Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


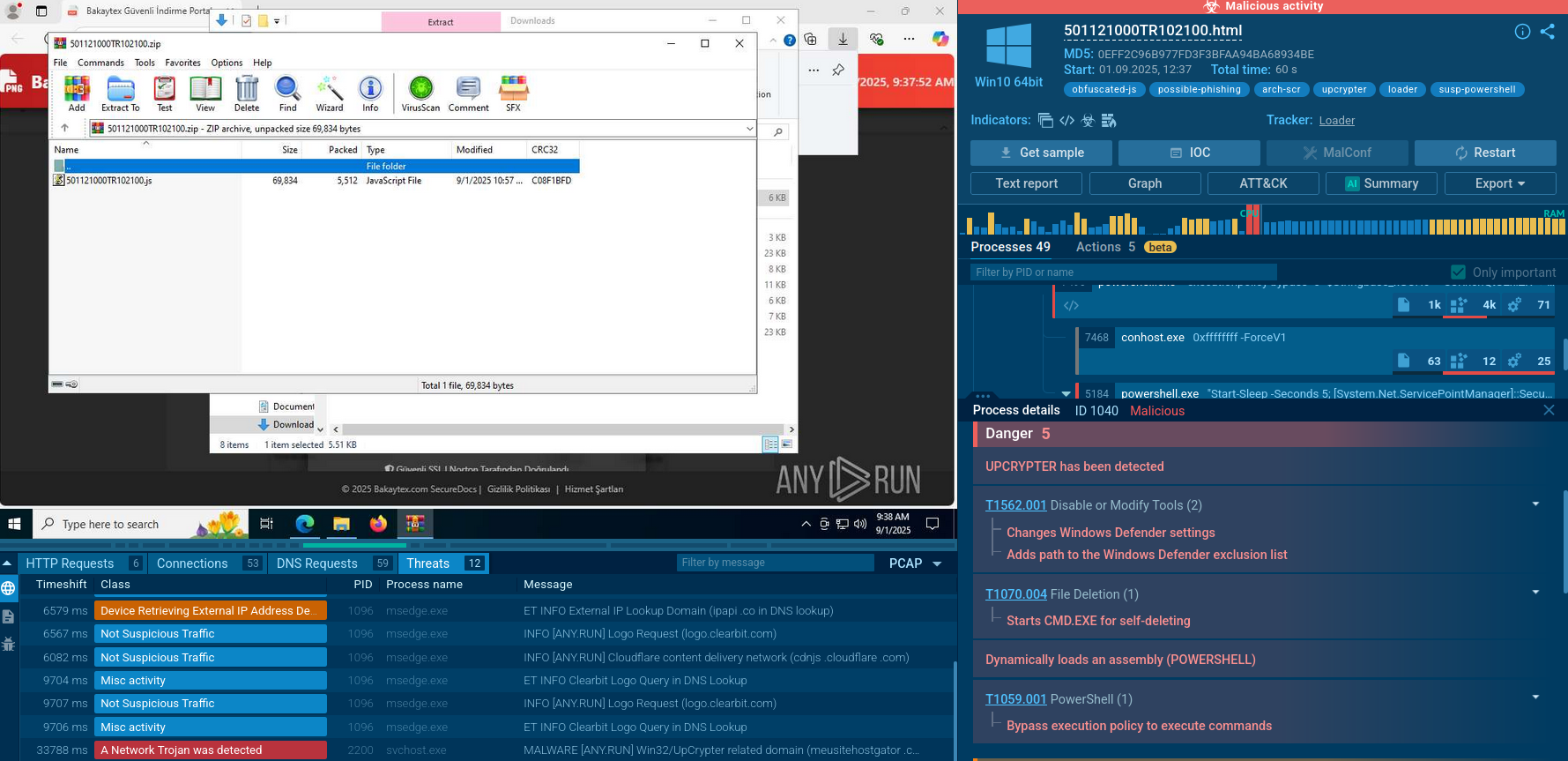
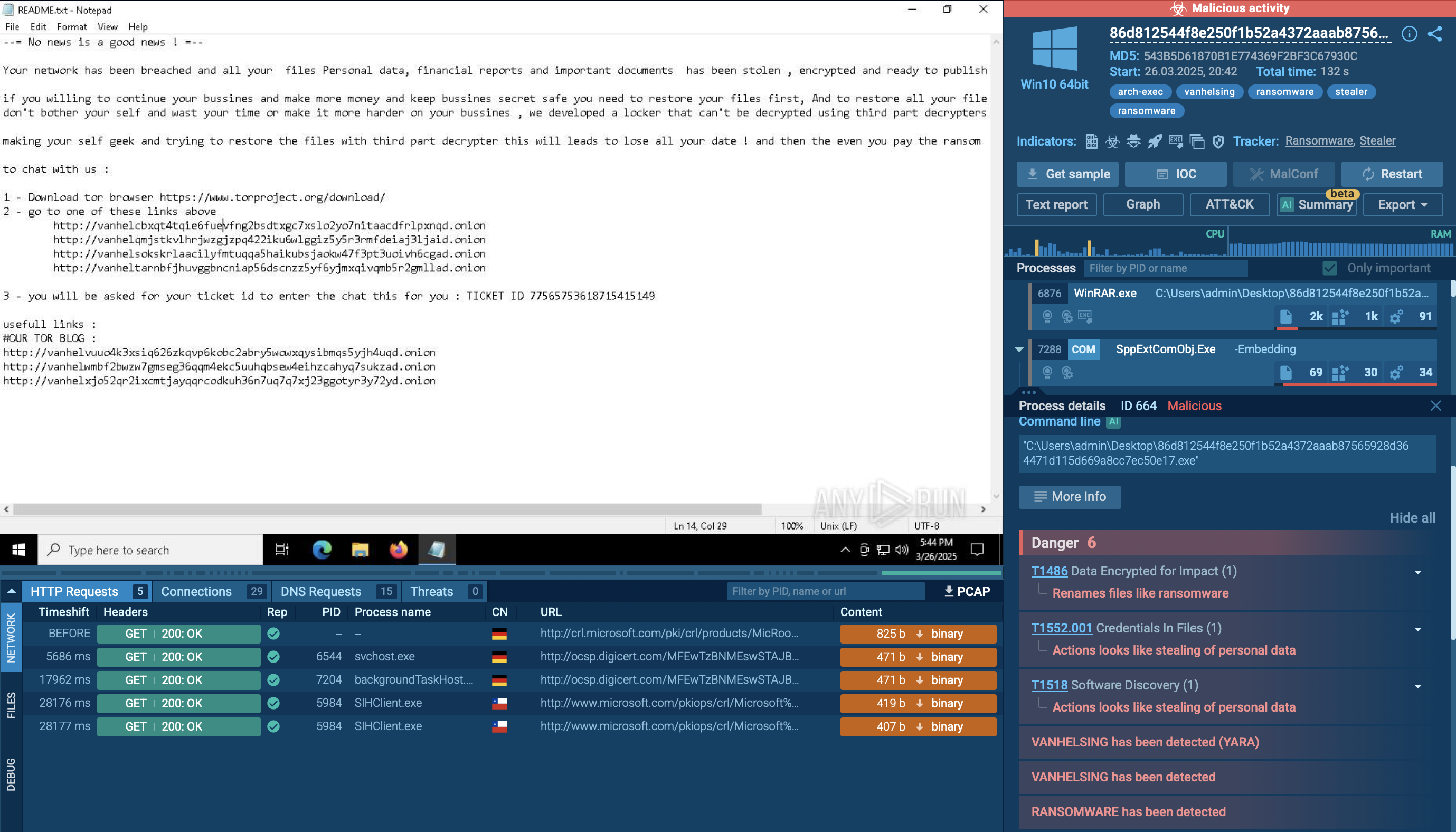
Maze is ransomware — a malware type that encrypts the victim’s files and restores the data in exchange for a ransom payment. One of the most distinguishable features of Maze is that it is one of the first malware of the kind to publicly release stolen data.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
29 May, 2019
First seen
:
|
23 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
29 May, 2019
First seen
:
|
23 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Maze, also called ChaCha, is ransomware — a malicious program that encrypts files of the victim and demands a ransom in exchange for a decryption key that restores information. A defining feature of Maze is that it publically releases sensitive files to the public unless the ransom is paid.
Maze ransomware has been operating actively since 2019 and, unfortunately, the attack volume from this malware has been on a steady rise since that time.
It’s not a new strategy among ransomware operators to issue threats about making sensitive data public unless the victim gives in to the demands of the criminals. However, before the occurrence of Maze, most of these threats remained largely idle. They served as a psychological weapon, helping threat actors to strongarm victims into paying.
However, the situation changed drastically with Maze.
In November 2019, the group behind Maze managed to infiltrate Allied Universal: one of the leading private security companies in the US. The cyber gang claimed that they have gained complete control of the Allied network and threatened to make the data public unless the company paid up.
Allied Universal decided to ignore the demands. In reply, hackers behind the virus first contacted a well-known computer help site, asking them to publish a story about the attack to serve as a public warning. When the website declined, the Maze gang uploaded 700MB worth of sensitive information on an underground forum. The data included lists of active users, email certificates, encryption keys, and more.
In another Maze ransomware attack, 2GB of files belonging to the City of Pensacola were made public. The attack severely damaged the computer network of Pensacola, forcing it to temporarily shut down the network. As per the data breach, the virus's actors declared that the information was leaked as evidence, showing how deeply they managed to infiltrate the network.
This is a very important point about Maze. Researchers should note that largely after Maze’s occurrence ransomware attacks can be considered data breaches, as more and more ransomware strains gain the ability to infiltrate networks and perform data-stealing activities before encrypting the files.
Furthermore, with the case of Maze, even backups are not safe. Actually, sometimes they become a week point. Maze creators revealed that after infecting the initial endpoint, their ransomware targets cloud backups by laterally spreading through the network and stealing needed credentials. This is useful for threat actors not only because it allows deleting the backup before encryption, but also because that backup most likely contains the most valuable data.
Unfortunately, this tactic has proved effective as at least one company fell victim to it and lost its backups. Of course, an incident like this can only happen if backup credentials are stored in the compromised network, thus correct backup configuration is incredibly important.
It should also be noted that the virus uses several advanced code obfuscation techniques that make static analysis very complicated. Threat actors behind the virus evidently stay on top of the progress done by security researchers on their malware. They contact cybersecurity media and like to tease industry professionals and play cat and mouse.
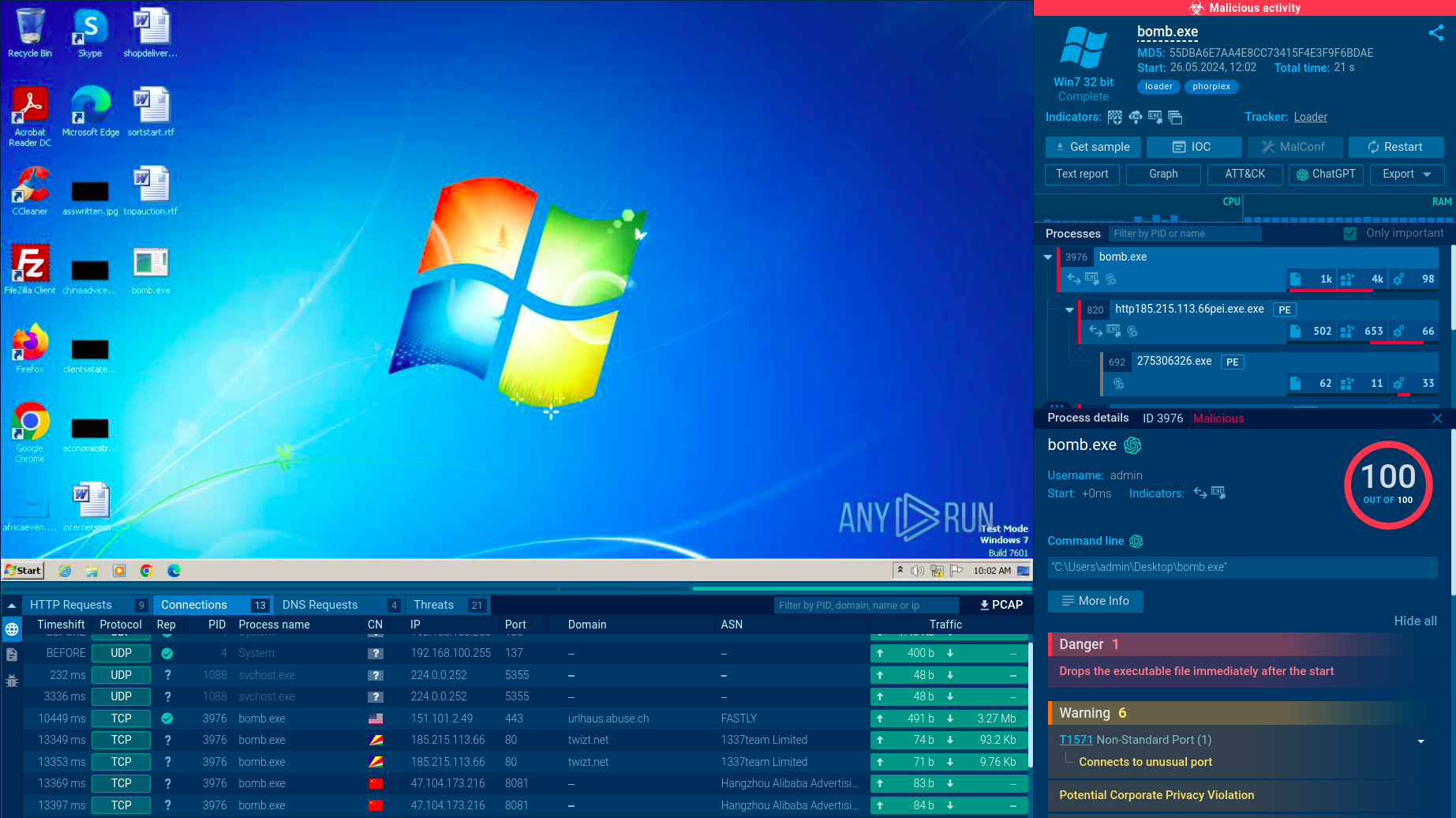
In this video recorded in the ANY.RUN interactive malware hunting service we can view how the Maze execution unfolds.
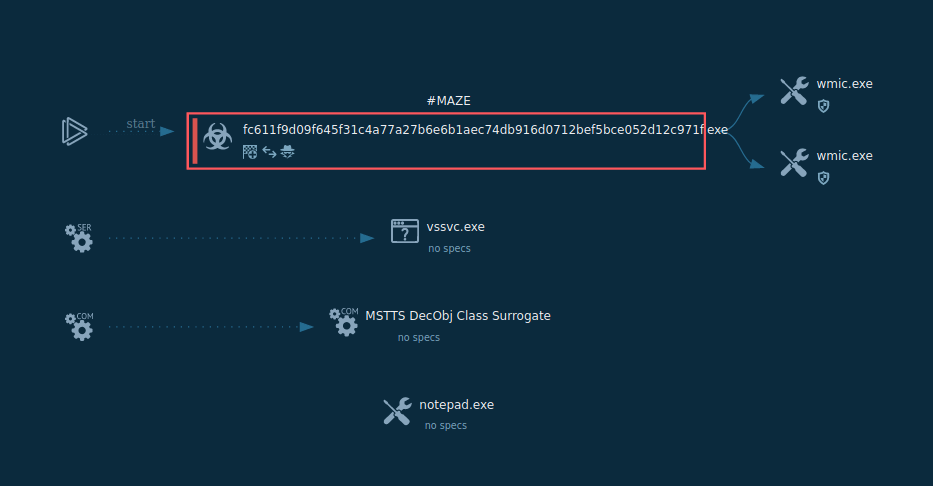
Figure 1: Shows the graph of processes created by the ANY.RUN interactive malware analysis service
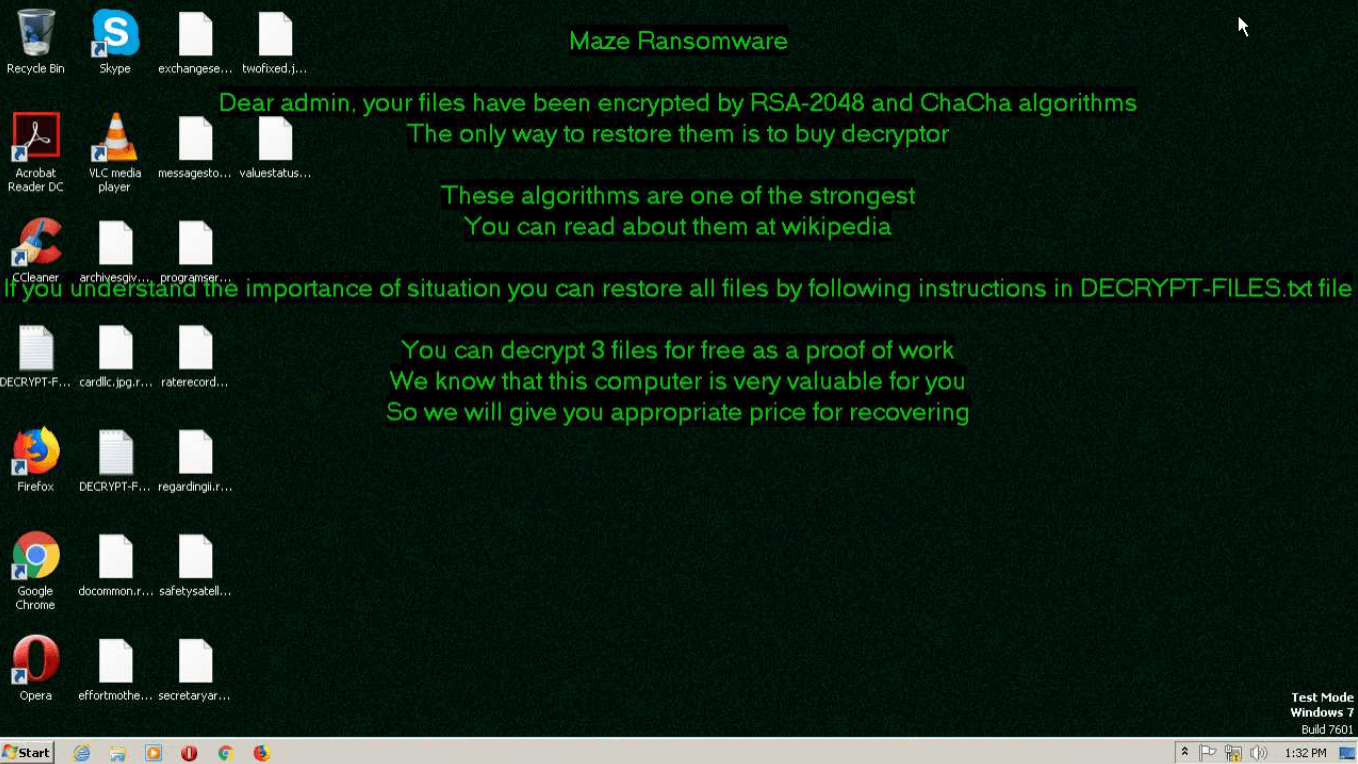
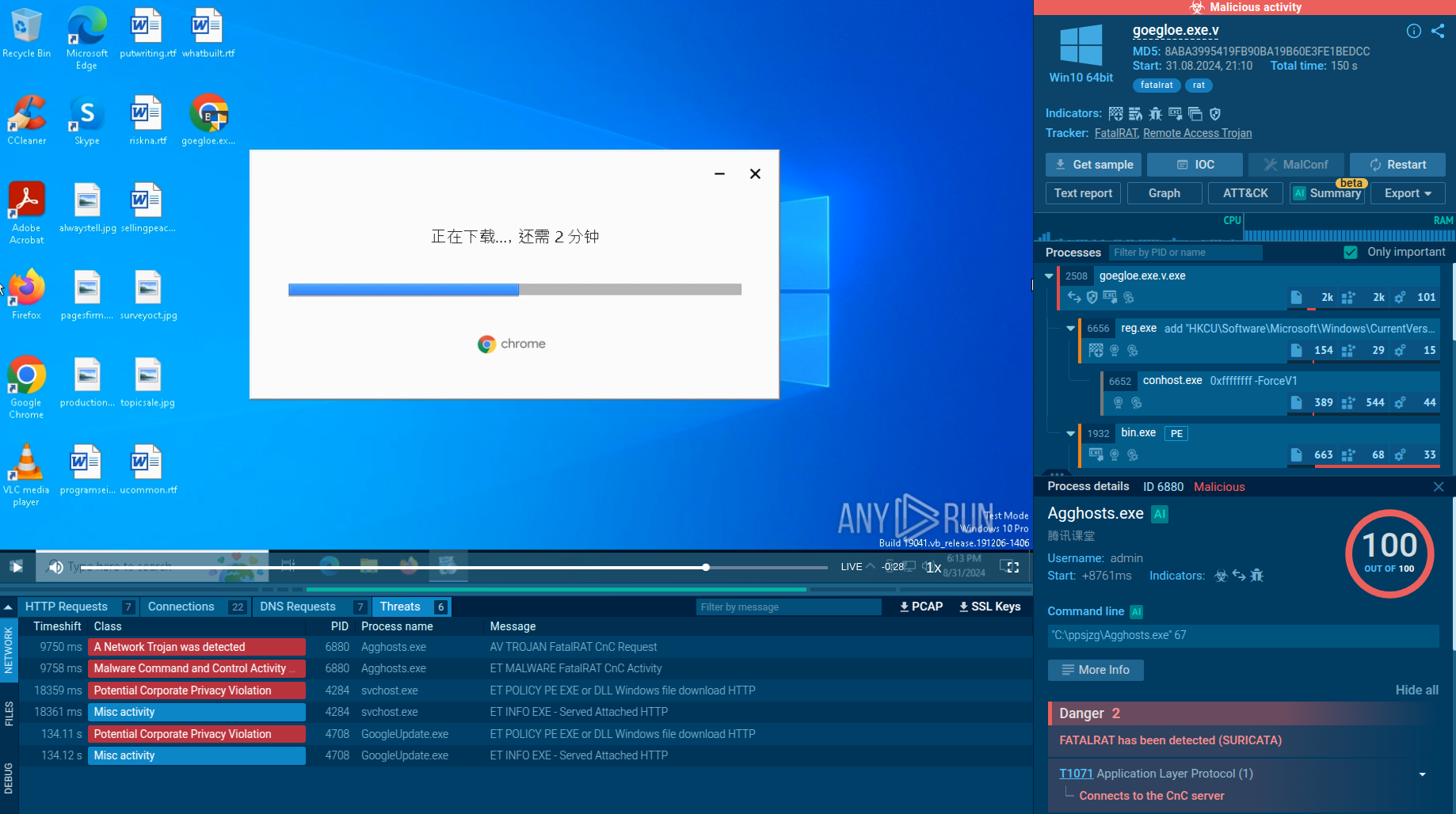
Figure 2: Wallpapers with ransom message set by Maze
The execution process of Maze is kind of typical for this type of malware, for example Phobos or Sodinokibi. After the executable file makes its way into an infected system and runs, the main malicious activity begins. After the start of execution, the ransomware deletes shadow copies. After it encrypts all targeted files, Maze drops a ransom note on the desktop. It also often changes the wallpaper to its own with a ransom text.
Notably, just like Sodinokibi aka REvil ransomware, this family has a similar infrastructure — websites with "tech support", information about cryptocurrency and ways to buy it, trial decryption, and chat. Crooks behind the Maze ransomware are also kind of cocky and post links to the information about their successful attacks on their website.
Maze is distributed using several different ways. It has utilized the Spelevo and Fallout exploit kits and one of the vulnerabilities that Maze is targeting is the CVE-2018-15982 vulnerability in Flash Player. It is also worth noting that in the case of the Fallout kit, the users were redirected to the exploit from a fake cryptocurrency trading platform.
Another observed attack vector is via email spam campaigns containing a Microsoft Office document with a malicious macro.
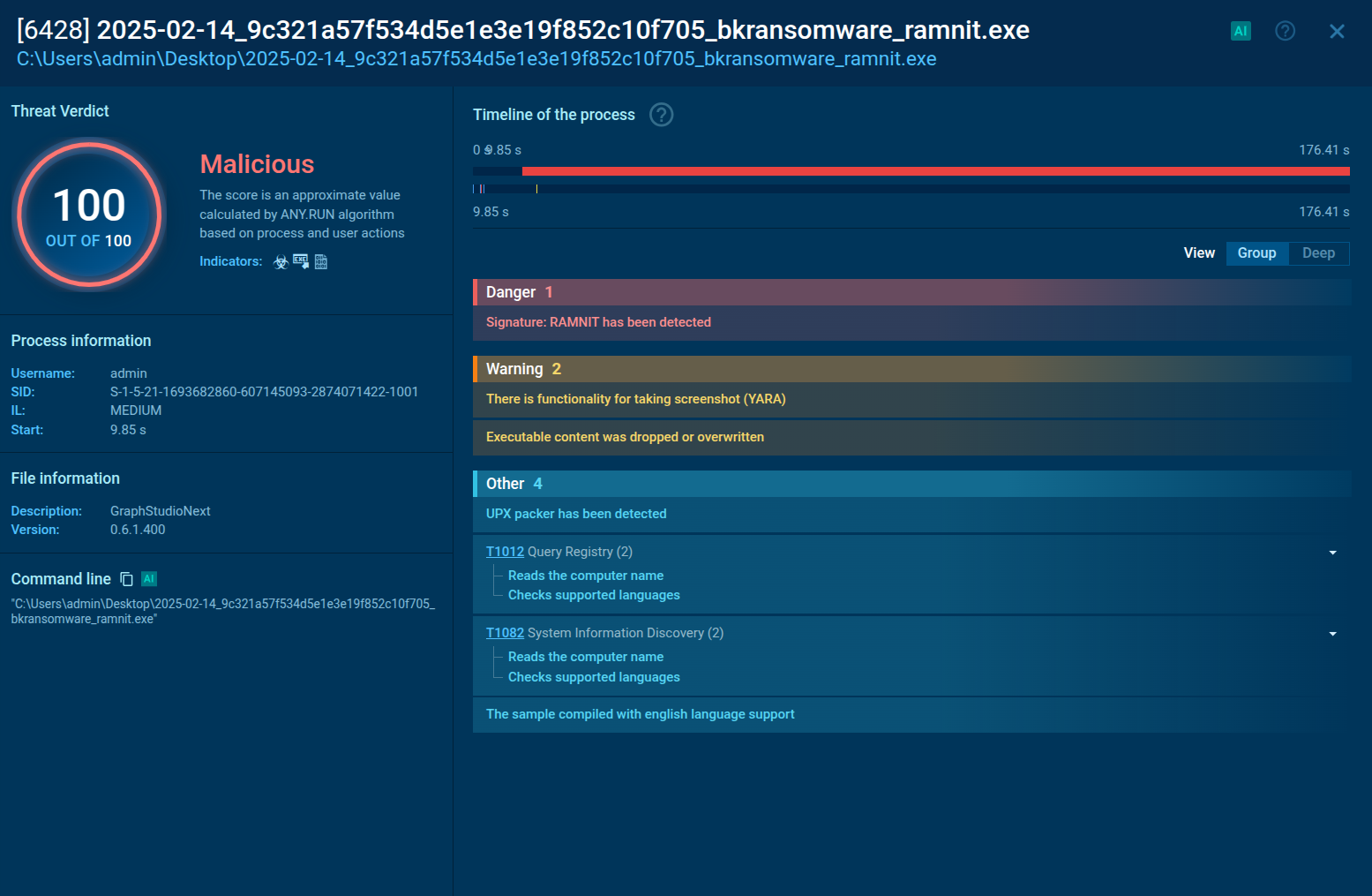
Maze ransomware can be detected by many different activities — sometimes it creates certain files or it can be detected by Suricata network threats. The most common is the Maze ransom note — not only does it have similarities with notes from other tasks, but it also contains self-defining strings: maze ransomware, mazedecrypt, and maze key.
Analysts can take a look at these notes by using ANY.RUN Static Discovering. Click on the "Files modification" tab, then find the file with the name such as " DECRYPT-FILES.txt". To take a look inside this file just click on it.
If you find word combinations such as "maze ransomware", "mazedecrypt" and "maze key", then be sure this sample is Maze ransomware.
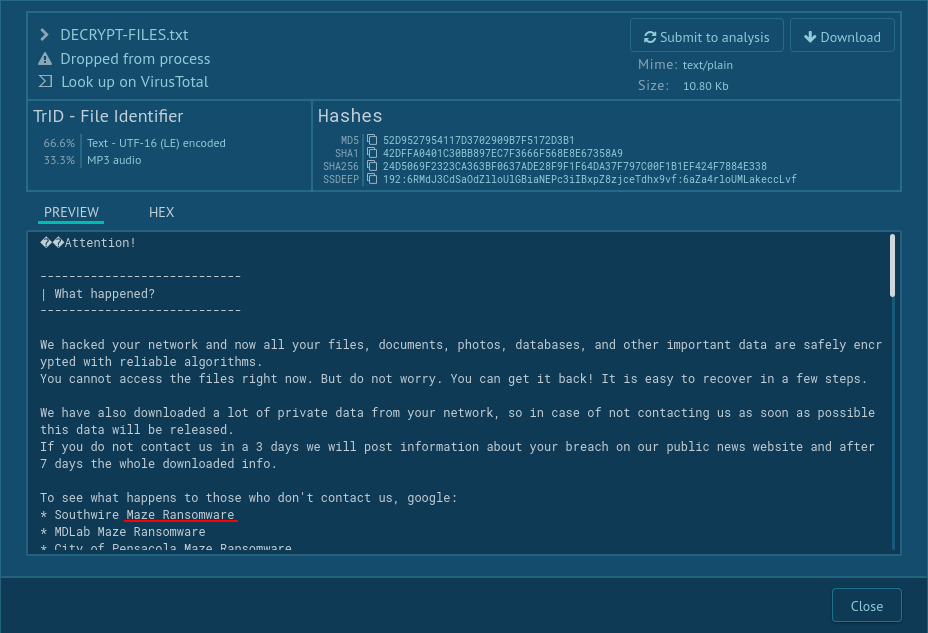
Figure 3: How to detect Maze ransomware by its ransom note?
Maze is a significant threat to organizations and private users. This virus not only encrypts information but also strong-arms the victims into paying the ransom, threatening to release sensitive information. Unfortunately, Maze launched a little bit of a trend among threat actors and more and more ransomware in the wild is starting to exhibit similar behavior.
The situation is further complicated by advanced code obfuscation techniques that the Maze features, making the static analysis process quite difficult. Thankfully, interactive malware analysis services like ANY.RUN allows to carry out dynamic analysis almost as quickly and easily as static, giving researchers a chance to collect invaluable information about this ransomware.
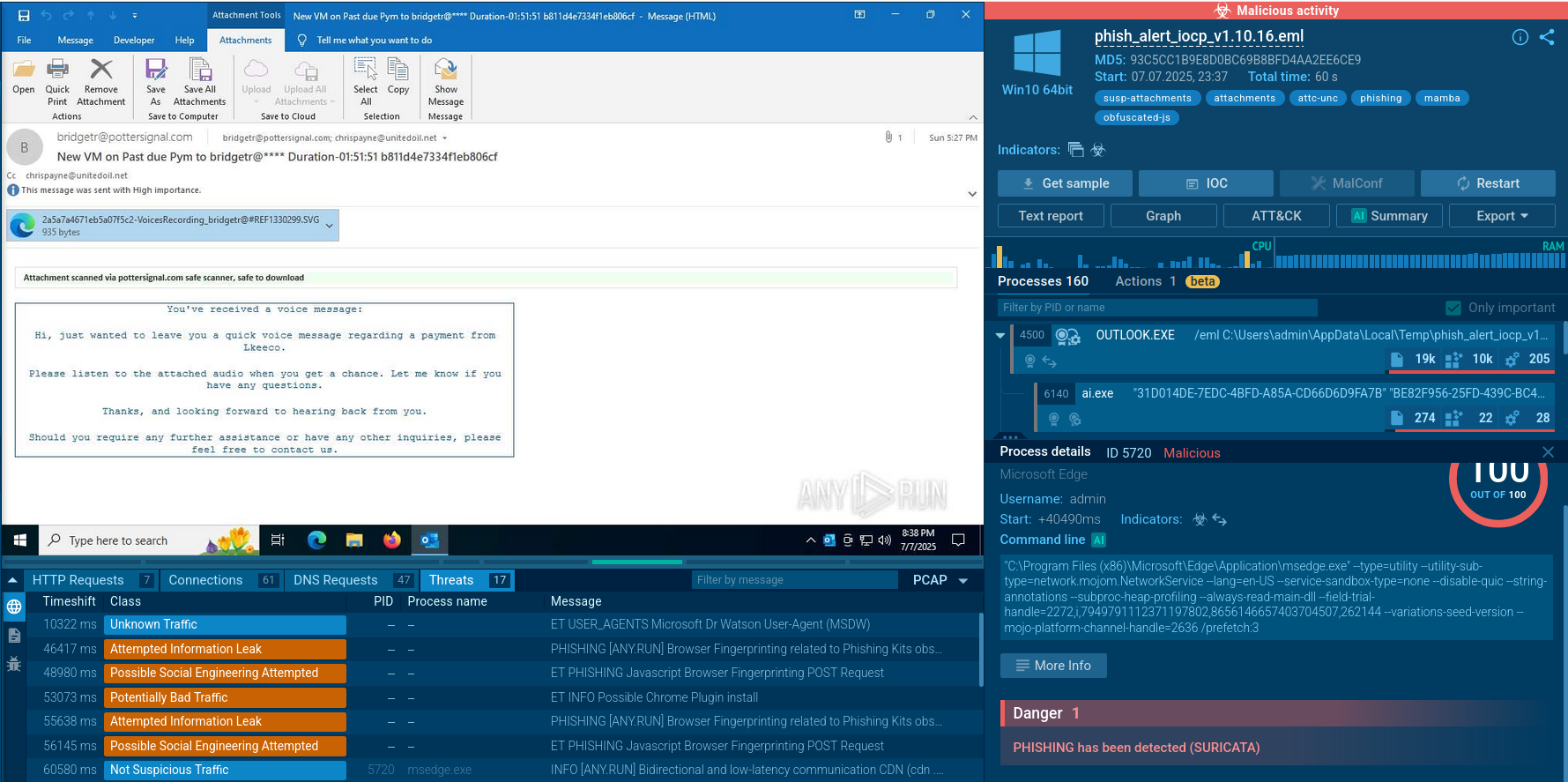
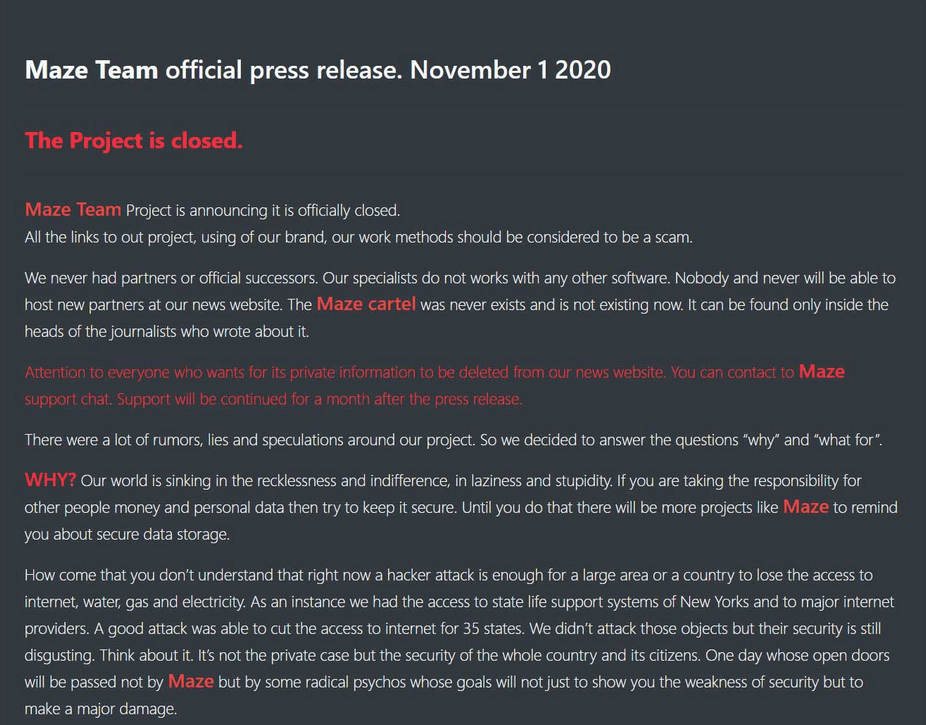 Figure 4: Screenshot of the Maze team press release
Figure 4: Screenshot of the Maze team press release
On the 1st November 2020, the "team" behind the Maze ransomware published their pretentious press release about the end of the "project" and it has shut down its operations. Unlike some other groups behind ransomware, they haven't published the encryption keys.