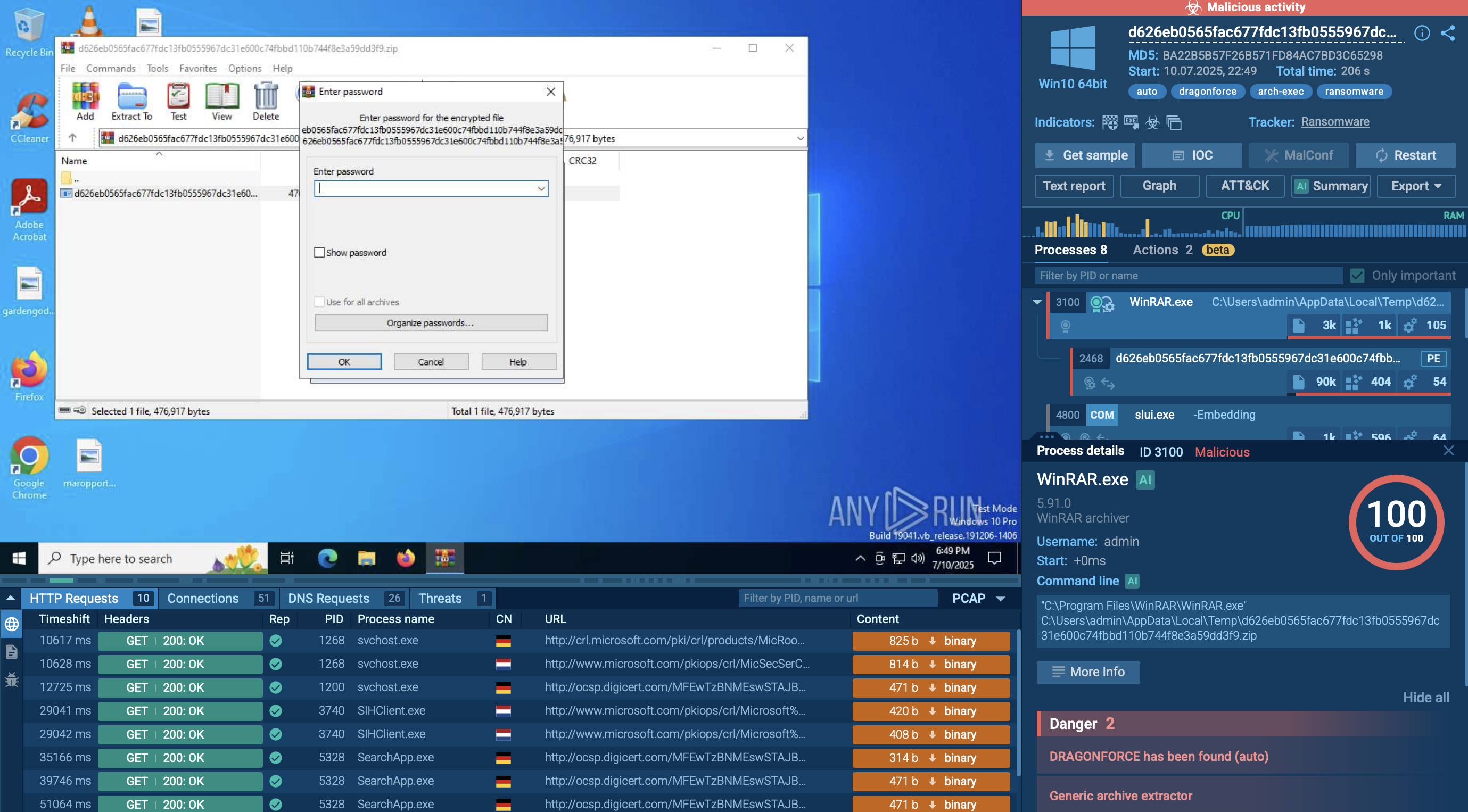
Once it's time to gather the data, Arkei compiles its findings into a .zip archive, gives it a random 12-character name, and sends it to its control server. In addition to the information specified by the config file, it captures a system screenshot and extracts system information.
You can obtain Arkei’s malware configurations in the ANY.RUN's sample.
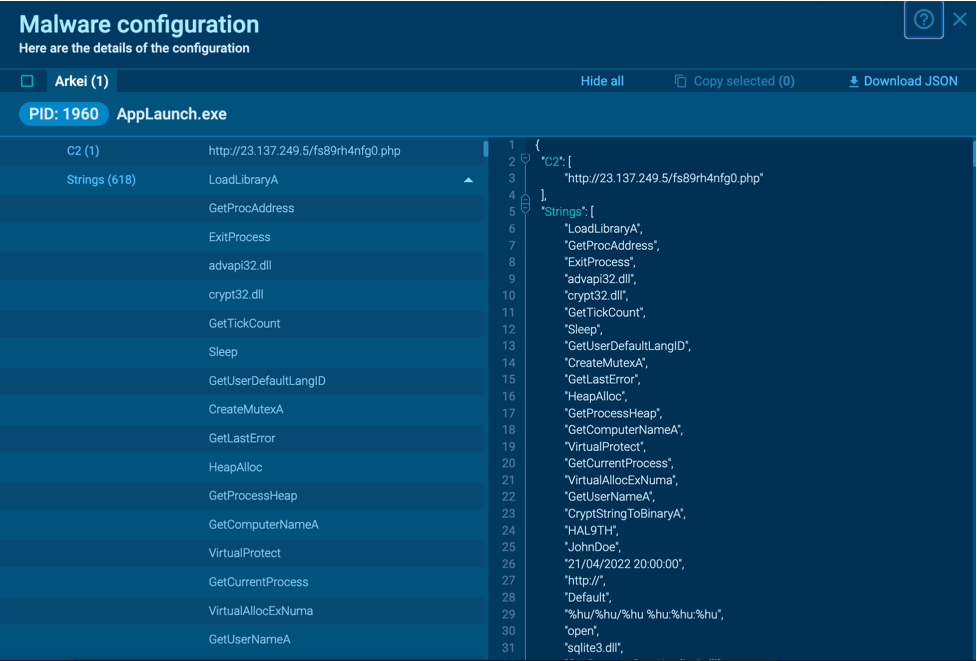 Figure 1: Arkei configuration automatically extracted by ANY.RUN
Figure 1: Arkei configuration automatically extracted by ANY.RUN
Users can access comprehensive malware configuration data on ANY.RUN interactive online sandbox in as little as 10 seconds after starting the sandbox. There's no need to wait for the emulation to finish running.
After a system is infected, a TCP connection is established with the hacker's remote server. The server sends encoded Base64 parameters to the malware, including search path templates and file search masks. Using these parameters, the malware determines which information it needs to steal from the victim's computer.
The malware then requests the libraries necessary for its operation from the remote server. These libraries are sent as ZIP archives.
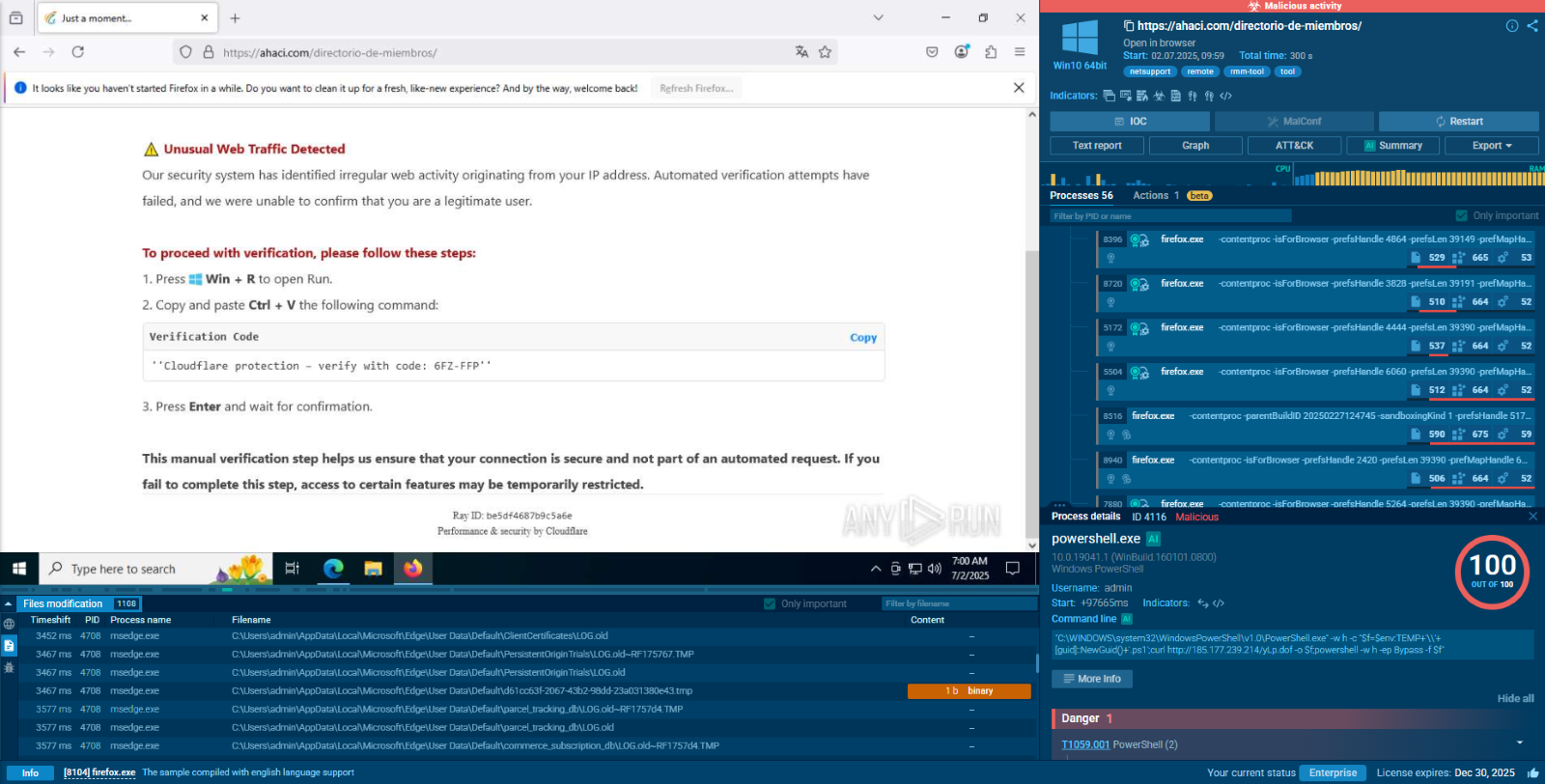
Subsequent communication with the server involves sending stolen files to the C2 server. Some threat actors use packing techniques on Arkei samples (T1027.002) to avoid detection by signatures. An example of this behavior can be seen in this task we recorded in ANY.RUN.
After launching the packed sample, the AppLaunch.exe process is created in the system, which is part of the .NET Framework. The malicious code is then injected into this process.
Arkei finds its victims in a number of ways. It’s delivered with malicious email campaigns in infected attachments, distributed through malicious ads, and is sometimes found in cracked software.
Adversaries use trojan horse tactics to entice potential victims into installing Arkei to their systems: social engineering techniques can be utilized, such as offering a free version of a premium software.
Arkei has also been tied to campaigns utilizing SmokeLoader — an advanced modular malware used to gain an initial foothold in the system and drop other executables. Although Smoke Loader, as you probably have guessed from its name, is primarily used as a loader, it can be armed with information stealing functionality itself — double the threat, when used together with Arkei.
Arkei is a that poses a significant risk to users' sensitive data, particularly crypto wallets.
But users can keep their login and password information, files, and 2FA data secure by following these best practices:
You can identify and analyze threats like Arkei — and more — in a matter of minutes using ANY.RUN’s interactive sandbox. Sign up for a demo!