Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Dharma is advanced ransomware that has been observed in the wild since 2016. It is considered to be the second most profitable RaaS operation by the FBI. The malware targets hospitals and state organizations, encrypts files, and demands a payment to restore access to lost information.
|
Ransomware
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
24 August, 2017
First seen
:
|
8 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
24 August, 2017
First seen
:
|
8 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 448
448
 0
0

 2345
2345
 0
0

 4534
4534
 0
0
Dharma is a ransomware-type malware. A malicious program that encrypted files and demands a ransom to restore information. Dharma, a member of the CrySIS family, has been around since August 2017, targeting organizations such as hospitals. It managed to earn attackers over $25 million in ransom payments.
Dharma is considered to be advanced ransomware that uses powerful encryption. As a new variant of the CrySIS family, it was first spotted in the wild in 2017. It was operated by an unknown cyber gang who managed to remain mostly in the shadows to this day. CrySIS was offered as a RaaS (Ransomware-as-a-Service), meaning that “clients” could use it, if they purchased the ransomware from the attackers. This means that those who purchase the malware carry out the actual attacks rather than original creators.
Threat actors changed the name over to Dharma after decryption keys for CrySIS were leaked in late 2016. That was the first, but not the only time somebody published the decryption keys, but it was the only time attackers renamed the malware and re-branded the product.
Some researchers believe that Dharma is one of the most popular RaaS malware out there right now. The popularity of this ransomware is partly due to the constant updates that attackers have been rolling out throughout the years it was active.
In fact, there were instances where three new versions of the malware were reported during the same week. In addition, Dharma proved to be very adaptive, changing distribution channels as the underground community moved from mass spam emails to more targeted attacks in 2018 and 2019.
Another part that contributed to the popularity of Dharma is its flexibility. Although the ransom amount is usually set to one Bitcoin, it can be customized depending on the victim profile. This means that for smaller organizations that can’t pay this much (mind you, Bitcoin cost almost 20,000 USD in 2017), the payment amount can be lowered.
Although not unique to this malware, this flexibility and customization greatly enhanced its effectiveness. In fact, the FBI named Dharma the second most profitable ransomware operation.
Now, despite all of the above, Dharma has never really been available to the general public. The only places it could be found were inconspicuous underground forums. At least, until recently.
In late 2019, the source code of Dharma was observed being put for sale for 2,000 USD.
This made many researchers worried, as some predicted that putting the source code for sale will result in somebody uploading it to the public internet. If ransomware as advanced as Dharma gets in the hands of a mass audience, we can be up for a lot of trouble.
It should also be noted that in 2019 researchers reported new ransomware called Phobos, which has almost the same code as Dharma. Although some speculated that this could be another rebranding, Dharma samples are still constantly being found about as often as instances of Phobos malware use.
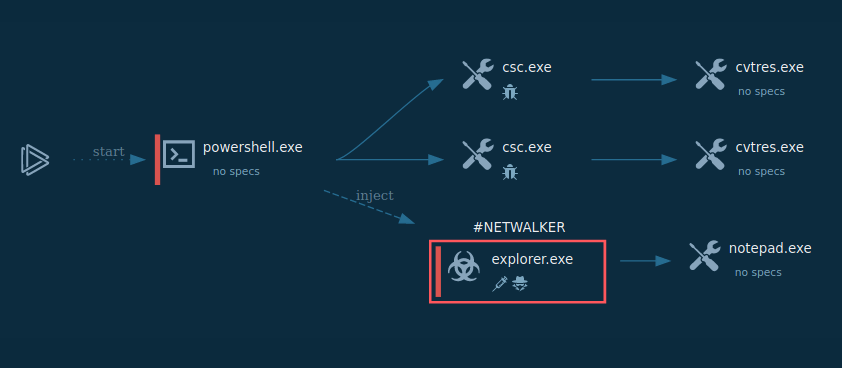
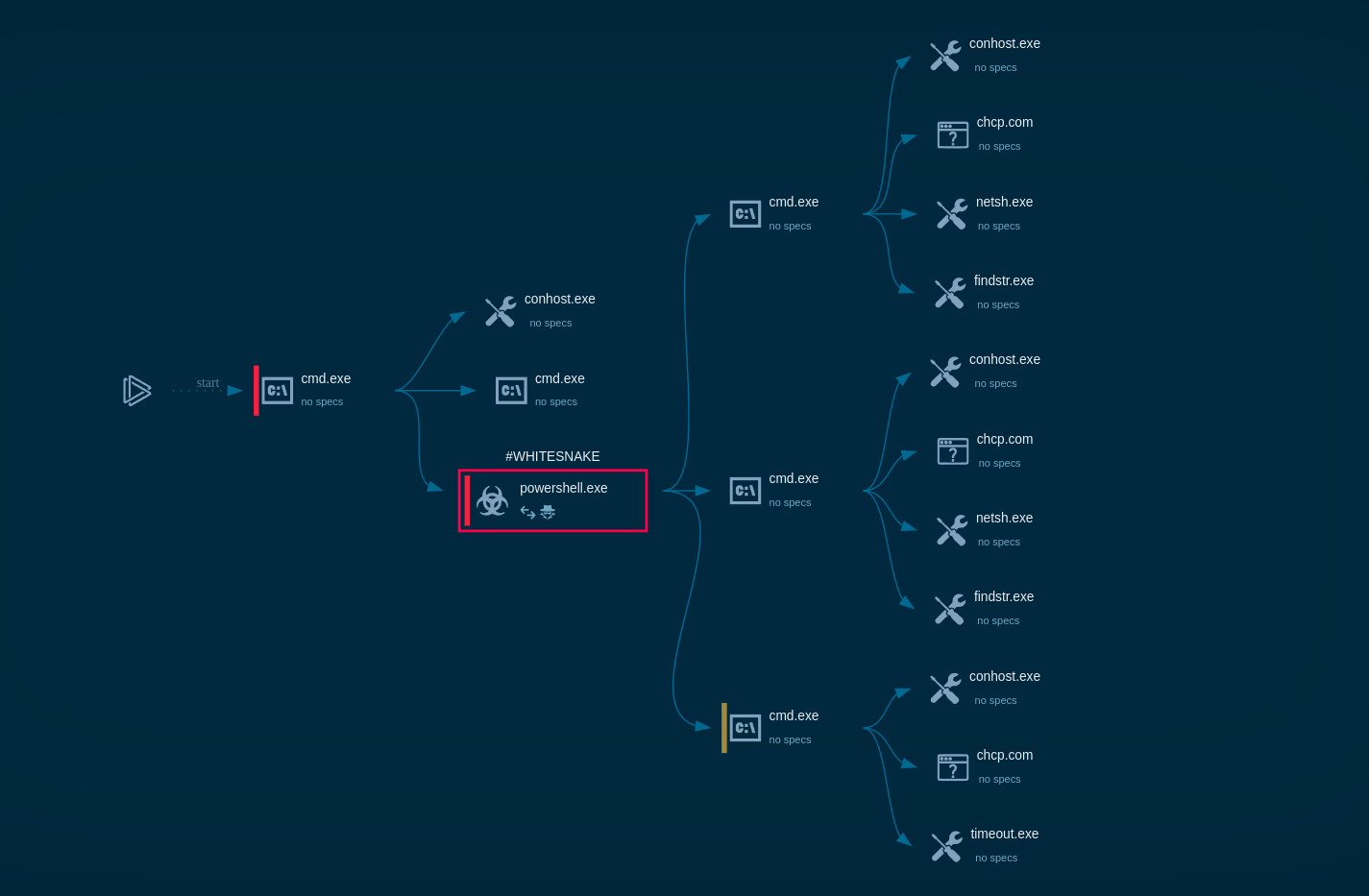
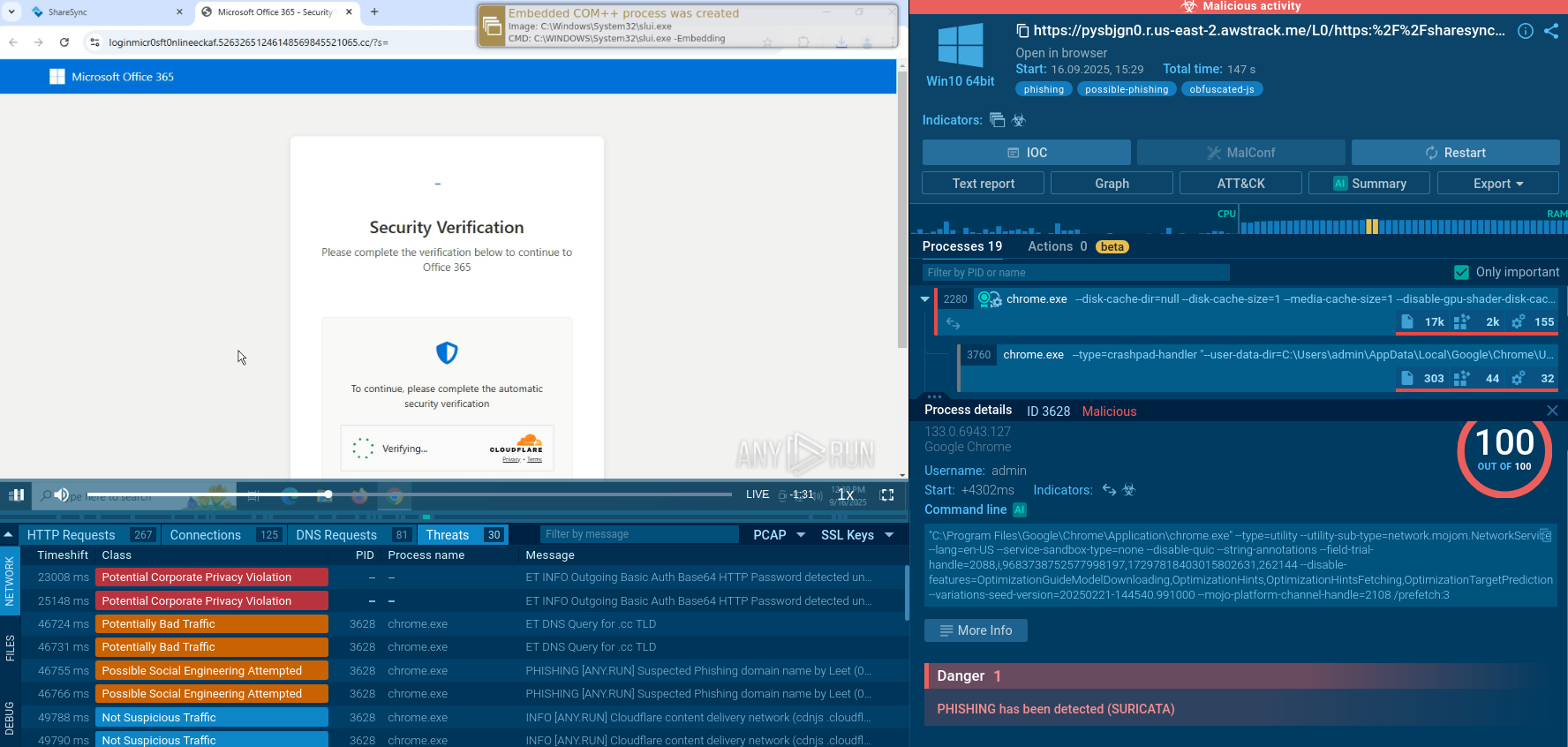
A video recorded in the ANY.RUN interactive malware hunting service shows how the execution of this ransomware unfolds from the victim’s point of view.
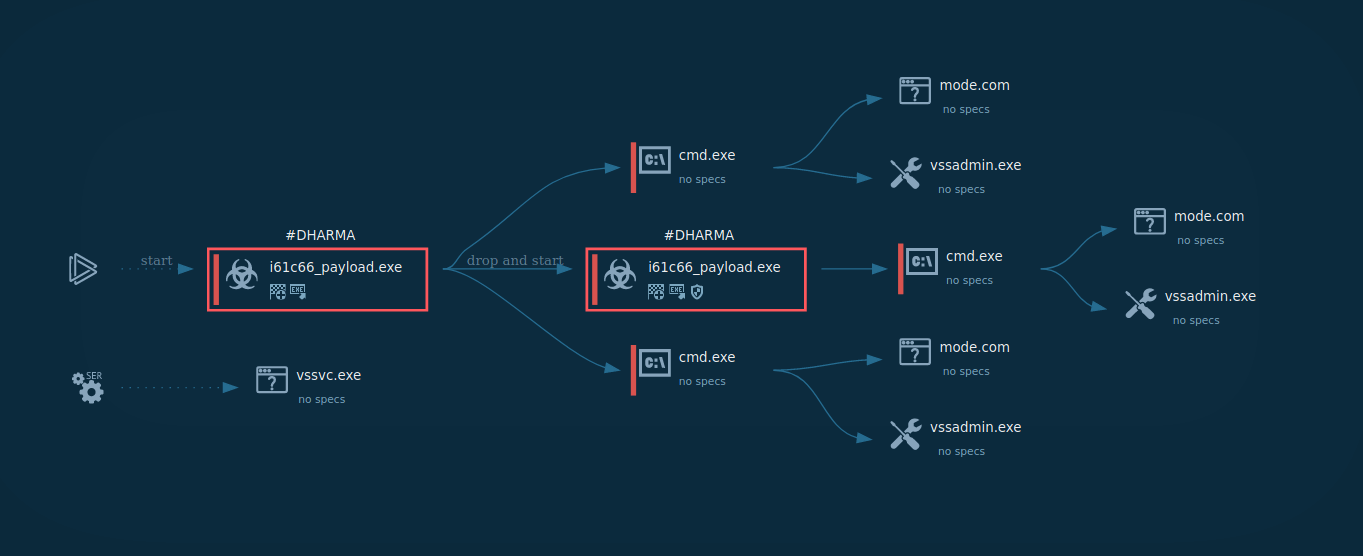
Figure 1: Displays the execution process of the Dharma ransomware This graph was generated by ANY.RUN.
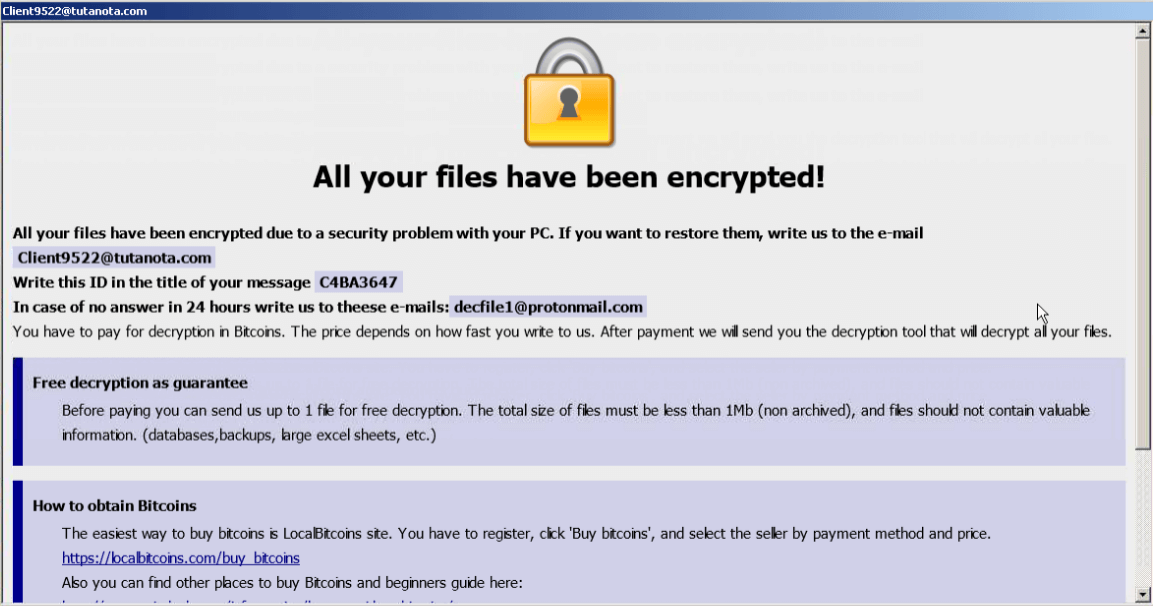
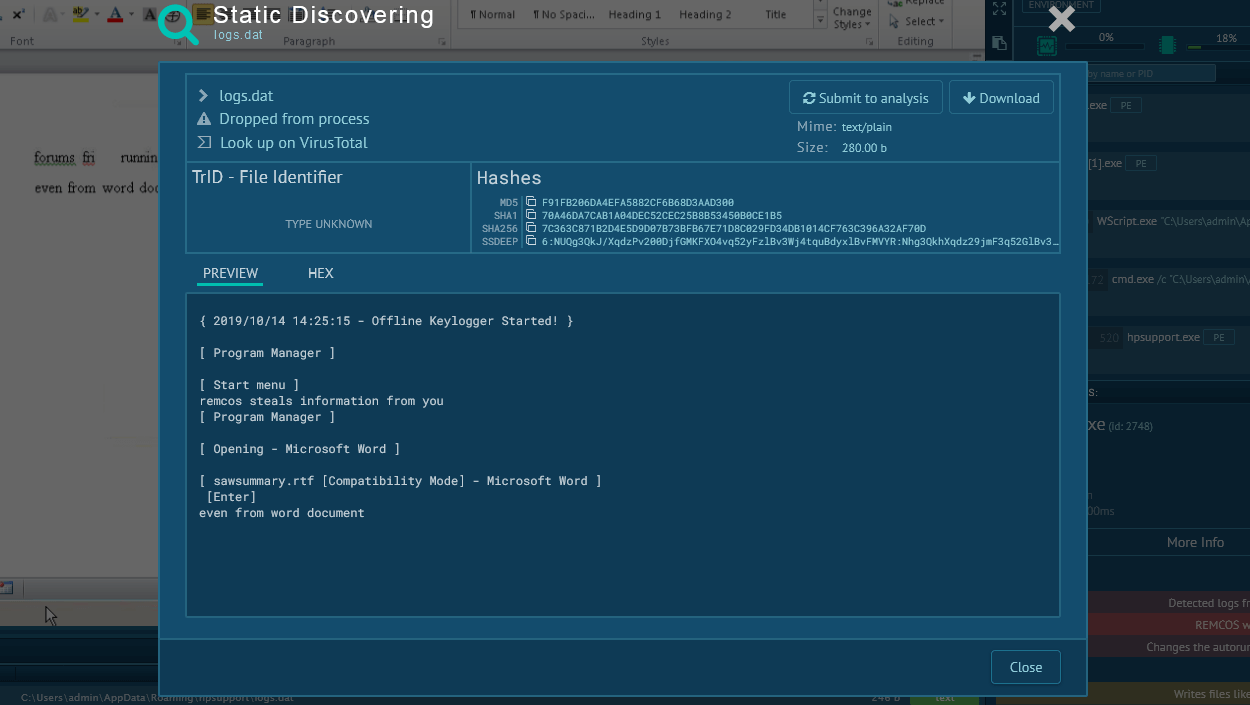
Figure 2: Displays the Dharma ransomware ransom note
The execution process of the Dharma ransomware is relatively typical for this type of malware such as WannaCry. After the executable file makes its way into an infected system and runs, the main malicious activity begins. After the start of execution, the ransomware deletes shadow copies. After it encrypts all targeted files, Dharma drops a ransom note on the desktop.
Dharma has been observed using multiple distribution methods, but the following three are the most common.
Out of the three distribution channels, spam email campaigns are the most straightforward. It is also how threat actors relied on the most during the first years of malware operation, launching widespread campaigns and relying on sheer numbers of potential recipients.
However, as users and organizations become more educated about the dangers of cyberattacks, spam emails lose effectiveness. Dharma operators quickly adapted and restored to the other two methods for payload delivery.
Another method that Dharma is known to use is utilizing real compromised software. For example, some attacks involved targeted email campaigns that contained a download link. What made these attacks stand out is that upon clicking the link, the payload would be downloaded along with a compromised legitimate program. The program then would launch an installer designed to direct the victim's attention while the executable file is running in the background.
Finally, the last common distribution method is through the use of compromised RDP. RDP is a protocol developed by Microsoft used to establish a connection between multiple PCs over a network. It’s a completely legitimate protocol that technicians use to carry out remote technical support, among other uses. However, if a session becomes compromised, it gives hackers the ability to download and execute the malicious file as long as they have access to the remotely connected PC.
Dharma is dangerous ransomware. Since 2017 its popularity has been only growing, and continued use indicates that members of the underground hacking community see it as a reliable option. Given that even the FBI considers Dharma to be one of the most effective malware in its class, it’s no wonder that this malware is in demand.
However, even more, worrying is that despite all the attention that Dharma has been getting over the years, creators of this ransomware managed to evade researchers and evolve the ransomware along the way continually.
Although decryptors do exist for some versions of Dharma, the only reason they could be created is that somebody from the inside leaked master keys. Apart from these instances, little progress has been made to crack the encryption algorithm used by Dharma.
And now, with the source code appearing for sale, we run the risk of it popping up on the global Internet, which can spawn a new, massive wave of Dharma attacks.
Keeping this in mind, researchers should take time to study Dharma behavior to prepare for potential attacks carefully. Thankfully, ANY.RUN provides all the necessary tools to carry out Dharma analysis in a secure online environment.