Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Havoc is an advanced post-exploitation framework used by hackers to take control of a system once they've breached it. With Havoc, attackers can run commands remotely, inject malicious processes, and access sensitive data. It's often used in targeted attacks, allowing cybercriminals to stay hidden in a network while stealing information or launching further attacks. Its flexibility and ability to bypass detection make it a serious threat, especially in environments that rely on traditional security tools.
|
C2 Framework
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2022
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
C2 Framework
Type
:
|
Unknown
Origin
:
|
|
1 October, 2022
First seen
:
|
27 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 793
793
 0
0

 482
482
 0
0

 2730
2730
 0
0
Havoc is a post-exploitation framework used by cybercriminals and penetration testers to perform a variety of attacks and gain deeper control over compromised systems. It is developed by C5pider, written in Golang, C++, and C.
First observed in 2022, it has become notable for its stealth, flexibility, and use of encrypted communications to avoid detection. The malware is used in advanced campaigns, often by threat actors conducting highly targeted attacks.
It has been linked to attacks targeting corporate networks, critical infrastructure, and government entities.
Key technical details include its ability to use reflective DLL injection and direct memory manipulation to execute payloads. It maintains persistence on compromised systems through registry modifications and scheduled tasks, while its communication with command-and-control (C2) servers is highly encrypted
Havoc malware has several powerful and dangerous capabilities, making it a significant post-exploitation tool. Some of its primary technical features include:
Havoc operates primarily as an open-source framework and is typically distributed through phishing campaigns or malicious downloads. Its advanced features include payload generation, encryption (using algorithms like AES and RSA), process injection techniques, and multiple communication channels (HTTP, HTTPS, DNS, and SMB).
To see how Havoc operates, let’s upload a Havoc sample to the ANY.RUN sandbox.
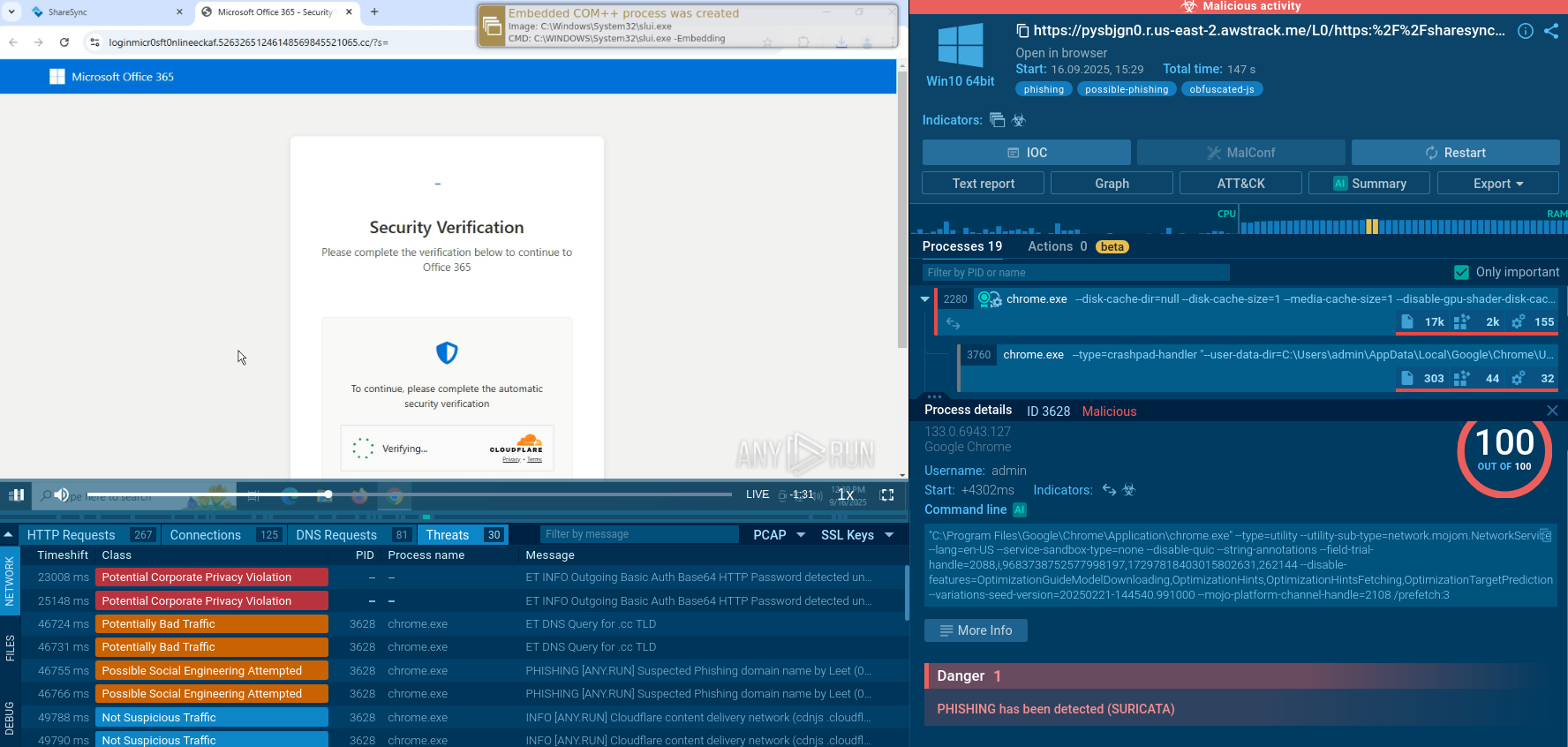
After executing the sample in the sandbox, the first thing that stands out is the red label in the upper right corner of the screen. This label provides a quick way to determine whether the activity is malicious. In our case, it’s highlighted in red, confirming that the behavior is indeed malicious.
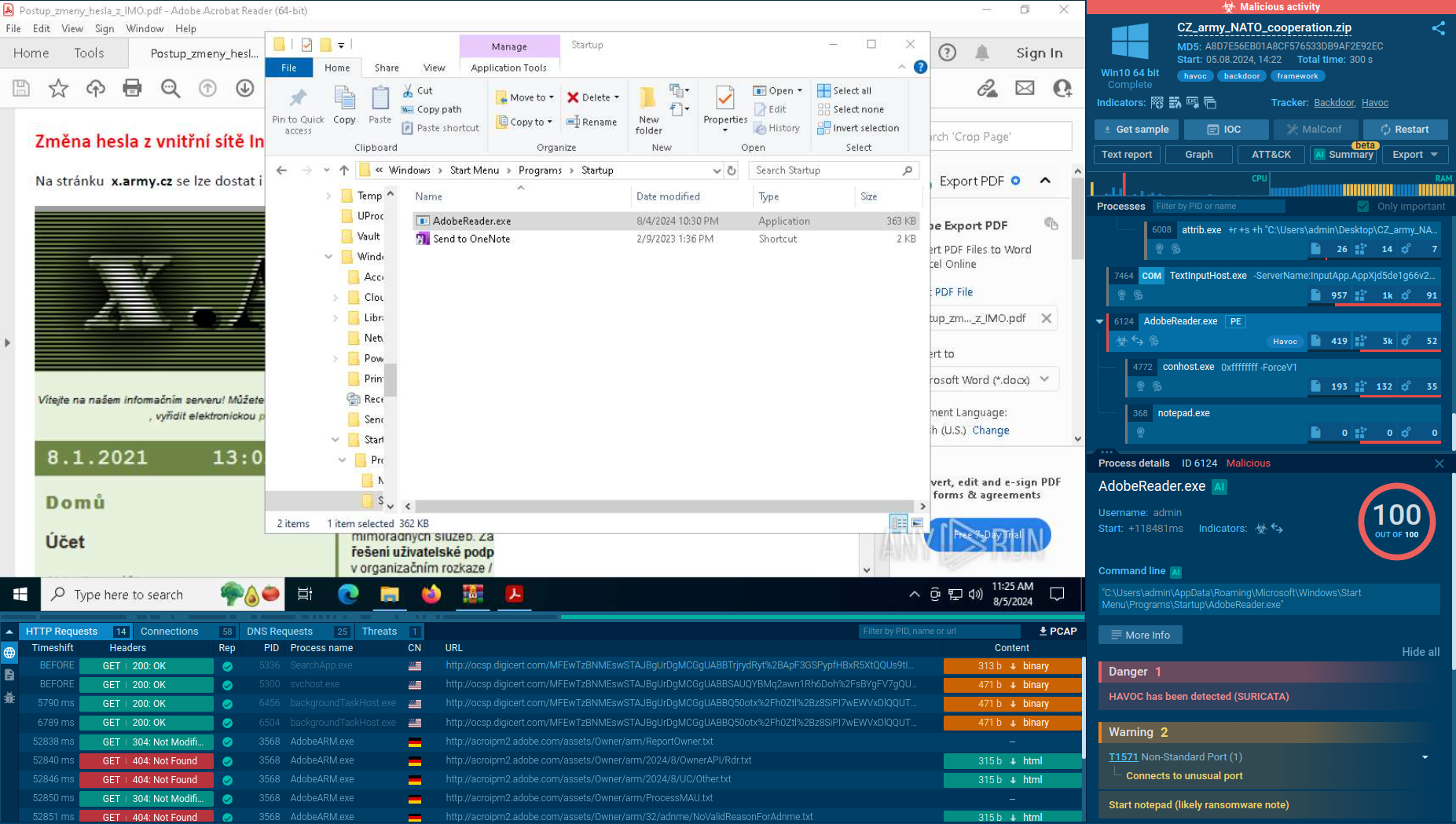 Analysis of Havoc in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Analysis of Havoc in the ANY.RUN sandbox
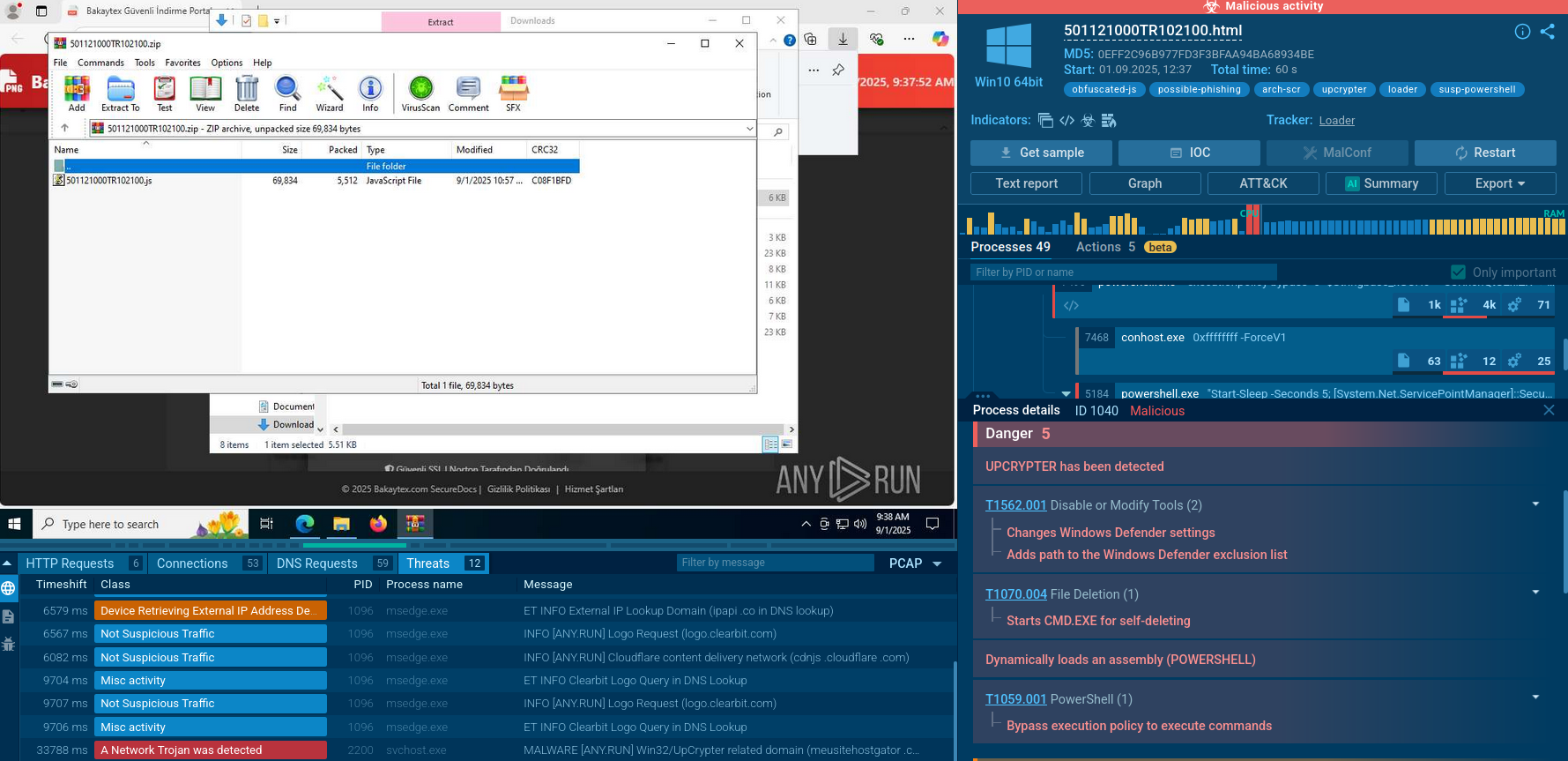
The ANY.RUN sandbox provides a Suricata rule flagging Havoc’s suspicious network activity, which is further evidence of its malicious behavior.
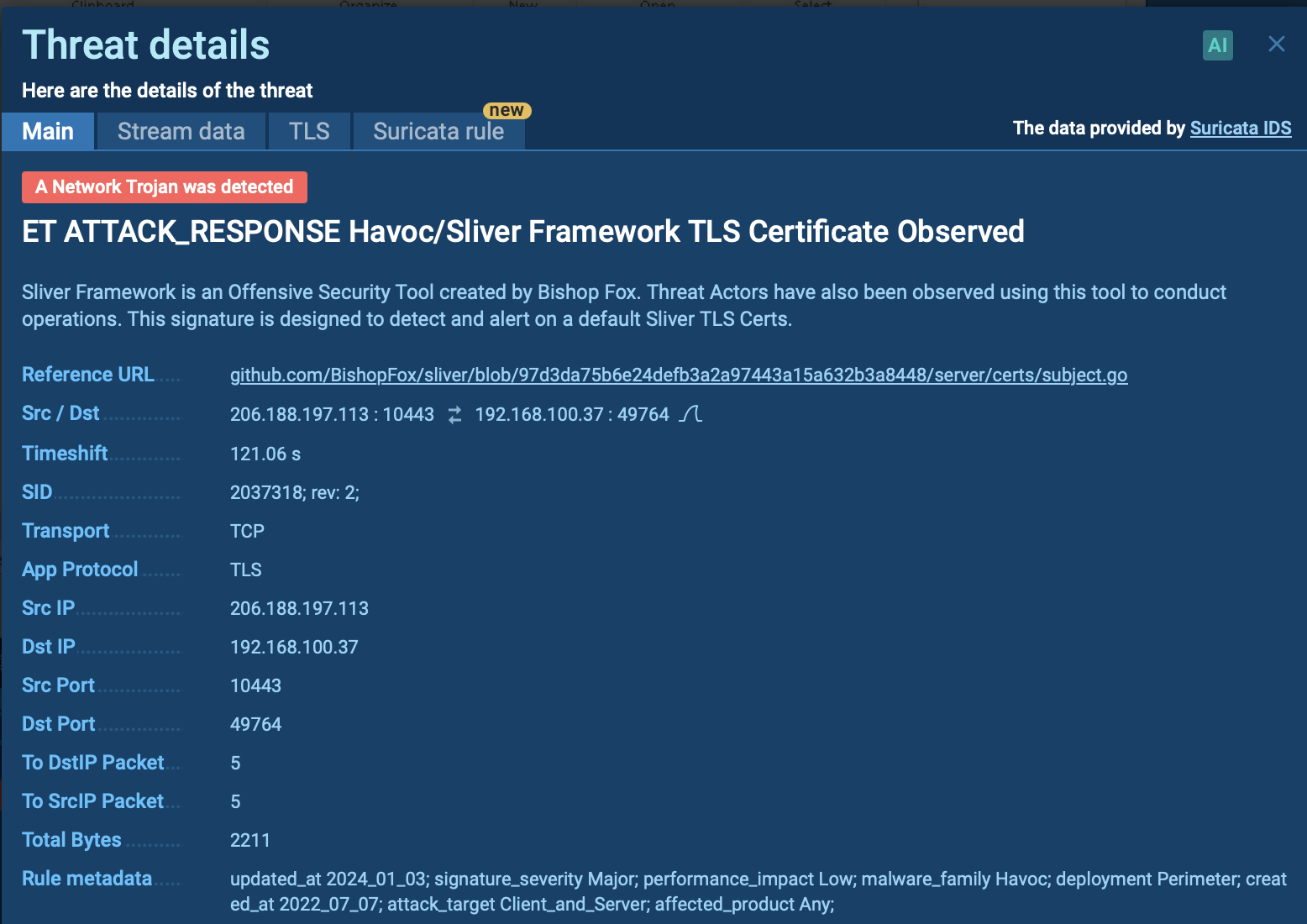 Malicious network activity detected by Suricata IDS in the ANY.RUN sandbox
Malicious network activity detected by Suricata IDS in the ANY.RUN sandbox
The Havoc framework establishes a Command and Control (C2) channel using encrypted protocols such as HTTPS and SMB to evade detection. Its modular architecture allows for functionalities like privilege escalation, lateral movement, and data exfiltration. The core agent, "Demon," written in C and Assembly, uses techniques like indirect syscalls for Nt* APIs, x64 return address spoofing, and sleep obfuscation to bypass defenses.
Havoc offers capabilities such as:
It supports execution with Beacon Object Files (BOFs), enabling direct memory interaction, and can execute commands using cmd.exe and powershell.exe and is capable of deploying additional payloads to infected systems. Havoc employs advanced evasion techniques, such as process injection and anti-VM/sandbox checks.
For persistence, Havoc can modify system settings, create scheduled tasks, or alter startup configurations, ensuring continued control over compromised systems.
Havoc malware is distributed through a variety of methods that are commonly seen in advanced cyber threats:
To collect the latest intelligence on Havoc malware, utilize Threat Intelligence Lookup.
This service allows you to access a vast database with insights from millions of malware analysis sessions in the ANY.RUN sandbox. You can customize your search using over 40 different parameters, such as IP addresses, file names, command line artifacts, and process indicators, to find relevant details on Havoc and its behavior.
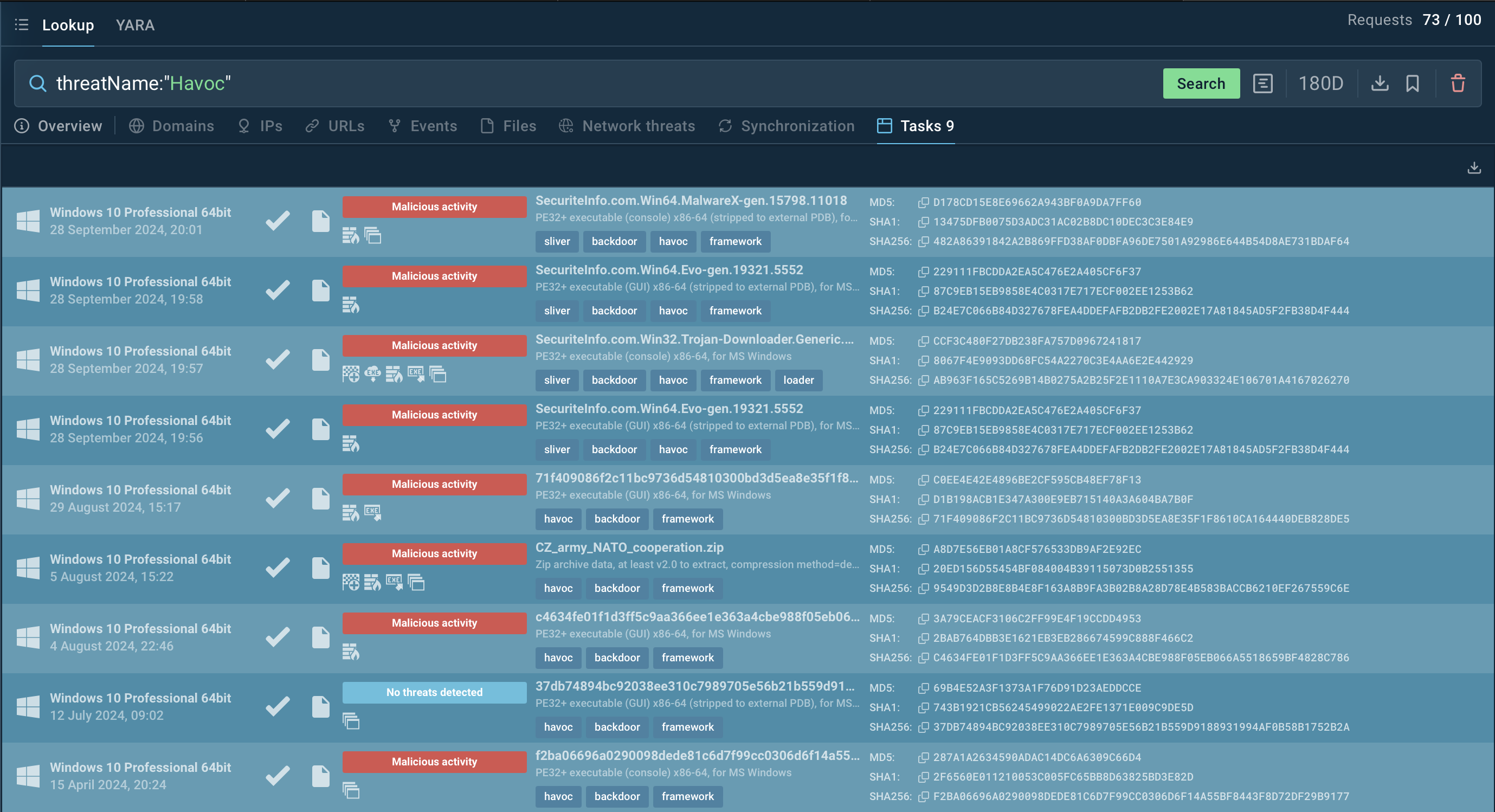 Search results for Havoc in Threat Intelligence Lookup
Search results for Havoc in Threat Intelligence Lookup
For example, by searching for Havoc's threat name (threatName:"Havoc"), you can uncover related samples and sandbox analysis results. This helps security professionals stay up to date on malware's evolution and techniques.
Start exploring these capabilities with a 14-day free trial of Threat Intelligence Lookup, alongside the ANY.RUN sandbox for deep, real-time analysis.
Havoc poses a significant threat due to its advanced evasion techniques, process manipulation, and ability to execute malicious payloads, making it highly dangerous for businesses. To protect against such threats, it’s important to carry out proactive malware analysis of suspicious files and URLs.
ANY.RUN provides real-time threat detection, allowing users to explore malware behavior, gather detailed reports on malware, such as Havoc.
Sign up for a free ANY.RUN account today and start analyzing threats in real-time!