Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Troldesh is ransomware — a malware that demands a payment in order to unlock encrypted files. It is also can search and steal information from the banking programs if such are found on the infected machine.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2014
First seen
:
|
15 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 January, 2014
First seen
:
|
15 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Troldesh, also known as Encoder.858, is ransomware belonging to the Shade ransomware family. It was created in 2014. The malware encrypts files on the victim's machine and demands a ransom for the data to be restored.
Attempting to get as much information as possible, the malware also scans the target PC for banking files or banking programs to squeeze every last penny.
Attacking Windows users mainly in Russia, Ukraine, and Germany, Troldesh is one of Russia's most commonly used encryption software.
In addition to this behavior, Troldesh ransomware often comes in conjunction with two particular malware samples, namely Mexar, and Teamspy, which allows attackers to control the victim's PC remotely and gives the virus the ability to install other malware, including trojans on the infecting PC.
In fact, unlike most other ransomware Nemty or others, this virus does not stop executing after encrypting the victim's files. Instead, it starts an infinite loop where it requests URLs of other malicious programs from the command server, downloading and installing them on a contaminated machine. This strategy means that most victims contaminated with Troldesh may end up with a whole host of infections on their PC. And even with removal tools and decryptors, it can be challenging to get rid of this issue.
Even though the malware itself has not evolved a lot throughout its lifespan, attackers' method to demand the ransom has changed. The first malware samples were used to provide an email address at which the victim could contact the hackers and negotiate the payment. In newer campaigns, ransom node demands victims to use the Tor browser to navigate to a payment page that is located on the Dark Web.
Trodlesh, as part of the Shade family, shares several familiarities with related malware: they are written in C++, utilize CTL, use a static link with a Tor client. Every particular malware sample also has a hardcoded URL of the command server. Malicious programs of this family are also known to exhibit similar or identical behavior. As such, they create ten identical ransom notes in two languages – Russian and English and name them README1.txt or README10.txt.
A video simulation recorded on ANY.RUN allows us to examine the lifecycle of the Troldesh malware in a lot of detail.
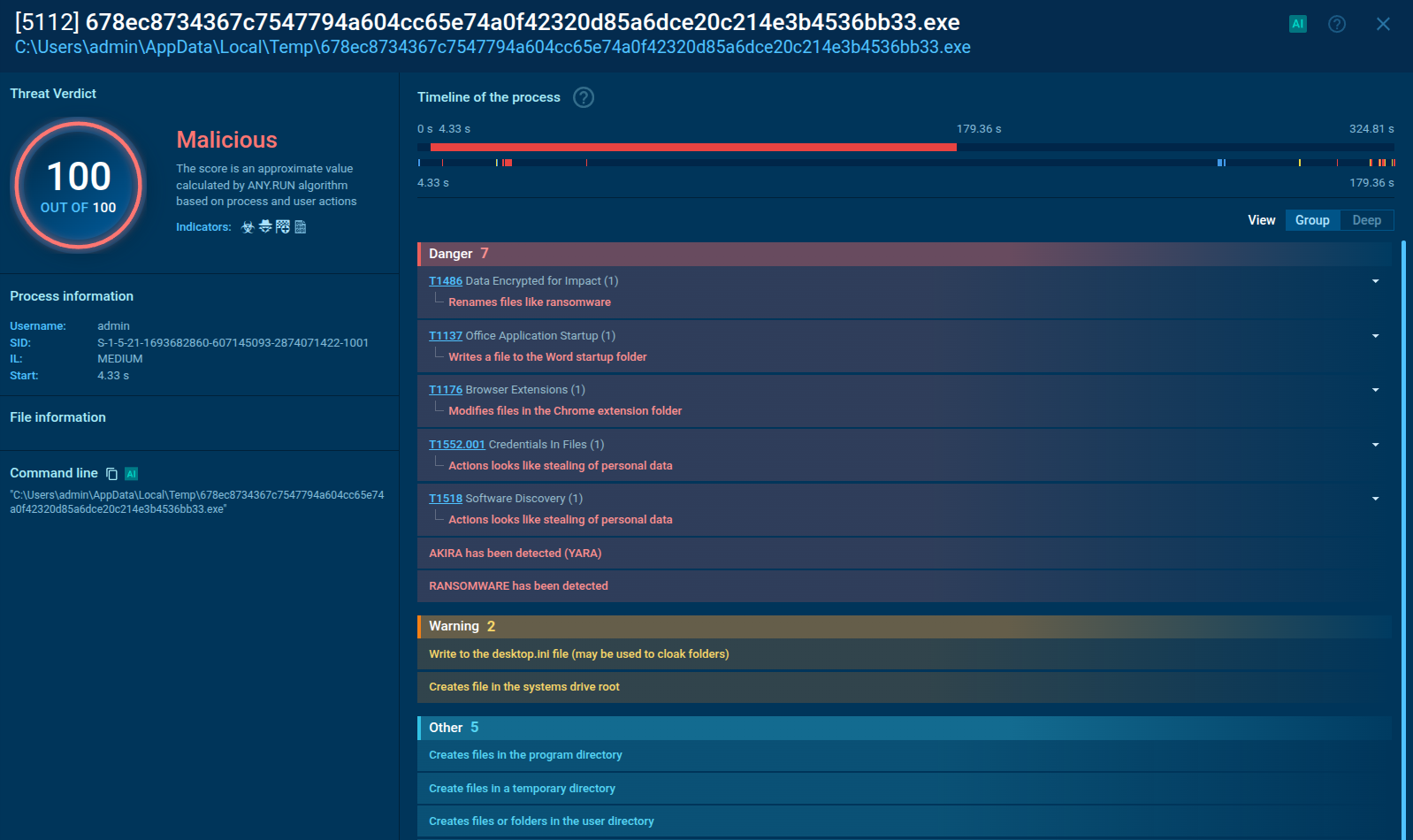
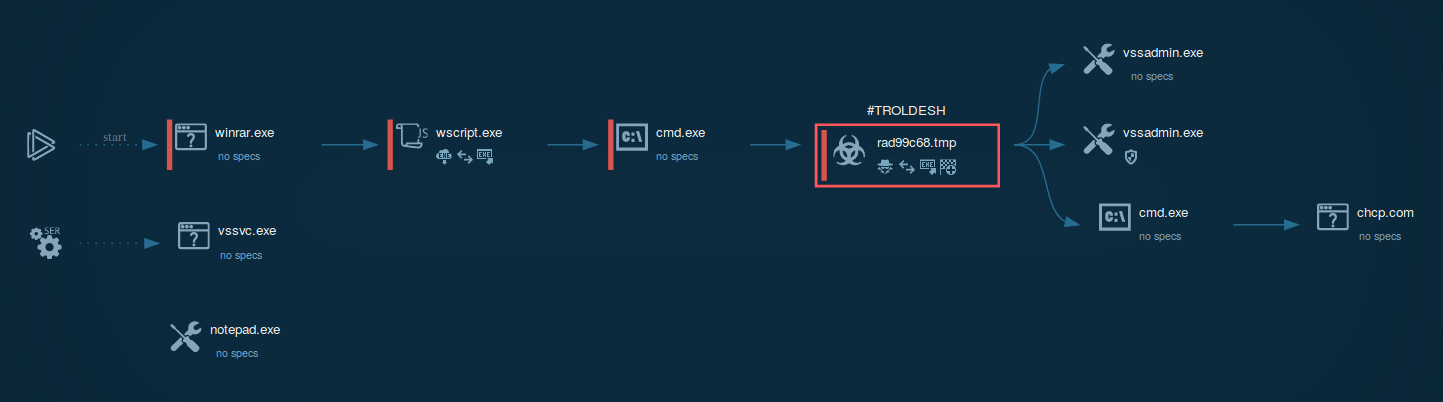 Figure 1: Process graph generated by ANY.RUN helps us visualize the life cycle of the virus
Figure 1: Process graph generated by ANY.RUN helps us visualize the life cycle of the virus
Troldesh ransomware is spread in the form of a script file, either Javascript or JScript. Usually, these files are packed in an archive file that is sometimes protected with a password. In the simulation performed on ANY.RUN, after a script file was unpacked and launched, it installed an executable file from the internet. It should be noted that in the case of Troldesh, executable files typically have "not suspicious" extensions along with the likes of .jpg. After being downloaded, the files are renamed and executed.
As shown in the ANY.RUN simulation, after running, the file immediately began performing the malicious activity, namely: encrypting files, stealing personal data, deleting shadow copies, and changing autorun values in the registry. Files encrypted by the latest versions of Troldesh are known to have a .crypted000007 extension which was also the case in our simulation. Lastly, after encryption was completed, the malicious executable file dropped ransomware instructions on the desktop.
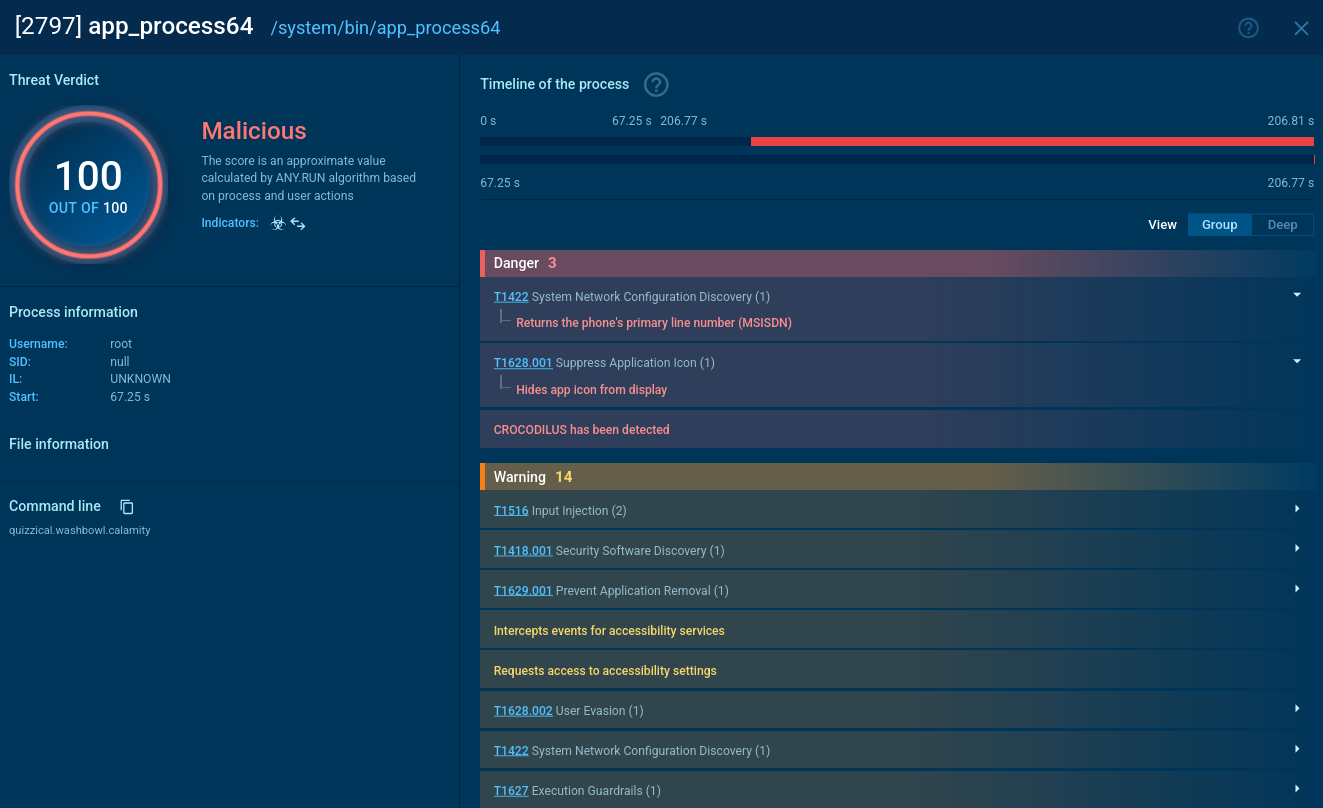
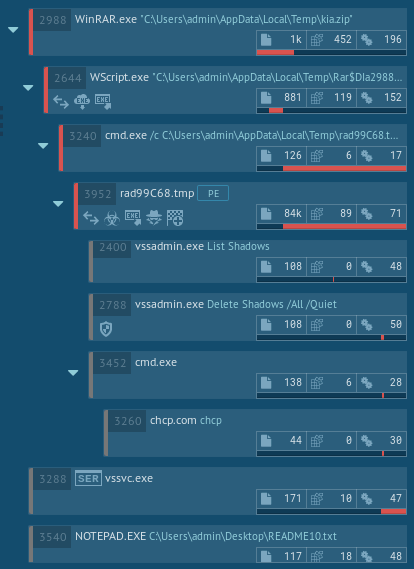 Figure 2: Process tree of a Troldesh ransomware execution
Figure 2: Process tree of a Troldesh ransomware execution
Since Troldesh is commonly distributed using malspam campaigns that mimic real company newsletters, a good way of staying safe is thoroughly checking for the authenticity of emails before downloading any attachments. If necessary, one can get in touch with a company that is the presumable author of the newsletter and verify that they have sent the email.
Once infected, Troldesh installs several secondary malware samples on the victim's PC, thus after Troldesh removal – malware deletes itself from the PC, it is vital to conduct a global system scan and make sure that one's machine is not swarming with other viruses as well.
Troldesh ransomware is known to utilize two main attack vectors – email spam and exploit kits. Malspam campaigns usually mimic legitimate information newsletters from actual Russian companies, including banks and large supermarket chains. The emails themselves contain an archive file in which another script file is included.
Upon unpacking the archive and clicking on the file, a malicious loader is installed. It in turn downloads and installs the main payload – Troldesh itself. The loader is known to be stored on legitimate but compromised WordPress websites where it is hidden as an image file.
Troldesh is also known to utilize Axpergle and Nuclear exploit kits, and these attacks are, arguably, more dangerous than email spam as they don't require active actions from the user for the contamination process to begin. Instead, upon visiting a compromised URL, which can be a website hosted by the attackers or a legitimate website that has been hacked, the malware utilizes a vulnerability either in the browser itself or in one of the browser plugins, successfully penetrating into the users PC and starting the execution automatically. Thus, victims can get infected without ever realizing the danger, so get a removal program and a decryptor.
Address information of C&C servers is embedded in the body of each malware sample. Servers themselves are hosted on the dark web and communication is established with the use of a Tor client.
Once installed on a victim's PC, the malware requests a public key value from the server to encrypt the victim's files. Should the connection attempt fail, the virus uses one of one hundred private key values stored in its memory.
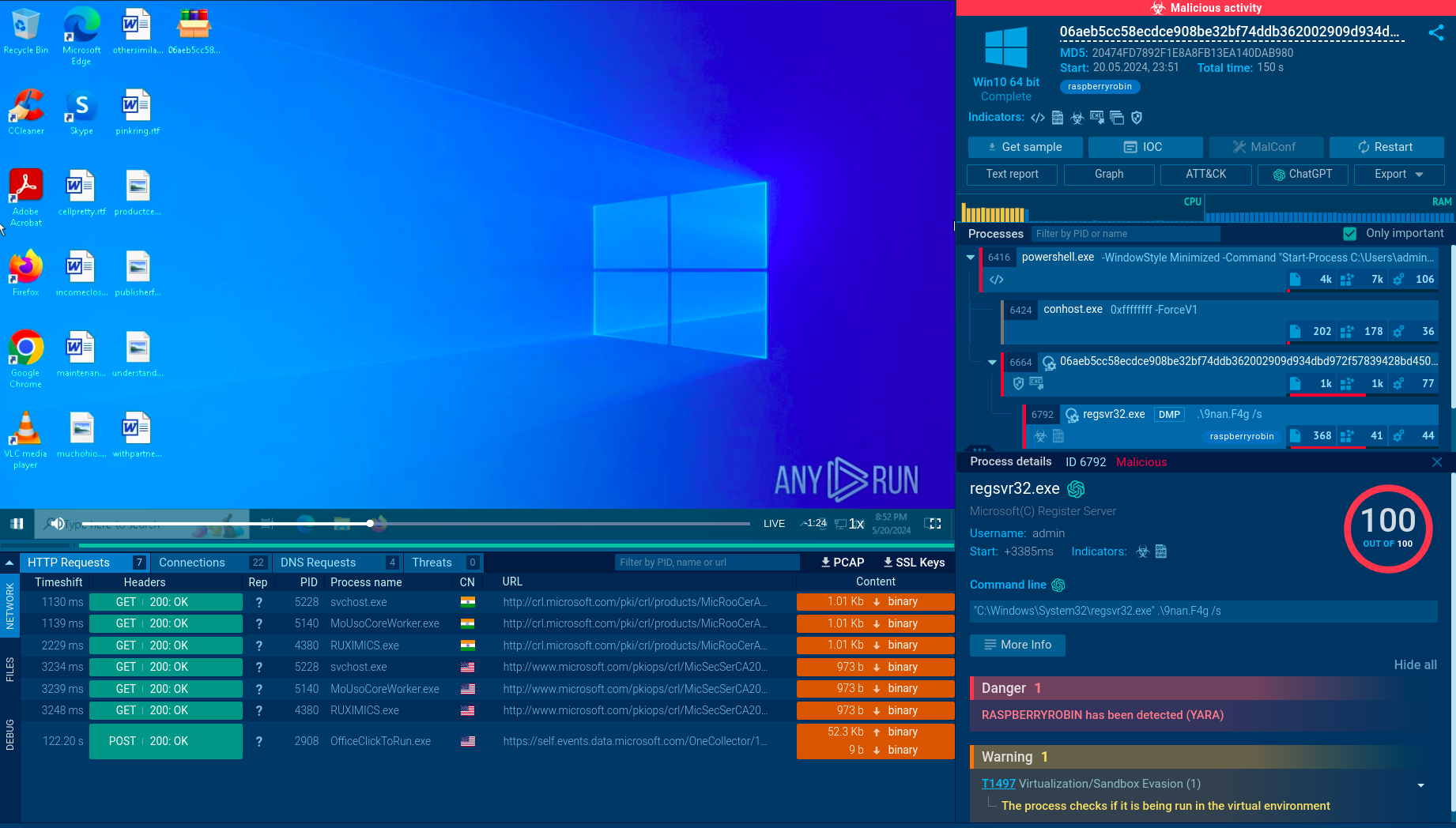
Since Troldesh ransomware writes into the registry analysts can detect it by looking at registry keys. Choose the process by clicking on it in the process tree of the task then click on the "More info" button. In the "Advanced details of process" window switch to the "Registry changes" tab and take a closer look. If the analyzed sample writes a value "906D0F2E2F604F839E04" with the name "xi" into the key HKLM\SOFTWARE\System32\Configuration it's Troldesh.
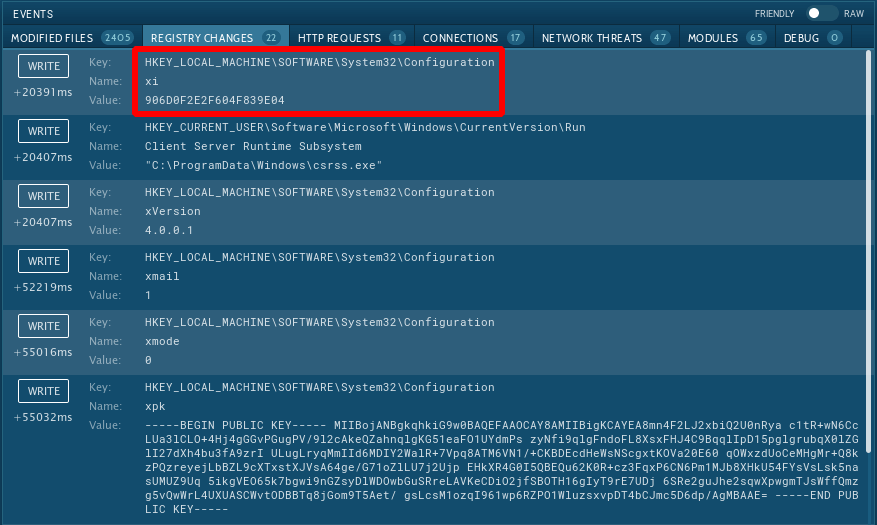 Figure 3: Registry changes created by Troldesh
Figure 3: Registry changes created by Troldesh
Troldesh is an extremely dangerous ransomware that is able to contaminate victims who simply end up browsing to the wrong place at the wrong time, ending up on a website hacked by the attackers. Unlike much other ransomware that simply demands money in exchange for user's encrypted data, Troldesh doesn't stop there and goes the extra mile to spread other dangerous malware samples on a victim's PC.
Utilizing analysis services like ANY.RUN is a great way to examine the virus from a safe environment and develop a sufficient defense strategy.
On the 27th of April, 2020 authors behind Troldesh ransomware announced that they stopped distribution of the ransomware and publish the decryption keys with a decryptor and instructions. They said that apologize to all the victims of the trojan and hope that the keys they published will help them to recover their data. The same scenario had a couple of other ransomware writers, even the infamous Maze.
You can take a look at the task in which their keys and tool were used to decrypt data.