Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Sality is a highly sophisticated malware known for infecting executable files and rapidly spreading across networks. It primarily creates a peer-to-peer botnet that is used for malicious activities such as spamming, data theft, and downloading additional malware. Sality has strong persistence mechanisms, including disabling security software, making it difficult to remove. Its ability to spread quickly and silently, along with its polymorphic nature, allows it to evade detection by traditional antivirus solutions.
|
Botnet
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2003
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 June, 2003
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Sality is a file-infecting virus and botnet malware first observed around 2003. It primarily targets Windows systems, infecting executable files (.exe) and spreading rapidly across networks and removable drives.
Over time, it has become highly persistent and adaptive, evading traditional security measures through polymorphism, constantly changing its code to avoid detection.
Similar to other botnet malware like Phorpiex and Mirai, Sality has infected hundreds of thousands of computers globally, creating a massive botnet. The malware operators use this network for various purposes, ranging from relatively "benign" tasks like generating spam to more malicious activities, such as distributing password stealers. In 2011, one of the programs distributed through the Sality botnet focused on stealing web credentials, particularly targeting Facebook and Google Blogger accounts.
The primary functionality of Sality malware includes:
Sality connects infected machines to command and control (C2) servers or other infected systems within its botnet. This allows attackers to issue commands, download additional malware, and update the virus, ensuring it remains persistent and adaptive in its attack methods. Through this botnet, Sality can be used for a wide range of malicious activities, including:
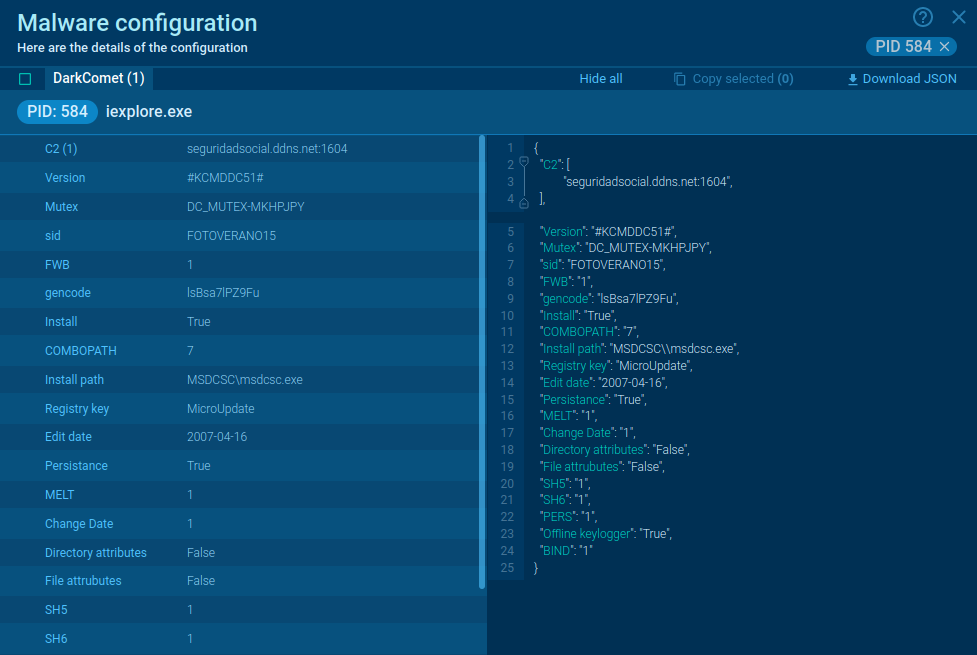
The data exchanged between the infected system and C2 servers is often encrypted, making it difficult for security experts to analyze the malware's activities.
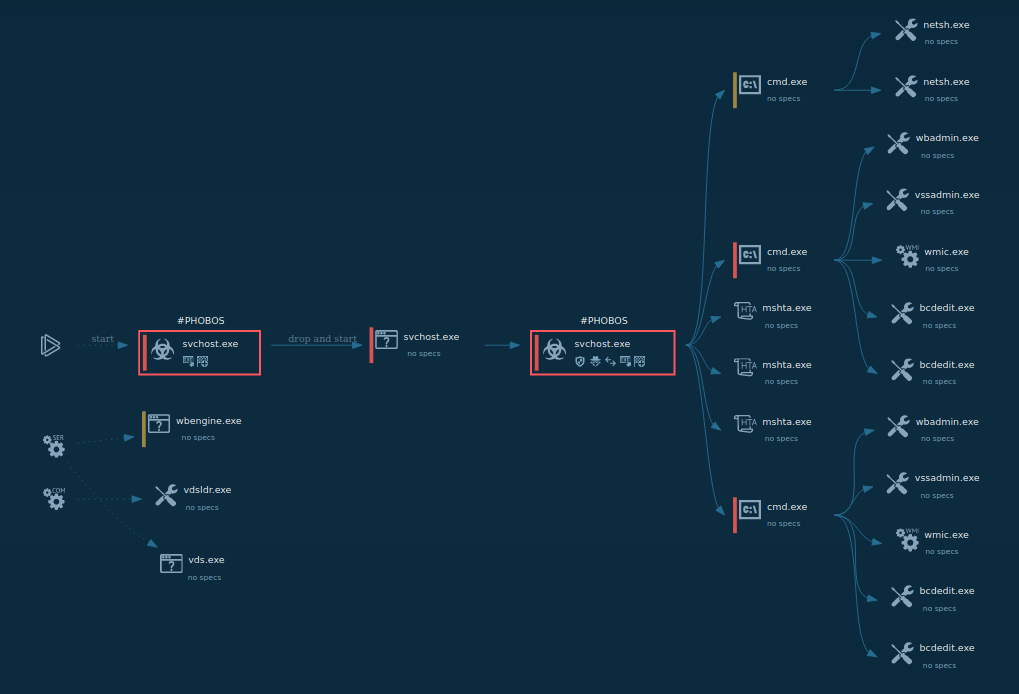
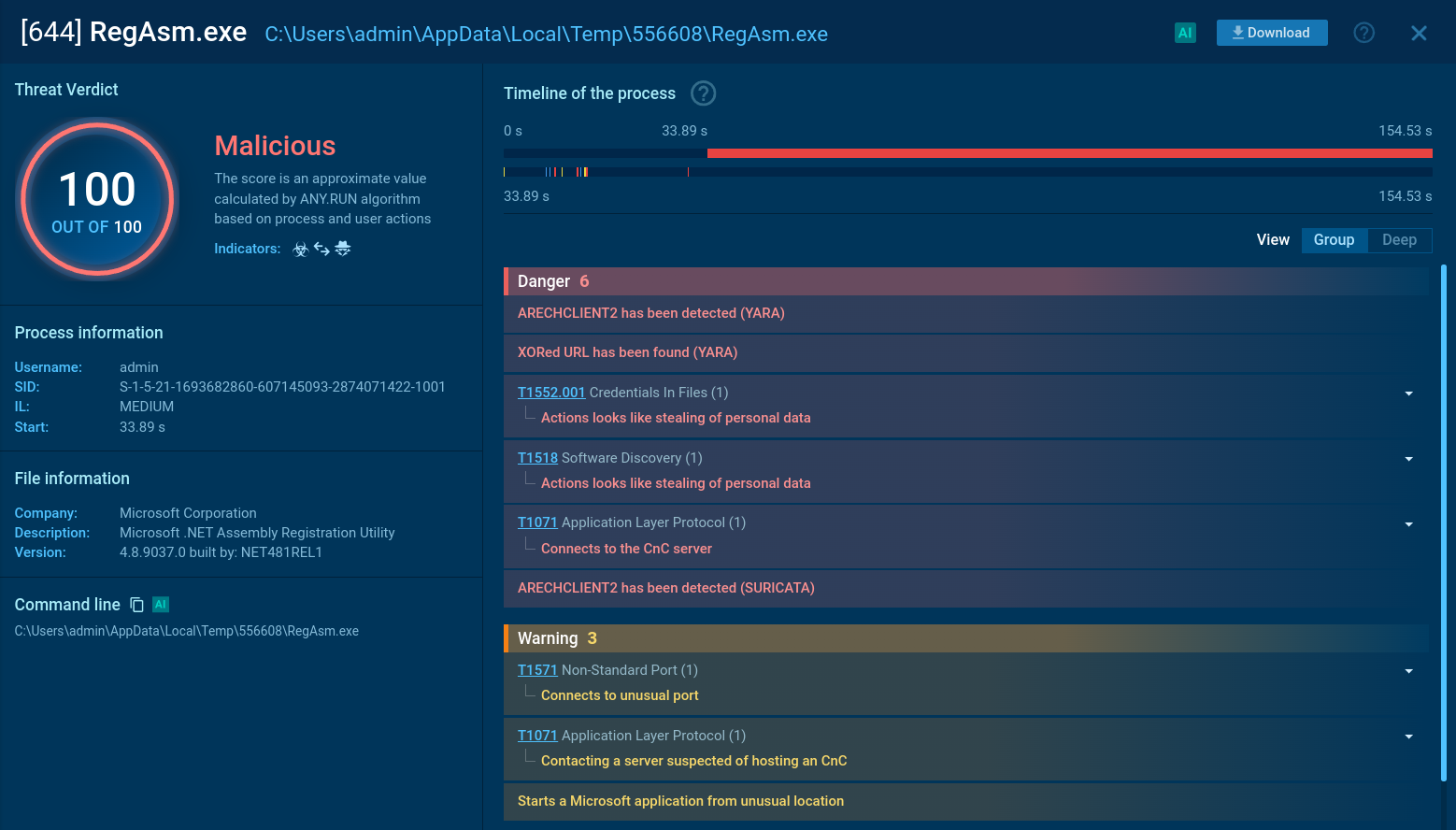
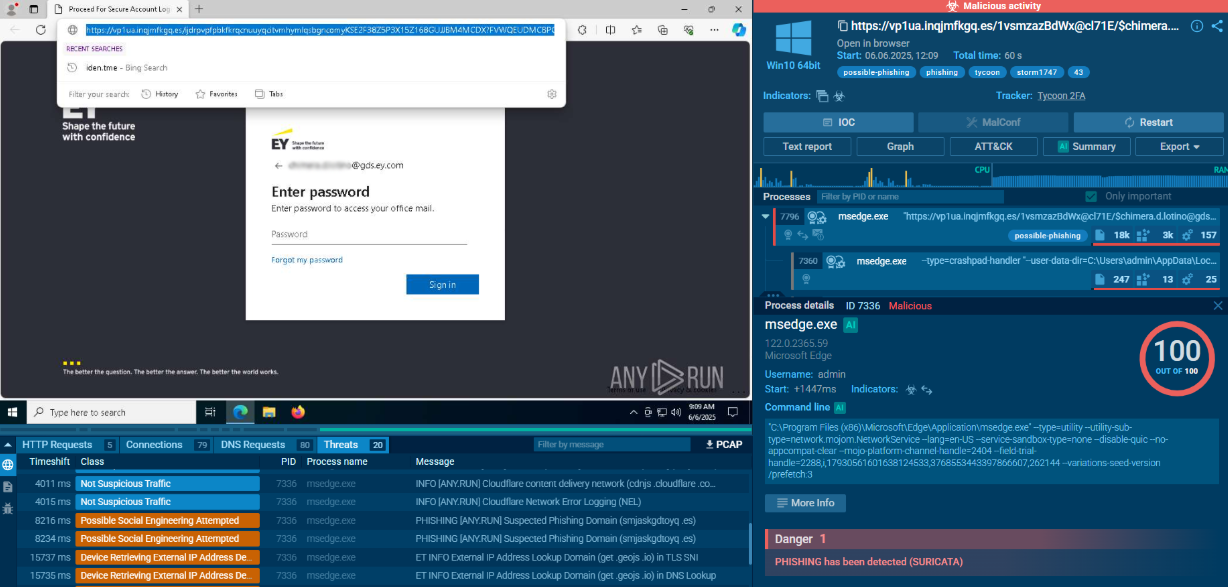
To see how Sality operates, let’s upload its sample into the ANY.RUN sandbox.
Once the Sality malware is executed, the stub decrypts and runs a secondary code segment known as the loader. The loader operates in a separate thread within the infected process and is responsible for executing the malware's main payload.
Sality actively targets security software by terminating antivirus-related processes and deleting files critical to system security. It may also modify system settings to reduce security levels and block the execution of security tools.
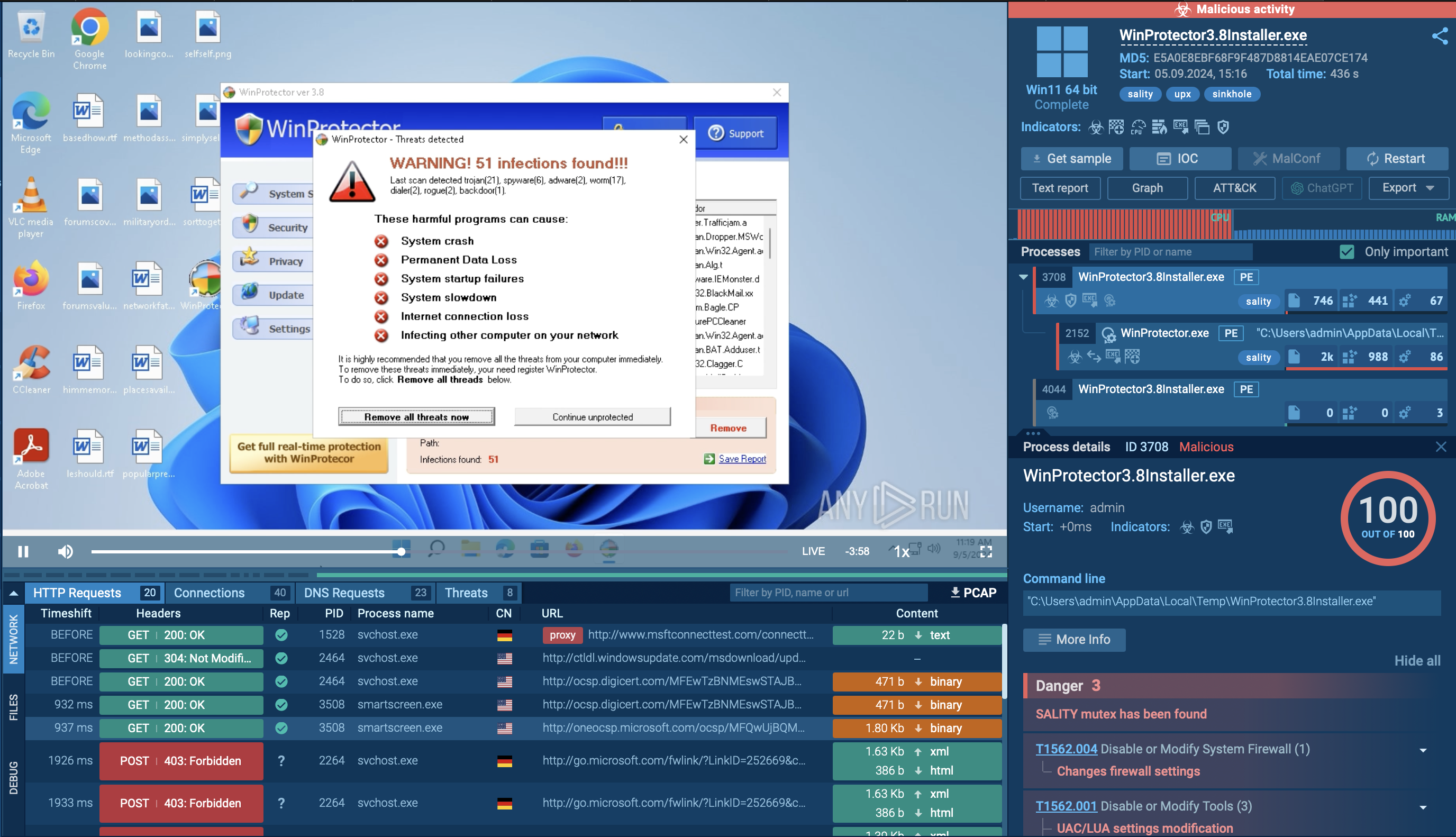 Sality malware analyzed in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Sality malware analyzed in the ANY.RUN sandbox
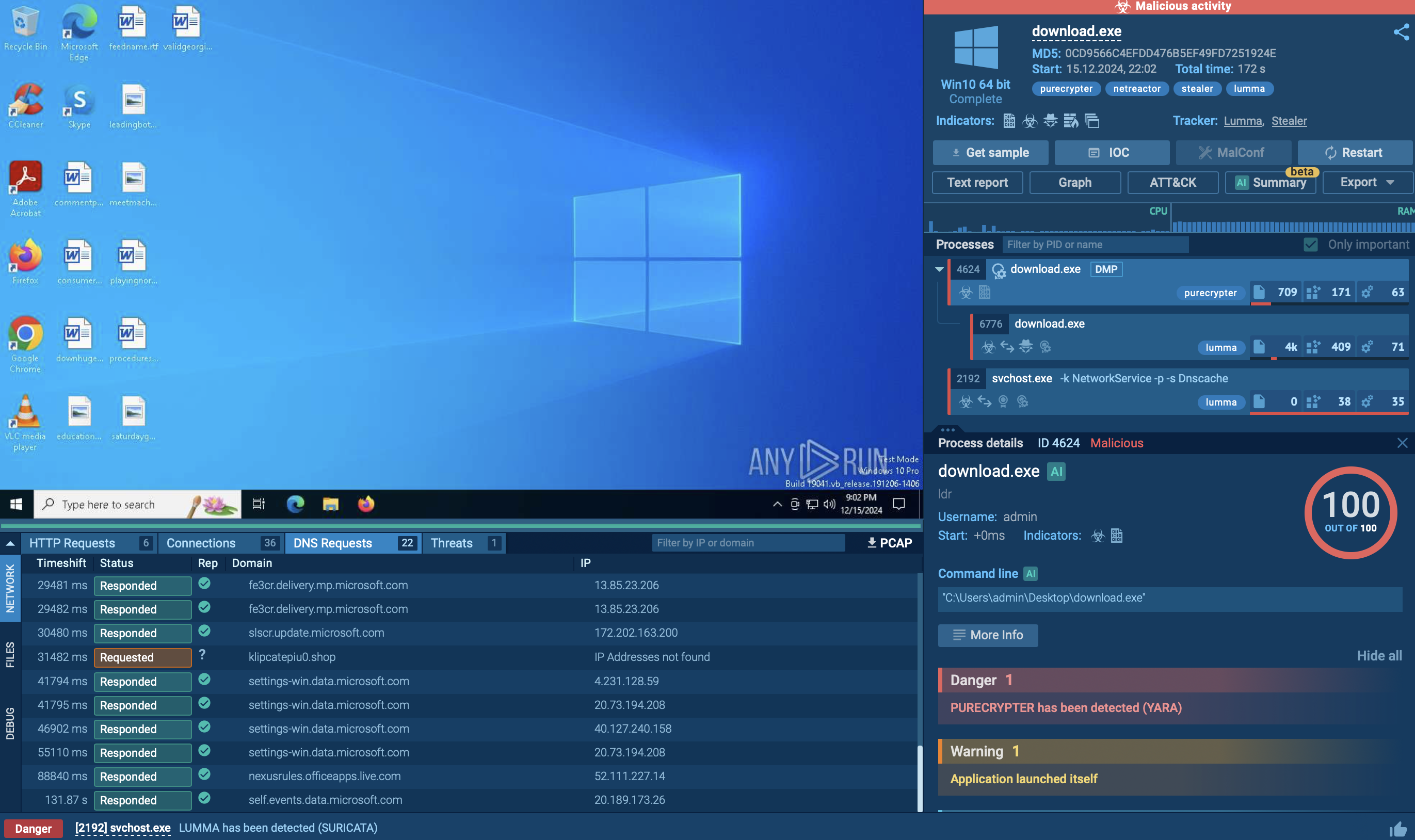
The malware is capable of stealing sensitive information, such as cached passwords and keystrokes, and can search for email addresses to send spam. It communicates with remote command and control (C2) servers, often utilizing a peer-to-peer (P2P) network to download additional malicious payloads or updates.
Modern Sality variants can form botnets, enabling attackers to control multiple infected machines. The botnets can be used for various malicious activities, including distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and further malware propagation.
Sality can also download and execute other malware, often through a preconfigured list of peers within its P2P network, allowing it to expand its capabilities and maintain persistence on infected systems.
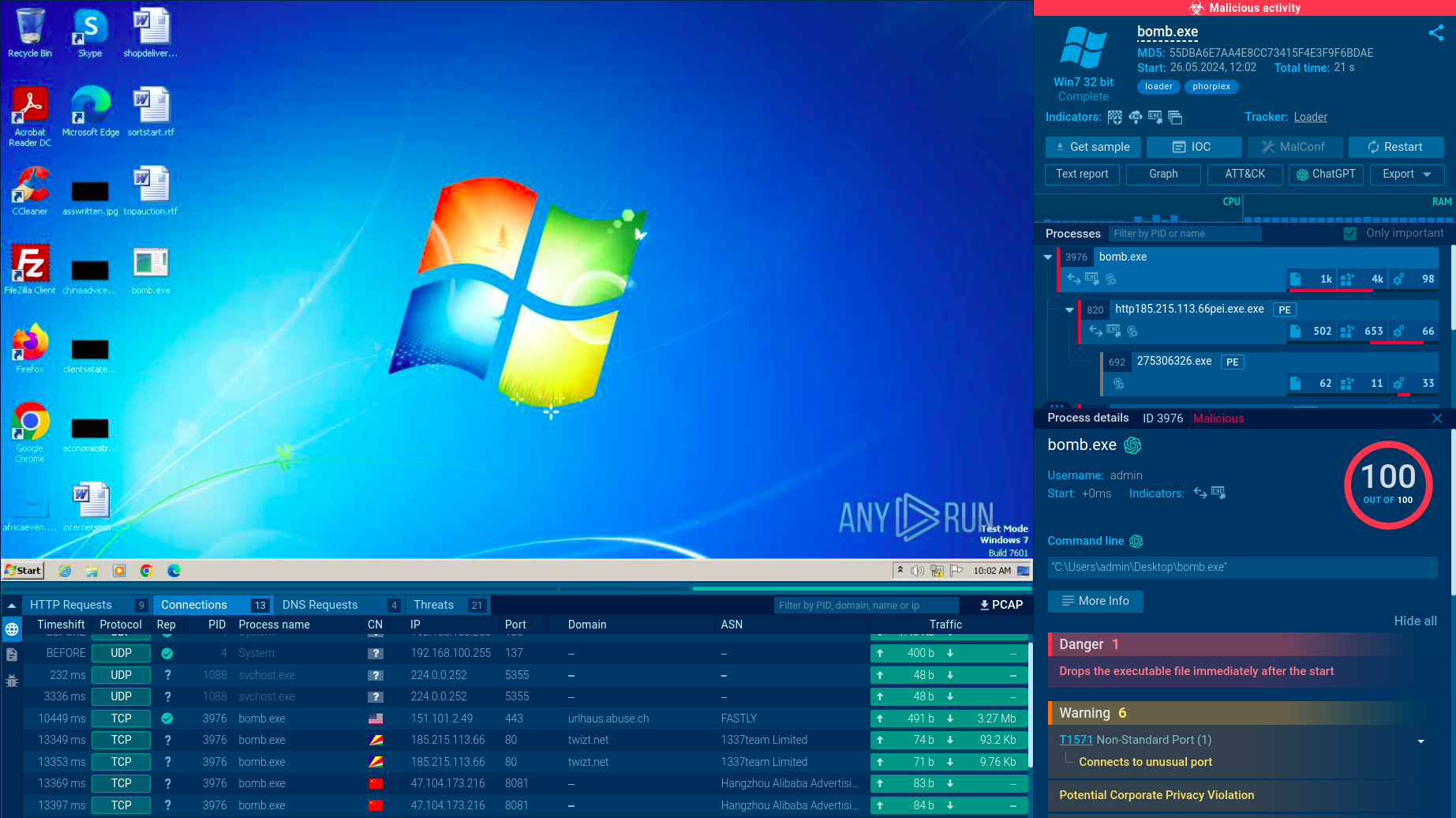
Sality malware employs several distribution methods that allow it to spread widely across networks and systems:
To collect up-to-date intelligence on Sality and its latest variants, use Threat Intelligence Lookup. The service helps you search across a vast database of quality threat data sourced from millions of malware analysis sessions conducted in the ANY.RUN sandbox. It lets you use over 40 different search parameters and their combinations, including IPs, domains, command line artifacts, and process names.
Let's use a mutex fragment found in one Sality sample to find more samples. To do this, we'll submit the following query: syncObjectName:".EXEM_"
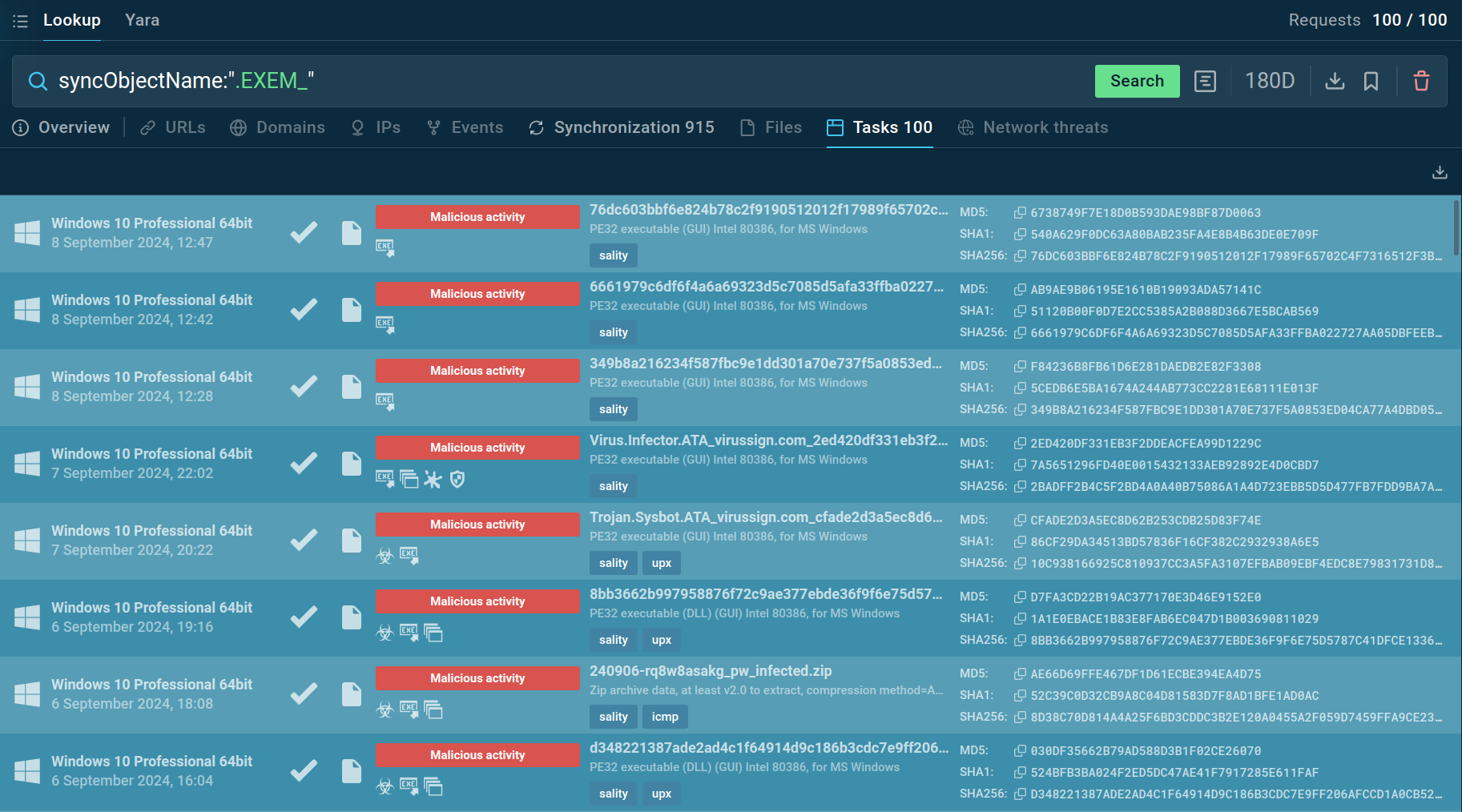 Sality mutex query in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Sality mutex query in Threat Intelligence Lookup
The service returns one hundred sandbox sessions that we can explore further.
Get a 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup along with the ANY.RUN sandbox
Sality’s ability to spread through infected files, disable security software, and form a botnet makes it a potential threat. Its focus on persistence and evading detection highlights the need for strong security measures. To effectively protect against Sality, it's important to use tools like malware sandboxes to thoroughly analyze suspicious files and detect threats early.
ANY.RUN offers a powerful solution, allowing users to safely examine and understand threats like Sality in real-time. By utilizing ANY.RUN, you can quickly detect and neutralize malware before it can cause harm to your systems.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today and start analyzing malware with no limits!