Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


GootLoader is an initial-access-as-a-service malware that operates by delivering the GootKit banking trojan and other malicious payloads. It utilizes techniques such as fileless execution and process injection to avoid detection. The malware is often distributed through SEO poisoning and compromised websites, deceiving users into downloading infected files.
|
Loader
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 November, 2020
First seen
:
|
4 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 November, 2020
First seen
:
|
4 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 868
868
 0
0

 515
515
 0
0

 2802
2802
 0
0
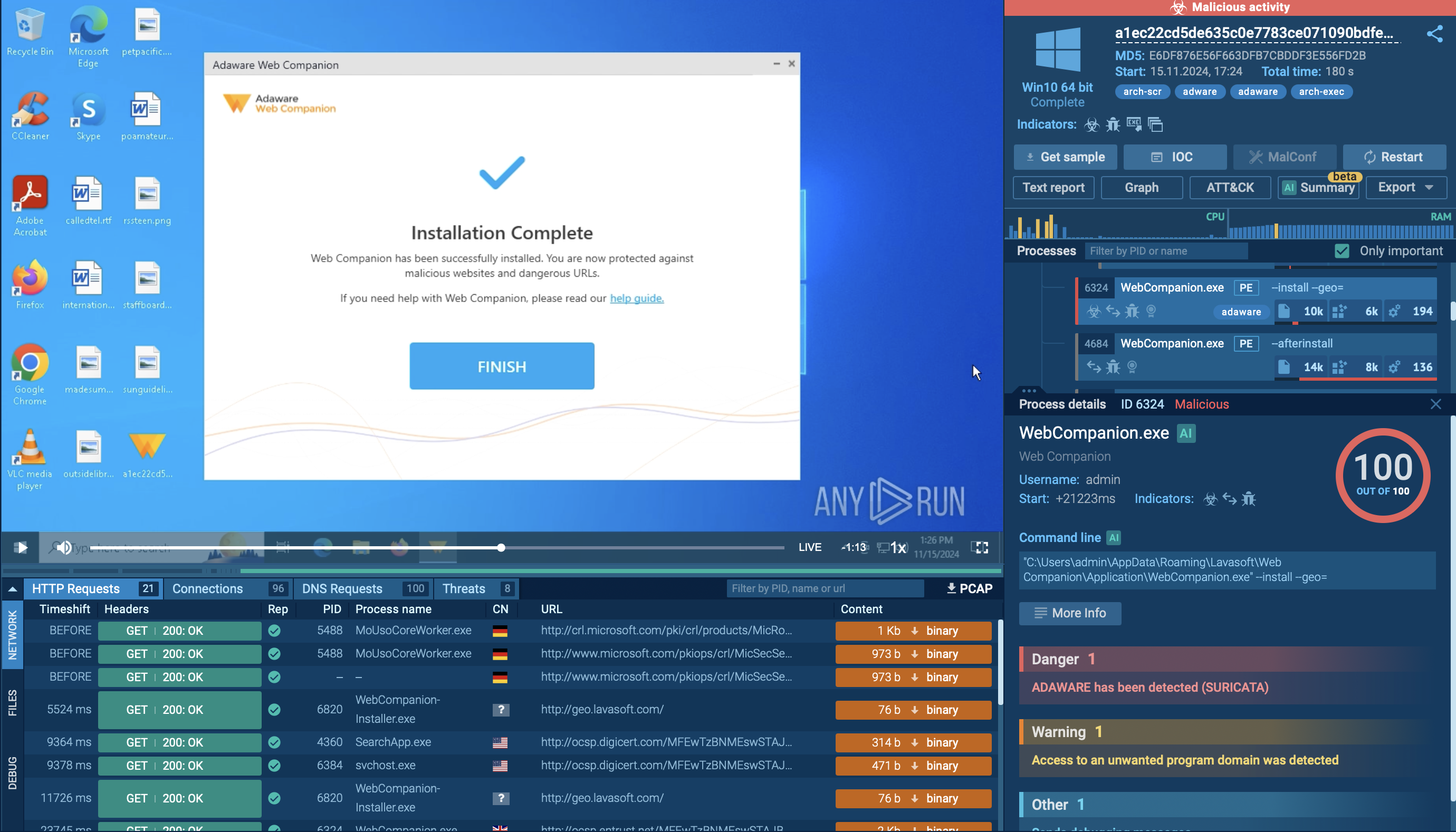
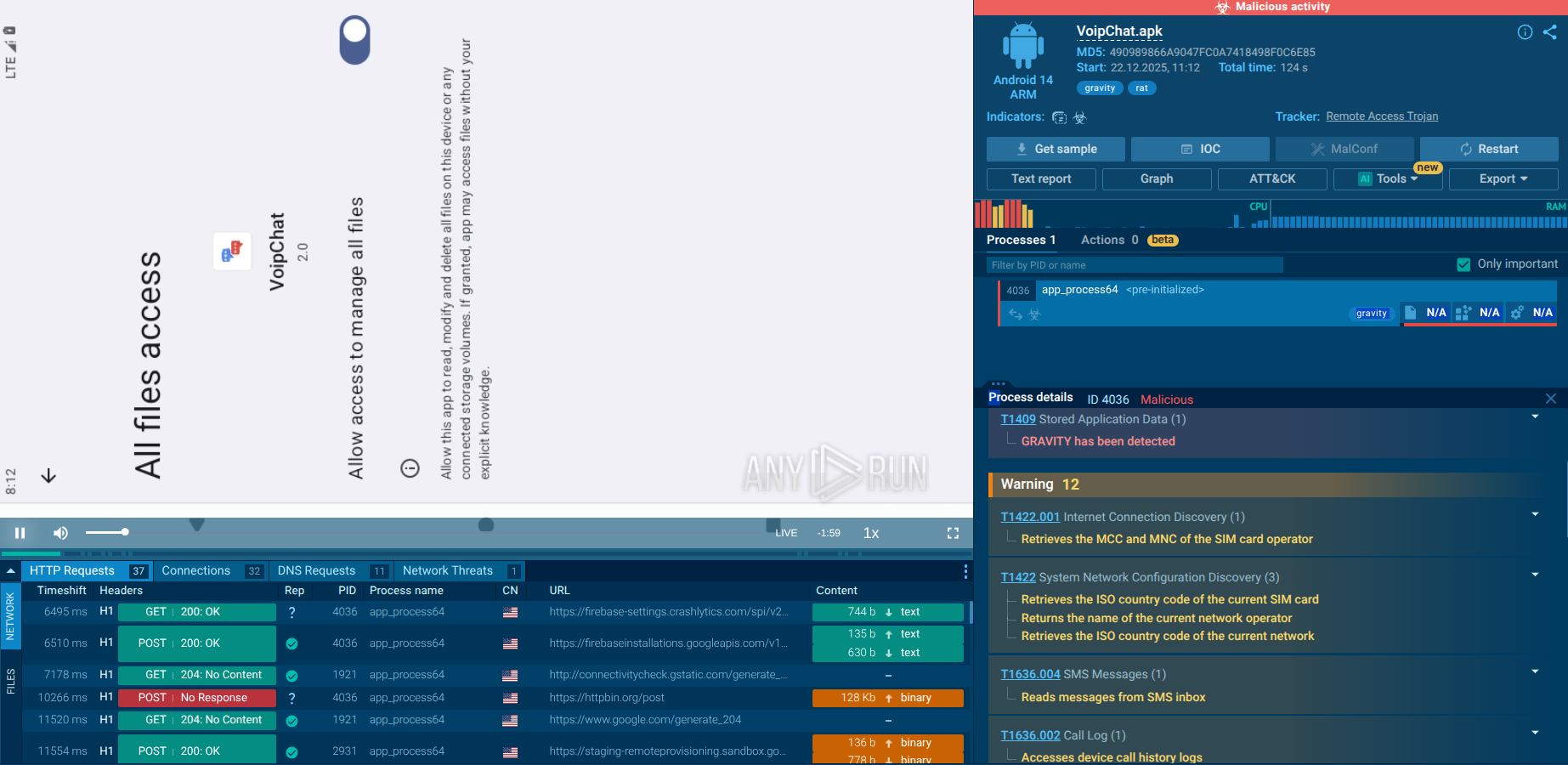
GootLoader is a loader malware initially designed to distribute the GootKit banking trojan. Operated by the UNC2565 threat group, today it functions as initial-access-as-a-service software, catering to cybercriminals who aim to deploy their malware, like Cobalt Strike, on already infected machines. While GootKit has been in circulation since 2014, GootLoader was introduced more recently in 2021. Campaigns involving GootLoader target users visiting hijacked WordPress websites and online forums. Attackers inject malicious code into these pages, deceiving visitors into downloading fake legal documents, which, in reality, turn out to be malicious files designed to infect their systems of GootLoader.
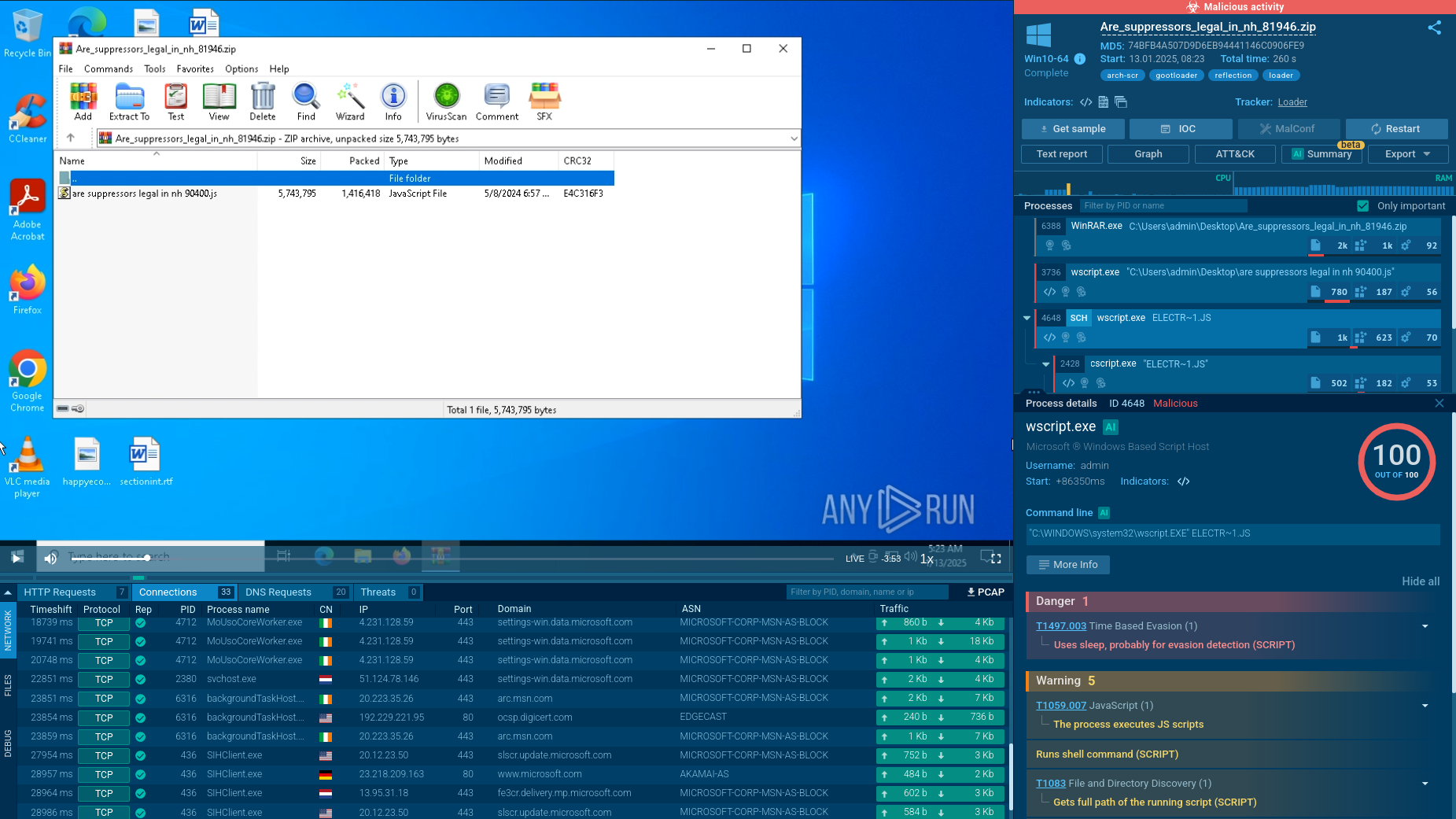 GootLoader analysis inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
GootLoader analysis inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
To observe the entire GootLoader infection process, use ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox that provides a safe virtual environment for hands-on analysis of cyber threats.
Check out this sandbox session showing the detonation of a GootLoader sample.
GootLoader employs a multi-stage execution process, characterized by several advanced capabilities:
GootLoader's infection process involves several steps. It usually starts when someone visits a compromised website and downloads a malicious archive, often disguised as a legitimate document like a template or contract. This archive typically contains a JavaScript file.
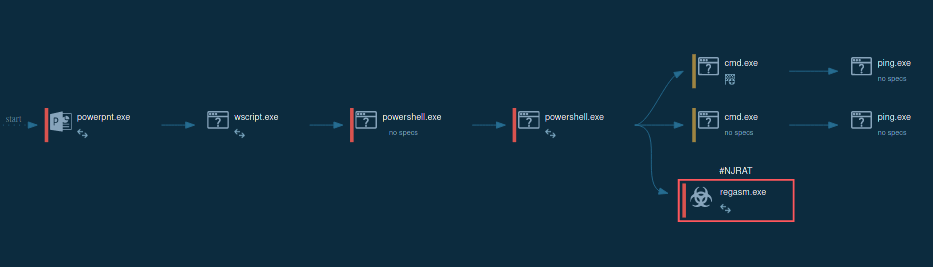
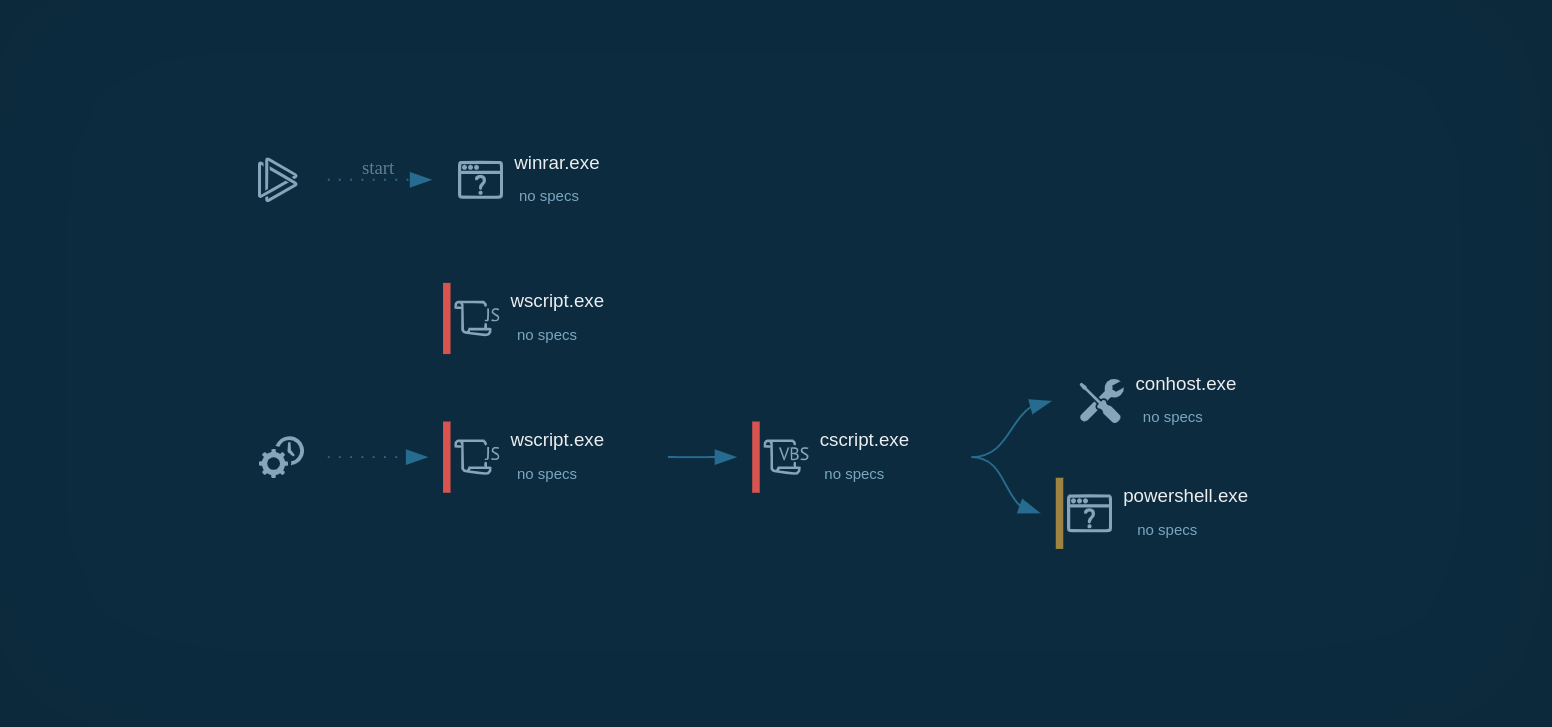 GootLoader process graph inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
GootLoader process graph inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
When the file is opened, the first stage of infection begins. It uses Windows Script Host (wscript) to run an obfuscated JavaScript payload. This payload creates a scheduled task to ensure the infection persists, leading to the execution of a second obfuscated JavaScript file stored on the disk.
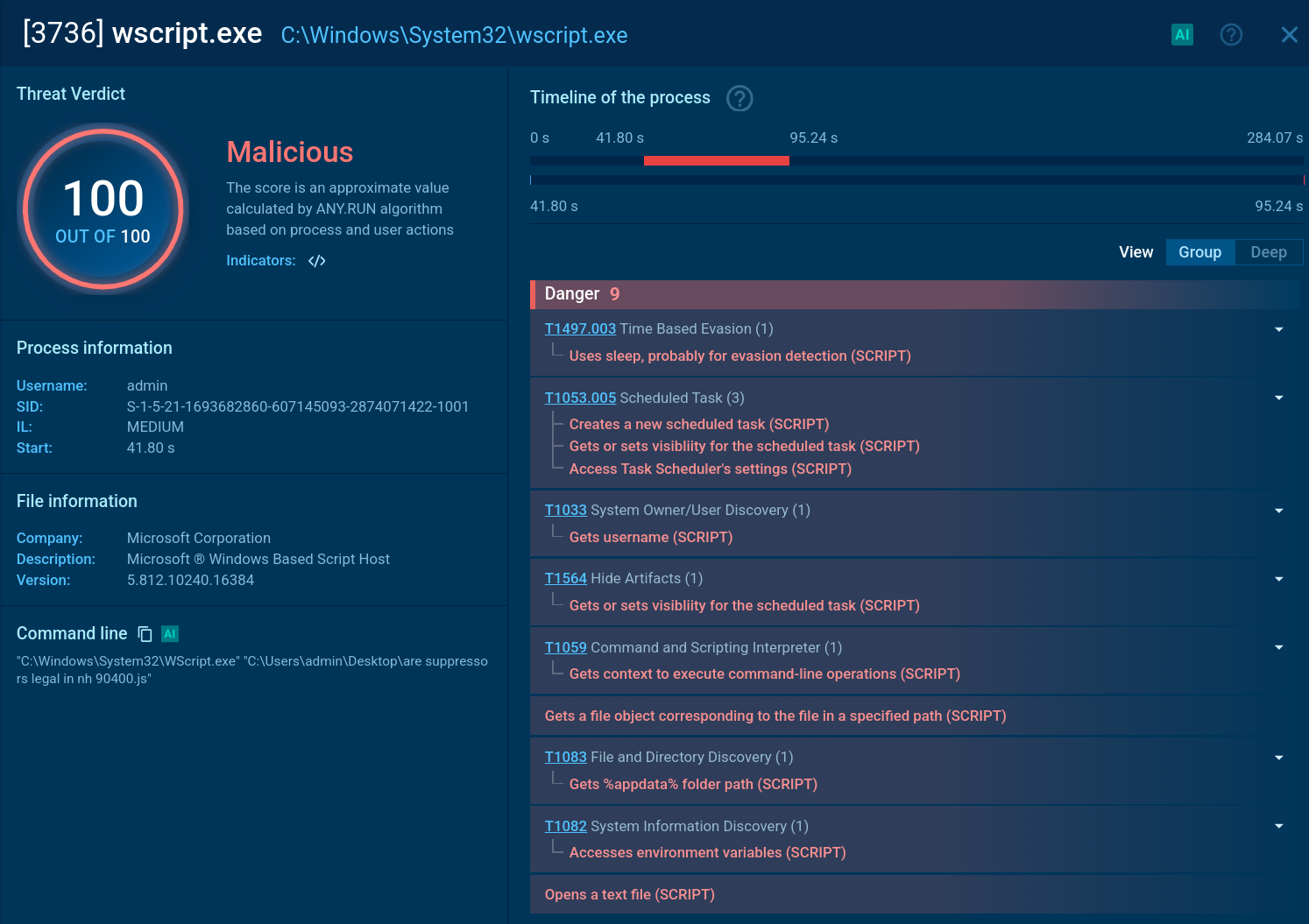 GootLoader script execution inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
GootLoader script execution inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
In the second stage, the execution shifts from wscript to cscript, which runs as a child process. This allows a PowerShell script to run, further deobfuscating and executing more malicious code. The PowerShell script collects information from the infected system, such as operating system details, running processes, and environment variables. It can also check the system's location and use sleep commands. The collected information is then compressed, encoded, and sent to a command-and-control (C2) server.
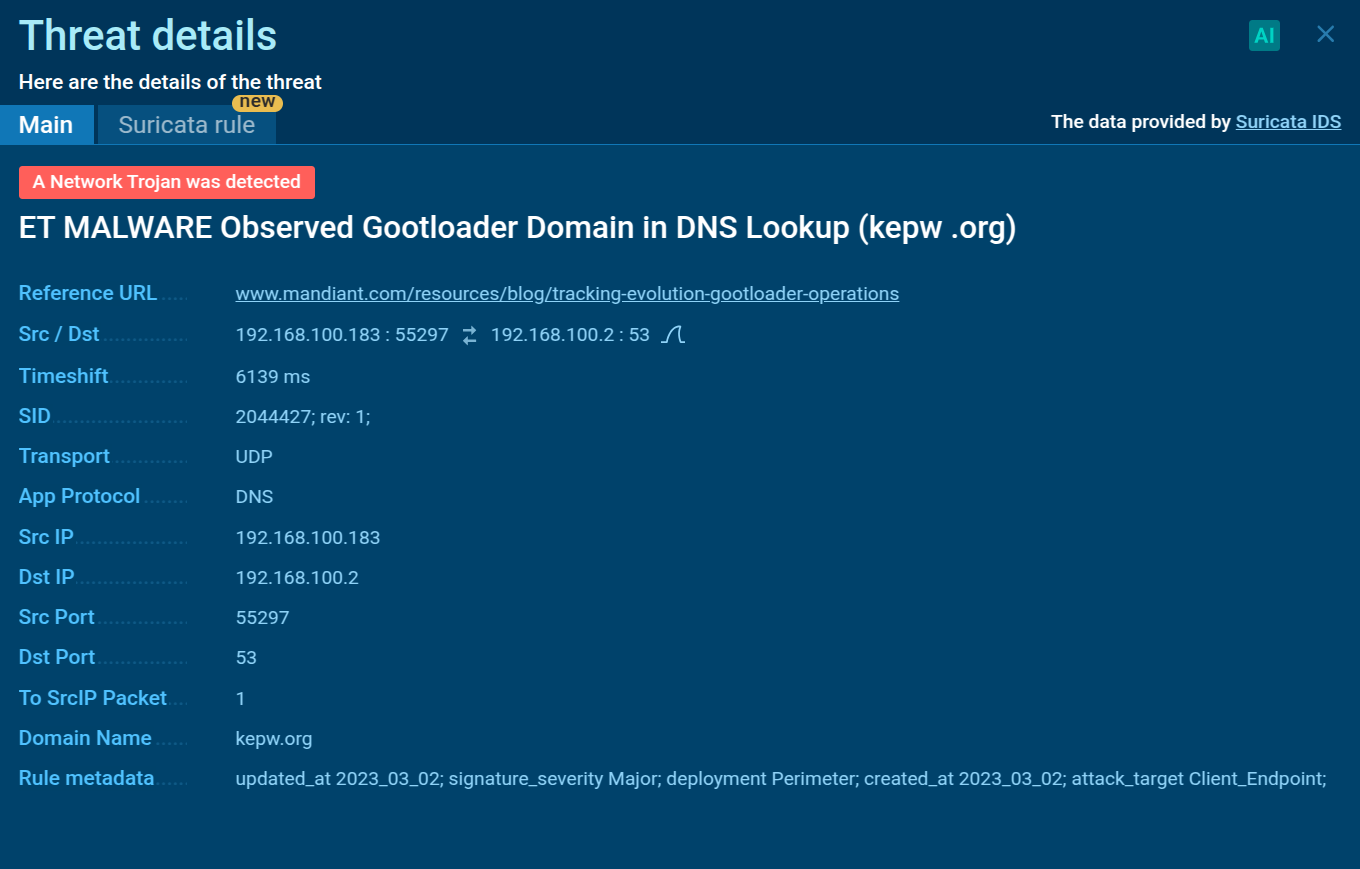 Suricata IDS detection of GootLoader inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
Suricata IDS detection of GootLoader inside the ANY.RUN sandbox
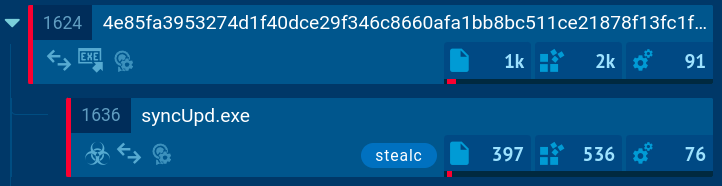
The third stage involves executing additional payloads, which might include components like a Cobalt Strike beacon or other malware. These payloads are often written into Windows Registry keys to ensure they persist and remain active even after the system is rebooted. GootLoader's use of obfuscation techniques makes it hard for traditional security methods to detect. Its sophisticated infection process highlights its effectiveness as a persistent threat to enterprise environments.
To stay informed about the latest GootLoader samples and attacks, use Threat Intelligence Lookup from ANY.RUN. This tool lets you access a large database filled with findings from millions of malware analyses done in the ANY.RUN sandbox.
With over 40 search options, including IPs, domains, file names, and process details, you can easily find relevant information about threats like GootLoader.
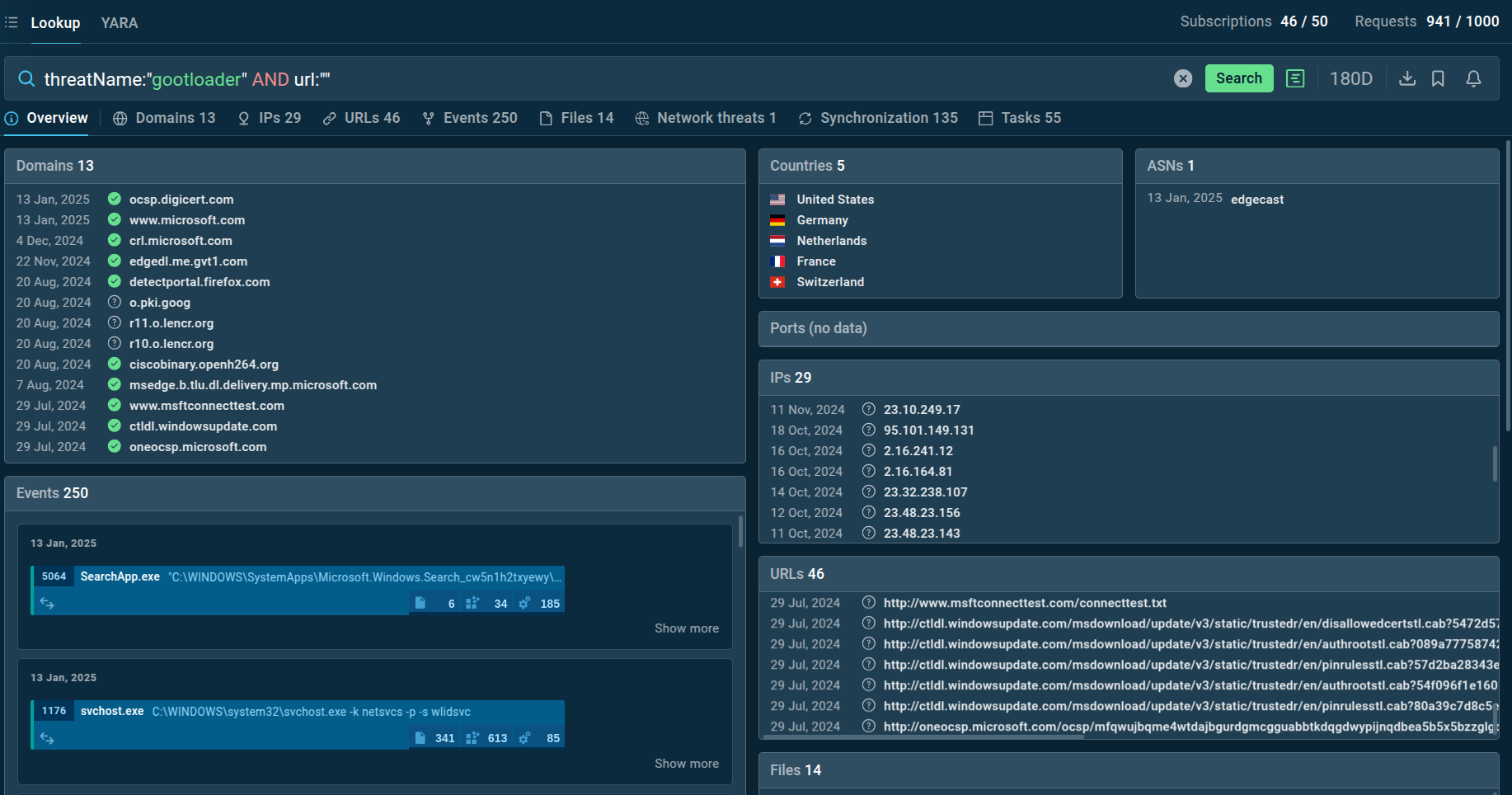 GootLoader search results in TI Lookup
GootLoader search results in TI Lookup
You can search directly by the threat name or use related clues like hash values or network connections. By entering a query like threatName:"GootLoader" AND domain:"", you'll get a list of files, events, domain names, and other data from GootLoader samples. These results, along with sandbox sessions, help you understand the malware's behavior in detail.
GootLoader uses SEO poisoning to rank attacker-controlled websites high in search results, ensuring that potential victims are more likely to encounter these malicious sites.
Once victims visit these websites, they are prompted to download files such as contract templates and other legal documents that appear legitimate and relevant to them.
These files are usually archives containing .js scripts that serve as the first stage of the GootLoader infection. By disguising malicious files as legitimate documents, the attackers increase the likelihood of successful infection.
GootLoader’s ability to evade detection through memory-only execution, encryption, and process injection makes it a serious threat for traditional security measures. The use of SEO poisoning to distribute the malware further complicates efforts to prevent its spread, as it targets unsuspecting users searching for legitimate information.
To proactively identify and mitigate the risks associated with GootLoader, organizations can use tools such as the interactive malware sandbox from ANY.RUN. This sandbox provides a controlled environment for analyzing suspicious files, allowing security teams to detect and understand the behavior of GootLoader and other malicious software.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account to analyze your first file or URL now