Webinar
February 26
Better SOC with Interactive Sandbox
Practical Use Cases


Raccoon is an info stealer type malware available as a Malware as a Service. It can be obtained for a subscription and costs $200 per month. Raccoon malware has already infected over 100,000 devices and became one of the most mentioned viruses on the underground forums in 2019.
|
Stealer
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 February, 2019
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|
|
Type
:
|
ex-USSR
Origin
:
|
|
1 February, 2019
First seen
:
|
7 February, 2026
Last seen
:
|

 421
421
 0
0

 2239
2239
 0
0

 4358
4358
 0
0
Raccoon is an information stealer malware — a virus that threat actors use to retrieve sensitive data from infected machines. Also known as Mohazo and Racealer, this is a modern malware that was first sighted in 2019.
Although some consider this a relatively basic malware, excellent service from creators, who distribute it as malware as a service and a user-friendly, simplistic dashboard, helped make Raccoon quite popular. In fact, the malware has already managed to infect upwards of 100,000 devices and became one of the most mentioned viruses in hacker communities.
Raccoon malware comes with fairly basic info stealer functions like RedLine and by itself lacks any kind of antivirus protection. There are also no functions that would complicate the analysis of the malware. However, Raccoon developers do suggest using a third-party crypter.
When it comes to the core functionality this virus depending on the configuration enabled by an attacker, can check system settings, capture screenshots, collect basic information like OS version, IP and username and steal passwords and logins from a variety of browsers. On top of that, the stealer can retrieve information from Microsoft Outlook as well as steal cryptocurrency wallets.
When the data collection process ends the data is packed into a .ZIP archive that is then sent to the attackers' server.
The functions described above are rather basic, however, reportedly excellent service provided by the malware creators helped make this virus quite popular. The team behind this virus pushes out constant improvements and fixes based on user feedback.
By providing an easy-to-use dashboard Raccoon developers ensured that even non-technically savvy attackers can operate this malware successfully by customizing its configurations effortlessly. Hundreds of thousands of infected victims in a matter of months since the malware’s release is the result.
Speaking of the team behind Raccoon. The identities of the people behind this virus are a mystery, but some known members of the hacker community are known to have connections with this virus. Evidence suggests that one of the people behind Raccoon is known in the online community as glad0ff. A long known hacker who is responsible for the development of multiple malicious programs like crypto miners and RATs.
However, he does not seem to be working alone as some information about the disputes within the team has been leaked online. For instance, in one message an individual accuses someone-else from the of stealing from a common account, leaving the project, and attempting to scam customers.
There is also reason to believe that Raccoon was developed by Russian-speaking hackers. This is suggested by mistakes in the English language found in the control panel as well as the fact that the malware stops execution if it detects that the victim is from Russia, Ukraine, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Armenia Tajikistan, or Uzbekistan. In addition, technical support is available in Russian and English languages, which also points to a potential x-USSR origin of the attackers.
A video available in the ANY.RUN malware hunting service shows how a machine gets infected with Raccoon in real-time.
Read a detailed analysis of Raccoon Stealer 2.0 in our blog.
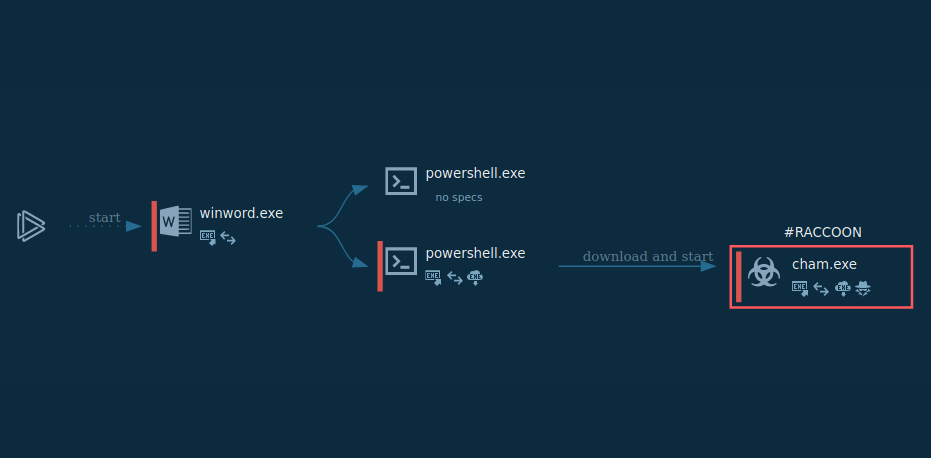
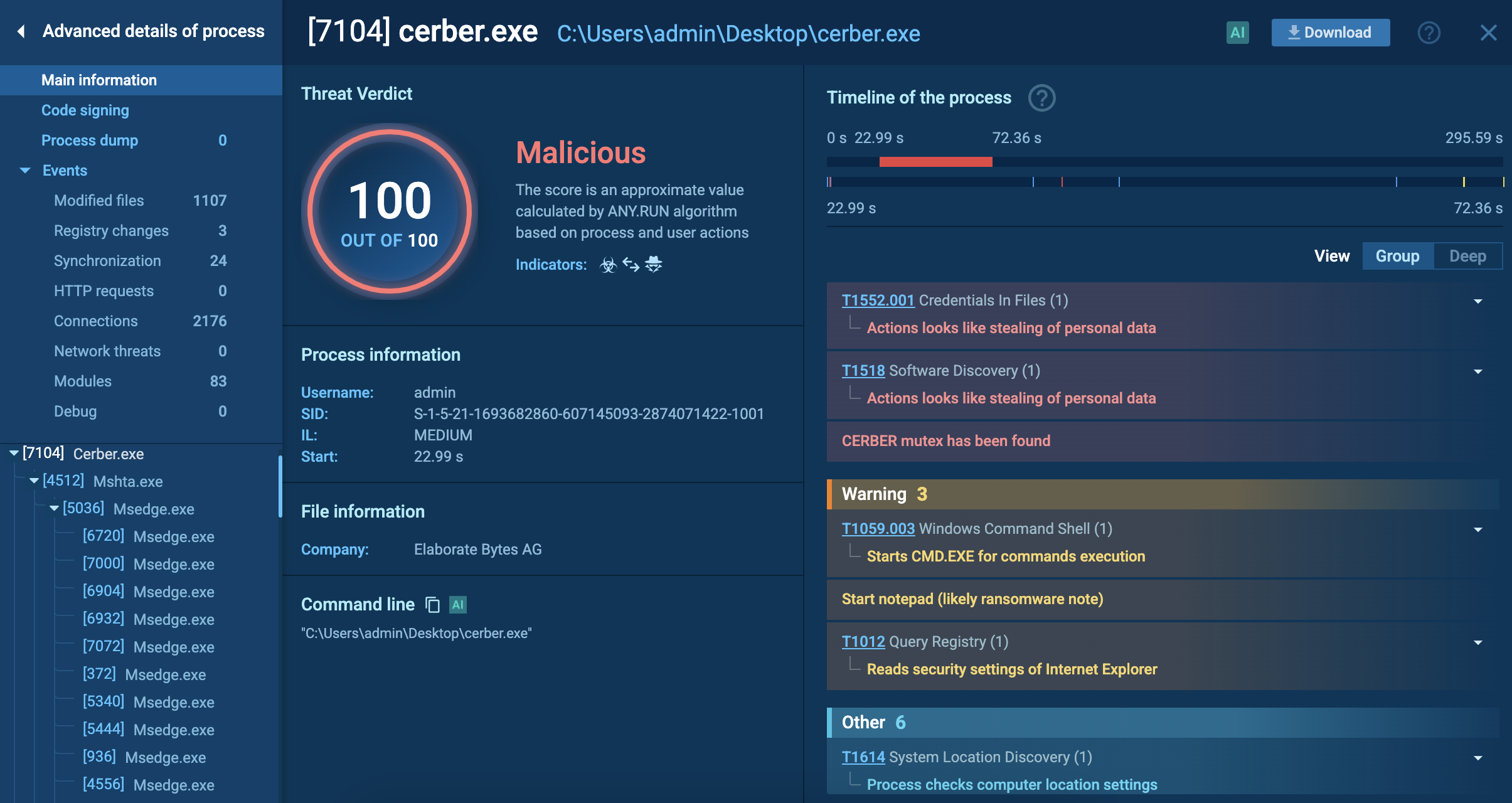
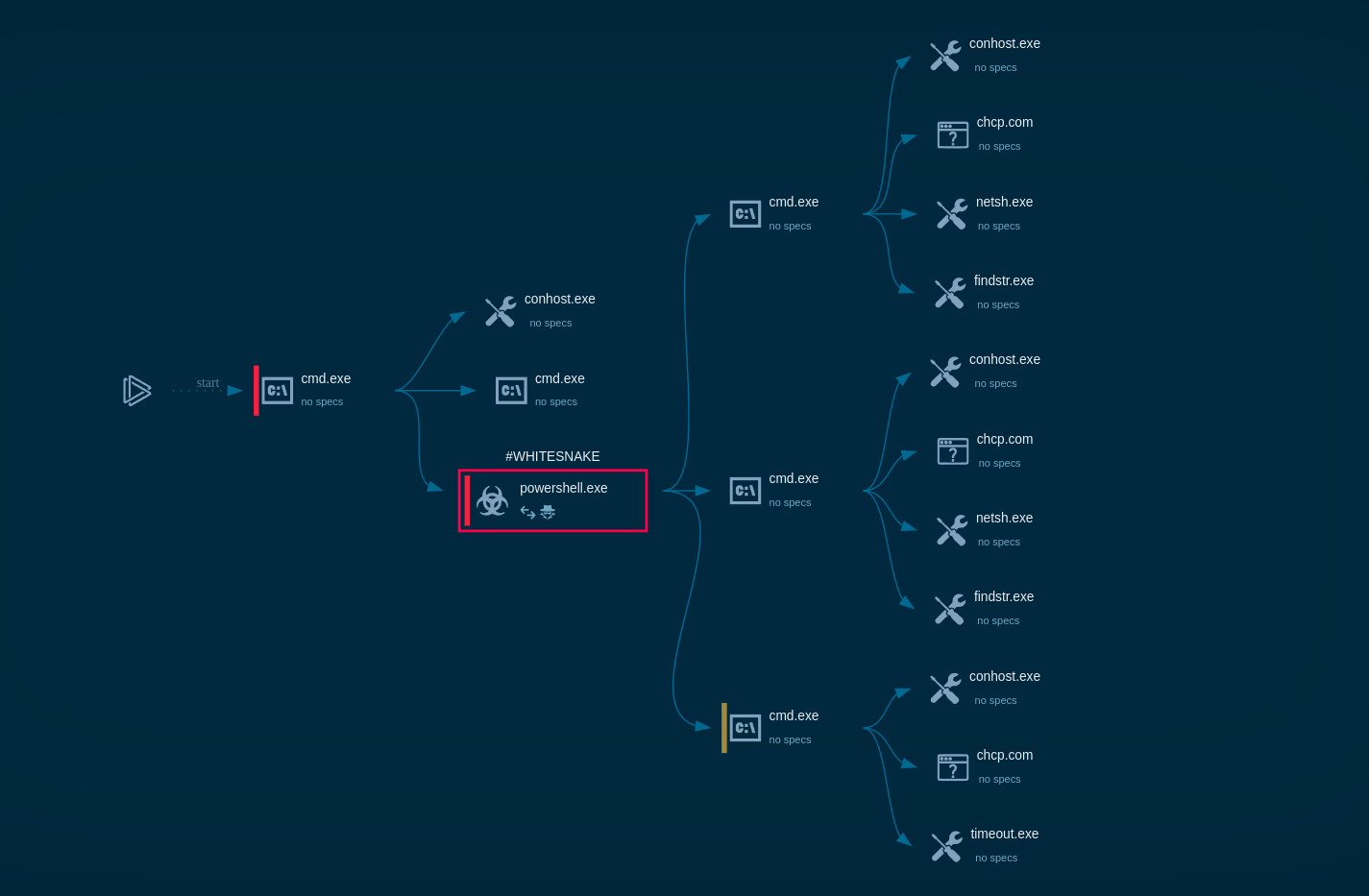
Figure 1: Here we can see the execution process of Raccoon. This graph was created in ANY.RUN.
Figure 2: Shows a text report that can help collect data about the malware execution in one place or make a presentation.
Since Raccoon malware is a pretty standard example of a stealer-type malware, its execution process does not exactly stand out. In our analysis case, after the malware made its way into the infected system (does not matter which delivery method it would use) it downloaded additional modules from the Internet. These modules are mostly DLL dependencies which Raccoon requires to work correctly. After that, the malware began stealing information from browsers and the system and stored stolen data in an archive file. The file, in turn, was sent to the C2 server. Probably the same C&C server it was built in. Note that some versions of the Raccoon malware delete themselves after execution while others don't.
Raccoon stealer malware is distributed using multiple channels like browsers, however, the most popular destruction method is through the use of exploit kits. Attackers can even manage campaign configurations via the control panel. The malware utilizes mainly the Fallout exploit kit. This delivery method makes it possible for the infection to occur even without active user interaction — victims get infected while simply surfing the web.
The malware also makes its way to victim’s PCs Microsoft Office document attachments that are being distributed in mail spam campaigns. The contaminated document contains a macro that downloads the malware when enabled.
In addition, hackers have set up a Dropbox account where the malware is stored inside a .IMG file. Attackers use social engineering to trick victims into opening a malicious URL and download the infected file.
Finally, the last distribution method is “bundled malware”. When users download real software from suspicious websites sometimes Raccoon comes as an unwanted part of the package bundled with the legitimate program.
Some malware creates files in which it named itself. You can find such info about Raccoon malware trojan using ANY.RUN's "Static Discovering". Open either the "Files" tab in the lower part of the task's window or click on the process and then on the button "More Info" in the appeared window. After that, all you need to do is just click on the file.
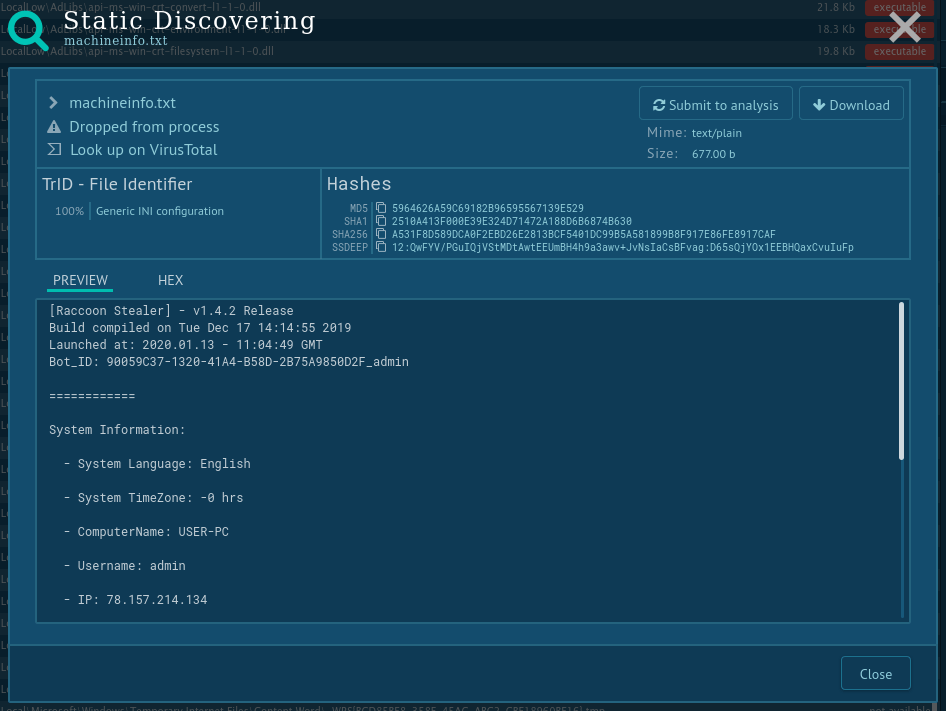
While Raccoon malware is not a very technically advanced malicious program like Ursnif or Hawkeye, Raccoon sure made a lot of noise in the underground community in 2019, when it was first released. Available as a service for $200 per month, it came equipped with everything necessary to start a malware attack. And if a customer couldn’t do it on their own, they could always get support from the team behind this malware.
In fact, underground forums are filled with raving feedback about the excellent work of Raccoon support staff. Some even say that they were treated like real VIPs.
Developers have also shown that they are capable of rolling out updates very quietly and promise to upgrade the malware with Keylogger functionality in the near future.
While technical simplicity makes this threat relatively easy to defend against at the moment, growing popularity, extreme ease of use, and potential future improvement certainly suggest that this malware can become a big phenomenon. Some even say that Raccoon will replace Azorult.
ANY.RUN malware hunting service provides researchers with the ability to study samples of Raccoon in a controlled interactive environment and learn as much as possible about this malware. Hopefully, together we will neutralize or at least medicate the fallout from this and other cybersecurity threats.