Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Sliver is an open-source command-and-control (C2) framework that has been increasingly adopted by threat actors as an alternative to tools like Cobalt Strike. Developed by security firm Bishop Fox, Sliver was initially intended for legitimate security testing and red teaming exercises. However, its robust features and open-source nature have made it attractive to malicious actors seeking to control compromised systems.
|
C2 Framework
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
3 June, 2019
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
C2 Framework
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
3 June, 2019
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 787
787
 0
0

 478
478
 0
0

 2728
2728
 0
0
Sliver is an open-source command-and-control framework designed for adversary emulation and red teaming. First released in 2019 by Bishop Fox, it has been adopted by both security professionals and threat actors.
Malicious users leverage Sliver to establish control over compromised systems, facilitating activities such as data exfiltration, lateral movement, and deployment of additional malware.
Its distribution methods include phishing emails, malicious documents, drive-by downloads, and exploitation of vulnerabilities.
Key technical features encompass cross-platform compatibility, support for multiple communication protocols, and capabilities like process injection and token manipulation.
To see how Sliver operates inside a secure environment, you can use tools such as ANY.RUN’s sandbox.
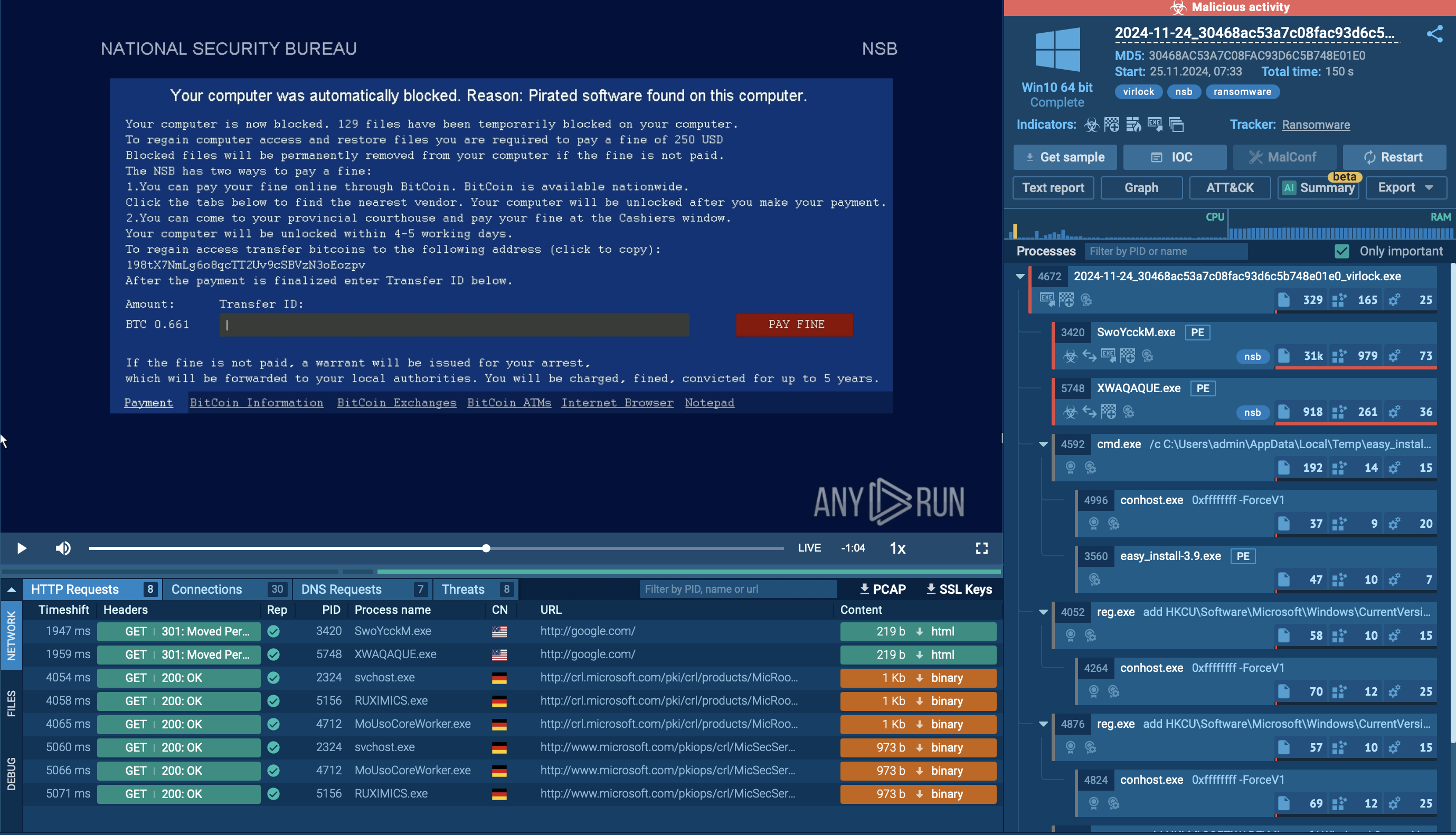
 Sliver analyzed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
Sliver analyzed inside ANY.RUN sandbox
One of the standout features of Sliver C2 is its accessibility. Being open-source, it's easy to download and set up, with compatibility across major operating systems like MacOS, Windows, and Linux. This cross-platform nature ensures that users can implement Sliver C2 in a variety of environments.
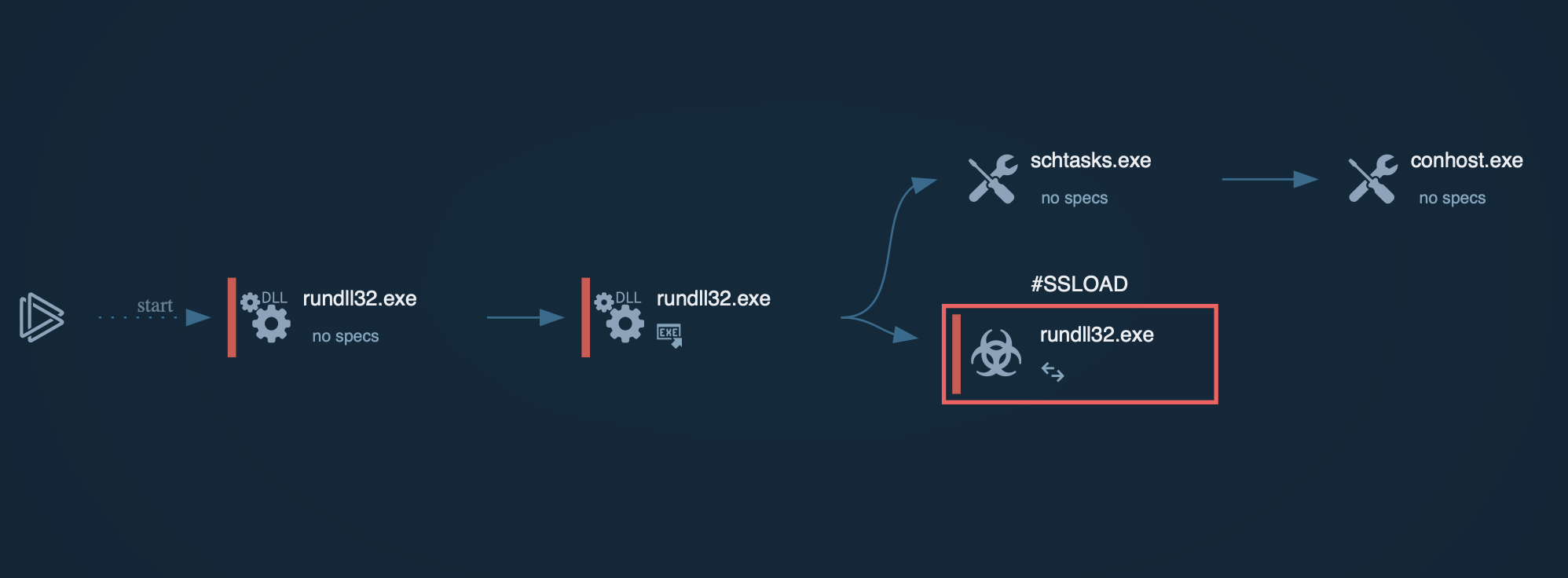
Sliver malware generates implants, commonly referred to as ‘slivers’, which consist of malicious code designed for remote control of compromised devices.
When a sliver is successfully deployed on a target system, it facilitates a communication channel with the central C2 server. This connection is crucial, as it enables the operator to send commands and receive data from the compromised device.
Sliver C2 supports various protocols for managing these connections, including Mutual TLS (mTLS), WireGuard, HTTP(S), and DNS.
Sliver’s primary functionalities include:
To see how Sliver operates, let’s upload its sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
The execution chain of Sliver typically follows these steps: Initial access vector involves payload generation by creating a malicious payload for the target OS, delivered via phishing, malicious documents, drive-by downloads, or vulnerability exploitation.
Payload execution occurs when the target runs the payload, establishing a foothold and connecting back to the Sliver C2 server.
Command and Control (C2) begins with the infected machine beaconing to the C2 server at set intervals, using encrypted channels to avoid detection.
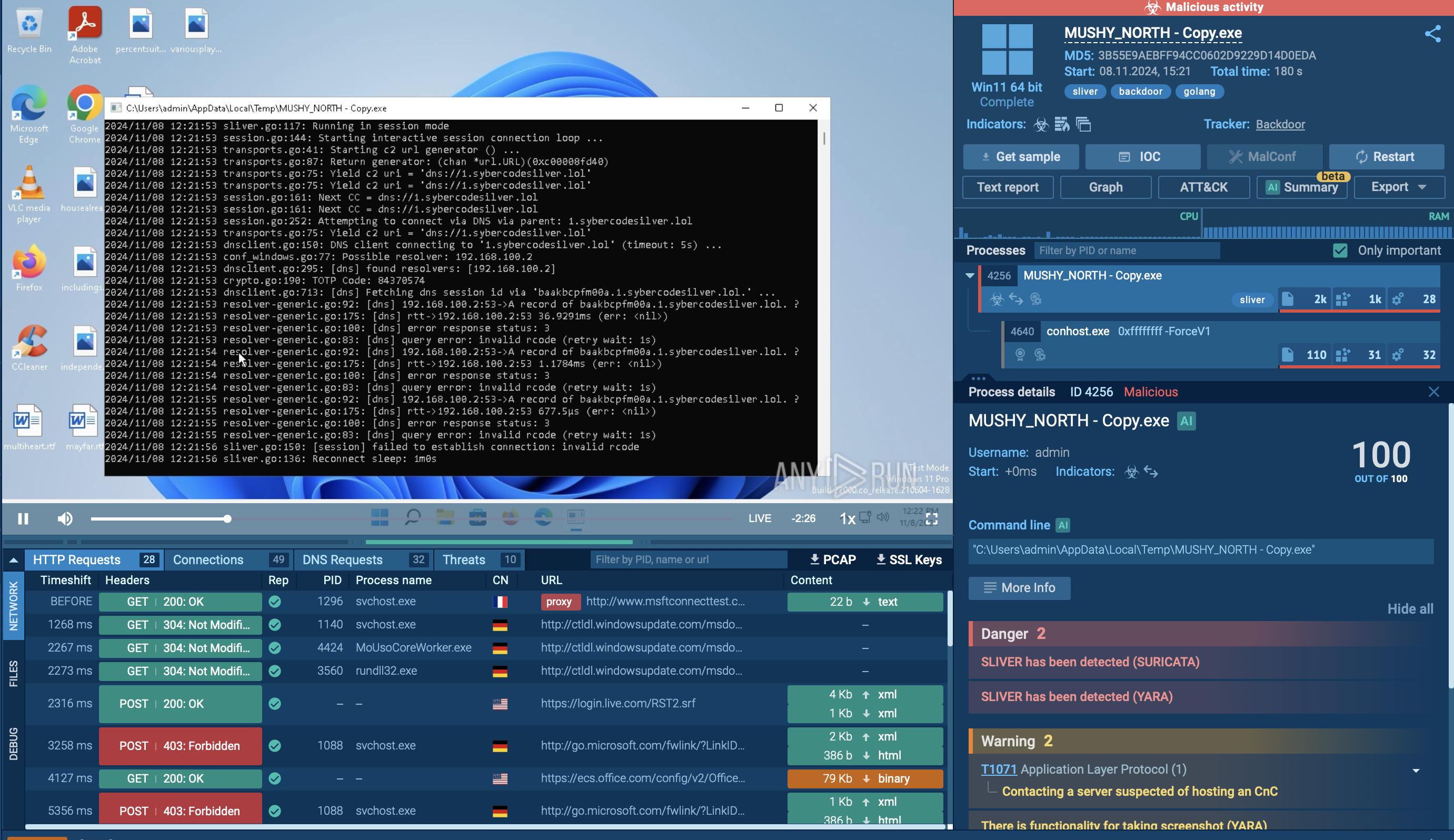
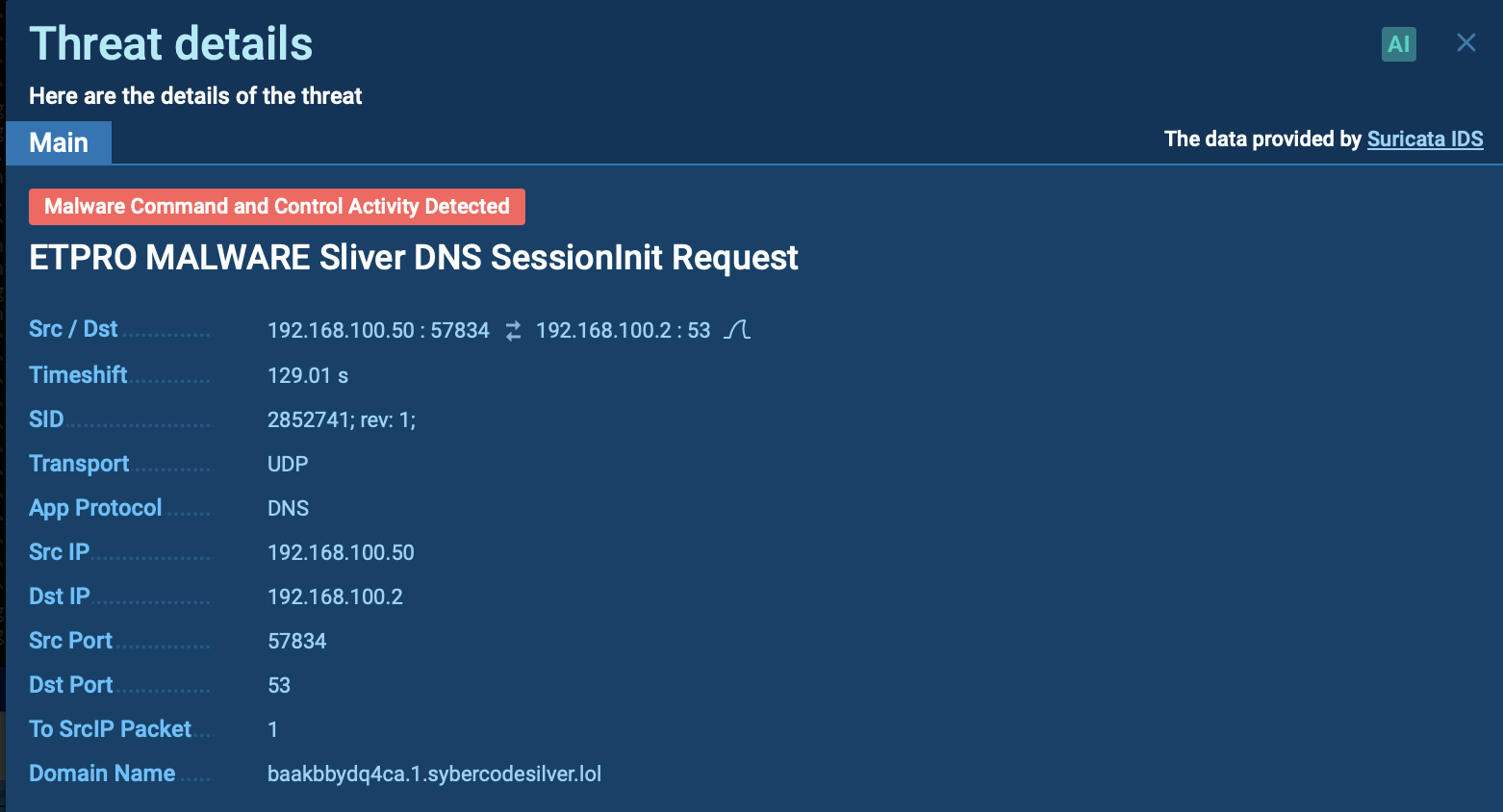 Suricata rule triggered by Sliver inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Suricata rule triggered by Sliver inside ANY.RUN’s sandbox
Post-exploitation activities include privilege escalation using built-in or custom tools, persistence through registry modifications or scheduled tasks, lateral movement within the network, and credential harvesting.
Data collection and exfiltration involve identifying valuable data and transmitting it back to the attacker's infrastructure, often encrypted.
Covering tracks includes log deletion and anti-forensics techniques like obfuscation and memory-only payloads. The termination or pivoting phase involves closing the C2 connection or leaving backdoors for future access and potentially pivoting to new targets to repeat the execution chain.
Attackers distribute Sliver through various methods, including:
To obtain up-to-date intelligence on Sliver, utilize the Threat Intelligence Lookup service.
This platform gives you access to an extensive database enriched with data from countless malware analysis sessions executed in the ANY.RUN sandbox. With over 40 customizable search parameters at your disposal, you can efficiently uncover important information on various threats, including details such as IP addresses, domains, file names, and process artifacts.
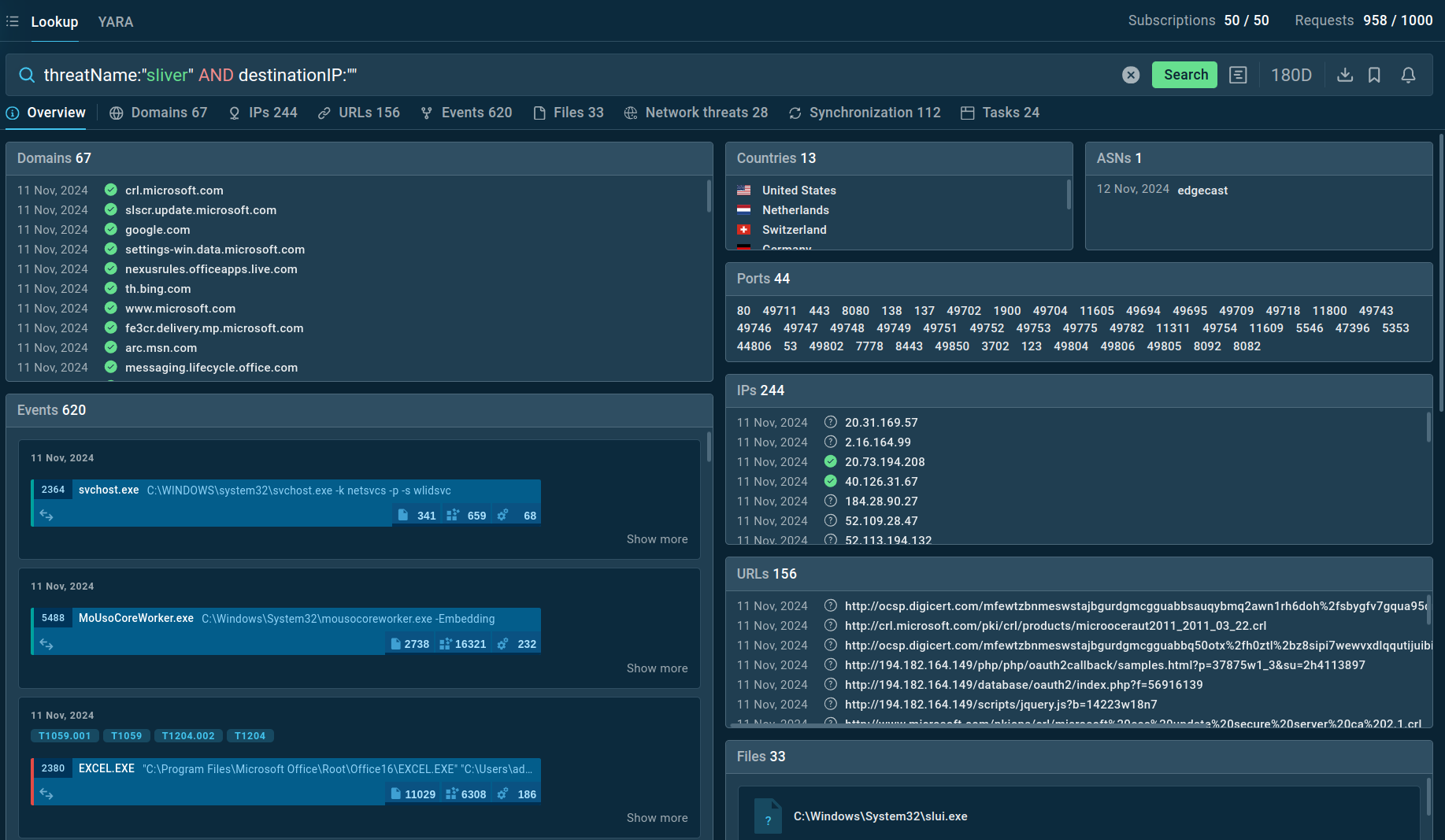 TI Lookup reveals key threat context related to Sliver C2
TI Lookup reveals key threat context related to Sliver C2
For instance, to retrieve intelligence on Sliver, you can either search for its specific threat name or utilize related artifacts. By creating a query like threatName:"sliver" and destinationIP:"", the TI Lookup will provide you with all relevant samples and sandbox analyses associated with this particular malware.
Get a 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup along with the ANY.RUN sandbox
Sliver’s open-source nature and cross-platform compatibility further enhance its appeal to threat actors. To defend against such threats, it’s crucial to integrate advanced analysis tools that can proactively identify and mitigate suspicious activities.
ANY.RUN is an interactive malware analysis sandbox that enables real-time examination of suspicious files and URLs. Its user-friendly interface and comprehensive analysis capabilities allow security professionals to dissect malware behavior, understand its impact, and develop effective countermeasures.
Sign up for a free account with ANY.RUN to stay ahead of emerging threats like Sliver