Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


BTMOB RAT is a remote access Trojan (RAT) designed to give attackers full control over infected devices. It targets Windows and Android endpoints. Its modular structure allows operators to tailor capabilities, making it suitable for espionage, credential theft, financial fraud, and establishing long-term footholds in corporate networks.
|
RAT
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 February, 2025
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 February, 2025
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 871
871
 0
0

 519
519
 0
0

 2811
2811
 0
0
Key Takeaways
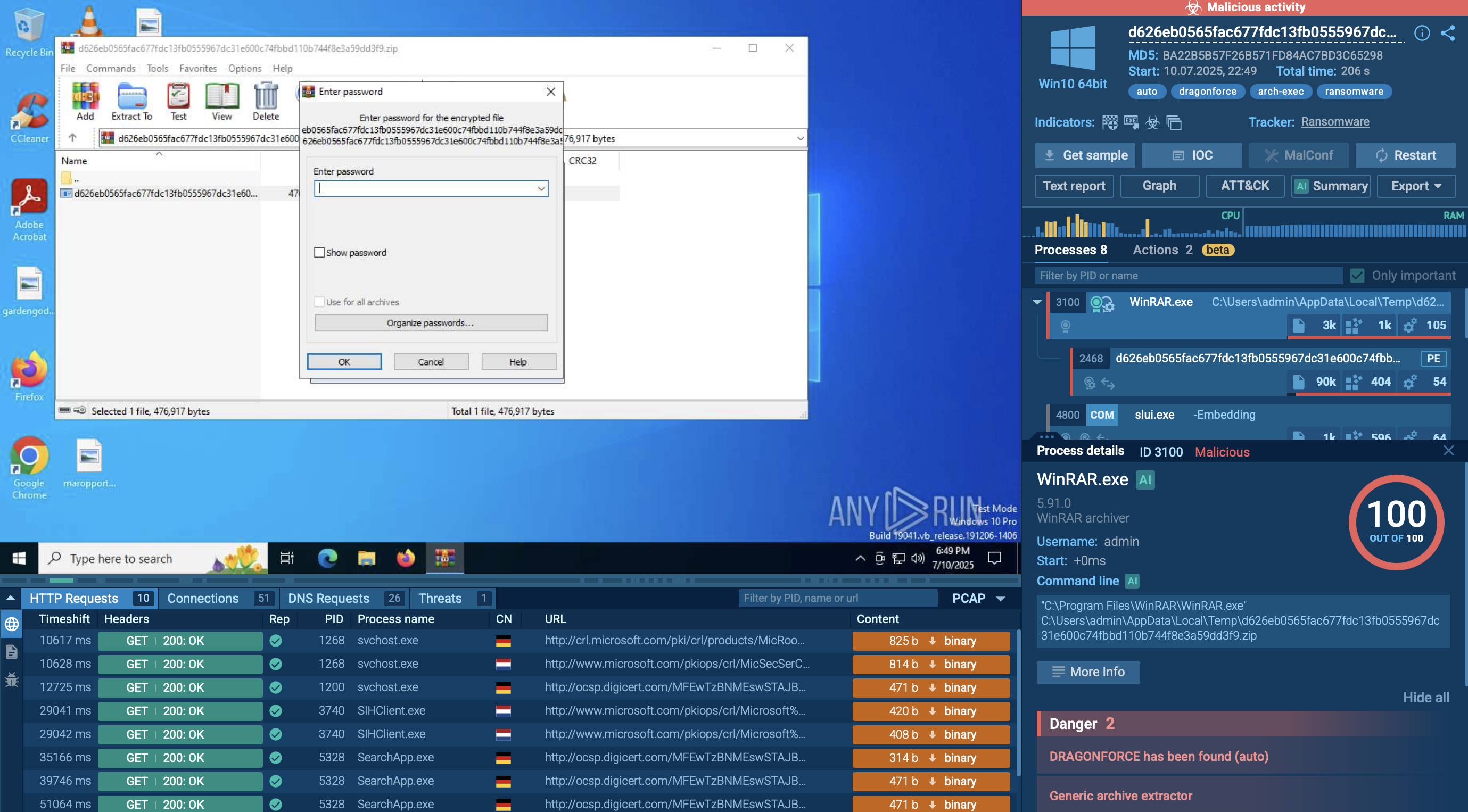
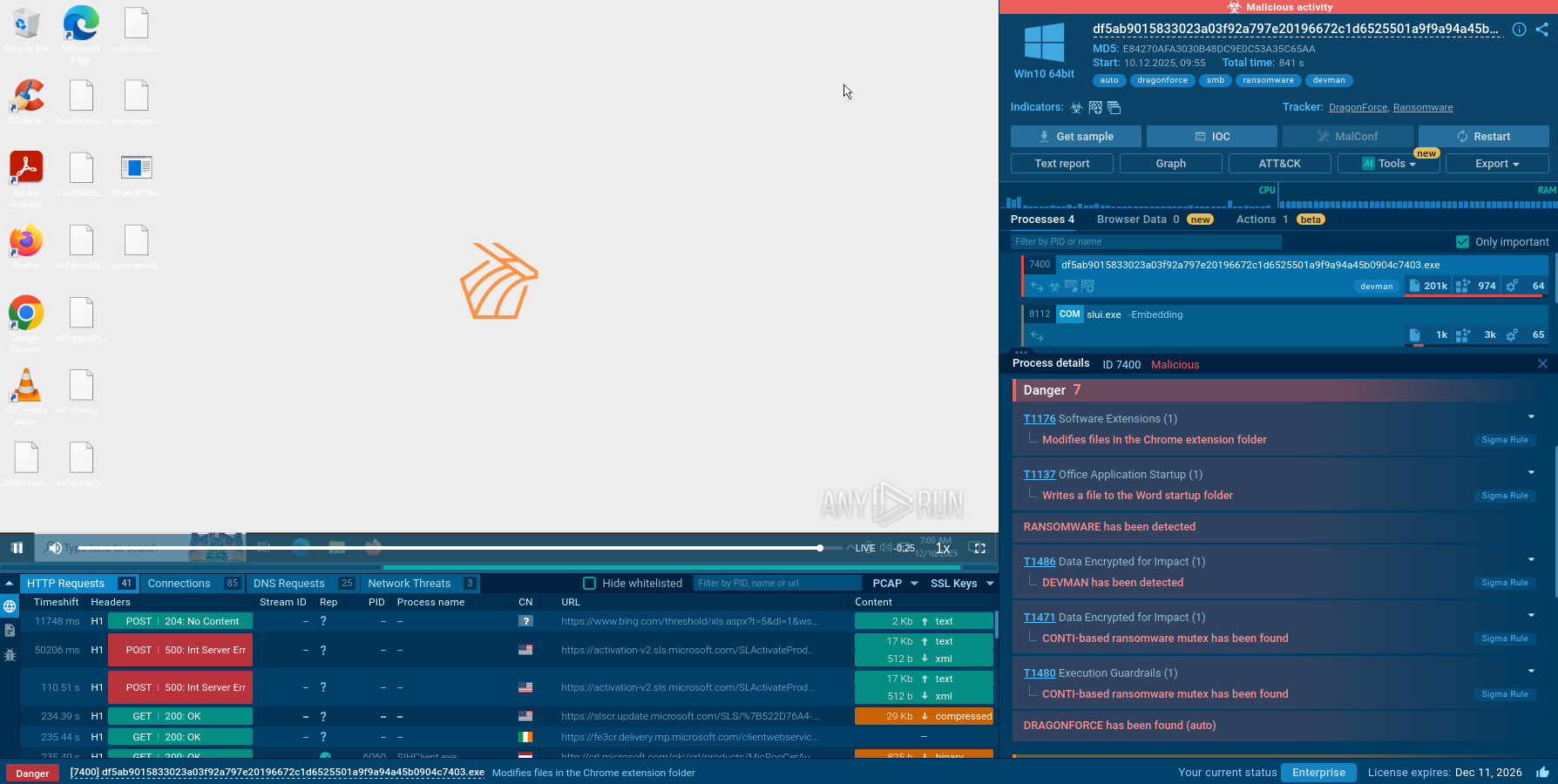
 Gather BTMOB RAT IOCs in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
Gather BTMOB RAT IOCs in ANY.RUN's Interactive Sandbox
BTMOB RAT represents a significant evolution in Android malware, emerging as one of the most sophisticated Remote Access Trojans targeting mobile devices in 2025. This advanced malware evolved from the SpySolr family and has rapidly gained notoriety for its comprehensive data theft capabilities, remote control features, and ability to bypass modern Android security measures. With over 15 variants identified since December 2024, BTMOB RAT poses a serious threat to both individual users and organizations worldwide. The malware operates as a comprehensive Remote Access Trojan specifically designed for Android platforms, leveraging the operating system's Accessibility Service to gain extensive control over infected devices. Unlike traditional mobile malware that focuses on single attack vectors, BTMOB RAT combines multiple techniques including credential theft, remote device control, banking fraud, and data exfiltration capabilities.
What sets BTMOB RAT apart from other mobile threats is its sophisticated use of overlay attacks, particularly targeting financial applications like Alipay. The latest version (v2.5) incorporates advanced obfuscation techniques and can perform real-time screen manipulation.
The malware is distributed through a Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) model, with cybercriminals advertising lifetime licenses for $5,000 through Telegram channels. This commercial approach has accelerated its adoption among threat actors and contributed to its rapid evolution and widespread distribution.
BTMOB RAT infiltrates via social engineering, primarily phishing sites masquerading as legitimate apps like iNat TV (e.g., tvipguncelpro.com) or fake WhatsApp mods (e.g., WhatsApp GB). Users are tricked into sideloading APKs, which prompt enabling Accessibility Service—framed as necessary for "enhanced features."
Spread occurs through:
Post-infection, it self-propagates by exfiltrating contacts for SMS phishing or using infected devices to host phishing pages. Geographic targeting, like Morocco's 2025 alerts, shows adaptation to local lures.
BTMOB RAT predominantly targets Android users in emerging markets with high mobile banking adoption, where digital financial services are rapidly growing but security awareness lags. In Morocco, it has been a focal point of national alerts, affecting smartphone users who enable accessibility features for convenience, leading to widespread banking data theft. Morocco ranks third in Africa for web-based threats, with over 12.6 million attack attempts in 2024, amplifying BTMOB's impact.
Globally, victims include casual users of streaming or mining apps, as well as financial app users in China (e.g., Alipay targets). Recent campaigns have hit Latin America, such as Argentina via fake government sites impersonating tax agencies. Over 500,000 installations of similar accessibility-abusing malware were recorded in 2024, suggesting BTMOB's victim pool could number in the tens of thousands by September 2025. Businesses in retail and finance are indirect victims through employee devices, but primary targets remain individual consumers vulnerable to phishing.
The trojan operates through several sophisticated mechanisms:
Accessibility Service Abuse:
It exploits Android's Accessibility Service, originally designed to help users with disabilities, to gain broad system permissions and control over user interface elements.
Overlay Attacks:
BTMOB RAT creates transparent or semi-transparent overlays on legitimate applications, particularly banking and payment apps, to capture user credentials and sensitive information without detection.
Remote Administration:
The malware establishes persistent command and control (C&C) communication channels, allowing attackers to remotely execute commands, update malware components, and extract data in real-time.
Dynamic Code Loading:
Advanced variants can download and execute additional malicious modules, expanding their capabilities based on specific attack objectives.
Anti-Detection Techniques:
The malware employs multiple evasion techniques including code obfuscation, runtime application self-protection (RASP), and behavioral analysis evasion to avoid detection by security solutions.
Data Exfiltration:
Stolen information is encrypted and transmitted to attacker-controlled servers through various channels, including HTTPS connections to legitimate-looking domains.
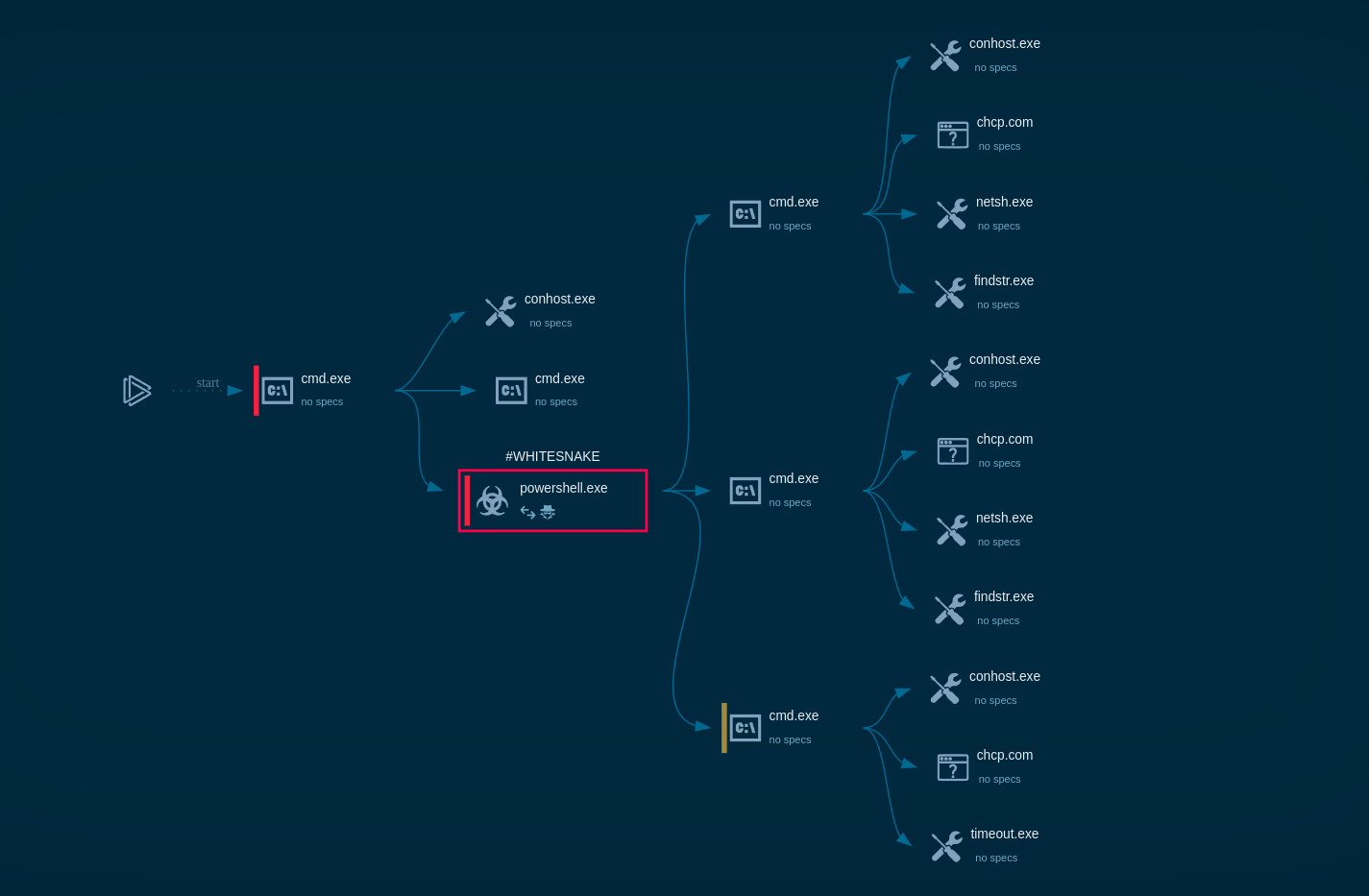
A dynamic analysis of a BTMOB sample in ANY.RUN’s Interactive Sandbox reveals key operating mechanisms and network activity of the malware.
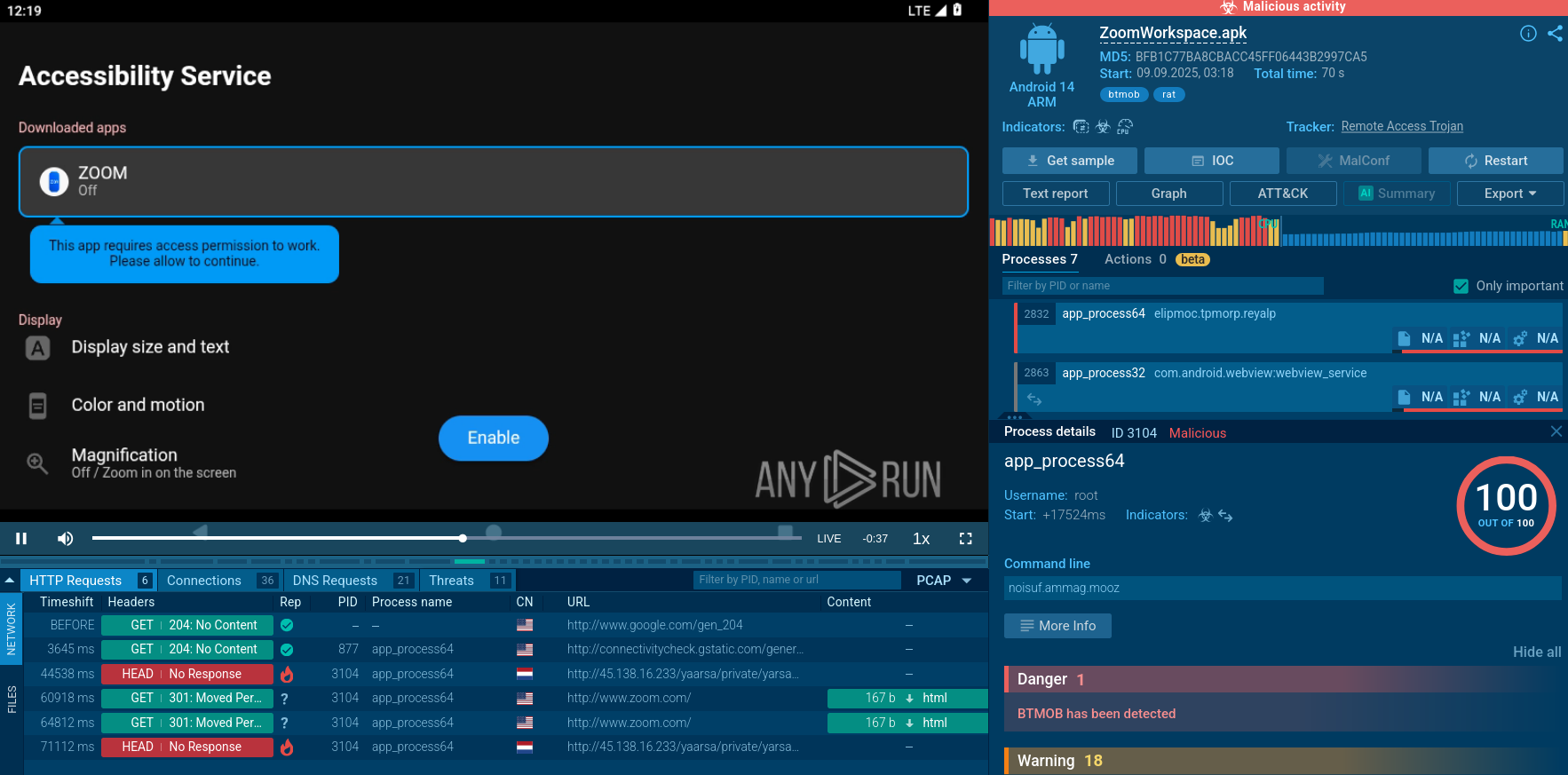 BTMOB RAT sample analysis in the Interactive Sandbox
BTMOB RAT sample analysis in the Interactive Sandbox
Analysis of network traffic revealed the malware’s attempts to establish a connection with the command and control (C&C) server via hxxx [://] ip/yaarsa/private/yarsap_80541 [.] php. A characteristic sequence of requests is observed: an initial HEAD request, followed by a repeated HEAD after a pause, which is part of the handshake connection establishment mechanism and server availability check.
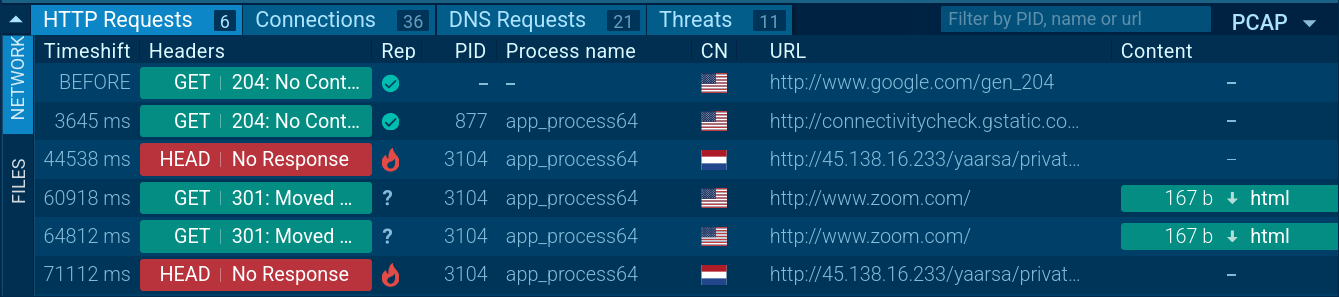 BTMOB RAT sample analysis in the Interactive Sandbox
BTMOB RAT sample analysis in the Interactive Sandbox
All commands and data are transmitted through an encrypted channel, which complicates analysis of the payload. To protect its configuration and the collected data, the malware actively uses cryptographic APIs.
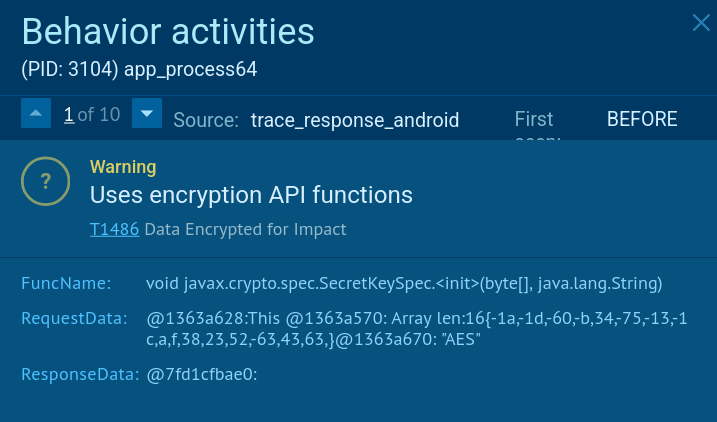 Encryption technique used by BTMOB RAT
Encryption technique used by BTMOB RAT
BTMOB RAT stores its configuration in the system SharedPreferences storage in XML format. The configuration file contains a complex map of boolean values, where each parameter defines the malware's functionality.
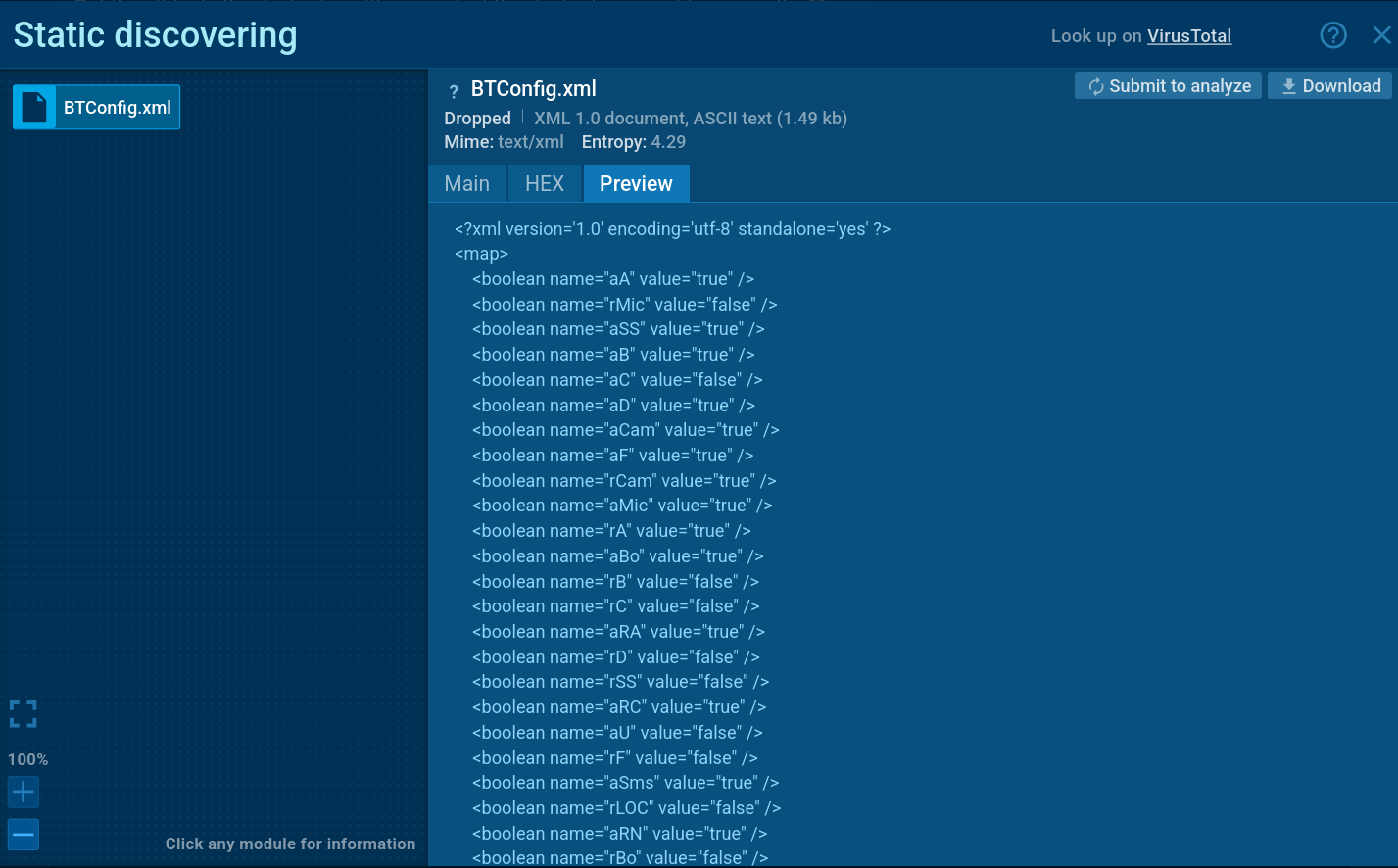 BTMOB RAT configuration file contents visible in Interactive Sandbox
BTMOB RAT configuration file contents visible in Interactive Sandbox
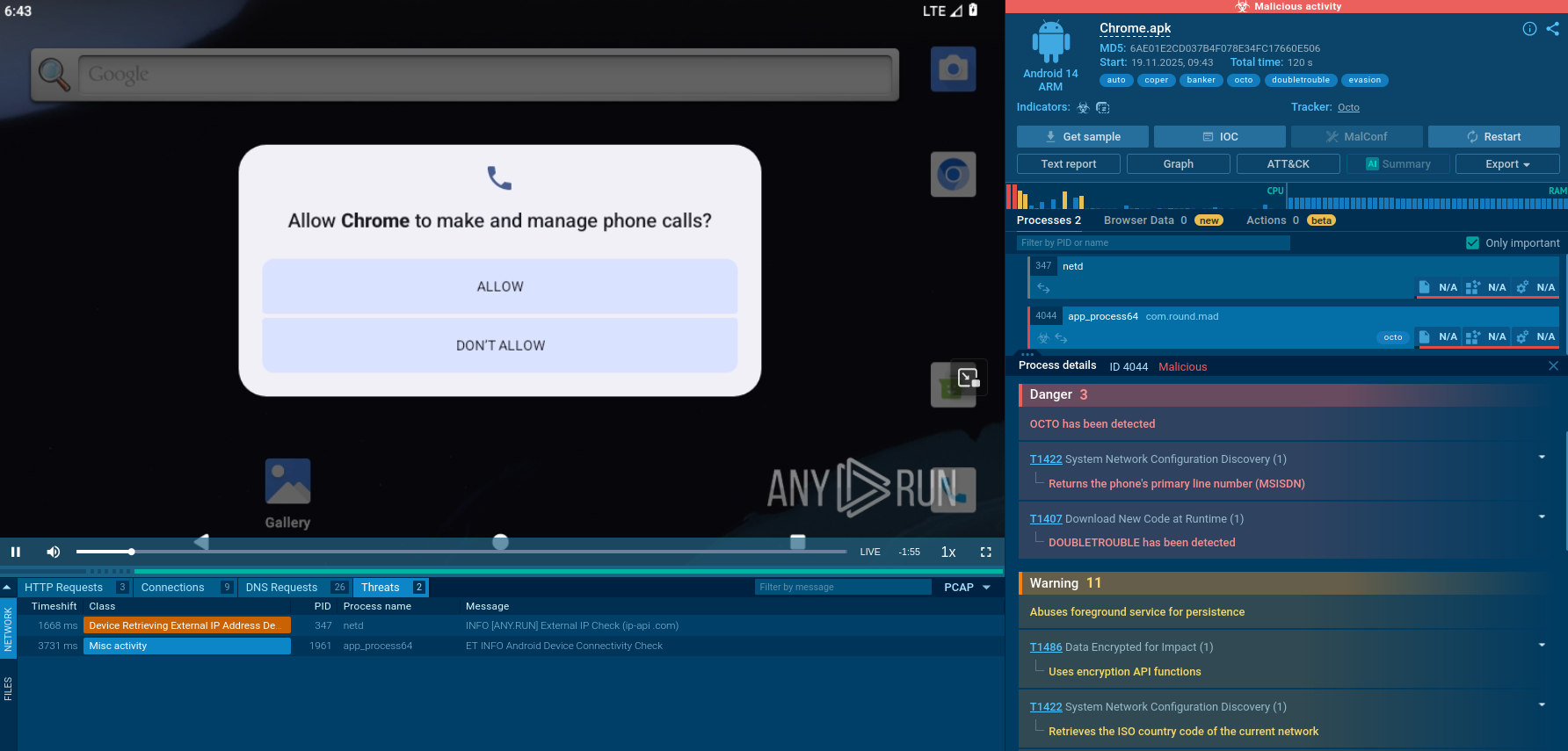
Aggressive permission acquisition appears to be the key attack vector. The malware doesn't simply request access but manipulates the interface using Input Injection to automatically press the "Allow" button.
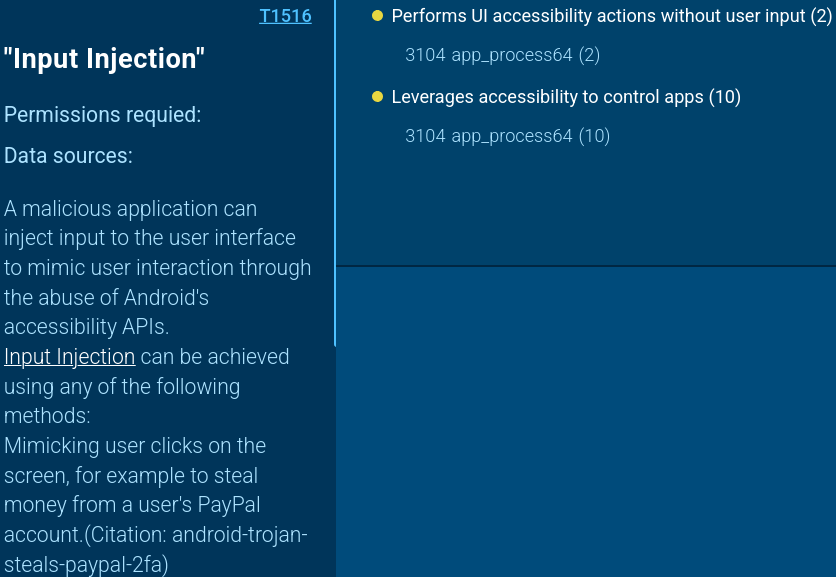 BTMOB RAT detected to use Input Injection technique
BTMOB RAT detected to use Input Injection technique
Once access is obtained, it gains control over the device, including implementing the Prevent Application Removal mechanism, intercepting events in Android Settings to block its own uninstallation.
To ensure continuous operation, the malware creates a background service immediately after launch and uses WakeLock, preventing the device from entering sleep mode. Additionally, it checks the lock screen state, which increases its stealth.
Before performing its main tasks, the malware conducts comprehensive reconnaissance: collects a list of installed applications, analyzes running processes, and obtains system data. This allows the operator to adapt the attack to the specific device.
Important malicious activity is conducting overlay attacks. The malware overlays phishing windows on legitimate applications, primarily banking and cryptocurrency ones, to steal credentials, PIN codes, and two-factor authentication.
You can view the succession of the above-mentioned processes in ANY.RUN’s Sandbox as a process tree with every behavior’s description.
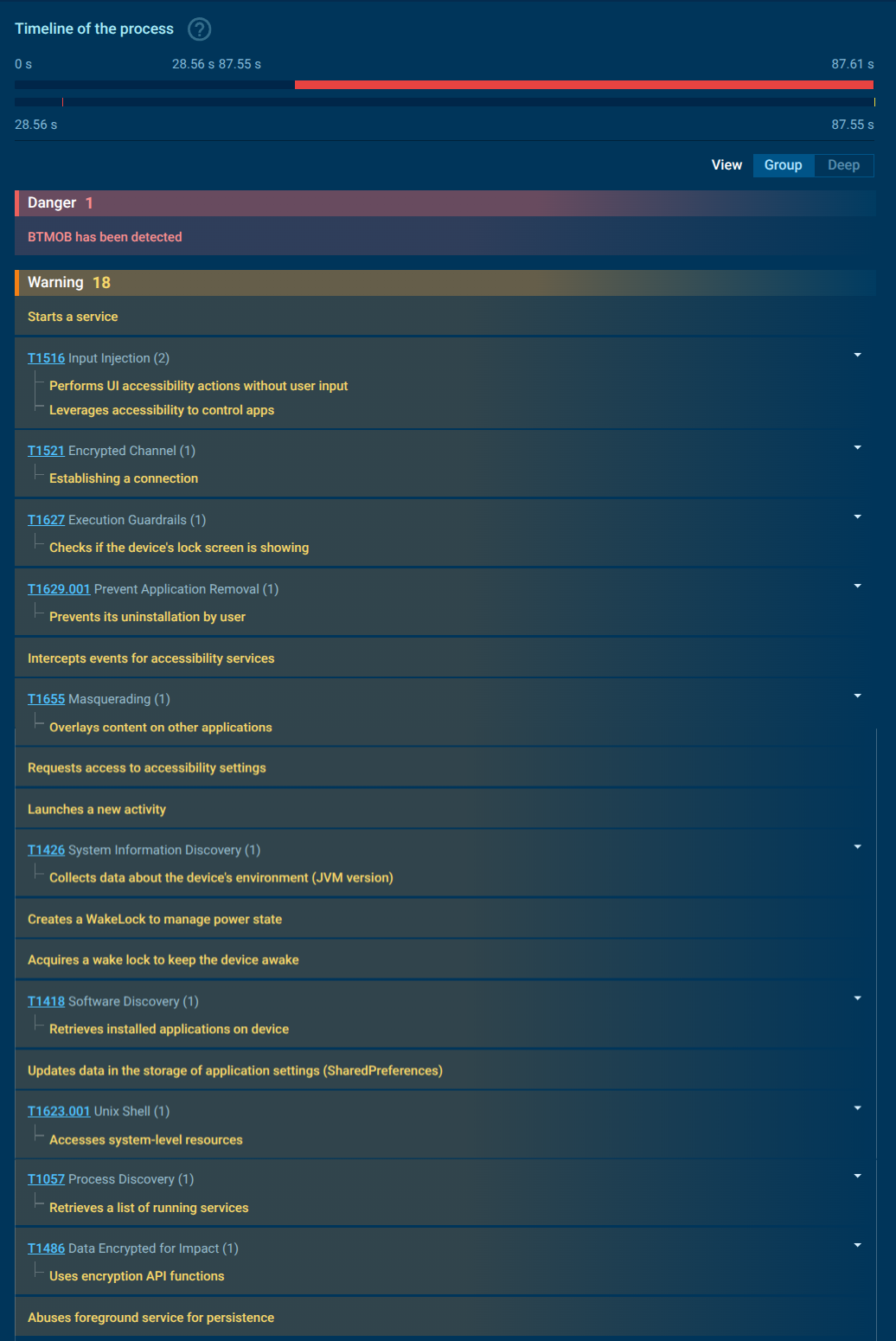 BTMOB RAT’s malicious processes
BTMOB RAT’s malicious processes
While specific large-scale BTMOB attacks are still emerging due to its recent discovery, several notable patterns have been identified:
Streaming Service Impersonation Campaigns:
Multiple campaigns have been observed where attackers created sophisticated fake websites mimicking popular streaming platforms, leading to thousands of downloads before detection.
Cryptocurrency Mining Fraud:
Significant campaigns targeting cryptocurrency enthusiasts through fake mining applications have resulted in substantial financial losses and credential theft.
Alipay PIN Theft Operations:
Recent versions specifically targeting Alipay users have demonstrated the malware's evolution toward financial fraud, with overlay attacks successfully capturing payment credentials.
Corporate Device Compromises:
Several incidents have been reported where employee devices were compromised through entertainment-focused phishing, leading to broader organizational security concerns.
These examples demonstrate the malware's versatility and the threat actors' ability to adapt their tactics based on current trends and user interests.
Threat intelligence plays a crucial role in defending against BTMOB RAT:
Start gathering intelligence by searching BTMOB in ANY.RUN’s Threat Intelligence Lookup. View the RAT’s fresh sample analyses to understand TTPs and harvest IOCs:
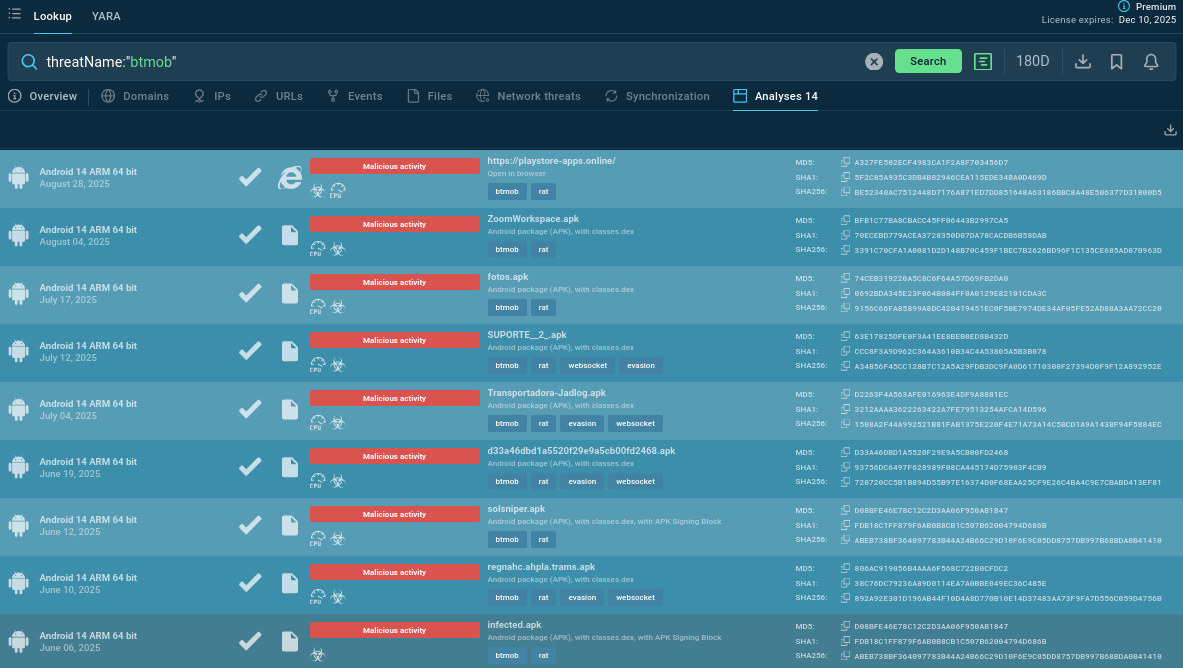 BTMOB RAT’s samples found via Threat Intelligence Lookup
BTMOB RAT’s samples found via Threat Intelligence Lookup
Threat Intelligence Lookup is available for free: collect indicators, browse sandbox detonations quick and easy.
BTMOB RAT remains a versatile and dangerous remote access Trojan capable of damaging both individuals and enterprises. Its modular architecture, stealthy operations, and adaptability make it a prime tool for cybercriminals and APT actors alike. Proactive defense powered by advanced detection, prevention strategies, and real-time threat intelligence is essential to reduce risks and prevent devastating breaches.
Sign up to use ANY.RUN’s TI Lookup for free: gather fresh actionable threat intelligence for timely detection and response.