Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Raspberry Robin is a trojan that primarily spreads through infected USB drives and exploits legitimate Windows commands. This malware is known for its advanced obfuscation techniques, anti-debugging mechanisms, and ability to gain persistence on infected systems. Raspberry Robin often communicates with command-and-control servers over the TOR network and can download additional malicious payloads.
|
Trojan
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2021
First seen
:
|
9 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 September, 2021
First seen
:
|
9 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 861
861
 0
0

 511
511
 0
0

 2797
2797
 0
0
Raspberry Robin is a worm malware that has been tracked since 2021. The malware has been used to target organizations across various industries and sectors, with finance, manufacturing, and government being particularly affected.
Initially, infections with Raspberry Robin appeared to lack a specific end goal. However, it soon began to distribute other malware, including the LockBit ransomware and SocGholish (FakeUpdates).
A notable characteristic of this threat is its utilization of compromised network-attached storage (NAS) devices from QNAP, as part of its infrastructure. Another distinctive feature of the malware is its exploitation of legitimate Windows commands, such as msiexec.exe and odbcconf.exe, to retrieve, deploy, and execute malicious DLLs.
Researchers have noted a connection between Raspberry Robin and the Dridex malware, a recognized banking trojan. It is likely that these two malicious programs have been operated by the same threat actor group.
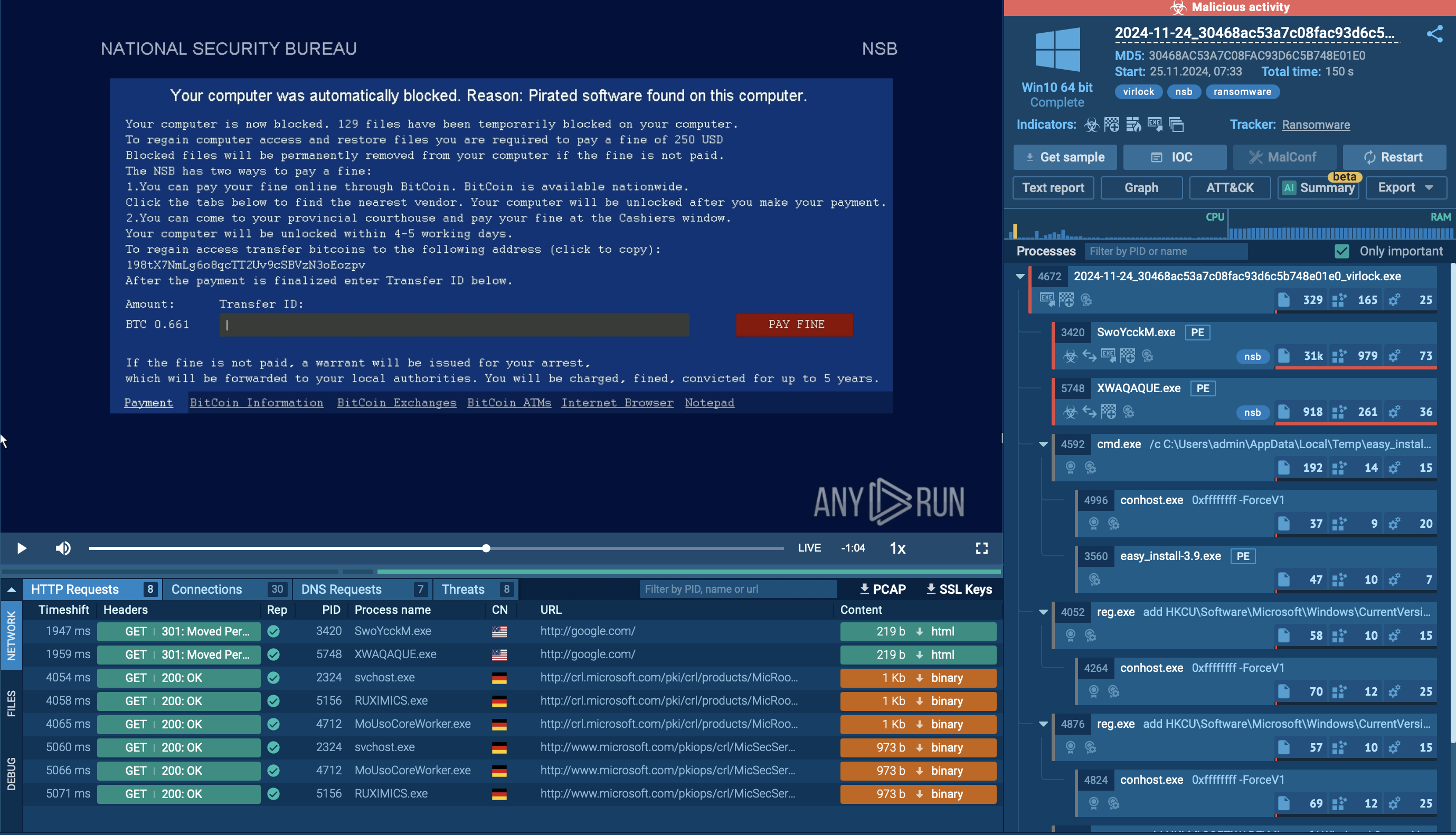
To take a closer look at Raspberry Robin’s functionality, we can submit its sample for analysis to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
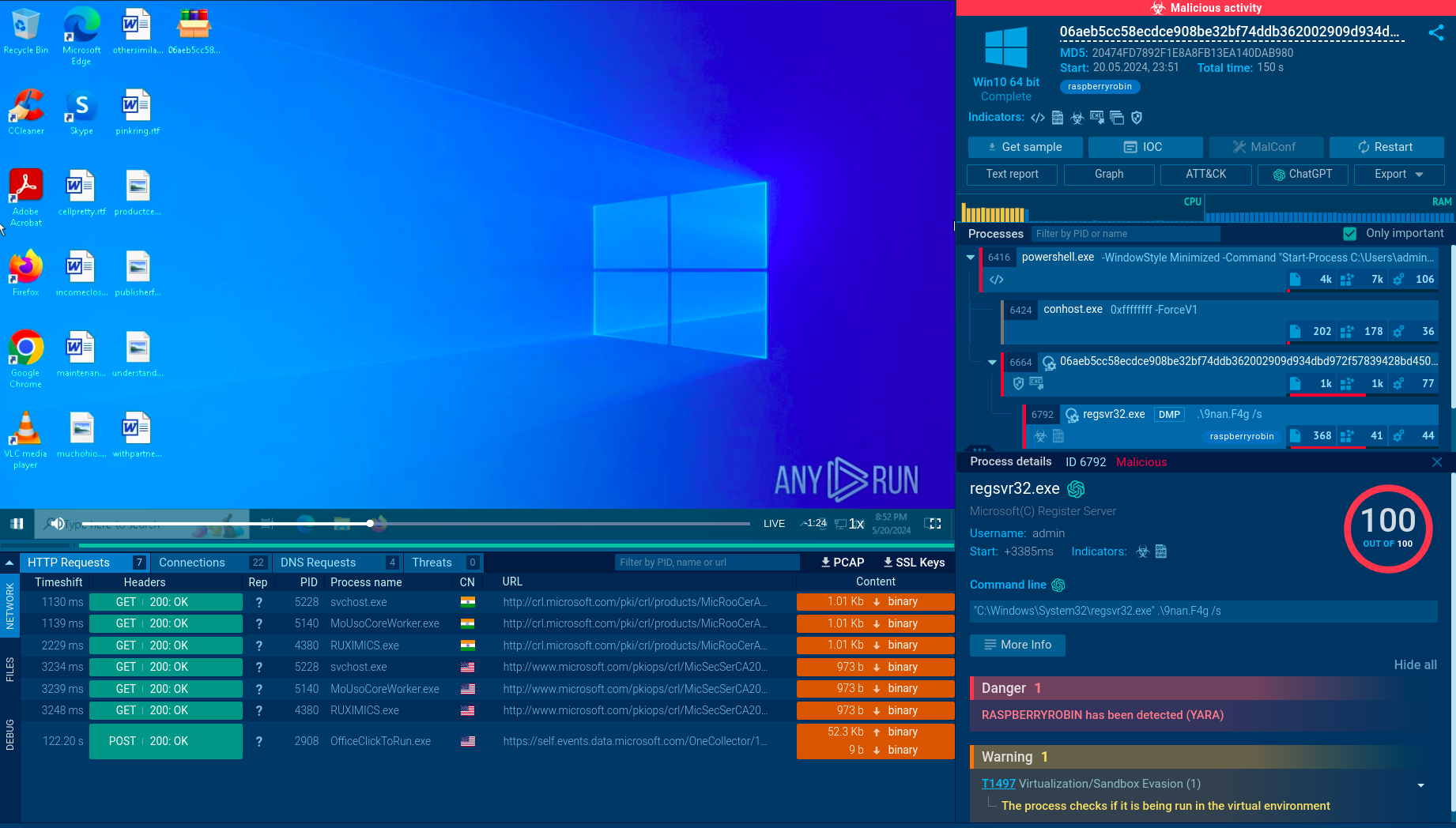 Analysis of Raspberry Robin in ANY.RUN
Analysis of Raspberry Robin in ANY.RUN
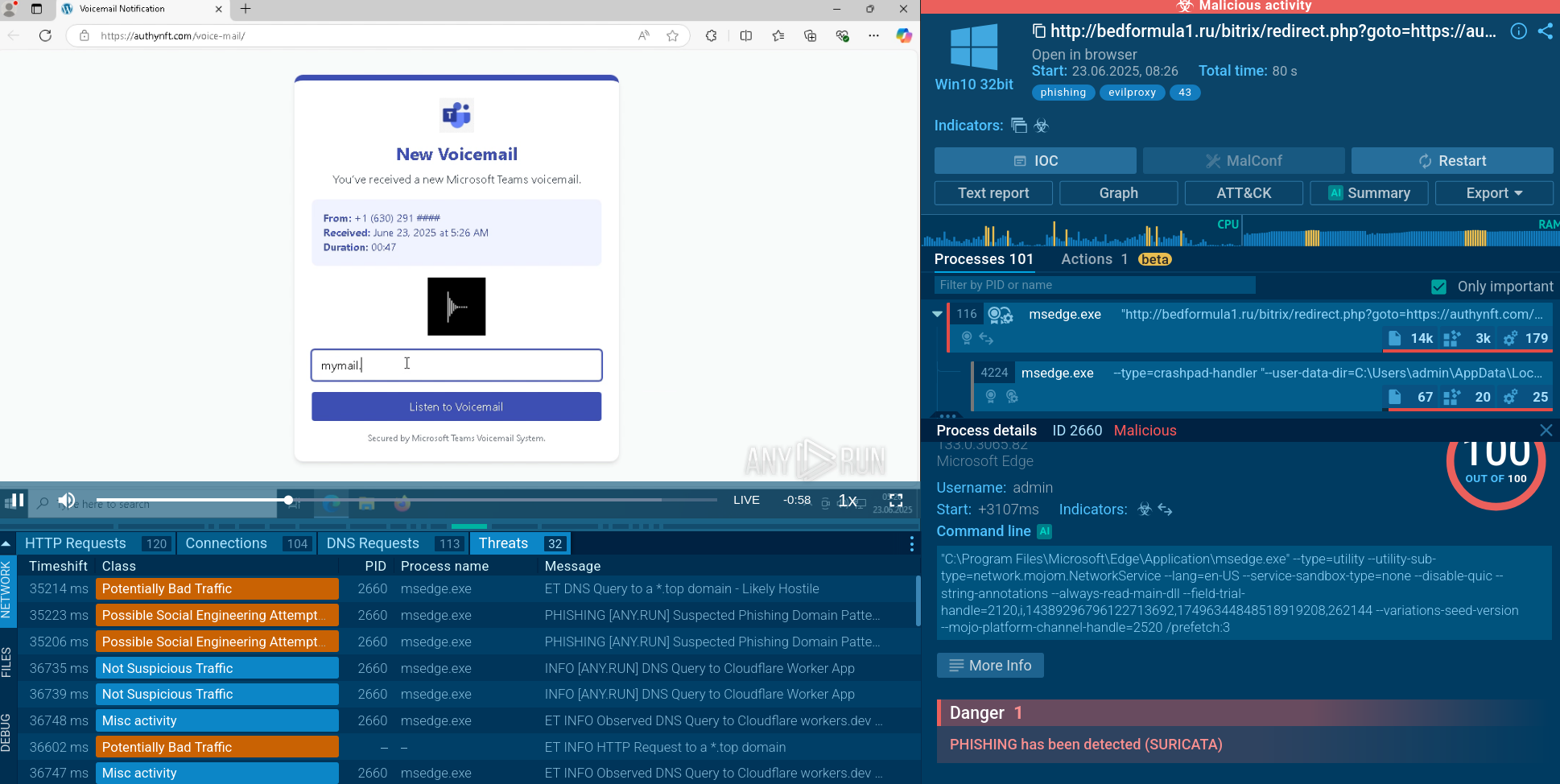
Raspberry Robin is typically delivered through infected external disks or USB drives containing a Windows Shortcut file (.lnk). Upon connecting the infected USB device and launching the .lnk file, a command processor (cmd.exe) is initiated and executes a Microsoft Installer Executable (MSIExec).
This action ultimately downloads a payload from a compromised QNAP network-attached storage (NAS) device or a web server.
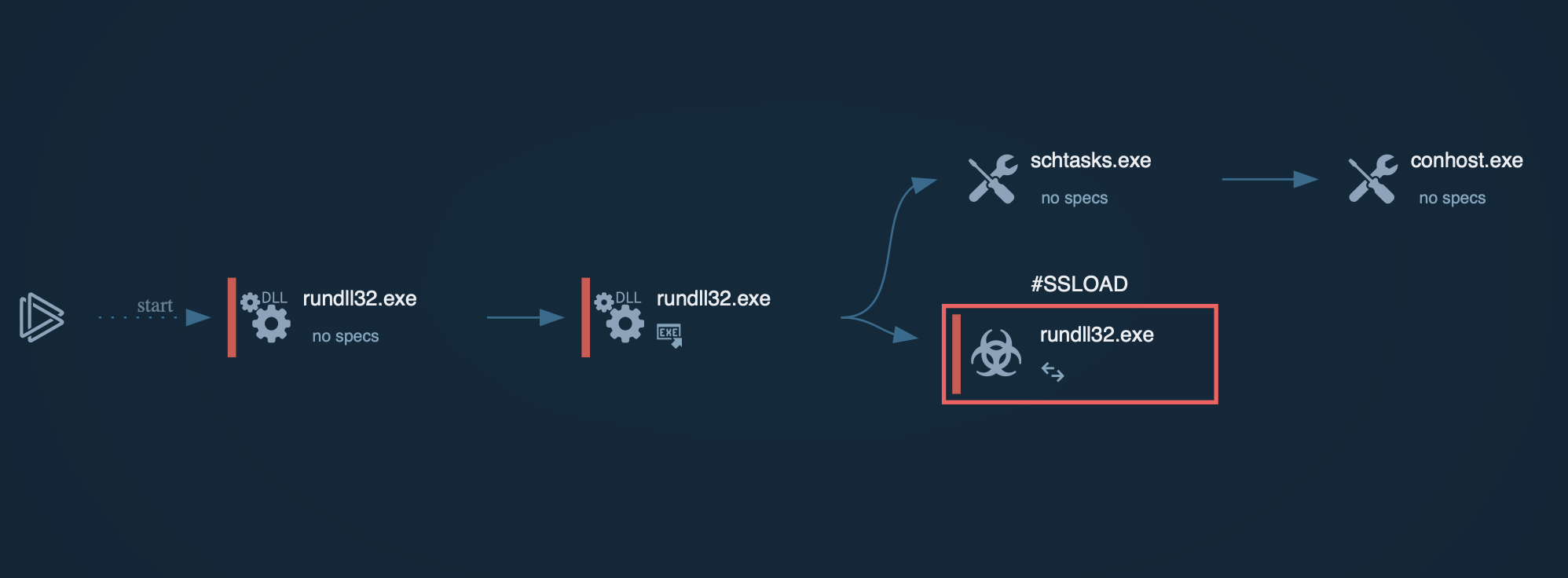
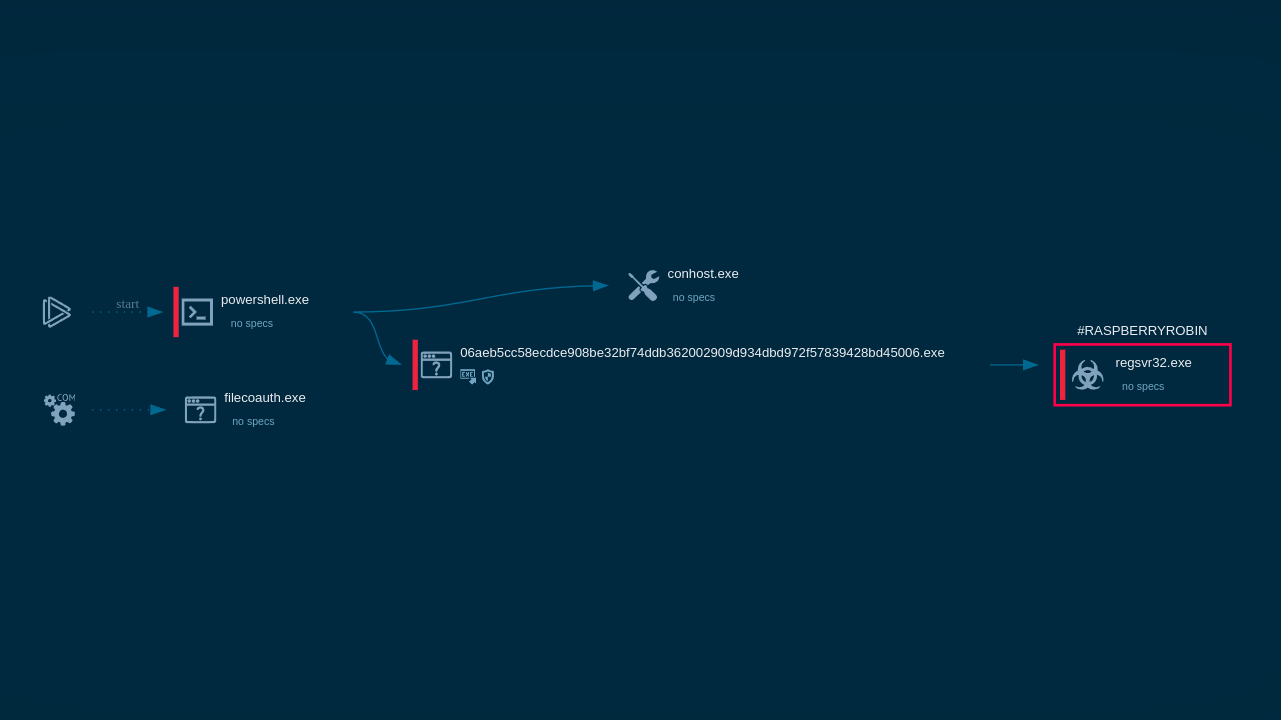 Raspberry Robin process graph demonstrated by ANY.RUN sandbox
Raspberry Robin process graph demonstrated by ANY.RUN sandbox
The payload is stored in the local AppData folder and executed using msiexec.exe, which activates the Raspberry Robin malware.
The malware communicates with command-and-control (C2) servers over the TOR network and is capable of downloading and executing additional payloads, including other malware families such as Cobalt Strike, IcedID, BumbleBee, and Truebot.
The malware often injects dozens of legitimate processes on the infected device, including dllhost.exe and rundll32.exe, which are then utilized to maintain command-and-control (C2) communication.
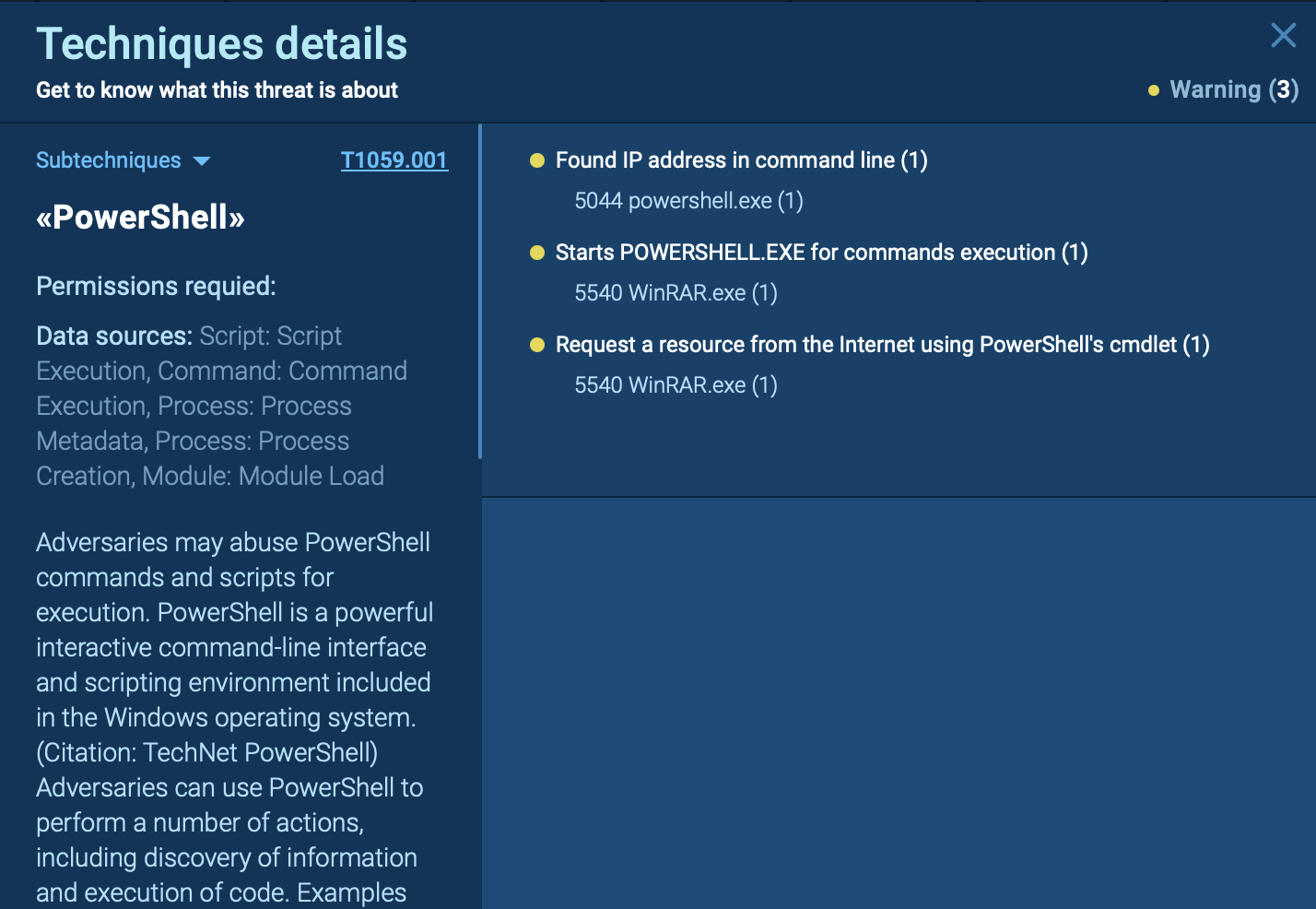
Some samples of the malware have been subjected to advanced obfuscation, packing, anti-debugging, and evasion mechanisms. One unique method involves downloading a fake payload after the threat detects a virtual environment. Other anti-VM techniques include identifying the system's Mac address and processor information. Learn more about how you can counter anti-VM techniques in a sandbox.
The malware can also detect common antivirus software, such as Avast and BitDefender, by checking if the system has active processes related to these programs.
Raspberry Robin establishes persistence on the system by adding registry keys and employing other techniques to ensure it runs automatically at startup. The malware can gain elevated privileges on the machine through a User Account Control bypass.
Once it gains persistence on the system, the malware may initiate connections to TOR nodes to communicate with its command-and-control (C2) server via TCP ports, such as 8080.
Since Raspberry Robin is a worm type of malware, it has the ability to self-replicate and spread without requiring human interaction. This malware has been spreading primarily through infected USB drives, which has allowed it to achieve a significant scale of distribution across numerous machines. As users unknowingly connect infected USB drives to their devices and execute the malicious files, the malware propagates to new systems, expanding its reach and potential impact.
In addition to infected USB drives, another vector of attack for Raspberry Robin may involve an archive distributed through Discord. It usually contains Oleview.exe, a legitimate Windows application, alongside a malicious .dll file. When a user extracts and launches Oleview.exe from the archive, it side-loads the malicious .dll file, leading to the infection.
Raspberry Robin is still an active threat, which means that thousands of systems worldwide are at risk of being targeted by it. To effectively counter Raspberry Robin, implement strong security policies, maintain updated software, and provide ongoing security awareness training. Using a quick and effective sandbox should be one of the core elements of this strategy.
ANY.RUN's cloud sandbox provides many benefits for examining malware, such as: