Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Phobos is a ransomware that locks or encrypts files to demand a ransom. It uses AES encryption with different extensions, which leaves no chance to recover the infected files.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2017
First seen
:
|
24 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2017
First seen
:
|
24 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Phobos Ransomware encrypts data until a ransom is paid. 77% of Phobos attacks are successful according to the latest research. This malicious program was recorded in the wild for the first time in October 2017.
Phobos ransomware appeared in 2017 in Dharma, also known as the CrySIS, family. A year later Phobos developed and spread rapidly. In 2019, it accounted for 8.9% of the submitted ransomware attacks. The First-quarter of 2020 showed that the Phobos strain was noted as one of the most common ransomware with 9.70% of submissions. It constantly gets updates and new versions.
The ransomware targets organizations all over the world. Phobos compromises RDP servers that are open or have weak security. Then cyber criminals send ransom notes, where the victim is asked to contact one of the emails to get the decryption key.
Phobos attackers exactly like Dharma ones can discuss ransom amounts depending on the company. The Ransom amount can reach 20,000 USD in Bitcoin. It is lower than usual ransomware demands because Phobos chooses small companies as victims. And sometimes cybercriminals don’t give up the decryption key even after the payment.
The malicious program uses encrypt data using AES and adds extensions to infected files such as .phobos, .phoenix, .actin, .help, .mamba and others. These files can be fully or partially encrypted.
Phobos is named after the Greek god of fear, but there is nothing divine about it. Criminals buy this malware in RaaS packages, so even without deep technical knowledge, they have an opportunity to design their own strain and organize an attack on the chosen victim.
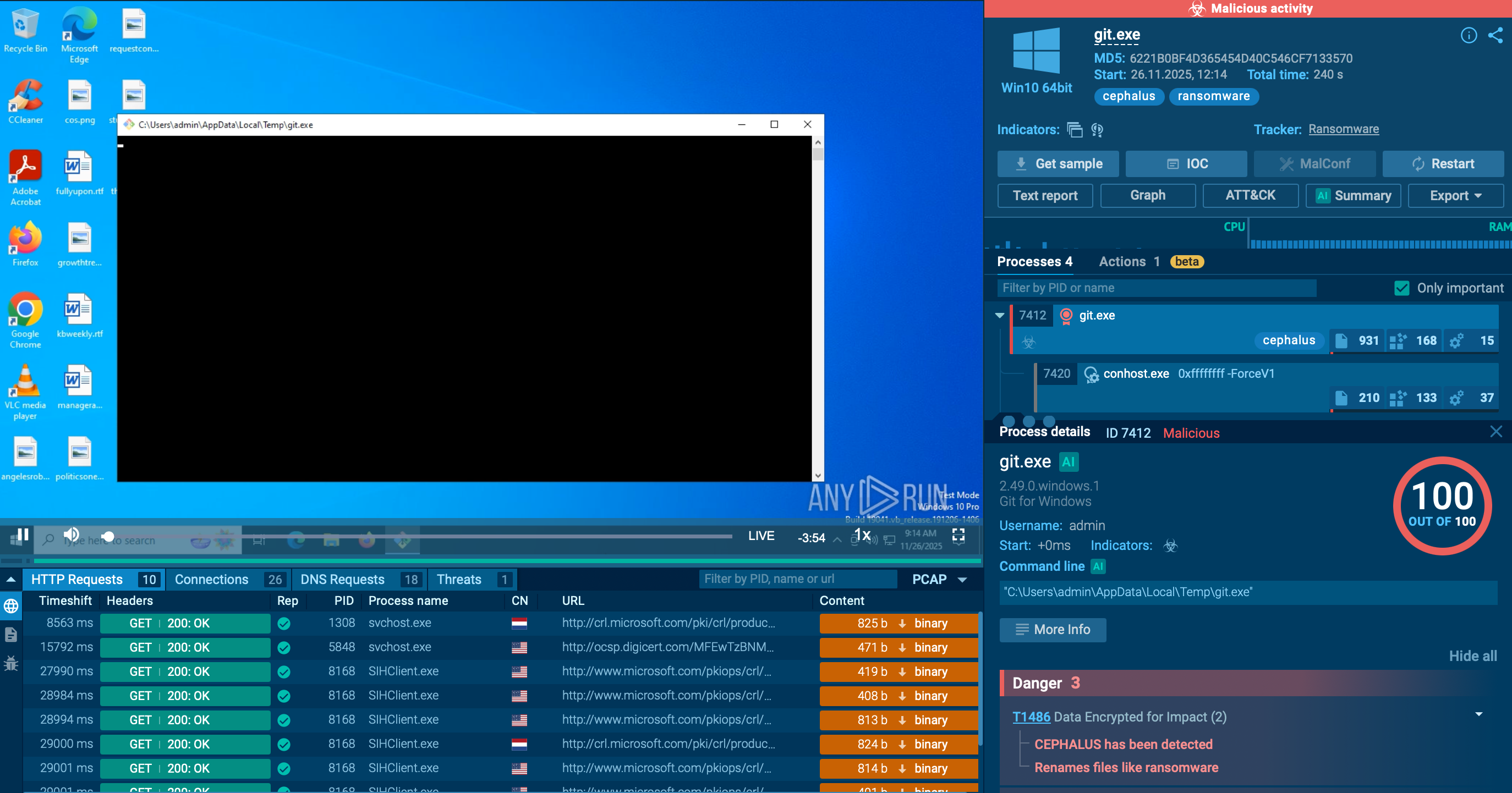
The ANY.RUN malware hunting service features a video that displays the complete execution process of Phobos.
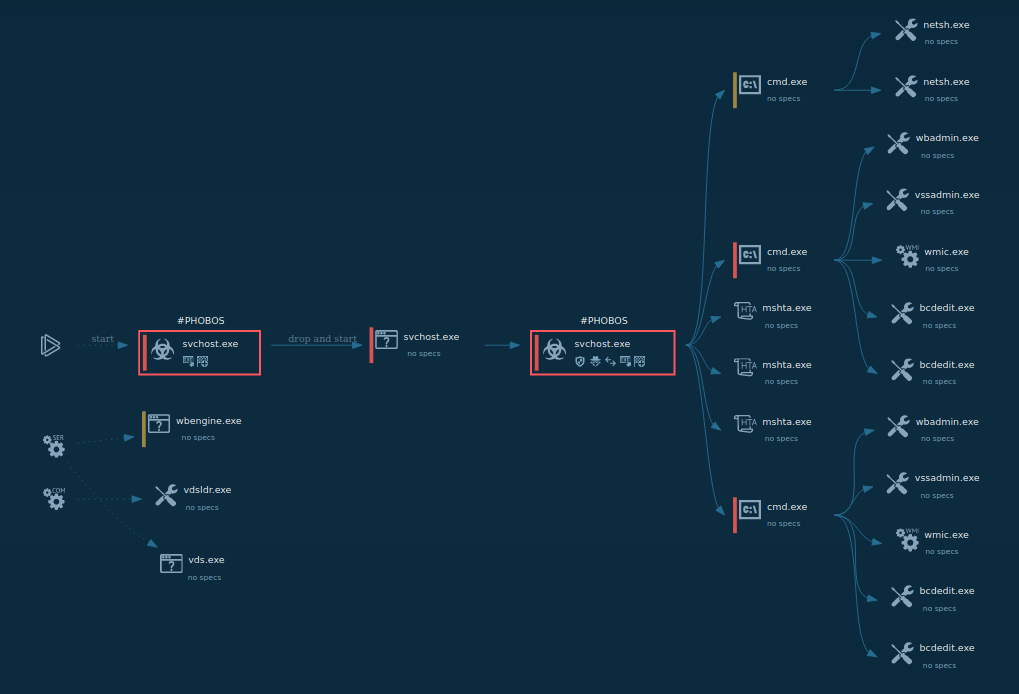
Figure 1: Shows the graph of processes created by the ANY.RUN interactive malware analysis service
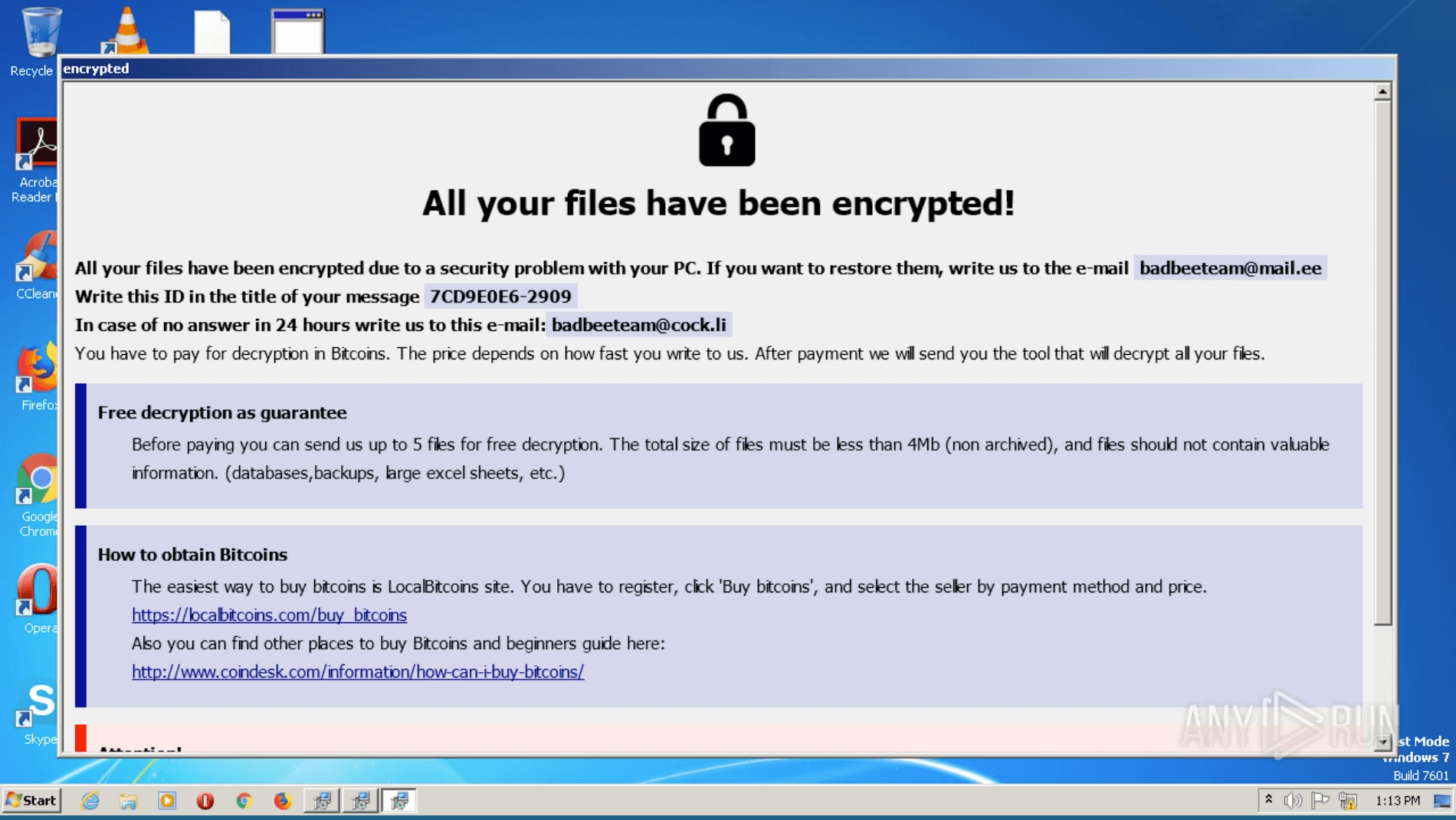
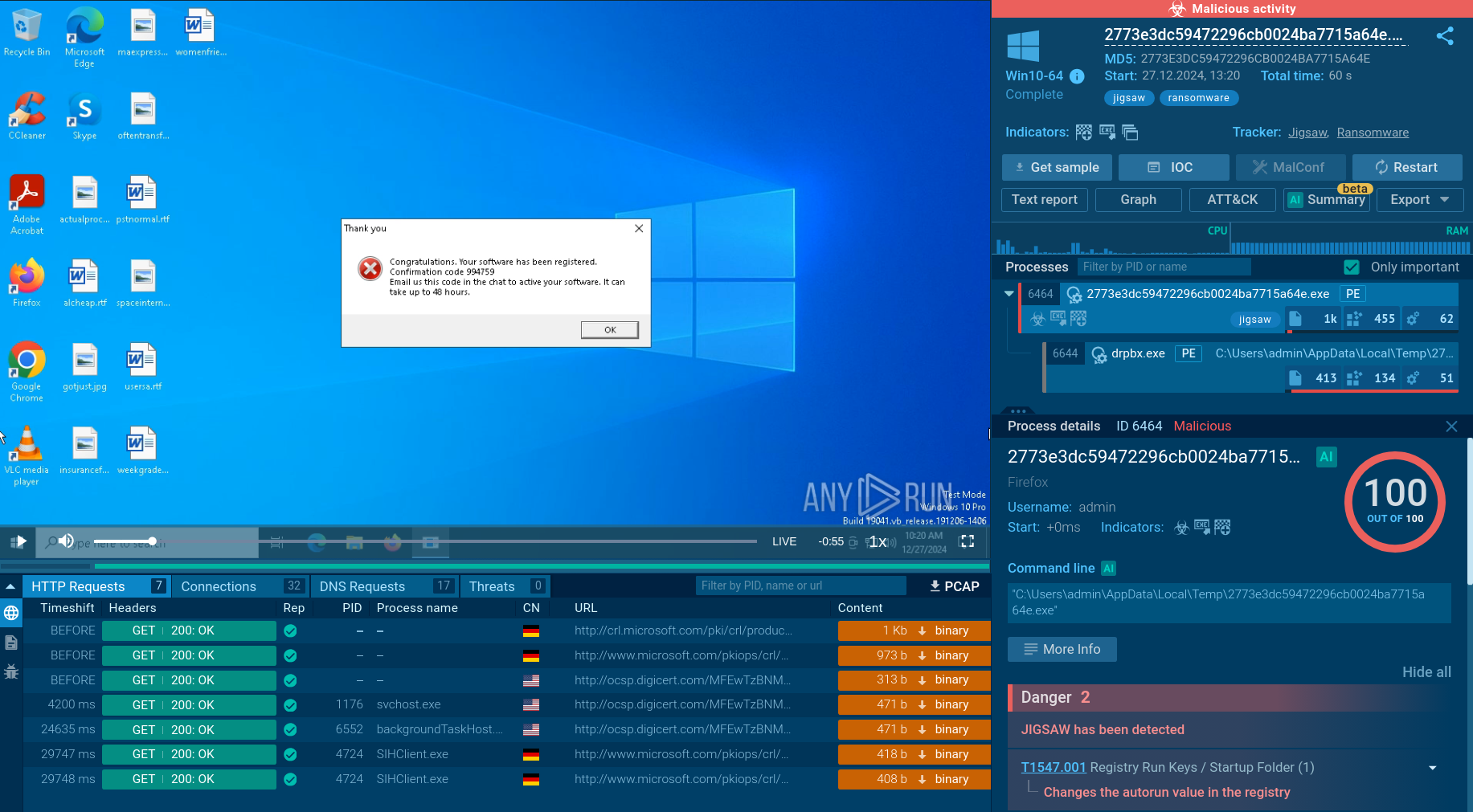
Figure 2: Phobos ransom note
The execution process of the Phobos ransomware is relatively typical for this type of malware such as Troldesh. The executable file makes its way into an infected system and runs, then the main malicious activity begins. After the start of execution, the Ransomware deletes shadow copies. Interestingly though, as soon as it encrypts all targeted files, Phobos pops up a ransom note on the desktop, which is the ransomware executable file itself.
Phobos has several ways to end up on your machine:
These distribution methods help attackers to steal victims’ information and encrypt the data by running Trojan or other malware. And a variety of the infected files is huge: documents, PDF and text files, databases, photos and videos, archives, etc. They can be located both in internal and external folders. Phobos gets rid of files’ shadow copies and backups.
Phobos is not a new type of ransomware, moreover, it has some similarities to Dharma. There is no need for criminals who use Phobos to be qualified specialists. Nevertheless, this ransomware always evolves, and its attacks are effective. It has a lot of ways to get into your device to get a ransom. That is why Phobos can be a serious threat to organizations.