Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


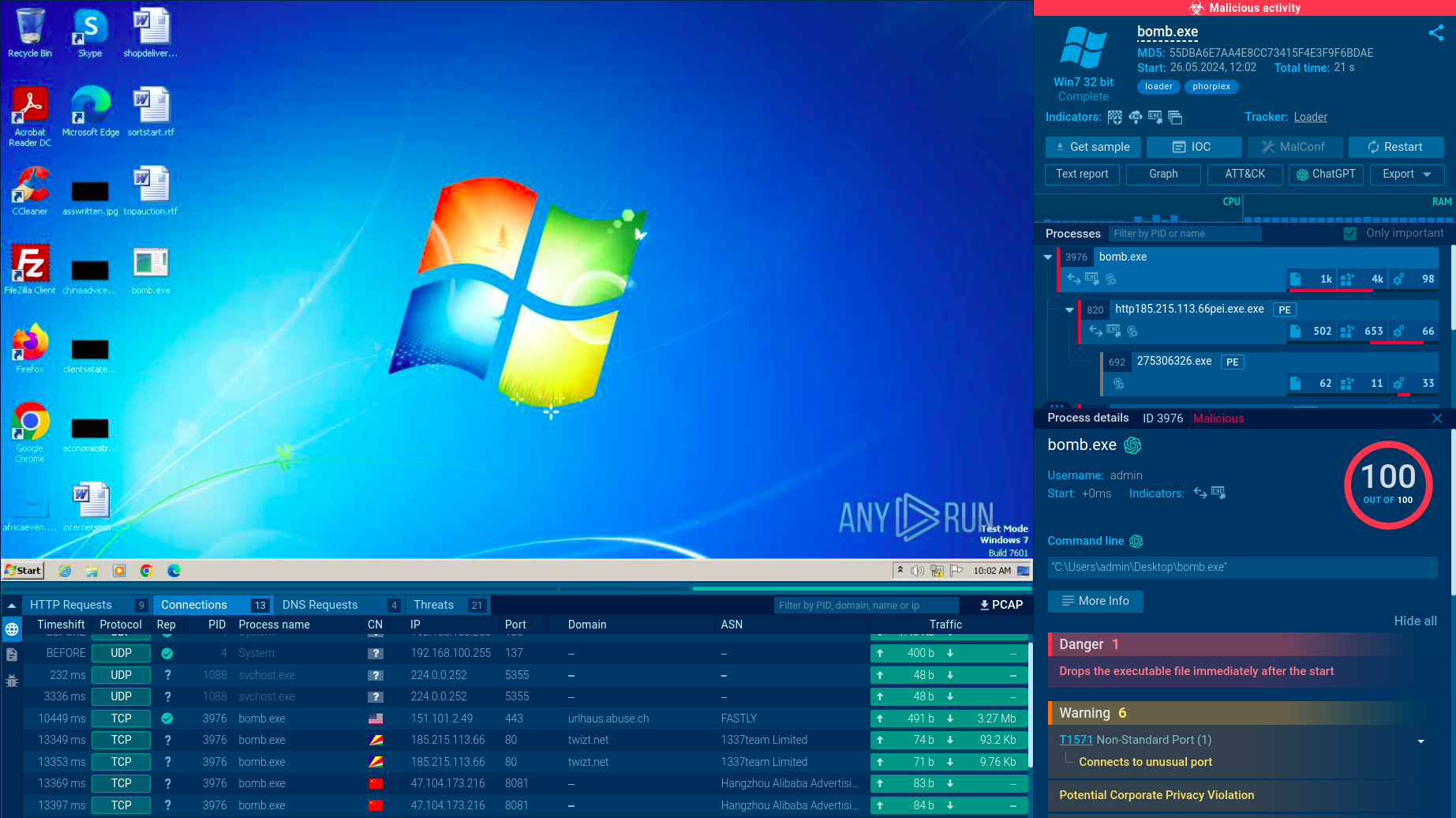
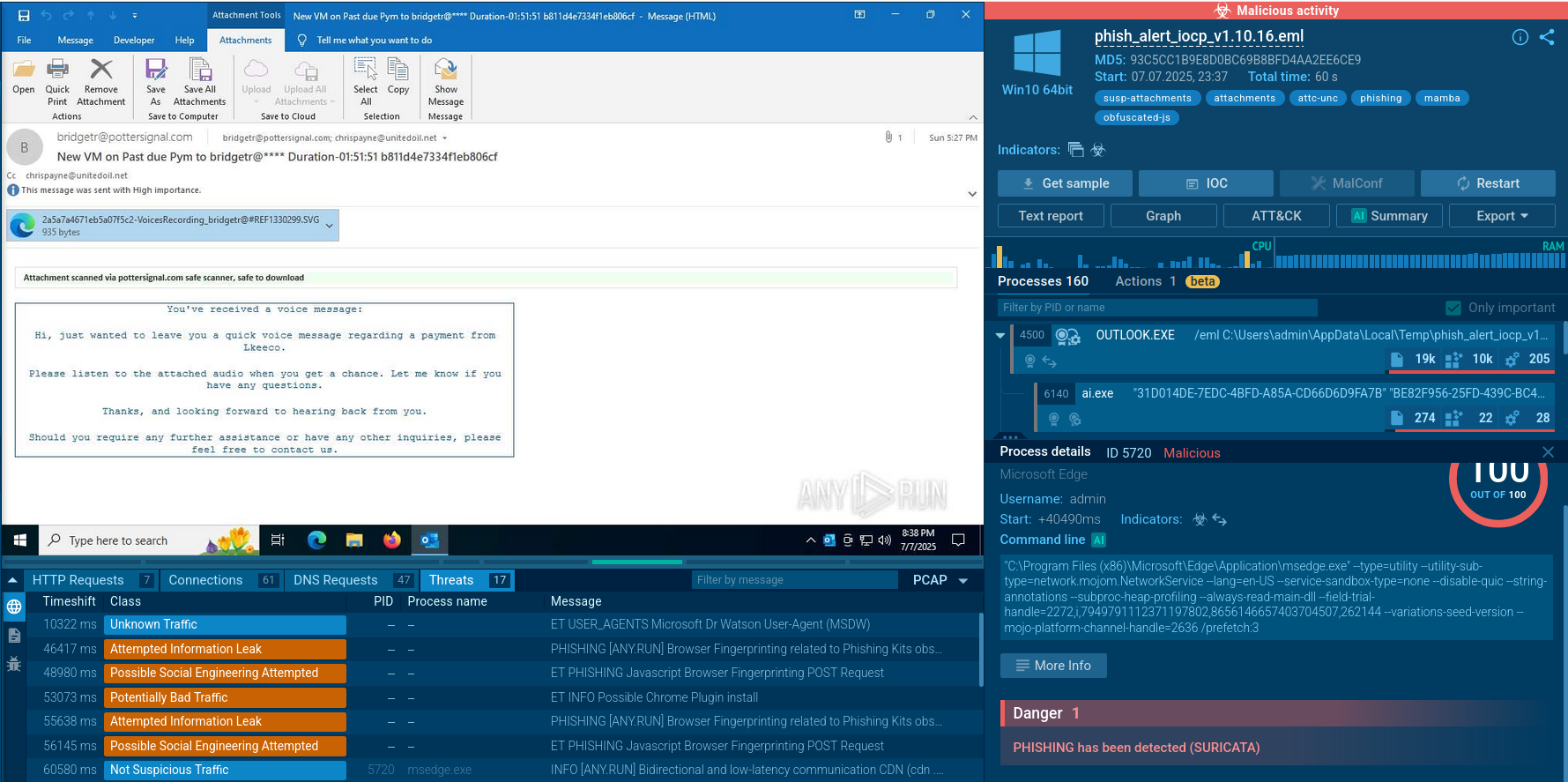
Razr is a destructive ransomware that infiltrates systems to encrypt files, rendering them inaccessible to users. It appends the ".razr" extension to the encrypted files and drops a ransom note, typically named "README.txt," instructing victims on how to pay the ransom to obtain the decryption key. The malware often spreads through phishing emails with malicious attachments or by exploiting vulnerabilities in software and operating systems. Razr employs strong encryption algorithms, making it challenging to decrypt files without the attackers' key.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2024
First seen
:
|
26 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 August, 2024
First seen
:
|
26 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 757
757
 0
0

 467
467
 0
0

 2699
2699
 0
0
Razr ransomware is a recent and sophisticated strain of ransomware that surfaced in 2024, targeting systems by encrypting essential files and demanding ransom payments from victims.
The malware has made headlines due to its unique use of cloud-based platforms, like PythonAnywhere, as part of its distribution strategy, leveraging these services to host malicious files and bypass security defenses.
Known for appending the ".raz" extension to locked files, Razr delivers a ransom note typically titled “README.txt” with instructions for payment.
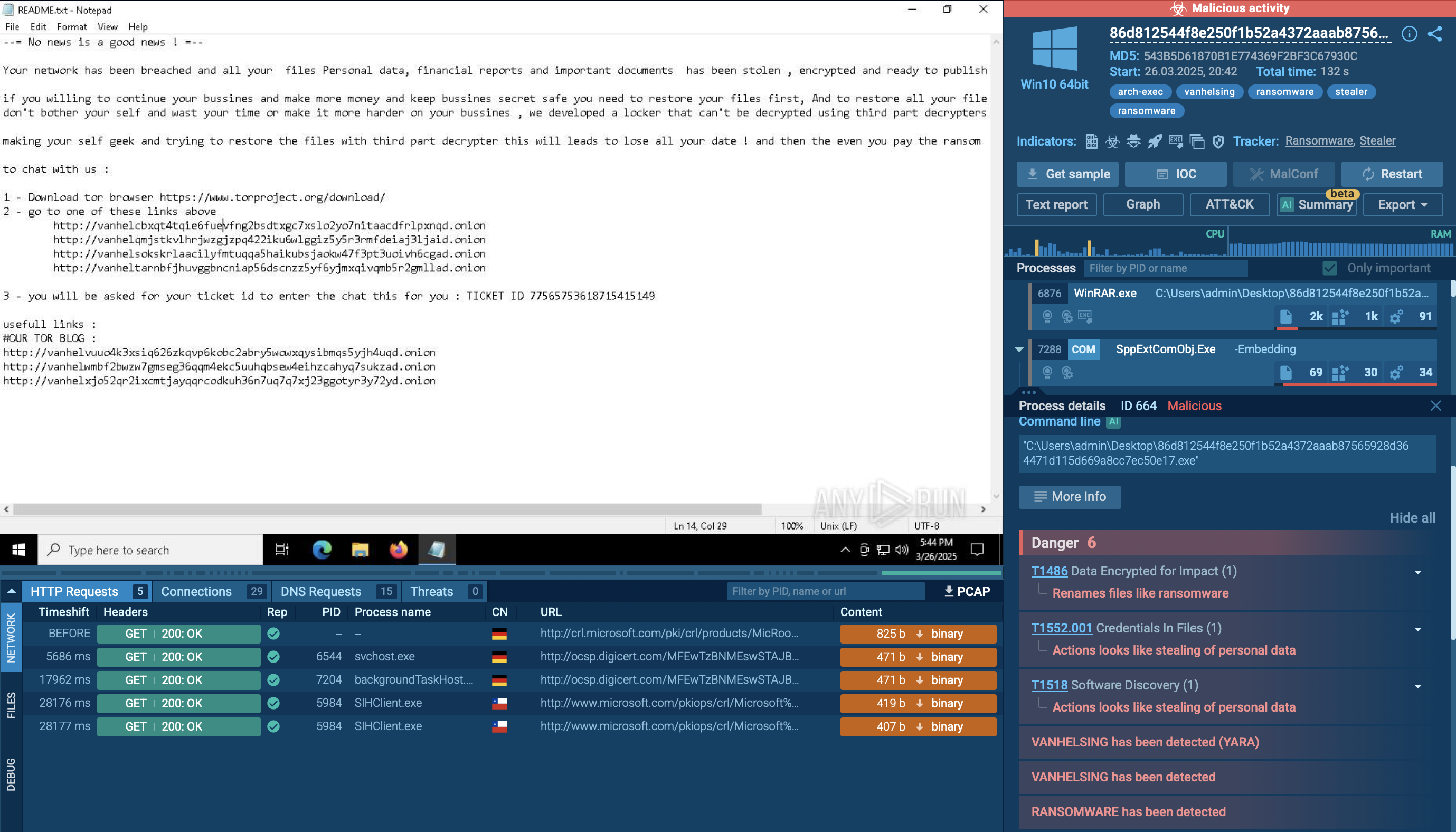
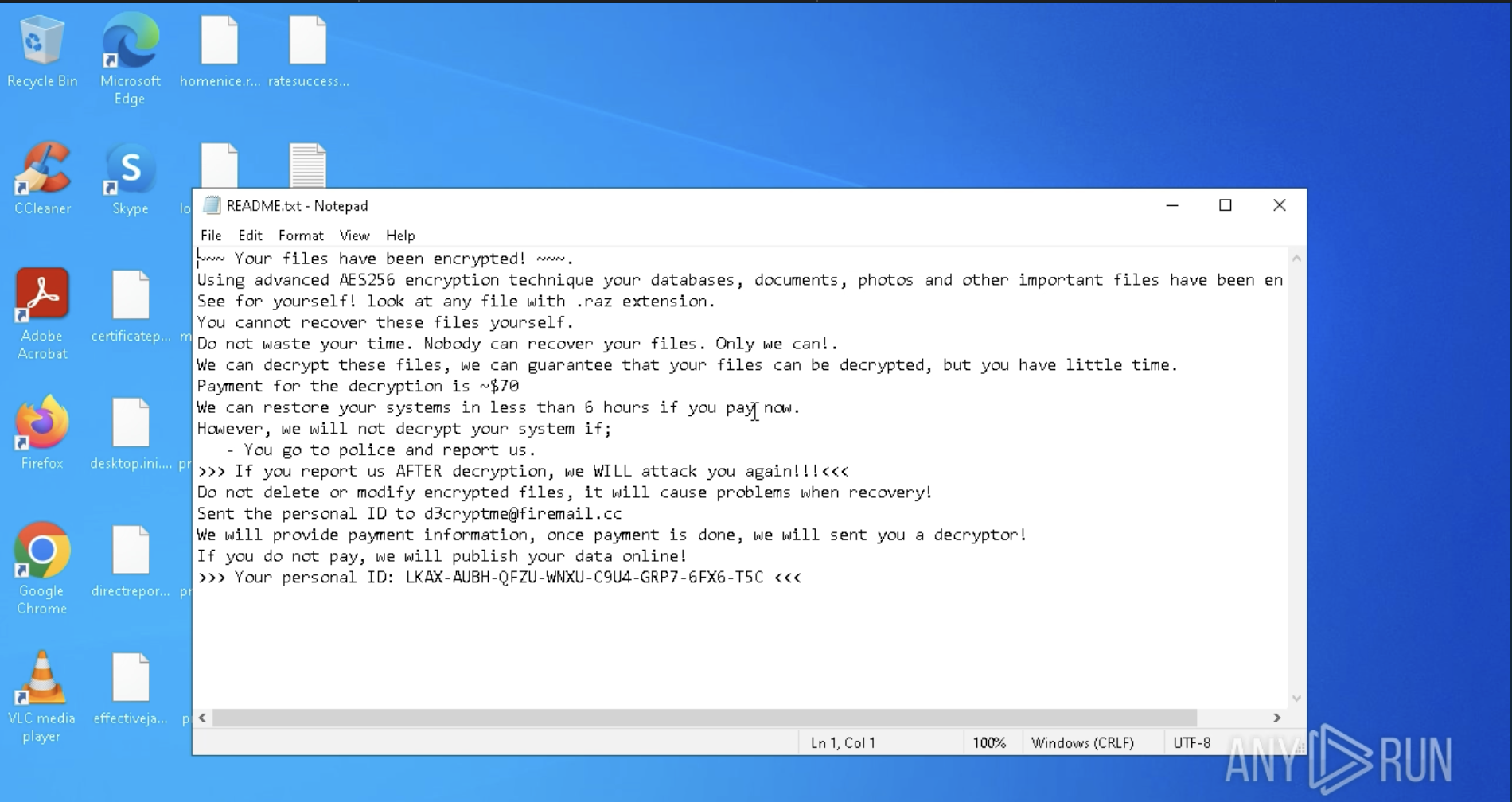 Ransom note displayed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Ransom note displayed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
This behavior and ransom note can be easily seen inside ANY.RUN’s interactive sandbox following analysis session: View analysis session
Razr’s rapid spread and its use of AES-256 encryption make it difficult for victims to regain access without paying the ransom, placing it among the newer threats that exploit trusted platforms for distribution.
The primary functionality of Razr is to exfiltrate sensitive data from infected systems. Its key features include:
To see how Razr ransomware operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
Razr ransomware typically gains access to systems through several attack vectors. Common methods include malicious email attachments or links that trick users into executing the ransomware, as well as attackers exploiting known software or operating system vulnerabilities to infiltrate networks. In some cases, compromised credentials enable attackers to access systems directly. Once inside, the ransomware establishes a foothold on the infected system.
After gaining access, Razr executes its payload by dropping and running a malicious binary that initiates the encryption process. It scans the system for valuable files, including documents, images, and databases, prioritizing those critical for operations. Razr may also exploit vulnerabilities to spread across the network, targeting other connected devices and servers.
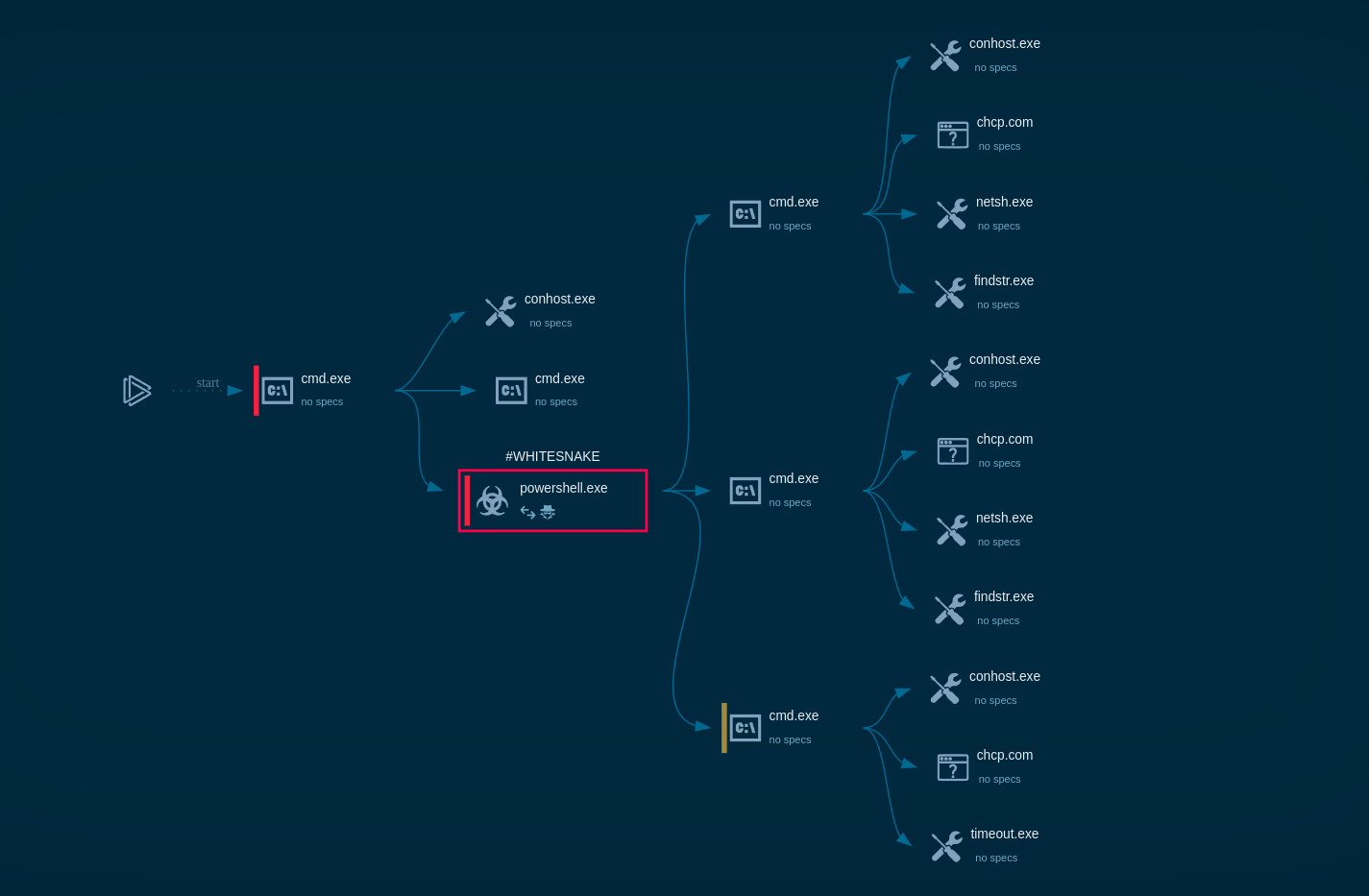
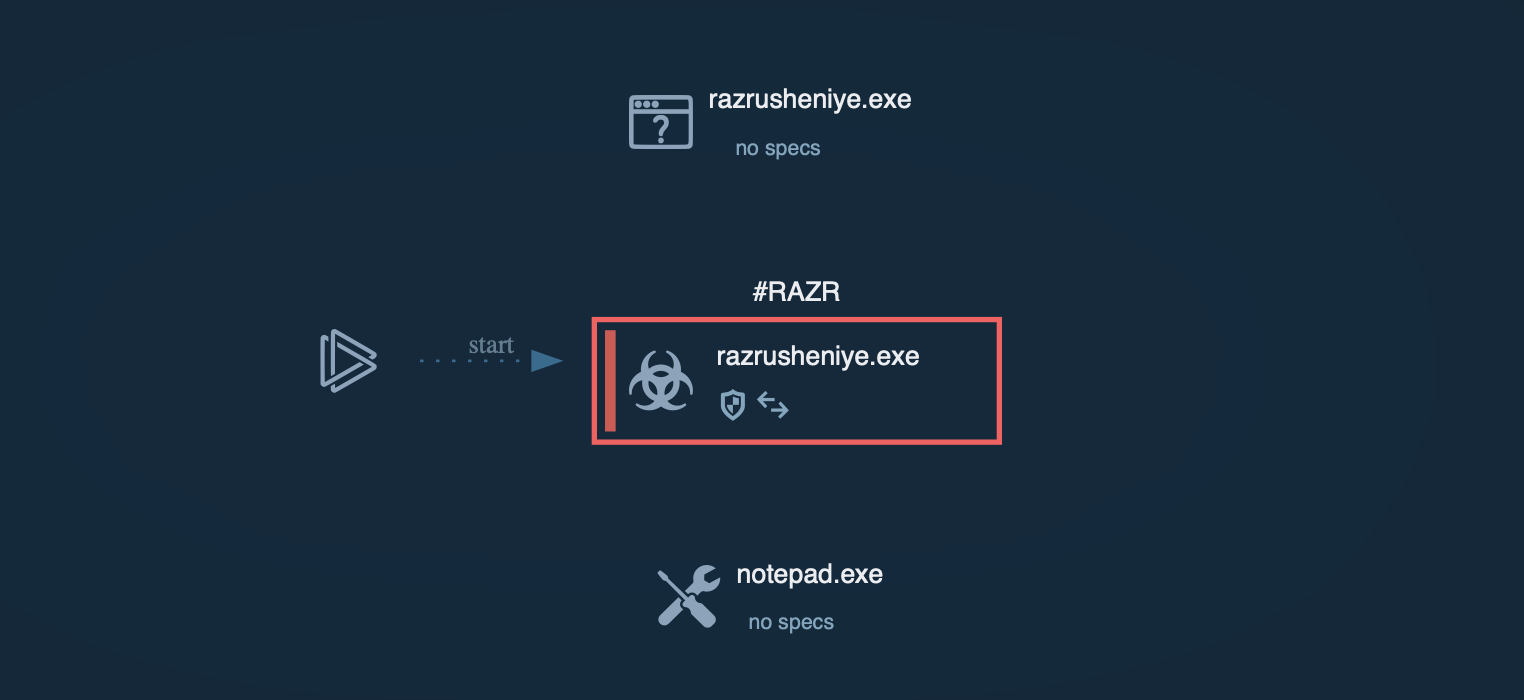 Process graph of Razr ransomware inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Process graph of Razr ransomware inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Razr's core functionality is file encryption, using the AES-256 algorithm in CBC mode. The ransomware is engineered to avoid encrypting system-critical files to ensure the operating system remains functional, thereby prolonging the attack’s effectiveness.
Once encryption is complete, Razr presents its ransom demand. Typically, it changes the desktop background or creates text files in each encrypted directory with instructions for paying the ransom.
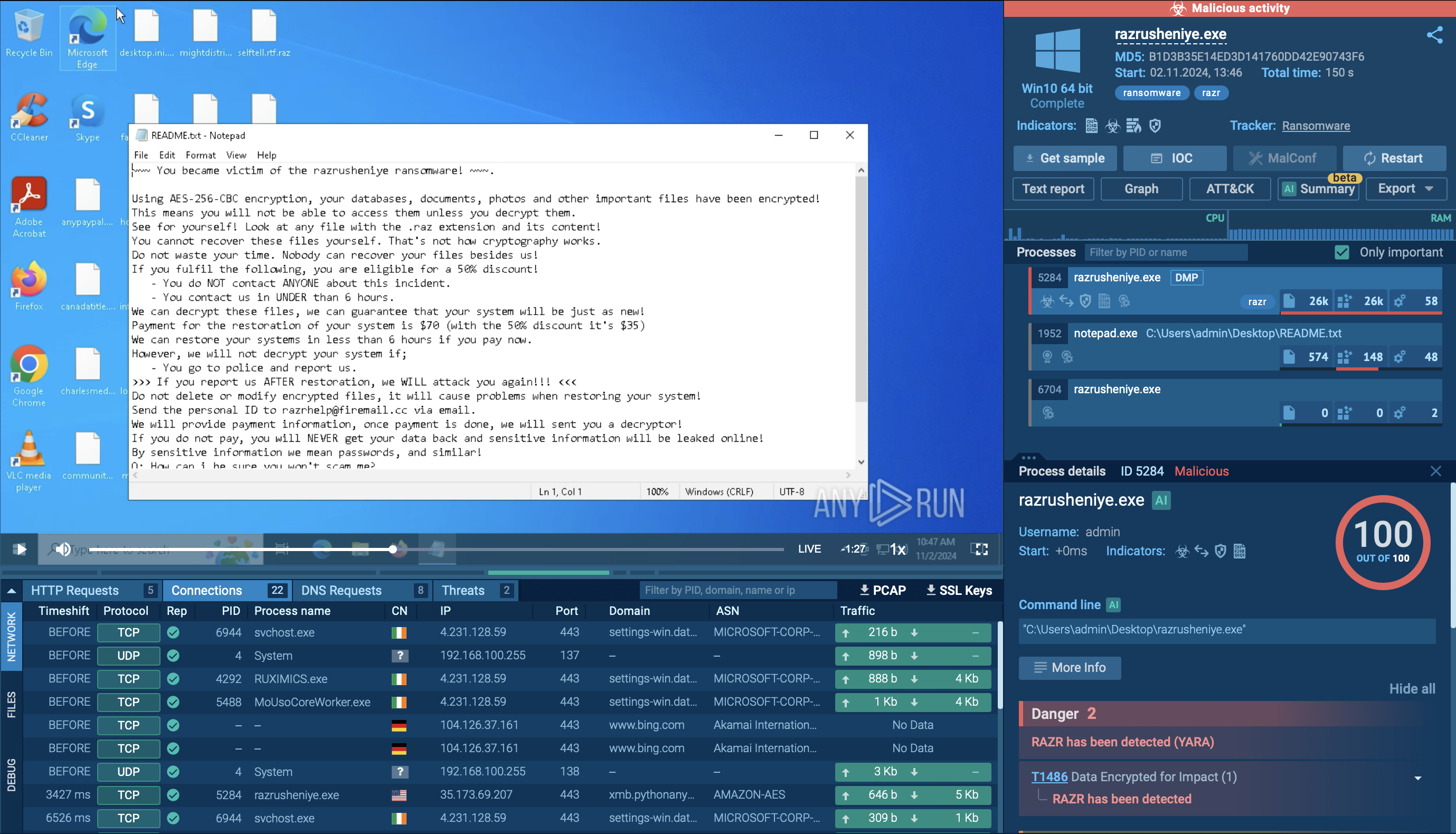 Ransom note displayed inside sandbox
Ransom note displayed inside sandbox
The ransom is generally requested in cryptocurrency, which makes transactions difficult to trace. Victims are often given a limited time frame, such as 24 to 48 hours, to pay before facing permanent data loss.
Some ransomware variants also threaten to leak sensitive data if the ransom is unpaid, increasing pressure on victims to comply. Without backups—or if backups are also encrypted—victims face significant challenges in recovering their data without paying the ransom.
Razr ransomware employs several distribution methods to infiltrate target systems:
To gather the latest intelligence on Razr ransomware, use the Threat Intelligence Lookup feature in ANY.RUN.
This service provides access to a comprehensive database with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox. With over 40 customizable search filters, users can locate data on threats like IPs, domains, file names, and process artifacts tied to Razr.
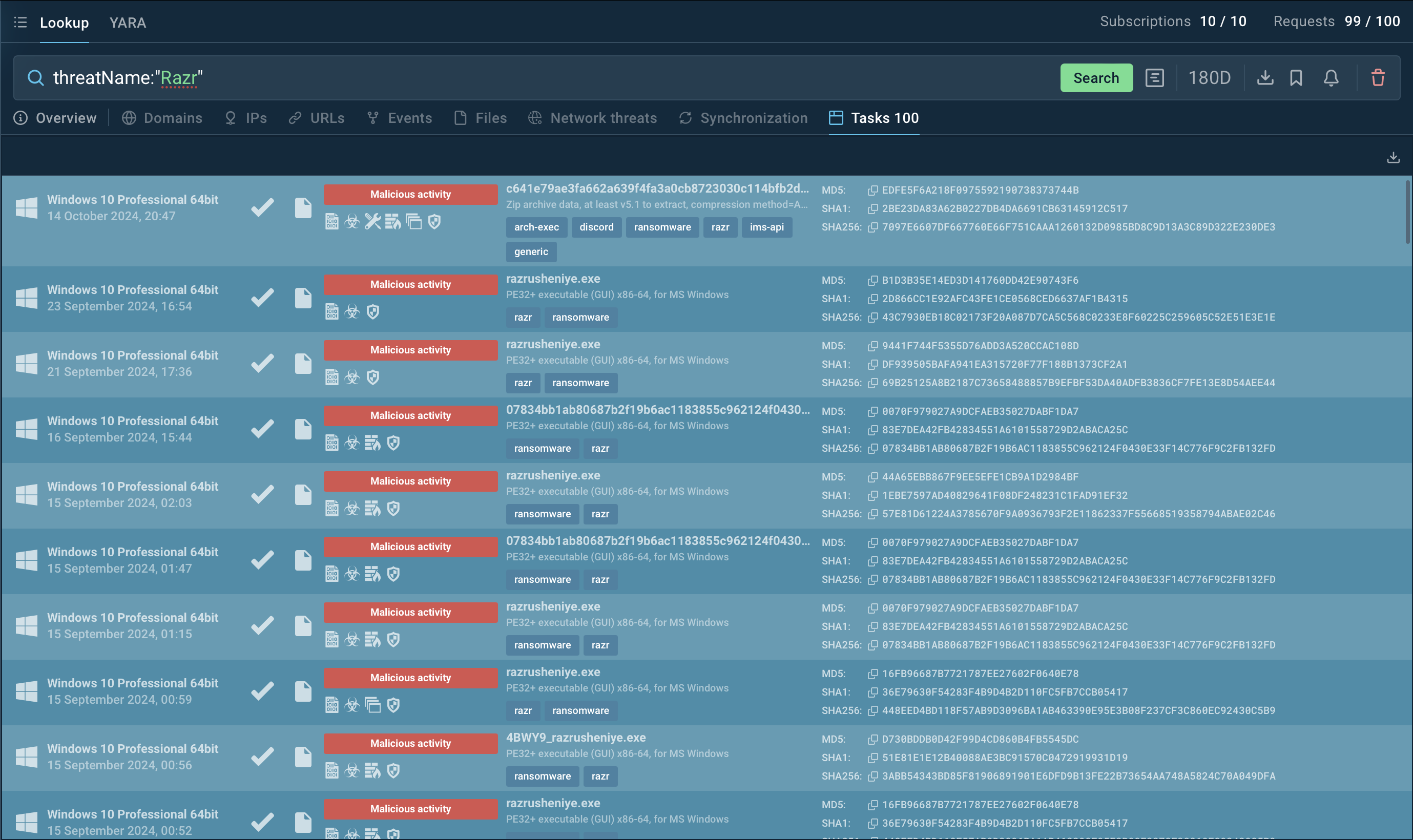 Search results for Razr in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Razr in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For instance, to collect information on Razr, you can search for its threat name or a related artifact. Entering a query such as threatName:"Razr" AND domainName:"" will generate a list of files, events, domain names, and other data extracted from Lumma samples along with sandbox sessions that you can explore in detail to gain comprehensive insights into this malware’s behavior.
Try a 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup with the ANY.RUN sandbox for hands-on intelligence gathering.
Razr ransomware is dangerous due to its strong encryption, cloud-based delivery, and ability to evade detection. Using tools like ANY.RUN is essential for proactively analyzing suspicious files and URLs, enabling early detection.
ANY.RUN offers real-time threat analysis in a sandboxed environment, providing insights into malware behavior visual tracking and other advanced features.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today and start analyzing emerging threats with no limits!